Medicine is one of the noble and traditional professions, which continues to be a prestigious, respectable and lucrative career. It is one of the most challenging and offers rewarding career opportunities both in service sector as well as in private practice.
Careers in Medicine – Personal attributes
Keeping in view the nature and requirements of the medical profession, one needs to have passion to serve the sick with passion and work for longer hours. One has to be mentally alert, willingness to learn and use sophisticated equipments, spirit of duty and responsibility and ability to lead a team.
Careers in Medicine – How to enter?
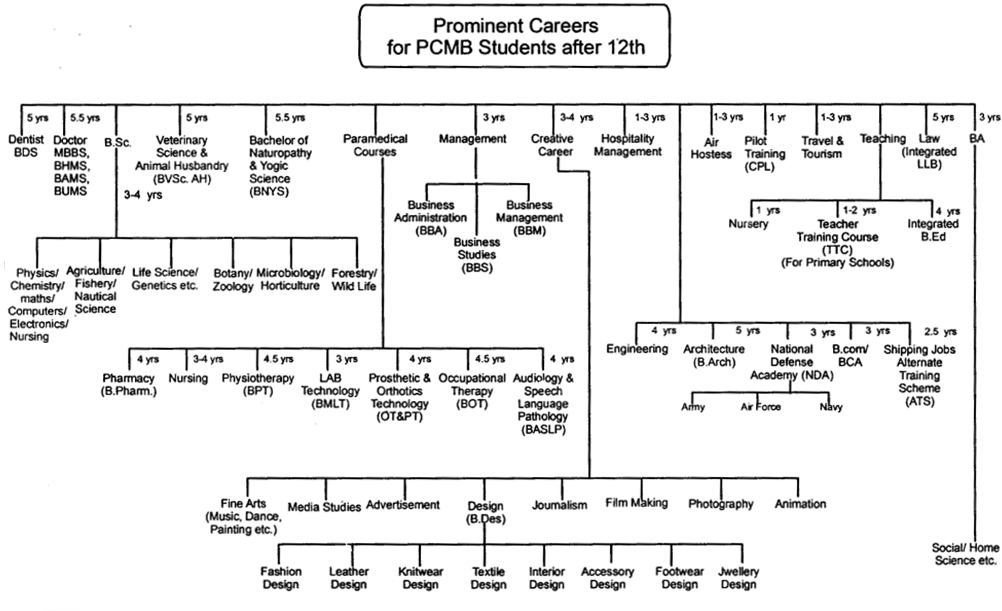
To be medical expert or practitioner, you must have passed 10+2 in science with Physics, Chemistry and Biology/Biotechnology with a minimum of 50% marks to be eligible for applying for admission to a 5V2 year Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) course, which is followed by one year compulsory rotating residential internship.
The degree is awarded only after completion of this internship which enables you to join as a doctor in a hospital or to do your own practice. To make you familiar with the various departments of a hospital and expose you to the different situations that crop up in a hospital, as an intern, you are posted in all the departments of the hospital on a rotation basis. This enables you to gain clinical and practical knowledge about all the disciplines of Medicine.
Admission to medical colleges throughout the country is maae on the basis of single eligibility cum entrance examination namely NEET, conducted by CBSE during May. Some Prominent institutes like AIIMS, JIPMER conduct their own entrance exam at all India level. Further details are given in the foregoing sections.
Besides MBBS and BDS (Bachelor of Dental Science), Bachelor in Homoeopathy (B.H.M.S), Bachelor in Pharmacy (B.Pharm), B.Sc Nursing, Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine (BAMS), Bachelor of Unani Medicine & Surgery (BUMS), Bachelor of Physiotherapy (BPT), Bachelor of Occupational Therapy (BOT), etc. are also important degrees related to the medical profession.
Know more Course Details:
Related Articles:
After completing your MBBS/BDS you can go for specialisation in Anaesthesiology, Anatomy, Biochemistry, Biophysics, Cardiology, Community Medicine, Dermatology/ Venereology, Endocrinology, Forensic Medicine, Gastroenterology, General Medicine, Medicine & Therapeutics, Microbiology, Neurology, Nuclear Medicine, Obstetrics & Gynaecology, Occupational Health, Ophthalmology, Ortho, Paediatrics, Pathology, Pharmacology, Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, Physiology, Psychiatry, Radio diagnosis, Radiotherapy, Orthopaedics, Otorhinolaryngology, Surgery, Nephrology, Neurosurgery, Pediatric Surgery, Urology, etc. Admission to these courses of specialisation is given on the basis of entrance examination.
Similarly, there is provision for pursuing further studies after completing BHMS, BAMS, BUMS, BPT, BOT degree courses. Admission is generally granted on the basis of your performance in the respective entrance examinations conducted by the concerned authorities.
Specialisations in Medical at a Glance
Oncology/Oncologist
An oncologist specializes in diagnosing and treating cancer using chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, biological therapy, and targeted therapy. Often, he is the main health care provider for cancer patients. The three main types of oncologists are medical, surgical, and radiation oncologists.
Pay & Perks:
In the government sector, a surgical/medical oncologist can easily earn Rs.50,000 to 80,0000 a month.approx. As one gains experience, he could earn 90,000 to Rs.l lakh approx., or above per month. Pay package varies in the private sector, depending upon the level and standard or the establishment vis-a-vis your knoweldge, expertise and reputation in the profession.
How to enter?
To be an oncologist, after completing high school, you need to study science with Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Complete your MBBS, after which you can do either of these three-year courses: (a) MS, followed by a three-year Mch programme, b) MD (Medicine/paediatrics), topped up with a DM (medical oncology) qualification or C) MD in radiotherapy. If you can’t do Ms or MD, opt for DNB (Diploma).\
Careers in Medicine – Surgery
General Surgeon
A general surgeon deals with common problems that occurs in abdomen, digestive tract, endocrine system, breast, skin, and blood vessels. He/she diagnoses the problems and treat the patient with the use of minimally invasive and endoscopic (looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope, an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body) techniques.
A general surgeon receives training in hand surgery, hospice and palliative medicine, paediatric surgery, surgical critical care, vascular surgery.
Colon and Rectal Surgeon OR Colorectal Surgeons
Colorectal surgery deals with disorders of the rectum, anus, and colon. Physicians specializing in this field are colorectal surgeons or proctologists. A colon and rectal surgeon is trained medical professional who has expertise in diagnosing and treating various diseases of the small intestine, colon, rectum, anal canal, and perianal area by medical and surgical means.
Orthopaedic Surgeon
Orthopedics is a surgical discipline that employs many tools to insert equipment such as pins, rods and bolts.
An orthopaedic surgeon has expertise in the preservation, investigation, and restoration of the form and function of the extremities, spine, and associated structures by medical, surgical, and physical means.
Orthopaedic surgeons can receive training in Orthopaedic sports medicine, Surgery of the hand.
Plastic Surgeon
A plastic surgeon deals with the repair, reconstruction, or replacement of physical defects of form or function. These could be of the skin, musculoskeletal system, head and facial structures, hands, extremities, breasts, and trunk. Or cosmetic enhancement of these areas. Cosmetic surgery is a part of plastic surgery.
Neurology/Neurologist
A neurologist deals with diagnosis and treatment of diseases pertaining to brain or impaired function of the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, muscles, and autonomic nervous system as well as the blood vessels that relate to these structures.
Obstetrician/Gynecologist
Obstetrics and Gynaecology is concerned with the care of the pregnant woman, her unborn child and the management of diseases specific to women. An obstetrician/gynecologist possesses special knowledge, skills, and professional capability in the medical and surgical care of the female reproductive system and associated disorders. He/she serves as a consultant to other physicians and as a primary physician for women.
Pathology/Pathologists
A pathologist deals with the causes and nature of diseases and contributes to diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment through knowledge gained by the laboratory application of the biologic, chemical, and physical sciences.
A pathologist receives training in Blood banking/ transfusion medicine, Chemical pathology, Cytopathology, Dermatopathology, Forensic pathology, Hematology, Medical microbiology, Molecular genetic pathology, Neuropathology and Pediatric pathology.
Neurological Surgeon
A surgeon who deals with prevention, diagnosis, evaluation, treatment, critical care, and rehabilitation of disorders of the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their supporting structures and vascular supply is called Neurological surgeon.
Careers in Medicine – Thoracic surgeon
Operations on the heart, lungs, oesophagus, and other organs in the chest are performed by a Thoracic surgeon. Types of thoracic surgeons include cardiothoracic surgeons, cardiovascular surgeons, general thoracic surgeons, and congenital heart surgeons.
Anesthesiologist
An anesthesiologist is a medical professional who has expertise in providing pain relief and maintenance or restoration of a stable condition of patient during and immediately after an operation or diagnostic procedure.
Careers in Medicine – Dermatologist
Deramtologist is a skin specialist. He/she diagnose and treat pediatric and adult patients with disorders of the skin, mouth, external genitalia, hair, and nails as well as a number of sexually transmitted diseases (STD).
Ophthalmologist
An ophthalmologist is a specialist who deals with medical and surgical eye problems. He takes care of eye and vision care for patients of all ages. He diagnoses, monitors, and medically or surgically treats all ocular and visual disorders. To provide consultative services for the diagnosis and management of ocular manifestation of systemic diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and infectious and non-infectious inflammation is also a part of his duty..
Careers in Medicine – Otolaryngology
An otolaryngologist is a head and neck surgeon. He deals with disorders of ears, nose, throat, the respiratory and upper alimentary systems, and related structures. He/she diagnoses and provides medical and surgical therapy or prevention of allergies, deformities, disorders and injuries.
Otolaryngologists can receive subspecialties in neurotology, pediatric otolaryngology, plastic surgery, reconstructive procedures within the head, face, neck, and associated structures, including cutaneous head and neck oncology and reconstruction, management of maxillofacial trauma, soft tissue repair, and neural surgery.
Pediatrician
A pediatrician is a specialized medical professional to diagnose and treat different types of chronic disorders, injuries and infections in infants, children and teens. He/she performs general check-ups, offers vaccination or immunization therapies to the new bom babies, treats certain diseases such as sinus infections, ear infections, sore throats, mononucleosis, and flu to name a few.
Pediatricians are generally trained in the subspecialties like neonatal-perinatal medicine, pediatric critical care medicine, pediatric emergency medicine, pediatric gastroenterology, pediatric cardiology, pediatric endocrinology, pediatric sports medicine, etc. ‘
Careers in Medicine – Psychiatrist
Psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental, addictive, and emotional disorders such as schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders, mood disorders, anxiety disorders, sexual and gender identity disorders, etc.
His job is to understand the biologic, psychologic, and social components of illness in order to uniquely treat the whole person.
Psychiatrists are trained in the subspecialties such as addiction psychiatry, child and adolescent psychiatry, clinical neurophysiology, forensic psychiatry, geriatric psychiatry hospice and palliative medicine, pain management, psychosomatic medicine, etc.
Radiologist
A radiologist uses imaging methodologies such as x-ray, ionizing radiation, radionuclides, electromagnetic radiation, ultrasound, and image-guided intervention to diagnose patients. Radiologists are trained in the following subspecialties: neuroradiology, nuclear radiology, pediatric radiology, vascular and interventional radiology.
Urologist
Urology is the study of the anatomy, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of genitourinary disorders. A urologist manages congenital and acquired conditions of the genitourinary system and contiguous structures including the adrenal gland.
Audiologist
An audiologist identifies, diagnoses, treats and monitors disorders of the auditory and vestibular system portions of the ear.
Haematologist
The core job of a Haematologist is to provide an advisory and consultancy service to all hospital specialists and general practitioners and manage diagnostic laboratories. He provides clinical interpretation of laboratory data and morphology of blood and bone marrow specimens. In addition, delivering clinical care, often for life-threatening disease, formulating chemotherapy protocols and managing their delivery; managing hemipoietic stem cell transplantion procedures; etc
Haematologists generally go for specialties in haemato-oncology, haemostasis/thrombosis, disorders of blood production and destruction (including bone marrow failure, anaemias and autoimmune blood diseases), transfusion medicine and paediatric haematology.
Histopathologist/ Histopathology
Histopathology is the diagnosis and study of disease by expert medical interpretation of cells and tissue samples. Histopathologist works in lab with laboratory scientists and doctors from other clinical specialties. He has in-depth knowledge of both pathological and clinical aspects of disease. His functions are to examine and dissect surgical resection specimens, to select the most appropriate samples for microscope slides, to observe and note down microscopic examination of tissues to prepare cinical reports.
Microbiologists and Virologists
Medical microbiologists and virologists are the specialists who diagnose, treat and help in prevention of the spread of infection in community.
Microbiologist works with hospital infection control teams to reduce the spread of infections in hospitals. He contributes to the protection of public health by monitoring the patterns of infectious diseases and reporting new or unusual occurrences of infections.
Rheumatologist
The role of the rheumatologist is to diagnose, treat and advise patients with arthritis and problems affecting the joints, muscles, bones and sometimes other internal organs (e.g., kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, brain).
Internal Medicine
Internal medicine or general medicine is the medical speciality dealing with the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of adult diseases. Physicians specializing in internal medicine are called internists. He provides long-term comprehensive care in the office and the hospital, managing both common and complex illness of adolescents, adults, and the elderly.
Internists are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of of cancer, infections, and diseases affecting the heart, blood, kidneys, joints and digestive, respiratory, and vascular systems.
Nuclear Medicine Specialist
A nuclear medicine specialist uses the tracer principle to evaluate molecular, metabolic, physiologic and pathologic conditions of the body for the purposes of diagnosis, therapy and research. Nuclear medicine encompasses molecular imaging. Imaging systems are used to detect the tracer signal to provide spatial and temporal information on the processes of interest.
NICU Basics: All That You Should Know About A Neonatal Intensive Care Unit