Do you know the answer to the question “What is the Longest River in the World?” If yes, then you have an execellent knowledge of World GK topics like the world’s longest river, etc. If not, don’t worry because this article will completely make you understand the topic of the longest river in the world.
Also, we help you to gain some basic knowledge on world GK by providing this direct General Knowledge Article. Make use of that and become pro in answering all General Awareness & current affairs questions asked in the competitive exams.
This page includes all necessary information about Top 10 biggest rivers in the world along with neat explanations and essential details. So, go through the below modules, and let’s grasp all the details of the World’s largest rivers.
Know More:
List of Top 10 Biggest & Longest Rivers in the World
The River Nile is the longest river that is 7088 kilometers in length whereas Amazon is the largest river in the world. Rivers are the most crucial aspect and always been the place where the greatest civilizations bloomed. Rivers offer water for the essential needs of both tiny towns and huge cities.
Also Refer: Longest River in India
The river is a part of the Hydrological cycle. Basically, it is a natural flowing watercourse, often freshwater, streamlined towards an ocean, sea, lake, or another river. Here in the below table, we have shared the Top 10 World’s Longest Rivers list along with length, location, drain name, drainage area, and covered countries.
| List of Longest Rivers of the World |
| River Name |
Location |
Length (Miles) |
Length (Km) |
Drain |
Countries |
| Nile |
Africa |
4130 |
6650 |
Mediterranean Sea |
- Ethiopia,
- Eritrea,
- Sudan,
- Uganda,
- Tanzania,
- Kenya,
- Rwanda,
- Burundi,
- Egypt,
- Democratic Republic of the Congo,
- South Sudan
|
| Amazon |
South America |
4086 |
6575 |
Atlantic Ocean |
- Brazil,
- Peru,
- Bolivia,
- Colombia,
- Ecuador,
- Venezuela,
- Guyana
|
| Yangtze |
China |
3917 |
6300 |
South China Sea |
China |
| Mississippi |
USA |
3902 |
6275 |
Gulf Of Maxico |
USA, Canada |
| Yenisei-Angara-Selenge-Ider |
Russia |
3445 |
5539 |
Kara Sea |
Russia, Mongolia |
| Yellow |
China |
3398 |
5464 |
Bohai Sea |
China |
| Ob-Irtysh |
Russia |
3364 |
5410 |
Gulf of Ob |
- Russia,
- Kazakhstan,
- China,
- Mongolia
|
| Parana |
Uruguay |
3030 |
4880 |
Rio de la Plata |
- Brazil,
- Argentina,
- Paraguay,
- Bolivia,
- Uruguay
|
| Congo |
Africa |
2922 |
4700 |
Atlantic Ocean |
- Democratic Republic of the Congo,
- Central African Republic,
- Angola,
- Republic of the Congo,
- Tanzania,
- Cameroon,
- Zambia,
- Burundi,
- Rwanda
|
| Amur |
Asia |
2800 |
4480 |
Sea of Okhotsk |
Russia, China, Mongolia |
Must Check: Rivers In India: List of Major Rivers of India for UPSC, Bank, SSC Exams
Detailed Analysis on Top 5 Longest Rivers of the World
A detailed analysis of the first 10 longest rivers in the world is presented below:
1. Nile River: 6650 Km – The longest river in the world

River Nile is the World’s First Longest River located in North-East Africa. It is the lifeline of a number of countries namely, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt share its water. The Longest River Nile has two central tributaries- the Blue Nile and the White Nile which is the origin of the river and starts from the Kagera river at the lake headwaters in Burundi, Central Africa. The length of the Nile River is 6650 Kms and flows into the Mediterranean sea. Moreover, it has a discharge of approximately 3.1 million litres per second.
2. Amazon River: 6575 Km – The first largest by waterflow & second-longest by length

The Second Longest River in the World with a length of 6,400 km is the Amazon River and it has 1100 tributaries and covers 40% of South America – Ecuador, Bolivia, Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil. Also, it is the largest river in the world by waterflow. A recent 2014 study demands that the origin of the Amazon can be drawn to the Cordillera Rumi Cruz. Its origin is the Peruvian rivers in the high Andes mountains.
3. Yangtze River: The longest river in Asia

The Third Longest River in the World is the Yangtze River and also it is Asia’s longest river that flows entirely within one country. Since ancient times, the government of China identifies the Tuotuo tributary found in the Tanggula Mountains as the origin of the river. It is 6,300 km long and it has 8 principle tributaries and more than 700 minor tributaries including 20% of China passing 9 provinces of the people’s republic. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River is the world’s largest Hydro-electric Dam and around 5000 constructed dams are across the river.
4. The Mississippi River
The 4th longest river in the world is the Mississippi River and it is discovered in North America. It is 6,274 km long and flows towards the Gulf of Mexico. The river system flows 31 US states and 2 Canadian territories. The Mississippi River originates in northern Minnesota where Lake Itasca is considered to be the origin of the river and drains into the Gulf of Mexico. For 360 species of fish, 326 species of birds, 145 species of amphibians, and 50 species of mammals, the river Mississippi became a house.
5. The Yenisei River
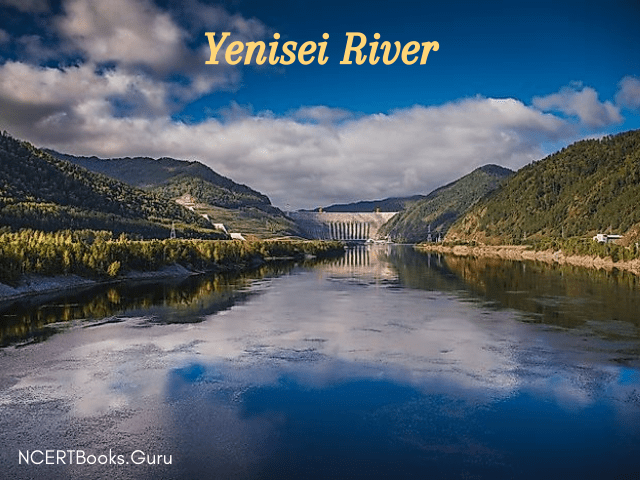
The total length covered by the Yenisei River is 5,539 miles and it mainly flows in Russia and the rest in Mongolia. Yenisei River is the fifth-longest river system in the world and the largest draining into the Arctic Ocean into the Kara Sea. Actually, it begins from the headwaters of the Selenga River about western Mongolia near the Khangai mountains. The Selenge River is 992 km long and flows into Lake Baikal.
Also, Check Related World GK Topics
List of Top 50 World’s Longest & Largest Rivers with Description
The following table enlists the top 50 biggest rivers in the world along with complete descriptions like the length of each river, their source, and the countries touch or crossed or flow through.
| Name Of River |
Description |
| Nile |
Source: Kagera – Ruvubu,in Burundi. Mouth: Egypt – Mediterranean Sea.
Length: 6695 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Uganda, Ethiopia, Sudan, Burundi, Egypt. |
| Amazon |
Source: Peruvian rivers in the high Andes mountains- Marañón – Apurímac – Mantaro.Mouth: Atlantic ocean.
Length: 6575 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela, Bolivia, Brazil. |
| Yangtze |
Source: Wulan Mulun river – Tanggula Mountains – southern Qinghai province -Tibet Autonomous Region.Mouth: East China Sea- near Shanghai.
Length: 6300 Kms.
Countries Crossed: 9 provinces of China. |
| Mississippi |
Source: Lake Itasca – Northern Minnesota.Mouth: Gulf Of Mexico.
Length: 3778 Kms.
Countries Crossed: 10 states of the U.S. |
| Yenisei-Angara-Selenge-Ider |
Source: The headwaters of the Selenga River – western Mongolia – Khangai mountains.Mouth: Yenisey Gulf – Arctic ocean – Russia.
Length: 3,487 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia, Mongolia. |
| Yellow |
Source: Bayan Har Mountains – Bayankala mountains – Qinghai province.Mouth: Bohai sea – Dongying – Shandong province.
Length: 5464 Kms.
Countries Crossed: 9 provinces of China. |
| Ob-Irtysh |
Source: Asian Altai Mountains- Biya river- Katun river.Mouth: Gulf of Ob- Arctic ocean.
Length: 5410 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia, Kazakhstan, China, Mongolia. |
| Río De La Plata – Paraná-Río Grande |
Source:Paranaíba -Grande.Mouth: Rio de la Plata – Atlantic Ocean.
Length: 4880 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay, Bolivia, Uruguay. |
| Congo- Chambeshi |
Source: Lake Mweru – East African Rift – Chambeshi River – Lake Tanganyika.Mouth: Atlantic Ocean.
Length: 4700 Kms.
Countries Crossed: The Democratic Republic of the Congo, Central African Republic, Angola, Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Cameroon, Zambia, Burundi, Rwanda. |
| Amur – Argun -Kherlen |
Source: Reka Argun – Onon river – Shilka river – Kherlen river.Mouth: Sea of Okhotsk.
Length: 4444 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia, China, Mongolia. |
| Lena |
Source: Baikal Mountains – Central Siberian Plateau.Mouth: Laptev Sea.
Length: 4400 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Mekong |
Source: Lasagongma Spring – plateaus of Tibet.Mouth: South China Sea.
Length: 4350 Kms.
Countries Crossed: China, Myanmar, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam. |
| Mackenzie–Slave-Peace-FIinlay |
Source: Thutade Lake – Northern Interior of BC.Mouth: Beaufort Sea.
Length: 4241 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Canada. |
| Niger |
Source: Guinea Highlands – southeastern Guinea.Mouth: Gulf of Guinea.
Length: 4200 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Nigeria, Mali, Niger, Algeria, Guinea, Cameroon, Burkina Faso, Côte d’Ivoire, Benin, Chad. |
| Brahmaputra–Tsangpo |
Source: Himalayas.Mouth: Ganges.
Length: 3848 Kms.
CountriesCrossed: India, China, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan. |
| Murray–Darling–Culgoa- Balonne-Condamine |
Source: Darling Downs – Queensland.Mouth: Southern Ocean.
Length: 3672 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Australia. |
| Tocantins–Araguaia |
Source: Brazilian Highlands – Alto Araguaia – Mato Grosso Estado.Mouth: Atlantic Ocean – Amazon
Length: 3650 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil. |
| Volga |
Source: Valdai Hills – northwest MoscowMouth: Caspian Sea.
Length: 3645 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Indus–Sênggê- Zangbo |
Source: Gêgyai County -Ngari Prefecture – near Mount Kailash.Mouth: Arabian Sea.
Length: 3610 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Pakistan, India, China. |
| Shatt-Al–Arab-Euphrates–Murat |
Source: Tigris- Euphrates confluence – Al- Qurnah – Karun river – Iran – Mount Ararat – Lake Van – Armenian Highlands- Turkey.Mouth: Persian Gulf.
Length: 3596 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Iran, Iraq, Turkey, Syria. |
| Madeira–Mamoré–Grande–Caine- Rocha |
Source: Madre de Dois- Mamoré rivers confluence.Mouth: Amazon.
Length: 3380 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil, Bolivia, Peru. |
| Purús |
Source: Southern Ucayali headwaters.Mouth: Amazon.
Length: 3211 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil, Peru. |
| Yukon |
Source: Llewellyn glacier – southern end – Atlin lake.Mouth: Bering Sea.
Length: 3185 Kms.
Countries Crossed: U.S.A, Canada. |
| São Francisco |
Source: Canastra mountains – state – Minas Gerais.Mouth: Atlantic Ocean.
Length: 3180 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil. |
| Syr Darya – Naryn |
Source: Tian Shen mountains – Kyrgyzstan – Uzbekistan.Mouth: Aral Sea.
Length: 3078 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan. |
| Salween |
Source: Tanggula mountains – Tibetan plateau – Mekong and Yangtze headwaters.Mouth: Andaman Sea.
Length: 3060 Kms.
COUNTRIES CROSSED: China, Myanmar, Thailand. |
| Saint Lawrence–Niagara–Detro–Saint- Clair- Saint Marys–Saint Louis–North |
Source: Lake Ontario – Lake Erie – Lake Saint Clair – Okefenokee swamp – Hoyt Lakes – Saint Louis river.Mouth: Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
Length: 3058 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Canada, U.S.A. |
| Rio Grande |
Source: Main Canby mountain.Mouth: Gulf of Mexico.
Length: 3057 Kms.
Countries Crossed: U.S.A, Mexico |
| Lower Tunguska |
Source: Central Siberian Plateau.Mouth: Yenisei.
Length: 2989 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Danube-Breg (Donau, Dunăre, Duna, Dunav, Dunaj) |
Source: Furtwangen – river Brigach – river Breg.Mouth: Black Sea.
Length: 2888 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Romania, Hungary, Austria, Serbia, Germany, Slovakia, Bulgaria, Croatia, Ukraine. |
| Irrawaddy River–N’MaiRiver–Dulong
River–Kelaoluo–Gada Qu |
Source: MaliKha river – Chayu river Tibet – Zhuxian river.Mouth: Andaman Sea.
Length: 2727 Kms.
Countries Crossed: China, Myanmar. |
| Zambezi |
Source: Mwinilunga District Zambia.Mouth: Mozambique Channel.
Length: 2693 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Zambia, Angola, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Malawi, Tanzania, Namibia, Botswana. |
| Vilyuy |
Source: Central Siberian Plateau.Mouth: Lena.
Length: 2650 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Araguaia |
Source: Nascente do Rio Araguaia.Mouth: Tocantins.
Length: 2627 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil. |
| Ganges–Hooghly–Padma(Ganga) |
Source: Gangotri glacier – Ganges – Himalayas.Mouth: Bay of Bengal.
Length: 2620 Kms.
Countries Crossed: India, Bangladesh, Nepal. |
| Amu Darya- Panj |
Source: Pamir mountains Kush.Mouth: Aral Sea.
Length: 2620 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan. |
| Japurá-(Rio- Yapurá) |
Source: Páramo de Las Papas.Mouth: Amazon.
Length: 2615 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil, Colombia. |
| Nelson–Saskatchewan |
Source: Lake Winnipeg – The Rocky Mountain.Mouth: Hudson Bay.
Length: 2570 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Canada, U.S.A. |
| Paraguay(Río-Paraguay) |
Source: The State Of Mato Grosso.Mouth: Paraná.
Length: 2549 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Brazil, Paraguay, Bolivia, Argentina. |
| Kolyma |
Source: Magadan – Okhotsk town.Mouth: East Siberian Sea.
Length: 2513 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Pilcomayo |
Source: Andes mountain range.Mouth: Paraguay.
Length: 2500 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Paraguay, Argentina, Bolivia. |
| Upper Ob-Katun |
Source: Near Biysk.Mouth: Gulf Of Ob.
Length: 2490 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Ishim |
Source: Kazakhstan.Mouth: Irtysh.
Length: 2490 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Kazakhstan, Russia. |
| Juruá |
Source: Ucayali river Peru.Mouth: Amazon.
Length: 2410 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Peru, Brazil. |
| Ural |
Source: Southern Ural Mountains, Russia.Mouth: Caspian Sea.
Length: 2428 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia, Kazakhstan. |
| Arkansas |
Source: The Rocky Mountains.Mouth: Mississippi.
Length: 2348 Kms.
Countries Crossed: U.S.A. |
| Colorado (Western U.S.) |
Source: La Poudre Pass lake headwaters.Mouth: Gulf of California.
Length: 2333 Kms.
Countries Crossed: U.S.A, Mexico. |
| Olenyok |
Source: Krasnoyarsk Krai – Vilyuy Plateau – Anabar plateau.Mouth: Laptev Sea.
Length: 2292 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
| Dnieper |
Source: Valdai Hills – Russia.Mouth: Black Sea.
Length: 2287 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia, Belarus, Ukraine. |
| Aldan |
Source: Stanovoy Range Russia.Mouth: Lena.
Length: 2273 Kms.
Countries Crossed: Russia. |
Facts About Important Rivers of the World
- The river Nile starts south of the Equator, crosses the Tropic of Cancer, and then drains into the sea.
- Throughout the entire length of the Amazon river, there are no bridges across it.
- The Congo River (former name – Zaire river) crosses the Equator twice.
- The river Limpopo passes the Tropic of Capricorn twice.
- Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Yemen, Bahrain, Qatar are the countries that do not have any rivers flowing through them.
- The River Hwang He or the Yellow River is known as China’s sorrow.
- River Danube passes through 4 capital cities, Belgrade (Serbia), Budapest (Hungary), Bratislava (Slovakia), and Vienna (Austria).
- Moreover, the Danube River flows through ten countries viz Austria, Bulgaria, Croatia, Germany, Hungary, Moldova, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, and Ukraine.
FAQs on Major Rivers in the World
1. Name the 5 longest rivers in the world in order?
The top 5 longest rivers in the world list are provided below:
1. Nile: Africa. 4,180,
2. Amazon: South America. 3,912,
3. Mississippi-Missouri-Red Rock: United States. 3,710,
4. Chang Jiang (Yangtze River): China. 3,602, and
5. Yenisei – Angara – Selenga River: Russia. 3,459.
2. Which is the deepest river on earth?
The deepest river on earth is Congo.
3. Which river is longer Nile or Amazon?
The Amazon is considered the world’s largest river by volume, yet scientists have thought it is somewhat shorter than Africa’s Nile in terms of length.
4. Which is the largest river in the world?
Amazon is the largest river in the world in terms of discharge volume of water.