Difference Between Economics, Economy, Economic and Economical: In some way or the other the terms economics, economy, economic and economical are related to each other, but they also lie some key differences between them based on their diverging factors. It is really important to know the difference between these four terms in order to avoid any confusions in the future.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference between Economics, Economy, Economic and Economical?
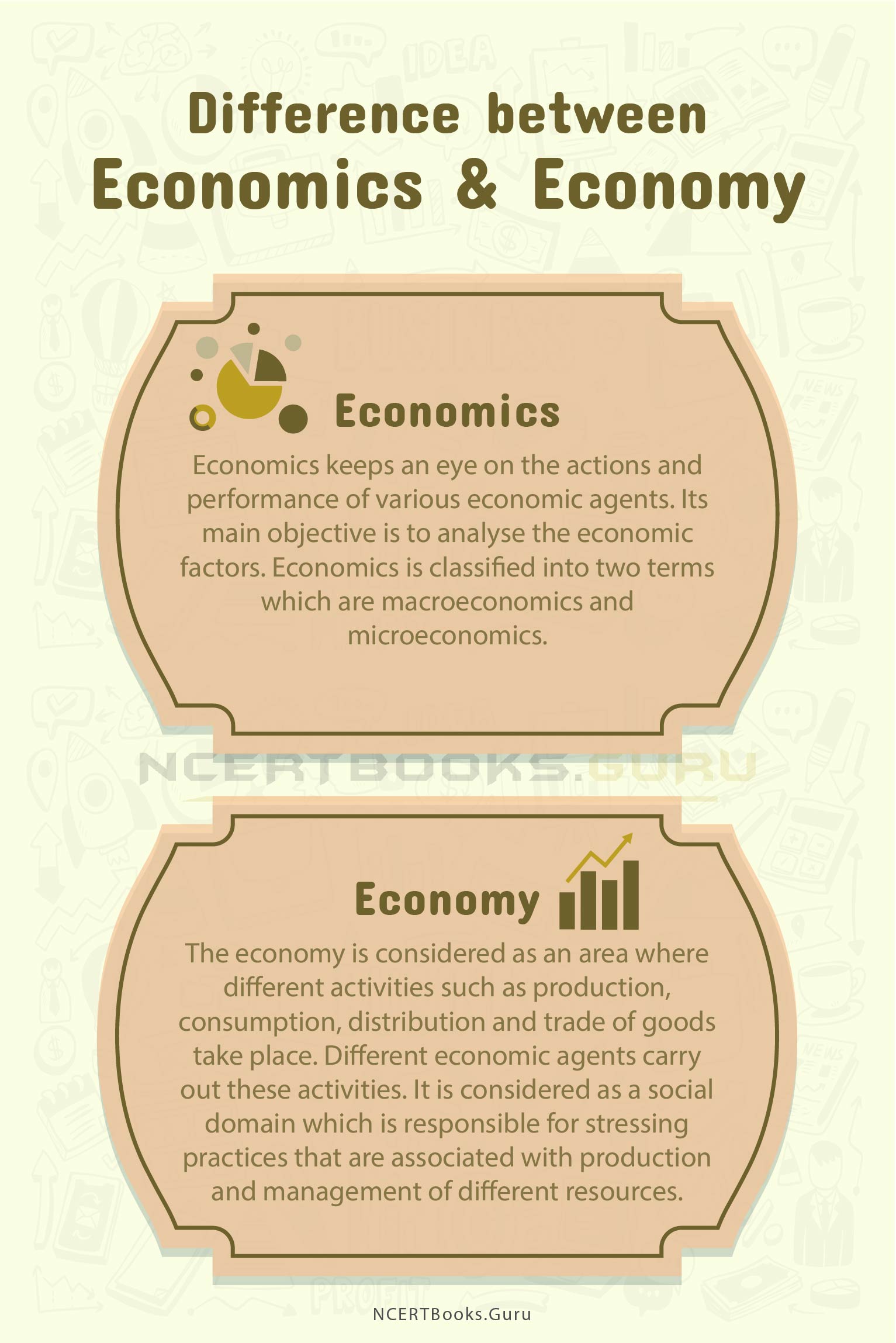
Economics is considered a social science. The economy is a social domain that is involved in stressing the importance of different practices that is involved in managing different resources. Economic term is used to specify a product or object which brings profit. Economical is a term used for the capability of an object or service to return the money that got invested.
Economic
Economics keeps an eye on the actions and performance of various economic agents. Its main objective is to analyse the economic factors.
Economics is classified into two terms which are macroeconomics and microeconomics.
Microeconomics is responsible for analysing economic factors such as individual agents, firms, sellers and buyers. In contrast, macroeconomic is considered as a study of the economy as a whole. This type of economy takes into account the consumption, production and manufacturing capabilities of an economy as a whole.
Economic analysis plays an important role in different sectors, such as real estate, finance, Information Technology, etc.
Economy
The economy is considered as an area where different activities such as production, consumption, distribution and trade of goods take place. Different economic agents carry out these activities. It is considered as a social domain which is responsible for stressing practices that are associated with production and management of different resources.
In an economy, activities are considered to be spurred due to production which is responsible for using natural resources, labour and capital. The economy got divided between two terms which are market-based economy and command-based economy. A market-based economy depends on the demand and supply of the market between the different intermediaries that exist in the market. A command-based economy depends on the political actions of the government authorities and the laws that are imposed by them.
Economic
The world economic is referred to as a term which is used to represent an object or action that is responsible for bringing profit to the party who is involved in this. This term is also used in situations where there are transactions involved; they can be monetary or otherwise. The term was discovered first in the late 19th century to refer to the practice of household management. India is considered to be one of the strongest economic powers in the world.
Economical
Economical is considered as the wise and efficient use of every resource that is available to us. To be economical, one has to avoid any wastage of resources during performing any activity. It involves efficient planning in order to avoid any wastage of resources. The word Economical was first introduced to the world in the late 16th century. Initially, it refers to the management of household activities.