Introduction
A judge can be portrayed as an arbitrator, i.e. the person who decides on a matter in the court. On the contrary, a magistrate may be a regional judicial officer who is elected by the judges or the arbiters of the Supreme Court of the state to take care of law and order in a specific region or area.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference Between Magistrate and Judge?
About Magistrate
A civil or judicial official vested with limited judicial powers a traffic magistrate. A municipal, state, or federal judicial officer commonly authorized to issue warrants, hear minor cases, and conduct preliminary or pretrial hearings. — also called magistrate judge.
There are four categories of magistrates within the Judiciary Of India. This classification is given within the Criminal Procedure Code, 1973 (CrPC). It specifies that in each sessions district, there shall be:
- A Chief Judicial Magistrate
- A Sub-Divisional Judicial Magistrate
- A Judicial Magistrates First Class, and
- An Executive Magistrates [including DM, ADMs, SDMs]
These magistrates are generally conferred on the officers of the Revenue Department, although a politician is often appointed exclusively as an Executive Magistrate. Usually, the Collector of the district is in charge as the DM.
About Judge
A judge is the one who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a neighbourhood of a panel of judges. The powers, functions, discipline, method of appointment, and training of judges vary widely across different jurisdictions. The judge is meant to conduct the trial impartially and, typically, in an open court.
The judge hears all the witnesses and the other evidence presented by the barristers or solicitors of the case, assesses the parties’ credibility and arguments, and then issues a verdict on the matter at hand based on their interpretation or understanding of the law and their judgment in personal. In some jurisdictions, the judge’s powers could also be shared with a jury.

Difference Between Magistrate And Judge
| Area Of Difference | Magistrate | Judge |
| Designation | The term magistrate is used in various systems of governments and laws to refer to a civilian officer who administers the law. | A judge is a person who supervises over court proceedings, either alone or as a neighbourhood of a panel of judges. |
| Discipline Of Work | There are four categories of magistrates within the Judiciary Of India. This classification is given within the Criminal Procedure Code, 1973 (CrPC). | The judge is meant to conduct the trial impartially and, typically, in an open court. |
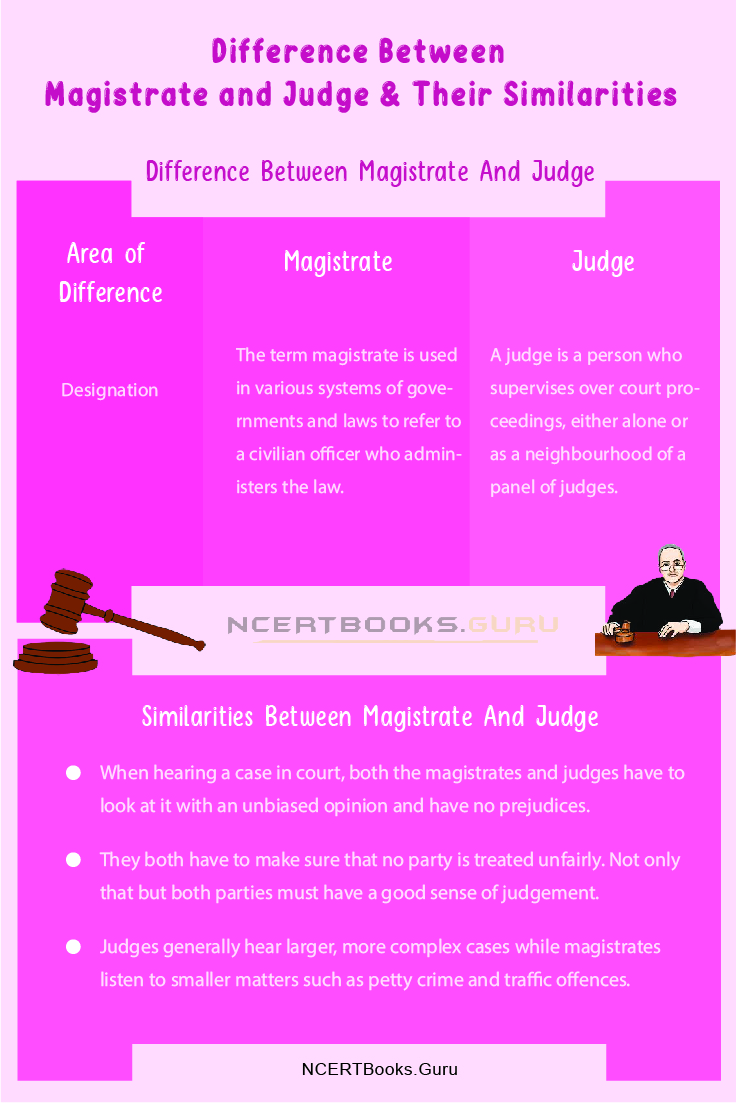
Similarities Between Magistrate And Judge
- When hearing a case in court, both the magistrates and judges have to look at it with an unbiased opinion and have no prejudices.
- They both have to make sure that no party is treated unfairly. Not only that but both parties must have a good sense of judgement.
- Judges generally hear larger, more complex cases while magistrates listen to smaller matters such as petty crime and traffic offences.
Frequently Asked Questions on Difference Between Magistrate and Judge
Question
Is magistrate and judge the same?
Answer
Judges generally hear larger, more complex cases while magistrates hear smaller matters such as petty crime and traffic offences.
Question:
Who is more powerful? The judge or the magistrate?
Answer:
A Judge is bestowed with more powers than a Magistrate. A magistrate has only administrative and limited law enforcement powers.