MCQ Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 14 Natural Resources with Answers
MCQs from Class 9 Science Chapter 14 – Natural Resources are provided here to help students prepare for their upcoming Science exam.
MCQs from CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 14: Natural Resources
Q1. What would happen, if all the oxygen present in the environment is converted to ozone?
(a) We will be protected more
(b) It will become poisonous and kill all living forms
(c) Ozone is not stable, hence it will be toxic
(d) It will allow harmful sun radiations to reach earth and damage many life forms
Answer/ Explanation
(b) It will become poisonous and kill all living forms
Q2.When we breathe in air, nitrogen also goes inside along with oxygen. What is the fate of nitrogen?
(a) It moves along with oxygen into the cells
(b) It comes out with the carbon dioxide during exhalation
(c)It is absorbed only by the nasal cells
(d) Nitrogen concentration is already more in the cells, so itis not at all absorbed
Answer/ Explanation
(b) It comes out with the carbon dioxide during exhalation
Q3. There is always a cycle of CO2 running in the atmosphere due to which the concentration of CO2 remains constant in the atmosphere. Choose the correct sequence of this cycle:
(a) CO2 in atmosphere→ decomposers → organic carbon in animals → inorganic carbon in soil
(b) CO2 in atmosphere → organic carbon in plants →organic carbon in animals → inorganic carbon in soil
(c)Inorganic carbonates in water →organic carbon in plants → organic carbon in animals → scavengers.
(d) Organic carbon in animals → decomposers → CO2 in atmosphere →organic carbon in plants
Answer/ Explanation
(b) CO2 in atmosphere → organic carbon in plants →organic carbon in animals → inorganic carbon in soil
Q4. You must have observed that during the winters sometimesit becomes quite difficult to see even the objects short distance apart. This low visibility during the cold weather is due to:
(a) Formation of fossil fuels
(b) Unburnt carbon particles of hydrocarbons suspended in air
(c) Lack of adequate power supply
(d) None of these
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Unburnt carbon particles of hydrocarbons suspended in air
Q5. The ‘water pollution’ can be defined in several ways. Which of the following statements does not give the correct definition?
(a) The addition of the undesirable substances to water bodies
(b) The removal of the desirable substances from water bodies
(c)A change in pressure of the water bodies
(d) A change in temperature of the water bodies
Answer/ Explanation
(c) A change in pressure of the water bodies
Q6. The amount of nitrogen in the atmosphere is maintained by a biological cycle which involves two processes, first is to withdraw nitrogen from the atmosphere and secondly to add the same to atmosphere.
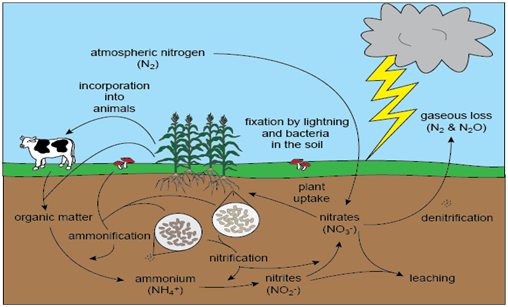
The nitrogen cycle
Can you guess the names of these two respective processes.
(a) Nitrogen fixation and nitrification
(b) Nitrogen fixation and denitrification
(c)Nitrification and denitrification
(d) Nitrification and nitrogen fixation
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Nitrogen fixation and denitrification
Q7. Ozone layer is a protective blanket in the atmosphere that protectsus from the harmful high energy UV radiations coming from the sun. But it has been observed that some harmful air pollutants like chlorofluorocarbons are causing hole in this protective layer. What does this ‘ozone hole’ exactly mean?
(a) A large sized hole in the ozone layer
(b) Thinning of the ozone layer
(c)Small holes scattered in the ozone layer
(d) Thickening of the layer
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Thinning of the ozone layer
Q8. Aquatic organisms are used to a certain range of temperature in the water bodies where they live. A sudden marked change in this temperature can affect:
i. Breeding of animals
ii. Growth of the aquatic plants
iii. Process of digestion in animals
iv. Availability of nutrients
Choose the correct option from the following:
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) Only (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer/ Explanation
(a) (i) and (ii)
Q9. Presence of the fertilizers and sewage in polluted water provides a lot of nitrogen, causing excessive growth of algae which subsequently reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.Can you name this process of reduction of dissolved oxygen due to the excess growth of algae.
(a) Biomagnifications
(b) Eutrophication
(c)Algal bloom
(d) Decopmposition
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Eutrophication
Q10. A cool breeze after a hot day brings all of us considerable relief. This breeze is actually the moving air. What is the basic process that causes this movement of air?
(a) Pressure difference between the air of two regions
(b) Moving leaves of the plants
(c)Temperature difference between the two regions
(d) Striking of air with the mountains
Answer/ Explanation
(c) Temperature difference between the two regions
Q11. If the carbon dioxide content in the atmosphere is increased then which one of the following would not get affected?
(a) Amount of the heat retained by the environment
(b) Process of photosynthesis in plants
(c) Global warming
(d) Existence of desert plants
Answer/ Explanation
(d) Existence of desert plants
Q12.The nitrogen molecules present in air can be converted into nitrates by:
(a) A biological process of nitrogen fixing bacteria present in the soil
(b) A biological process of carbon fixing factor present in the soil
(c) Any of the industries manufacturing nitrogenous compounds
(d) The plants used as cereal crops in field
Answer/ Explanation
(a) A biological process of nitrogen fixing bacteria present in the soil
Q13. Top soil is the best for the vegetation. The main components ofthis productive top layer are:
(a) Humus and living organisms only
(b) Humus and soil particles only
(c) Humus, living organisms and plants
(d) Humus, living organisms and soil particles
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Humus and soil particles only
Q14. The process of nitrogen fixation by bacteria does not take place in the presence of:
(a) Molecular form of hydrogen
(b) Elemental form of oxygen
(c) Water
(d) Elemental form of nitrogen
Answer/ Explanation
(b) Elemental form of oxygen
Q15. Following is the diagram showing the natural Ecosystem comprising both of abiotic as well as biotic components.
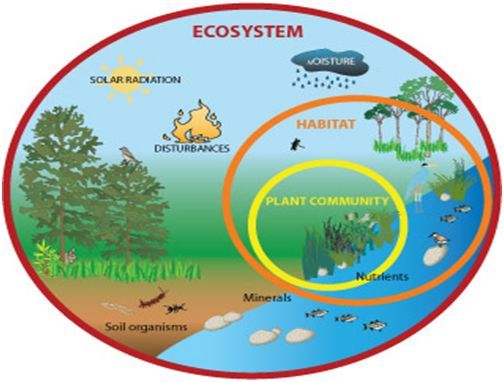
The Biotic components of an ecosystem consist of:
(a) Producers
(b) Consumers
(c) Decomposers
(d) All of these
Answer/ Explanation
(d) All of these