The Yamuna river is one of the largest tributaries of the Ganges and originates from Champasar (Yamunotri) Glacier. It is widely known for its historical significance related to Lord Krishna. The Yamuna River runs through Uttarakhand, Haryana, Delhi and Uttar Pradesh, meeting the Ganga River at Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj, UP.
Top 10 Largest Rivers in India, you would also find the details about Indian River Systems and major rivers of India.
|
Name of the River
|
Yamuna River |
|
Source of Origin
|
Yamunotri Glacier, Bandarpunch Peak, Uttarkashi district in Uttaranchal |
|
Location
|
Northern India – Uttarakhand, Haryana, Delhi, Uttar Pradesh |
|
Tributaries
|
Tons, Hindon, Sindh, Kens, Chambal, |
|
Length
|
1376 kilometres (855 mi) approx. |
About Yamuna River
The Yamuna River is the longest tributary in all of India, running a length of approximately 1376 kilometres, which is about 855 miles. It is also the second largest tributary of the river Ganga and is highly responsible for maintaining the alluvial fertility of the soil in the regions through which it passes.
The Yamuna River originates in the Himalayas, at the Yamunotri Glacier in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand close to Dehradun, at the mighty altitude of 6387 metres. In a town called Yamunotri, this glacier starts and extends for 1376 kilometres as the river Yamuna that brings great solace and fertility to the lands that it passes on its way to Prayagraj.
At the Triveni Sangam in Prayagraj or Allahabad, the Kumbh Mela is held every twelve years, as it is the place where Lord Ganesha was said to have offered penance. The occurrence of the festival here majorly adds to the sacredness of the river, which is often equated to that of the Ganga as well.
To add to the river’s sacredness, one of the many notable things about the Yamuna River is that at its origin, there is a hot water body emerging from it, which is said to be so hot that if a bag of potatoes or rice is put in it, it will cook. People often use the water of the Yamuna at Yamunotri for this purpose as well.
Yamuna River History
There are a few stories that have been told about how the Yamuna River was given its name. One story is closely linked to the river Ganga and goes that “yama” is the Sanskrit word for “twin,” and the sacredness of both rivers is equated in that the ganga and Yamuna Rivers can be called twins.
The other, more widely told story, relates to the goddess Yamuna. She was the daughter of Surya, the sun god; her brother was Yama, the god of death. Because Yamuna’s brother was the god of death, it was believed, and still is, to this day, that taking a dip in the holy water of the Yamuna River will rid one of the fear of death.
The history of the Yamuna River is also very closely linked with Lord Krishna, who, as a young child, crossed the river with his father Vasudev. Lord Krishna spent a lot of his time by the Yamuna River as he was growing up and, thus, the river is also very significant to the followers of Hinduism and especially those of Lord Krishna.
Yamuna River Map
One of the most major rivers in Northern India, the Yamuna River originates in the lower Himalayas, specifically in the Bandarpunch Peak in the Uttarkashi district of Uttaranchal. The origin of the Yamuna River lies in the Yamunotri Glacier in the town of Yamunotri in this Uttarkashi district. From here, the river makes its way to Himachal Pradesh at Paonta Sahib and enters Haryana.
In Haryana, at the Hathni Kund Barrage, the Yamuna River splits into the Western Canal and Eastern Canal, and then the river enters the city of Delhi. From Delhi, the Yamuna makes its way to Uttar Pradesh, passing through various important cities like Mathura, Agra, Etawah, and then on to its final destination, Prayagraj or Allahabad. At Allahabad lies the Triveni Sangam, where the sacred Yamuna River meets the sacred Ganges.
All throughout, the Yamuna River stretches to about 1376 kilometres and is responsible for taking care of approximately 57 million people along its way. This not only includes sustaining people for drinking water and water to be used for cooking and cleaning, but also for irrigation purposes in the fields on the banks of the Yamuna River as well.
Yamuna River System
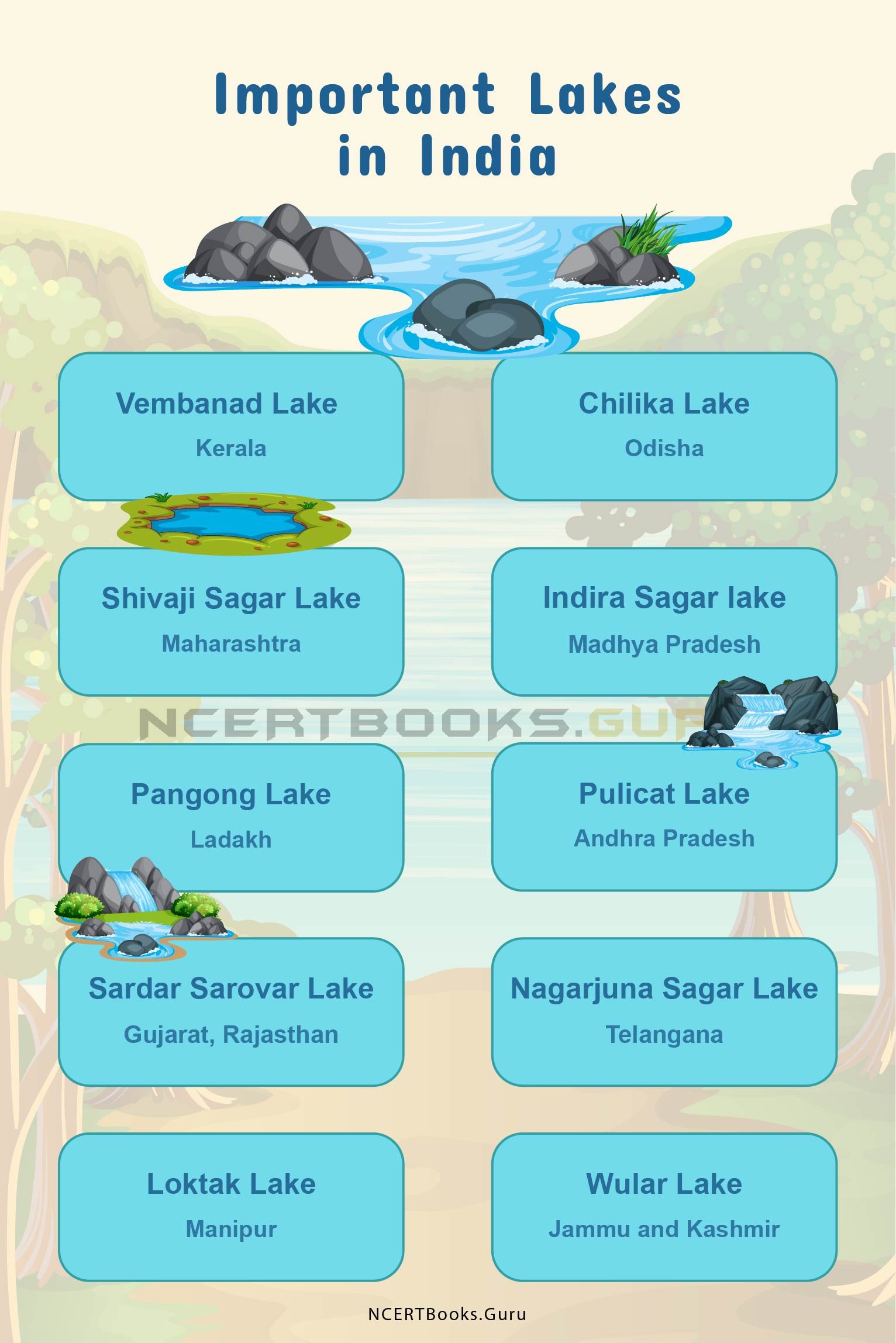
The Yamuna River itself is a tributary of the Ganga River, but the Yamuna also has several tributaries of its own. The following are the most important tributaries of the Yamuna River:
- Tons River: This river also originates at the Bandarpunch Peak in the lower Himalayas and is the Yamuna River’s largest tributary. Tons River meets the Yamuna close to Dehradun, under Kalsi.
- Sindh River: This river originates on the Malwa Plateau from Central India and flows north-eastwards to meet Yamuna in Etawah in Uttar Pradesh.
- Hindon River: Originating in Saharanpur between the Shivalik and Himalayan mountain ranges, the Hindon River meets the Yamuna just outside of Delhi towards the Uttar Pradesh side.
- Ken River: This river finds its origin in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, and meets the Yamuna in a village called Chilla near Fatehpur in Uttar Pradesh.
- Chambal River: Originating in the Vindhya Ranges of Madhya Pradesh, Chambal River merges with the Yamuna near Sohna Gaon in Etawah.
- Betwa or Vetravati River: This river originates in the Vindhya Ranges and meets the Yamuna in Uttar Pradesh at Hamirpur Town.
Yamuna River Pollution
In recent years, more than its sacredness, the Yamuna River has come to be known for how polluted it has gotten. Owing to many years of dumping city waste such as the propelling of sewage, drainage, garbage and dirt into the river, the Yamuna is one of the most polluted rivers in the world today. Industries are also responsible for having dumped their waste in the Yamuna River, adding to its desecration and pollution.
Efforts have been made over the years to clean up the river, but only in vain due to corruption, dirty politics and laziness of the people in charge of cleaning the Yamuna that came in the way. Thus, the river remains a dumping ground for all sorts of waste. This is due to lack of awareness, or lack of care despite awareness.
Toxic waste emptied into the river is not only harmful for the people, households and crops that are dependent on the river, but also the aquatic life that lives in the river. The oxygen levels of the river are reduced, leading to the killing of aquatic life in the river, terrible odours and also a high amount of turbidity of the water.
Importance of the Yamuna River
The Yamuna River is incredibly important for Northern India for several reasons, one of them being that its deposits help maintain the fertility of the soil in the regions it passes, as mentioned before. People living near to the banks of the Yamuna use its flowing water for several purposes, which mostly accounts for irrigation purposes. The Yamuna River is responsible for providing water supply to all four states through which it passes, and it is accountable for approximately 70 percent of Delhi’s water system.
Aside from providing sustenance to tonnes of people, the Yamuna River is also home to a lot of wildlife, such as the Asian Elephant. The forests in the Shivalik Mountains through which Yamuna passes is home to many herds of Asian Elephants and the river acts as a safe passageway for the elephants to cross between forests and such.
For stringent devotees of Hinduism, the Yamuna River holds immense importance, as it is one of the most important places associated with Lord Krishna, Yama the god of death, Surya the sun god, and Yamuna the goddess of the river herself. Taking a dip in the Yamuna River is considered very holy and a true spiritual event, as the river is considered to be almost as holy as the Ganga herself.
Short Essay on Yamuna River
The Yamuna River is one of the largest tributaries of the Ganga and also one of the longest. It has a length of about 1376 kilometres from the point where it starts to the point where it meets the Ganga. The origin of the Yamuna River is at Bandarpunch Peak in the lower Himalayas from Yamunotri Glacier and it meets Ganga River at Triveni Sangam at Allahabad.
Yamuna is considered to be a very holy river as a large part of its history is attached to Lord Krishna. Alongside, the river was named after goddess Yamuna, who was the daughter of Surya (the sun god) and Yama (the god of death). Because of this, it is also historically significant to Hindu devotees.
The Yamuna River has several tributaries, the most important of which are the Tons River, Sindh River, Hindon River, Ken River, Betwa River and Chambal River. Some of these rivers originate from the Himalayas or Shivalik Mountains and the others come from the Vindhya Ranges and other parts of Central India.
Recently, the Yamuna River has been found to be very polluted because of all the city waste that is being dumped in it. While the river provides sustenance to 57 million people along its way, the people do not give it the appropriate respect. Sewage, garbage, toxic industrial waste, etc. is dumped in the Yamuna without any remorse. Even with government plans to rehabilitate the river, it has not yet worked out and remains in the same dirty condition.

10 Lines of Yamuna River
- The Yamuna River is the longest tributary of the Ganga.
- The length of the Yamuna River is approximately 1376 kilometres (855 miles).
- The Yamuna River has a lot of religious significance as Lord Krishna spent his childhood beside it.
- Yamuna originates at Bandarpunch Peak in Uttaranchal at the Yamunotri Glacier.
- The Yamuna River meets the Ganga at Triveni Sangam in Allahabad, where the Kumbh Mela takes place every twelve years.
- The Yamuna River has several tributaries and its main ones are Tons River, Hindon River, Ken River, Betwa River, Sindh River and Chambal River.
- The Yamuna River was named after the goddess Yamuna who was the daughter of the sun god Surya and the god of death Yama.
- Recently, the Yamuna River has become highly polluted due to the dumping of waste by the cities.
- The Yamuna passes through several states, namely Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Delhi and Uttar Pradesh.
- The Yamuna River provides sustenance to about 57 million people for drinking water, non-drinking water and for irrigation for crop fields.
Frequently Asked Questions about Yamuna River
Question 1.
How did Yamuna River get its name?
Answer:
Yamuna River is named after the goddess Yamuna, who was the daughter of Surya, the sun god, and the sister of Yama, the god of death. Another story says that because the Yamuna and Ganga are both considered to be very sacred, and “yama” is a Sanskrit word meaning ‘twin’, the origin of the name of the river lies here.
Question 2.
Where does the Yamuna River start and end?
Answer:
The Yamuna River originates in the lower Himalayas, at the Bandarpunch Peak in Uttarkashi, Uttarakhand as the Yamunotri Glacier. It makes its way down to Himachal Pradesh from there, then to Haryana, Delhi and then Uttar Pradesh. It finally culminates in Uttar Pradesh at Allahabad, at the Triveni Sangam.
Question 3.
How did the Yamuna River get so polluted?
Answer:
Over recent years, the Yamuna River has become extremely polluted. Yamuna pollution is all we now associate with the river rather than how sacred it is to Hindus or important to the people it sustains. It has become this polluted because of the consistent dumping of untreated sewage and garbage into the river, and also industrial waste that comes from several factory units nearby in Haryana, Delhi and Uttar Pradesh.
Question 4.
What is being done to reduce pollution in the Yamuna River?
Answer:
The government has tried to put in measures to reduce the pollution in the Yamuna River, but none have worked. A few years ago, a large fund was allocated to clean up the river but it disappeared due to corruption and the river was left untouched. The government now levies fines on companies whose factories do not treat their waste before disposing of it.