Introduction
Fundamental Rights are human rights conversed on the citizens of India. The Constitution originally provided seven fundamental rights. The Fundamental Duties of citizens were added to the Constitution by the 42nd Amendment in 1976.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference Between Fundamental Rights And Fundamental Duties?
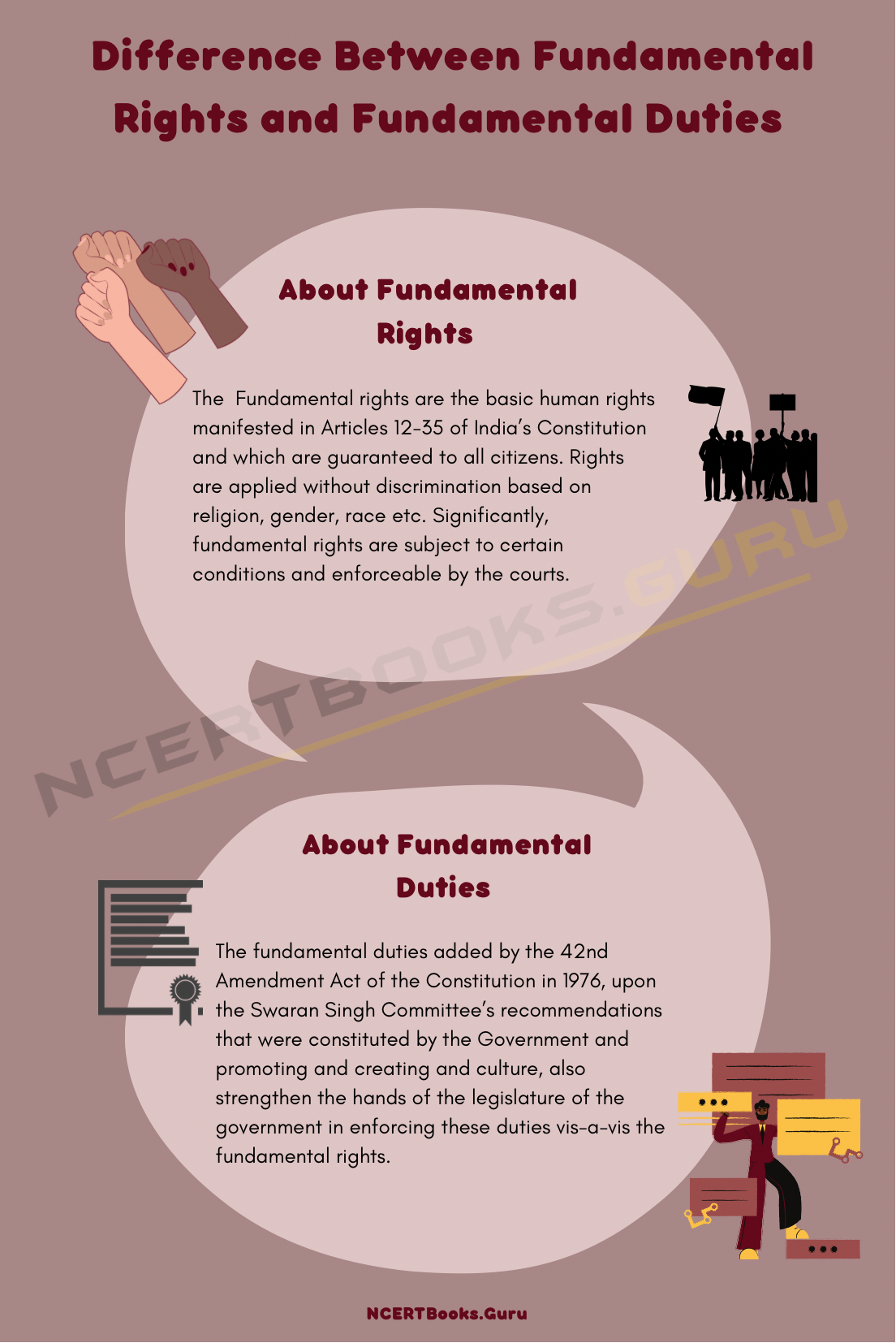
About Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are the basic human rights manifested in Articles 12-35 of India’s Constitution and which are guaranteed to all citizens. Rights are applied without discrimination based on religion, gender, race etc. Significantly, fundamental rights are subject to certain conditions and enforceable by the courts.
Constitution tells that these rights are inviolable and these human rights are conferred upon the citizens of India.
About Fundamental Duties
The fundamental duties added by the 42nd Amendment Act of the Constitution in 1976, upon the Swaran Singh Committee’s recommendations that were constituted by the Government and promoting and creating and culture, also strengthen the hands of the legislature of the government in enforcing these duties vis-a-vis the fundamental rights.
Difference between Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties
| Area of differentiation | Fundamental rights | Fundamental duties |
| Placement in the Amendment: | The Fundamental Rights are present in Part III of India’s Constitution and is guaranteed to the citizens of India. | Fundamental Duties deals in Part IV A of the Constitution of India. |
| Purpose of the Articles: | Fundamental Rights deals with Articles 12-35 of the Constitution of India. | Article 51-A of the Constitution of India deals with Fundamental Duties. |
| Native source of Article: | Fundamental Rights was borrowed from the Constitution of the United States of America. | From the Constitution of the former Soviet Union (USSR), Fundamental Duties were taken. |
| Application: | These rights are defined and applied irrespective of religion, caste, race, place of birth, creed, or gender. | These duties’ are defined as the moral obligations of all citizens to uphold India’s unity and help promote a spirit of patriotism. |
Similarities between Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties
- The Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties are the two faces of a coin that aims to serve a single purpose.
- Fundamental Rights and Fundamental Duties are defined under Part III and Part IV-A of the constitution.
- Fundamental Duties and Fundamental Rights go to the roots of how a citizen acts in the society.
- Fundamental Duties and Rights are enforceable in courts.
- They both are complementary as well as supplementary to each other.
FAQs on Difference Between Fundamental Rights And Fundamental Duties
Question:
What are the differences between rights and duties?
Answer:
Rights are legal, social or ethical principles of freedom that people are entitled uefor by a governing body. In contrast, duties are responsibilities or obligations of an individual, by the governing body, that are required to do by the said individual.
Question:
How are the fundamental duties related to fundamental rights?
Answer:
The important natural rights necessary for the development of human beings are guaranteed under Part III of the Constitution by the Fundamental Rights. Through the court of law, they are enforceable. On the other hand, while interpreting any fundamental rights, Fundamental Duties is not enforceable, but always taken into account.
Question:
Who can claim fundamental rights?
Answer:
Rights are the social claims and the Fundamental Rights that are guaranteed by Articles 14, 20, 21, 21A, 22 – 28 are available to all persons whether citizens of India or foreigners without which a man cannot give his best to society.
