Introduction
The reasonable claims which are approved by the law and accepted by society are called Rights. For the development and very existence of the citizens, the Fundamental Rights are very important. At the time of making laws and framing policies, these are the guidelines that are considered.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy?
About Fundamental Rights
Fundamental rights are the basic human rights manifested in Articles 12-35 of India’s Constitution and which are guaranteed to all citizens. Rights are applied without discrimination based on religion, gender, race etc. Significantly, fundamental rights are subject to certain conditions and enforceable by the courts.
Constitution tells that these rights are inviolable and these human rights are conferred upon the citizens of India.
About Directive Principles of State Policy
Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) is dealt under Articles 36-51 under Part-IV of the Indian Constitution. DPSP’s are borrowed from the Constitution of Ireland, which rather had been copied from the Spanish Constitution.
DPSP are ideals which are made by our constitution and are meant to be kept in mind by the state when it enacts laws and formulates policies. There are various definitions to the Directive Principles of State.

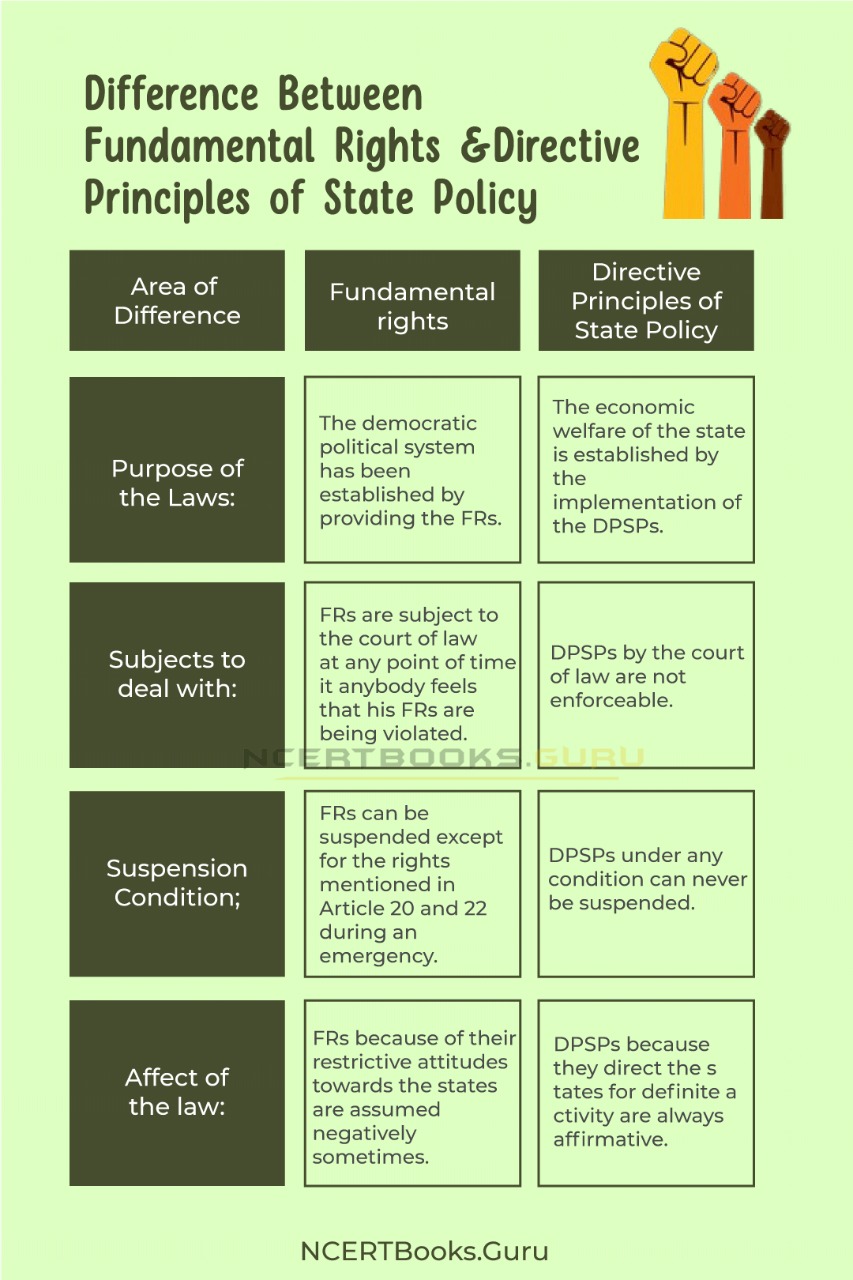
The Differences between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
| Area of difference | Fundamental rights | Directive Principles of State Policy |
| Purpose of the Laws: | The democratic political system has been established by providing the FRs. | The economic welfare of the state is established by the implementation of the DPSPs. |
| Subjects to deal with: | FRs are subject to the court of law at any point of time it anybody feels that his FRs are being violated. | DPSPs by the court of law are not enforceable. |
| Suspension Condition; | FRs can be suspended except for the rights mentioned in Article 20 and 22 during an emergency. | DPSPs under any condition can never be suspended. |
| Affect of the law: | FRs because of their restrictive attitudes towards the states are assumed negatively sometimes. | DPSPs because they direct the states for definite activity are always affirmative. |
Similarities between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental Rights are often contrasted and compared with the (DPSP) Directive Principles of the State Policy.
- The State must take note of the Directive Principles in determining the scope of Fundamental Rights.
- While adopting the doctrine of harmonious construction, the Court should give effect to both the Directive Principles and the Fundamental Rights.
- Fundamental rights are facilities or rights given by the state to the people.
- Directive Principles are directions that are provided by the constitution to the state.
FAQs on Difference between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles Of State Policy
Question:
What is the difference between the Constitution and fundamental rights?
Answer:
A supreme right that is guaranteed by our Constitution is known as a Constitutional Right. These rights are not basic and do not apply to everyone, unlike fundamental rights.
Question:
What is the primary key difference between fundamental right and duties?
Answer:
The fundamental right is based on the privilege granted to you, whereas fundamental duty is based on accountability is the primary difference between fundamental right and fundamental duty.
Question:
What is the difference between right and duty?
Answer:
Rights: Rights are ethical, legal, or social principals of freedom that are entitled to the people by a governing body.
Duties: something that you or one is expected or required to do by moral or legal obligation is called duty.
