A Shirt in the Market Class 7 Questions and Answers Civics Chapter 9
Class 7 Civics Chapter 9 NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Did Swapna get a fair price on the cotton?
Answer:
No, Swapna did not get fair price on the cotton.
Question 2.
Why did the trader pay Swapna a low price?
Answer:
Because Swapna had borrowed Rs. 2,500 from the trader at the time of cropping season at high rate of interest.
Question 3.
Where do you think large farmers would sell their cotton ? How is their situation different from Swapna?
Answer:
Large farmers would sell their cotton in the wholesale market where these can fetch high rates.
Their situation is different because they are selling their produce in the wholesale market at high rates while Swapna is selling her produce to the trader who is giving her less amount.
Question 4.
What are the following people doing at the Erode cloth market-merchants, weavers, exporters?
Answer:
On the market days at the Erode cloth market, the weavers bring clothes that have been made on order from the merchants. The merchants supply clothes on order to garment manufacturers and exporters, who supply the clothes throughout the country and other countries.
Question 5.
In what ways are weavers dependent on cloth merchants?
Answer:
The merchant distributes work among the weavers based on the orders he has received for cloth. The weavers get the yam from the merchant and supply him the cloth.
The dependence on the merchants both for raw materials and markets means that the merchants have a lot of power. They give orders for what is to be made and they pay a very low price for making the cloth. In these ways the weavers are dependent on cloth merchants.
Question 6.
If the weavers were to buy yarn on their own and sell cloth, they would probably earn three times more. Do you think this is possible? How? Discuss.
Answer:
Yes, the weavers can earn more by buying their cloth, finishing it and selling it directly to the exporter.
Question 7.
You might have heard of cooperatives in your area. It would be in milk, provisions, paddy, etc. Find out for whose benefit they are set up?
Answer:
Cooperatives are set up for the benefit of the producers, so that they can earn more and get reasonable rates for their products.
Question 8.
What are the demands foreign buyers make on the garment exporters ? Why do the garment exporters, agree to these demands?
Answer:
Foreign buyers demand the lowest prices from the supplier. In addition, they set high standards for quality of production and timely delivery. Any defects or delay in delivery is dealt with strictly. The exporter agrees to these demands in order to get bulk orders from the foreign buyers.
Question 9.
How do the garment exporters meet the conditions set by the foreign buyers?
Answer:
Faced with pressures from the buyers, the garment exporting factories try to cut costs. They get the maximum work out of the workers at the lowest possible wages. This way they can maximise their own profits and also supply the garments to foreign buyers at a cheap price.
Question 10.
Why do you think more women are employed in the Impex garment factory? Discuss.
Answer:
The main work of Impex garment factory is tailoring, ironing, thread cutting and buttonning which are suitable for women. These work mostly women do at home. For this reason more women are employed in the Impex garment factory.
Question 11.
Write a letter to the Minister asking for what you think would be proper payment to the workers.
Answer:
Date: ……….
To
The Minister of Textiles
Govt, of India
New Delhi 110001
Subject: Proper payment to textile workers.
Hon’ble Sir,
The condition of the textile workers is not satisfactory. They are exploited due to their ignorance and their need. I would request you to please ensure proper payment for these workers.
Following are a few suggestions, your office can cross-check and the same can be announced so that factory owners follow them.
- Tailoring: ₹ 8000 per month
- Ironing: ₹ 3 per piece
- Checking: ₹ 6000 per month
- Thread cutting: ₹ 5000 per month
- Buttoning: ₹ 2 per shirt
We would be obliged for the same.
Thanking your
Your’s sincerely
ABC
Question 12.
The shirt below’ shows the profit made by the business person, and the various costs that he had to pay. Find out from the diagram below, what the cost price includes.
Answer:
The cost price includes purchase, storage, and advertising.

Question 13.
Compare the earnings per shirt of the worker in the garment factory, the garment exporter and the business person in the market abroad. What do you find?
Answer:
The worker in the garment factory earned Rs.15 per shirt. The garment exporter earned Rs.100 per shirt. The businessperson earned Rs. 600 per shirt.
We find that the maximum profit is earned by the business person.
Question 14.
What are the reasons that the businessperson is able to make a huge profit in the market?
Answer:
The businessperson is able to make a huge profit in the market because of the following reasons :
- He sells the shirt in a foreign country, where rates are always high.
- He has more capital (money), so he can motivate his business properly.
Question 15.
You have read the chapter of advertising. Why does the businessperson spend Rs. 300 per shirt on advertising. Discuss.
Answer:
Advertising a product costs a lot of money. Producing and showing advertisements in the media is very expensive. Companies have to show the advertisement again and again to have it stick in people’s mind. For this reason, the businessperson spend Rs. 300 per shirt on advertising so that it may sell quickly.
Question 16.
What made Swapna sell the cotton to the trader instead of selling at the Kurnool cloth market?
Answer:
Swapna had burrowed Rs. 2,500 from the trader at the beginning of the cropping season, at a very high rate of interest to buy seeds, fertilizers, pesticides, etc., for cultivation. While giving her the money, the trader made an agreement with Swapna that she will sell all her cotton to him. For this reason, Swapna had to sell the cotton to the trader instead of selling at the Kurnool cloth market.
Question 17.
Describe the conditions of employment as well as the wages of workers in the garment exporting factory. Do you think the workers get a fail deal?
Answer:
The condition of the employees working in the garment factory is very poor. They work for at least 10 to 12 hours a day but they get very low wages. Their job is also not permanent. They are appointed on temporary basis. Whenever the employer feels that a worker is not needed, he or she is asked to leave. Their wages are also fixed according to their skills. The highest paid among the worker is the tailor, who gets maximum salary of Rs. 3000 per month. Many women are also employed in these factories. Their wages are also very low. No, according to the fixed government wages, the workers are not getting a fair deal.
Question 18.
Think of something common that we use. It could be sugar, tea, milk, pen, paper, pencil, etc. Discuss through what chain of markets this reaches you. Can you think of the people that help in the production or trade?
Answer:
A chain of markets links the producer to the buyer. Both selling and buying takes place at every step in the chain. For example :
- The producer supplies goods to retailer who sells them to us (customers).
- The producer may supply goods to the wholesaler who is turn sells to the customers in small quantities. In this case, there is no place for retailer.
- The producer may sell through agents. The agents may sell it to the wholesalers who may sell it to the customers.
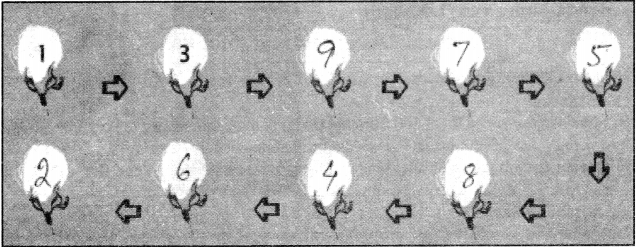
Question 19.
Arrange the statements given in the correct order and then fill in the numbers in — the cotton bolls accordingly. The first two have already been done for you.
1. Swapna sells the cotton to the trader.
2. Customers buy these shirts in a supermarket.
3. Trader sells cotton to the Ginning Mill.
4. Garment exporters buy the cloth from merchants for making shirts.
5. Yarn dealers or merchants give the yarn to the weavers.
6. The exporter sells shirts to the businessperson from the USA.
7. Spinning will buys the cotton and sells yarn to the yarn dealers.
8. Weavers return with the cloth.
9. Ginning mill cleans the cotton and makes it into bales.
Answer: