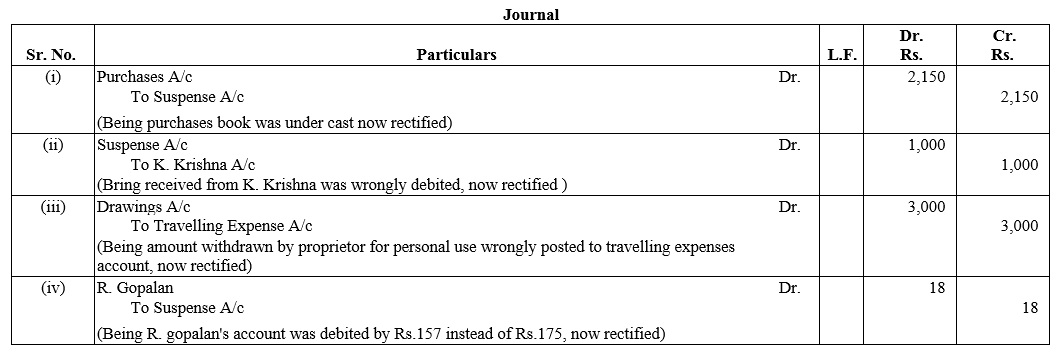
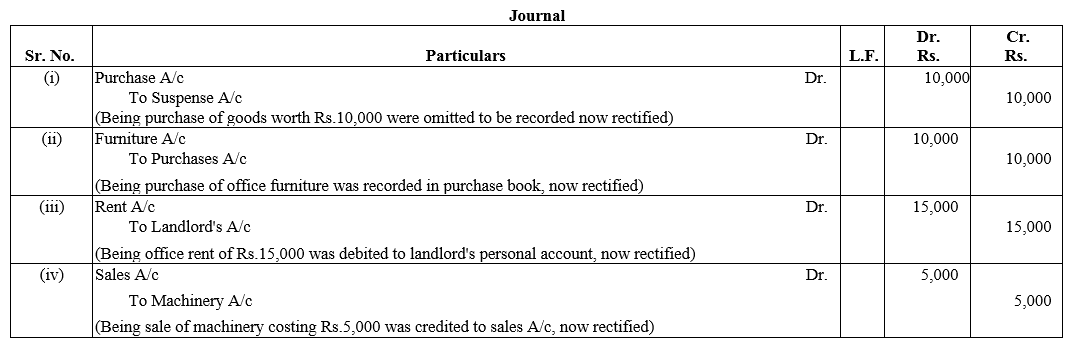
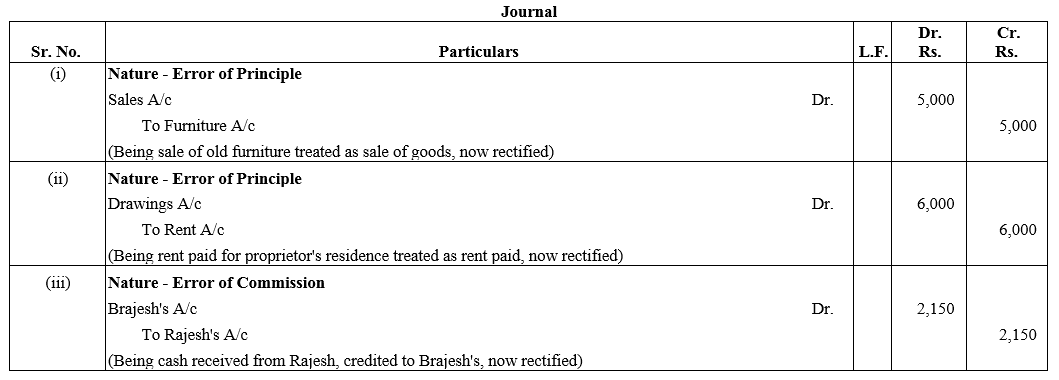
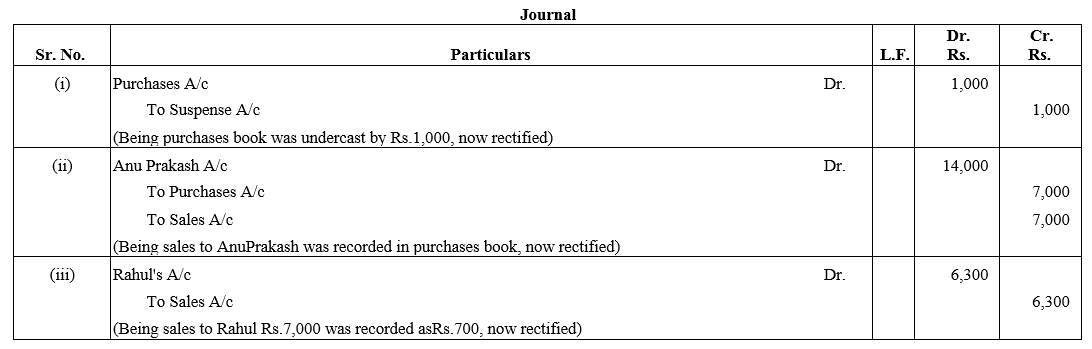
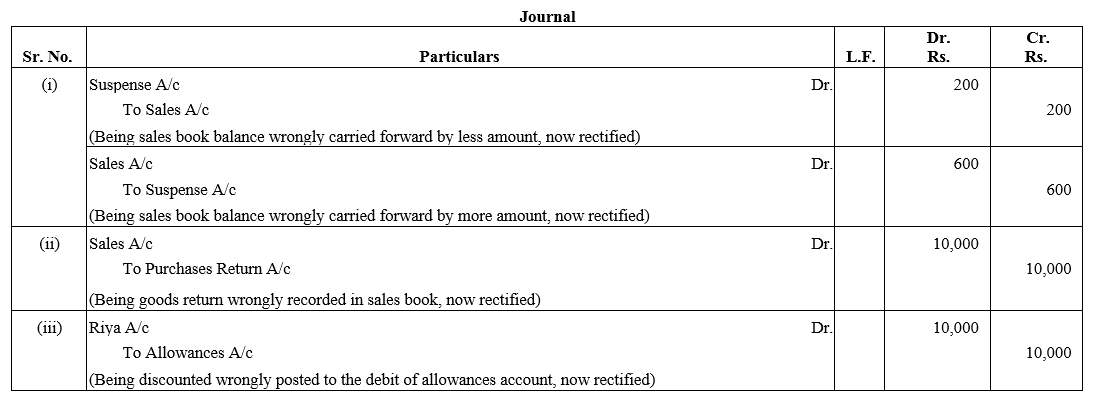
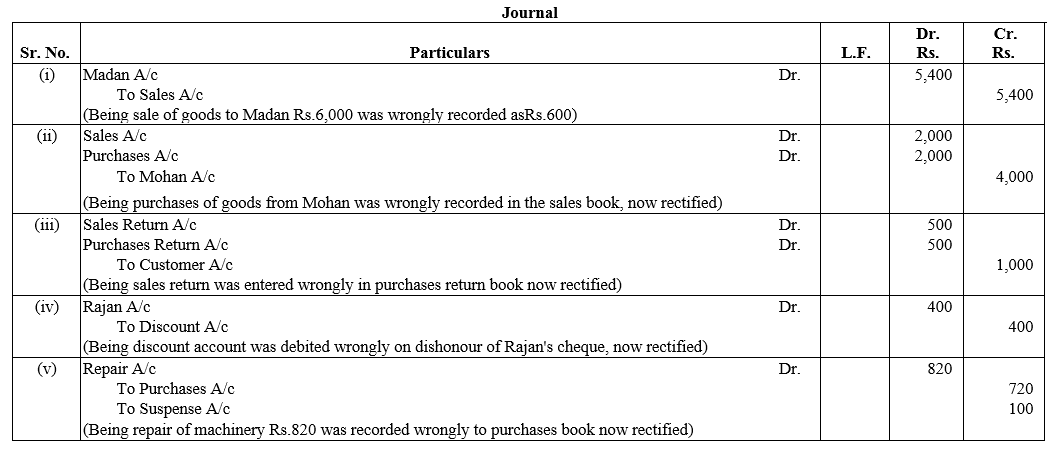
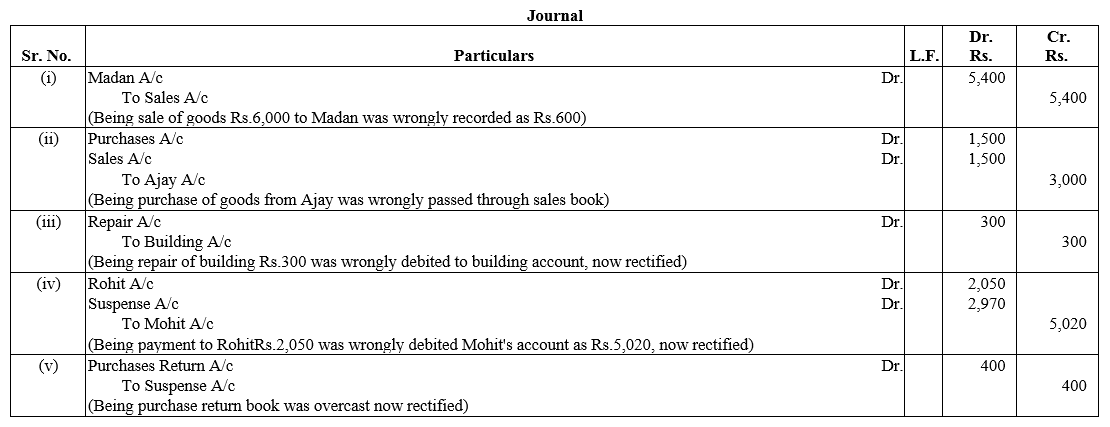
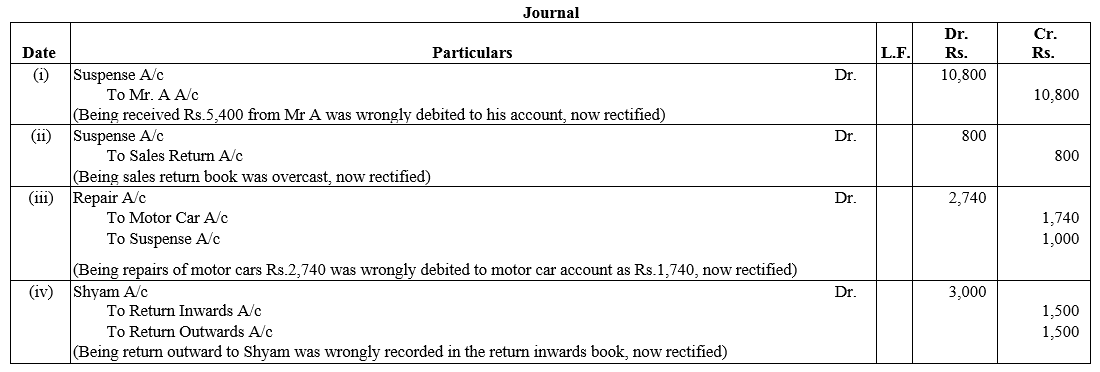
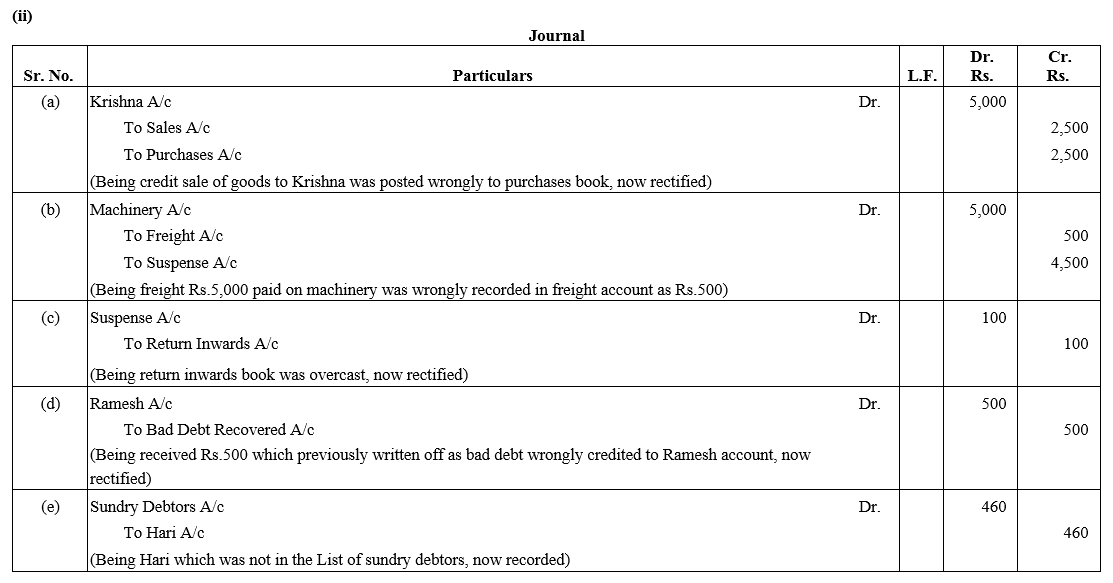
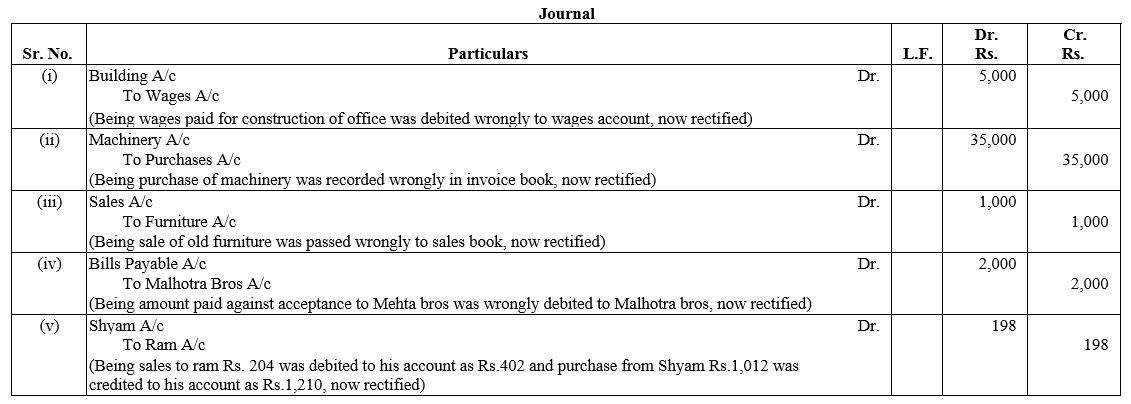
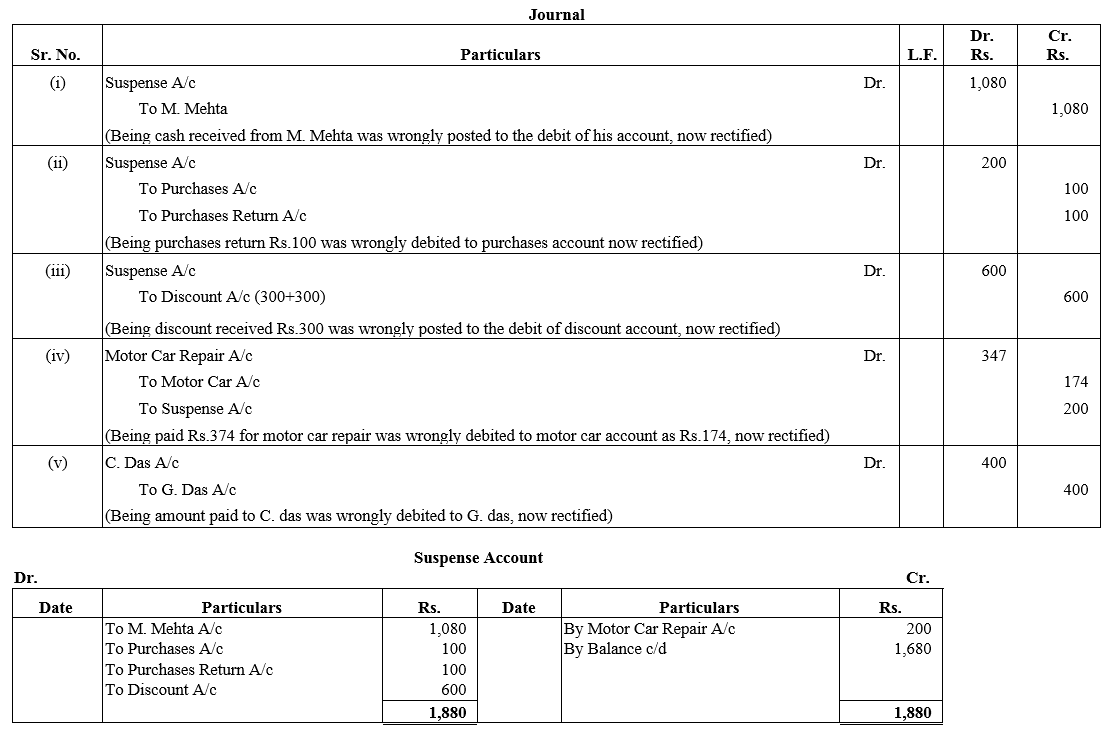
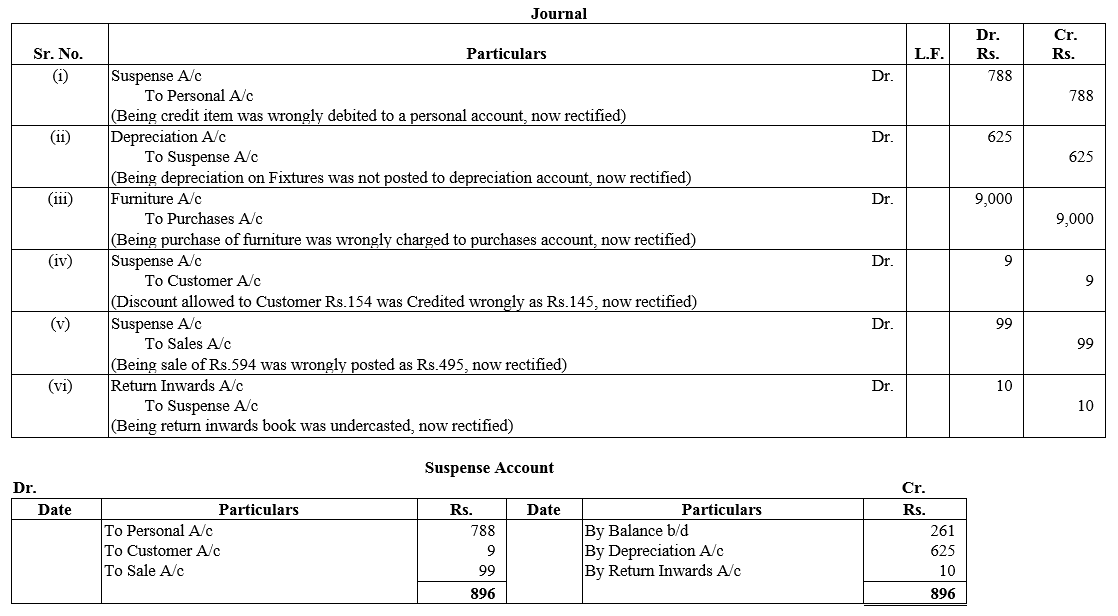
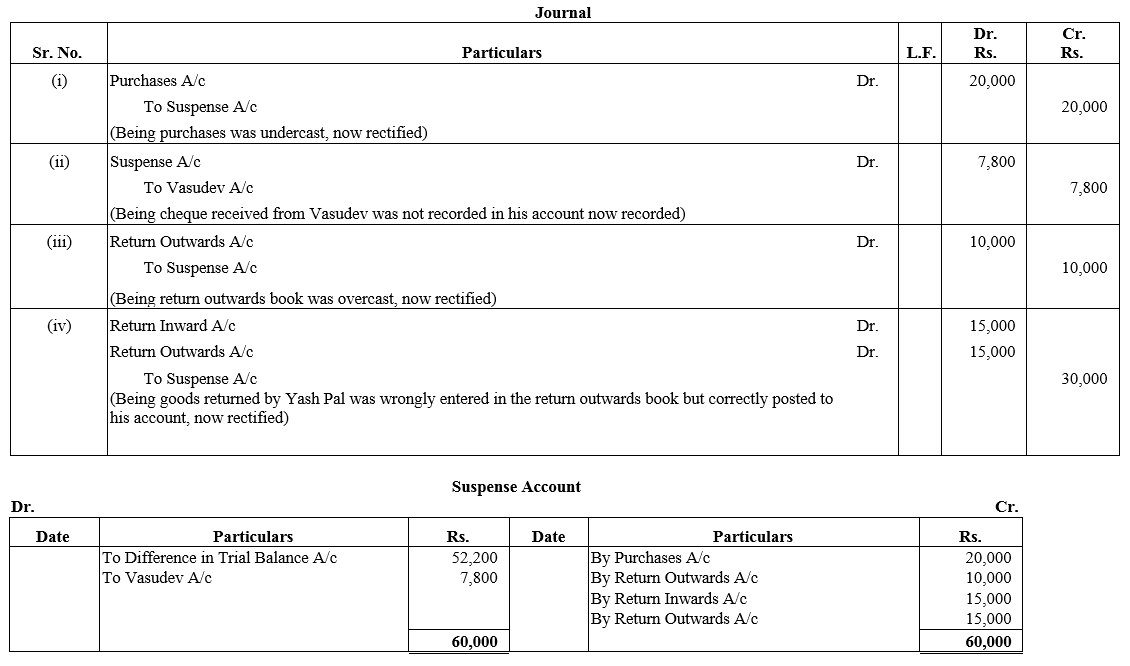
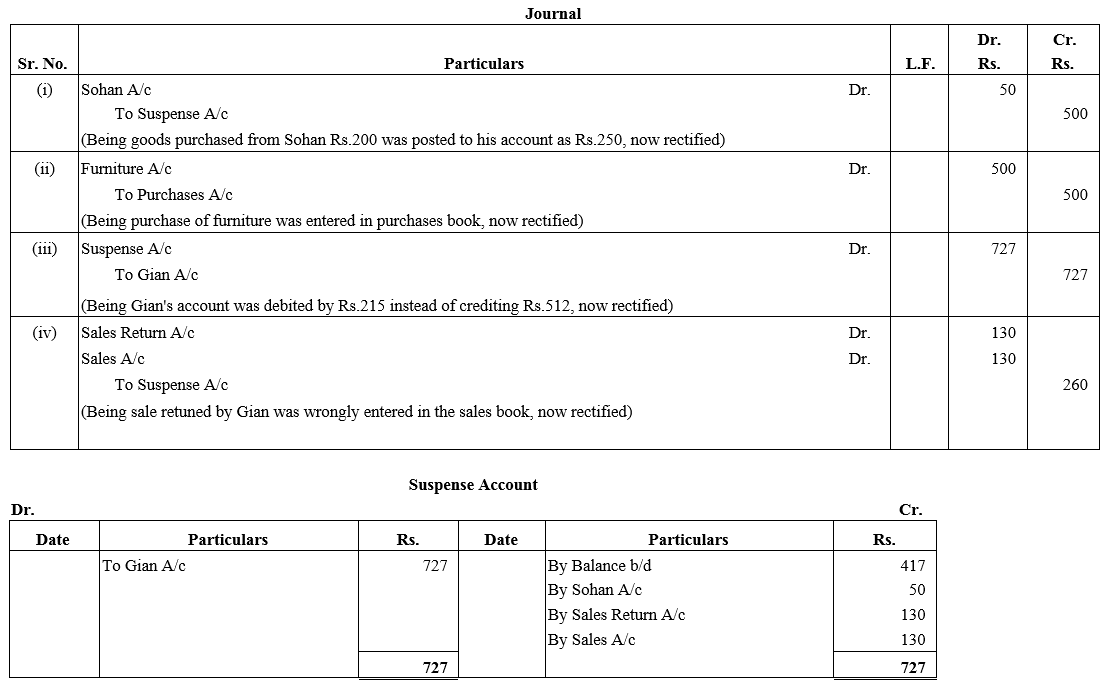
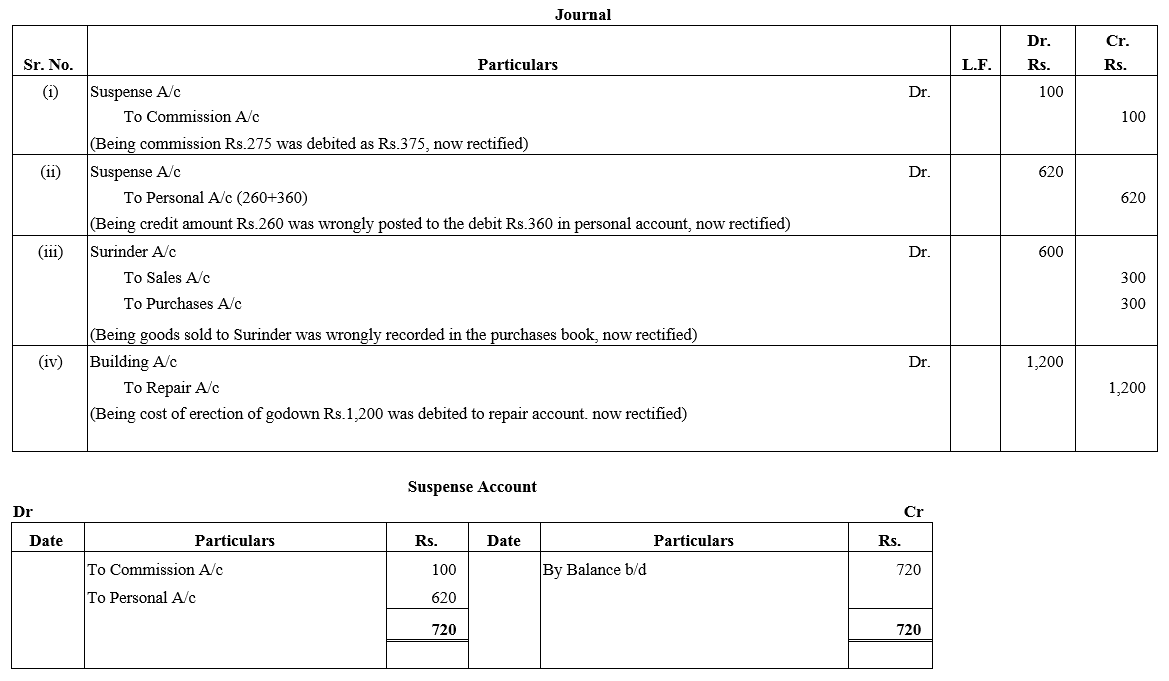
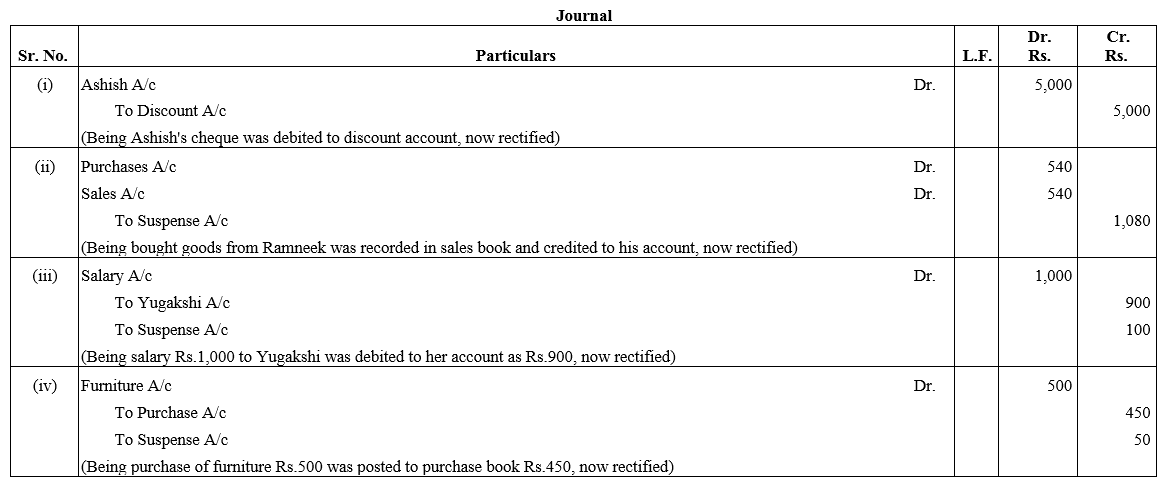
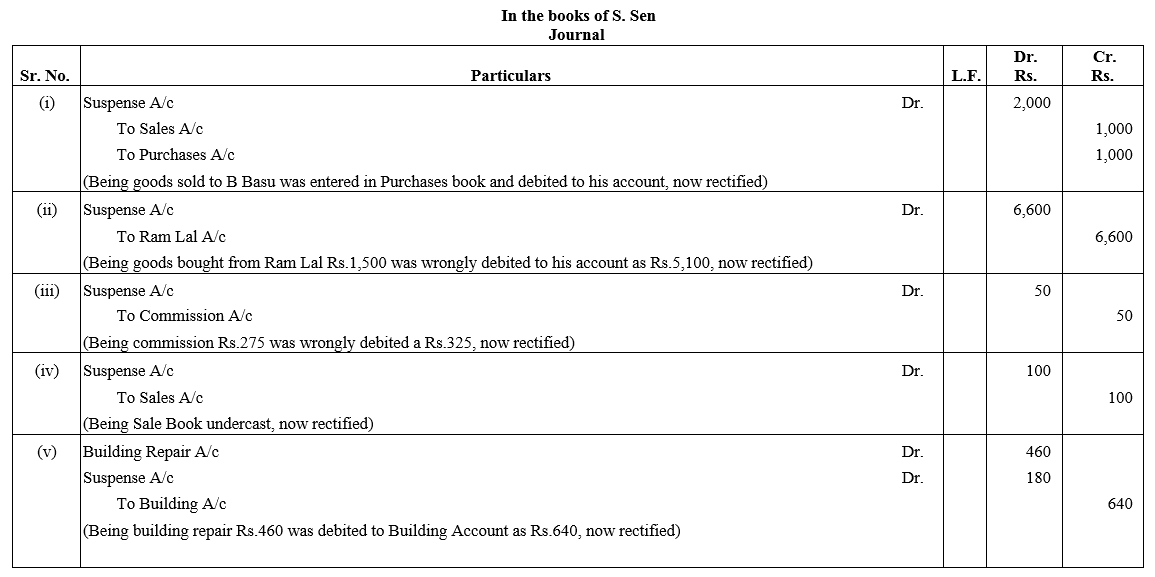
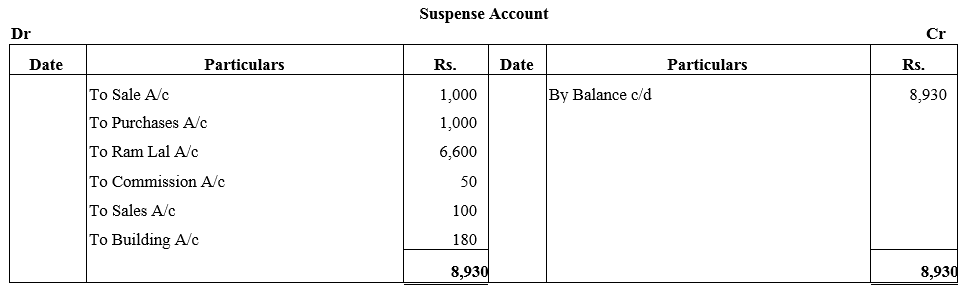
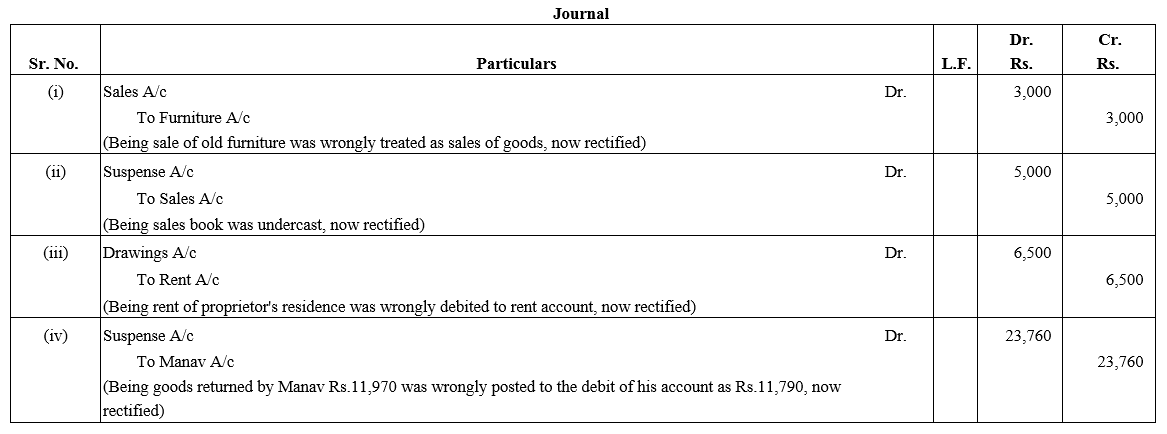
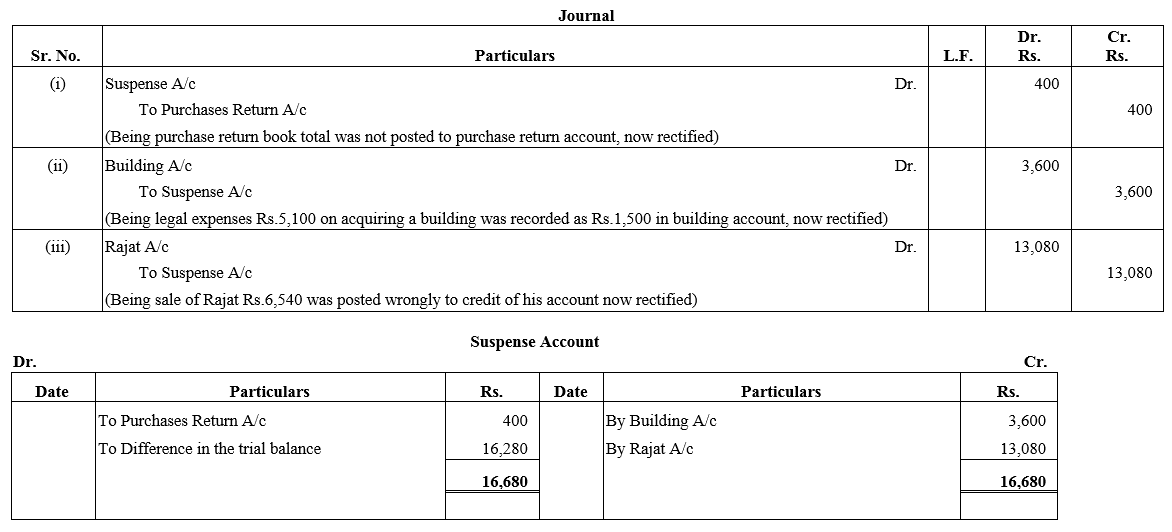
TS Grewal Accountancy Class 12 Solutions Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals – Here are all the TS Grewal solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1. This solution contains questions, answers, images, explanations of the complete Chapter 1 titled Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals of Accountancy taught in Class 12. If you are a student of Class 12 who is using TS Grewal Textbook to study Accountancy, then you must come across Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals. After you have studied lesson, you must be looking for answers of its questions. Here you can get complete TS Grewal Solutions for Class 12 Accountancy Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals in one place.
TS Grewal Accountancy Class 12 Solutions Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals
Question 1.
In the absence of Partnership Deed, what are the rules relation to
(a) Salaries of partners,
(b) Interest on partners capitals
(c) Interest on partners loan
(d) Division of profit, and
(e) Interest on partners drawings
Solution:

Question 2.
Following differences have arisen among P, Q and R. State who is correct in each case:
(a) P used ₹ 20,000 belonging to the firm and made a profit of ₹ 5,000. Q and R want the amount to be given to the firm?
(b) Q used ₹ 5,000 belonging to the firm and suffered a loss of ₹ 1000. He wants the firm to bear the loss?
(c) P and Q want to purchase goods from a Ltd., R does not agree
(d) Q and R want to admit C as partner, P does not agree?
Solution:

Question 3.
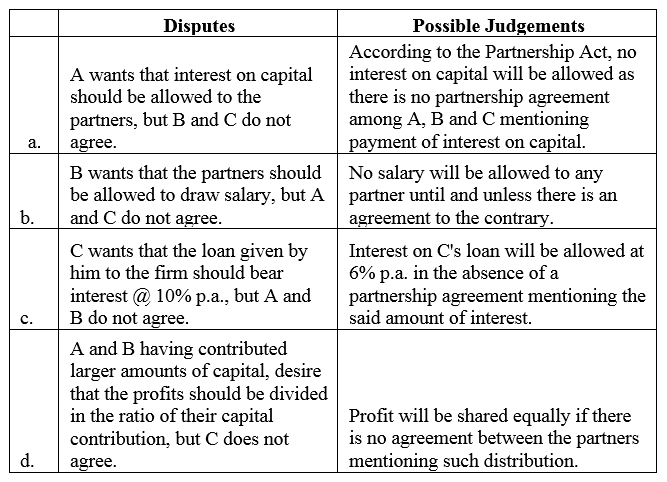
A, B and C are partners in a firm. They do not have a Partnership Deed. At the end of the first year of the commencement of the firm, they have faced the following problems:
(a) A wants that interest on capital should be allowed to the partners but B and C do not agree.
(b) B wants that the partners should be allowed to draw salary but A and C do not agree.
(c) C wants that the loan given by him to the firm should bear interest @ 10% p.a. but A and B do not agree.
(d) A and B having contributed larger amounts of capital, desire that the profits should be divided in the ratio of their capital contribution but C does not agree.
State how you will settle these disputes if the partners approach you for purpose.
Solution:
Question 4.
Jaspal and Rosy were partners with capital contribution of ₹ 10,00,000 and ₹ 5,00,000 respectively. They do not have a Partnership Deed. Jaspal wants that profits of the firm should be shared in their capital ratio. Rosy convinced jaspal that profits should be shared equally. Explain how Rosy would have convinced Jaspal for sharing the profit equally.
Solution:
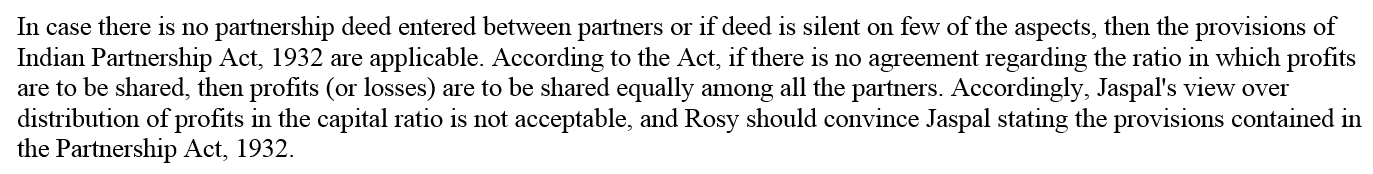
Question 5.
Harshad and Dhiman are in partnership since 1st April, 2017. No partnership agreement was made. They contributed Rs 4,00,000 and 1,00,000 respectively as capital. In addition, Harshad advance an amount of Rs 1,00,000 to the firm on 1st October, 2017. Due to long illness, Harshad could not participate in business activities from 1st August to 30th September, 2017. The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to Rs 1,80,000. Dispute has arisen between Harshad and Dhiman.
Harshad Claims:
(i) He should be given interest @ 10% per annum on capital and loan;
(ii) Profit should be distributed in proportion of capital;
Dhiman Claims:
(i) Profit should be distributed equally;
(ii) He should be allowed Rs 2,000 p.m. as remuneration for the period he managed the business in the absence of Harshad;
(iii) Interest on Capital and loan should be allowed @ 6% p.a.
You are required to settle the dispute between Harshand and Dhiman. Also prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
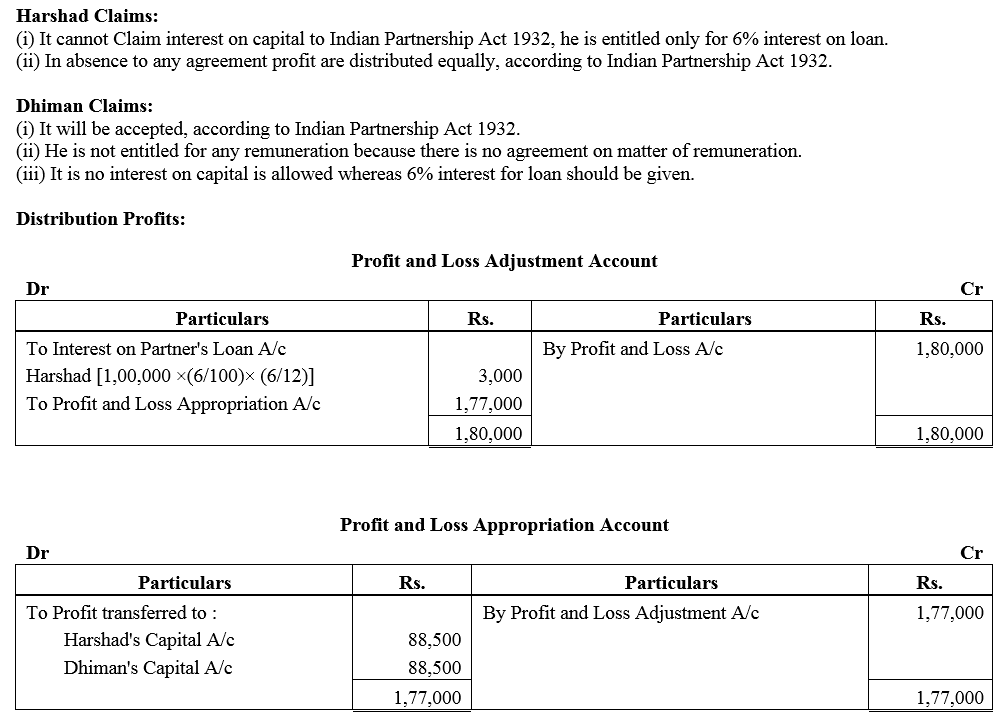
Question 6.
A and B are partners from 1st April, 2017, without a Partnership Deed and they introduced capitals of ₹ 35,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively. On 1st October, 2017, A advances a loan of ₹ 8,000 to the firm without any agreement as to interest. The profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 shows a profit of ₹ 15,000 but the partners cannot agree on payment of interest and on the basis of division of profits.
You are required to divide the profits between them giving reasons for your method.
Solution:
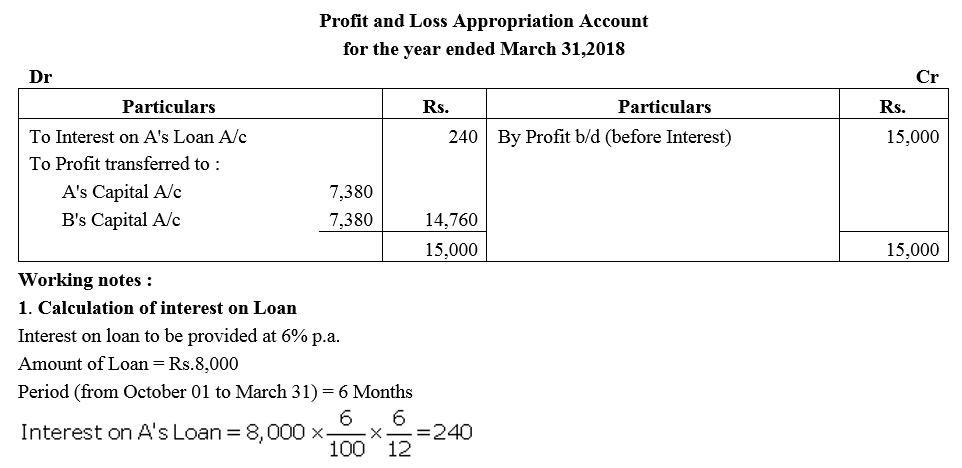

Question 7.
A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. They had advanced to the firm a sum of ₹ 30,000 as a loan in their profit-sharing ratio on 1st October, 2017. The Partnership Deed is silent on interest on loans from partners. Compute interest payable by the firm to the partners, assuming the firm closes its books every year on 31st March.
Solution:
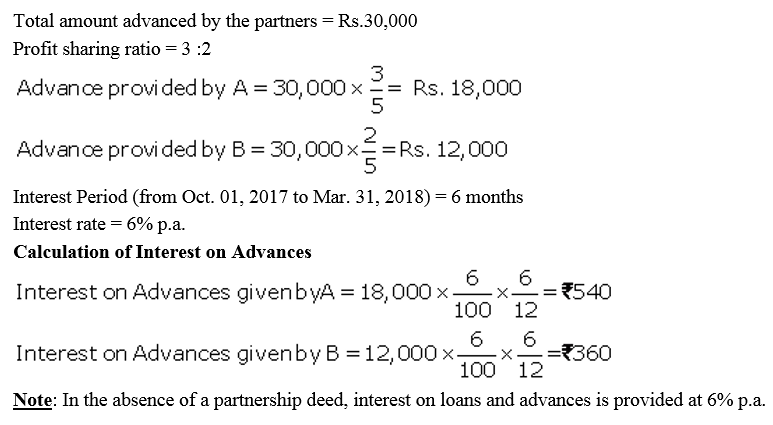
Question 8.
A and B are partners in a firm sharing profits equally. They had advanced tot he firm a sum of ₹ 30,000 as a loan in their profit-sharing ratio on 1st October, 2017. The Partnership Deed is silent on the question of interest on the loan from partners. Compute the interest payable by the firm to the partners, assuming the firm closes its books on 31st March each year.
Solution:
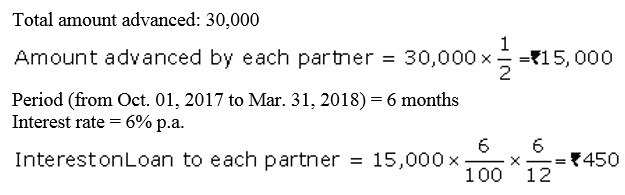
Question 9.
X and Y are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 3 with capitals ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 3,00,000 respectively. On 1st October, 2017, X and Y granted loans of ₹ 80,000 and ₹ 40,000 respectively to the firm. Show distribution of profits/losses for the year ended 31st March, 2018 in each of the following alternative cases:
Case 1 : If the profits before interest for the year amounted to ₹ 21,000.
Case 2 : If the profits before interest for the year amounted to ₹ 3,000.
Case 3 : If the profits before interest for the year amounted to ₹ 5,000.
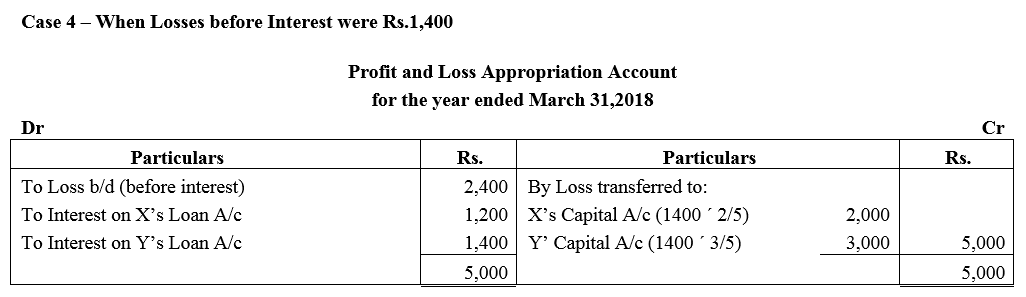
Case 4 : If the loss before interest for the year amounted to ₹ 1,400.
Solution:

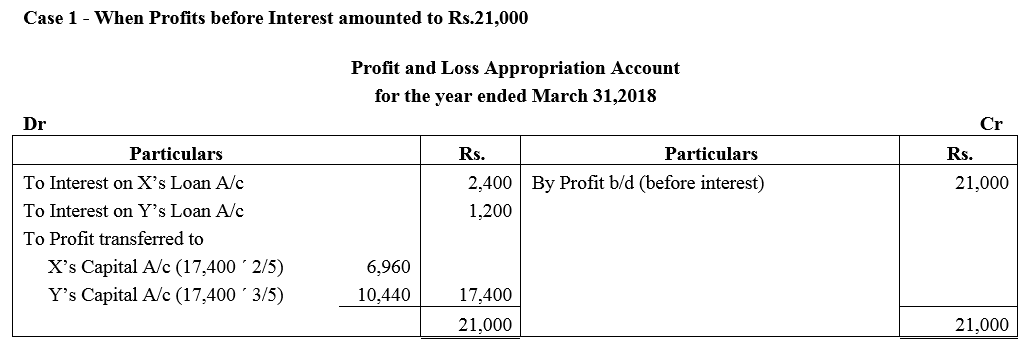
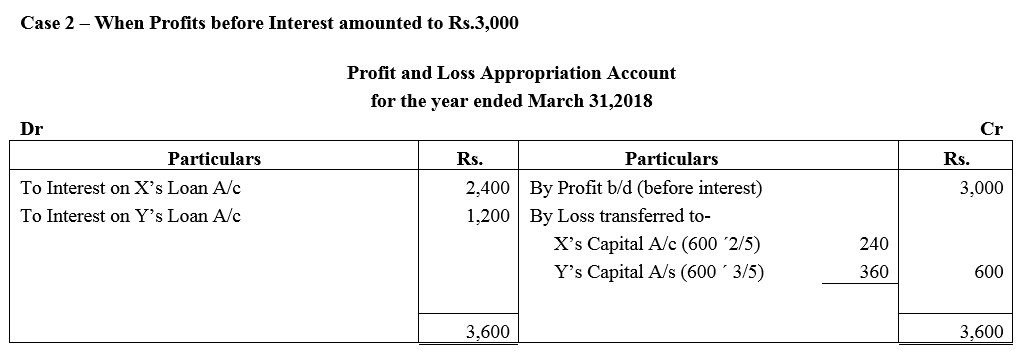
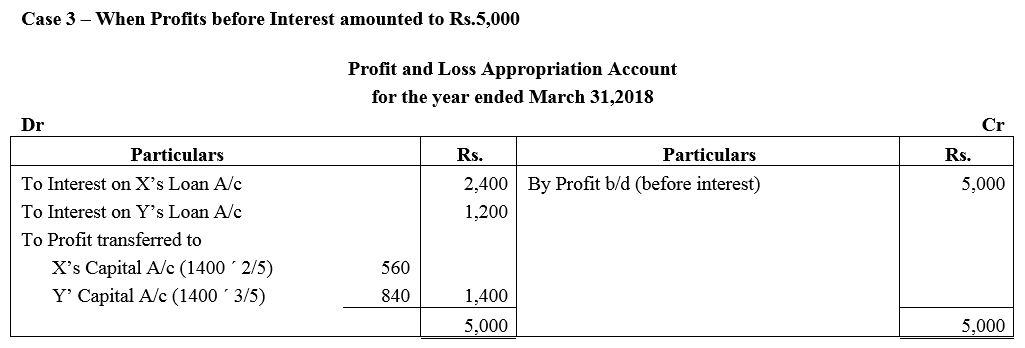
Question 10.
Bat and Ball are partners sharing the profits in the ratio of 2 : 3 with capitals of ₹ 1,20,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively. On 1st October, 2017, Bat and Ball granted lonas of ₹ 2,40,000 and ₹ 1,20,000 respectively to the firm. Bat had allowed the firm to use his property for business for a monthly rent of ₹ 5,000. The loss for the year ended 31st March, 2018 before rent and interest amounted to ₹ 9,000. Show distribution of profit/loss.
Solution:
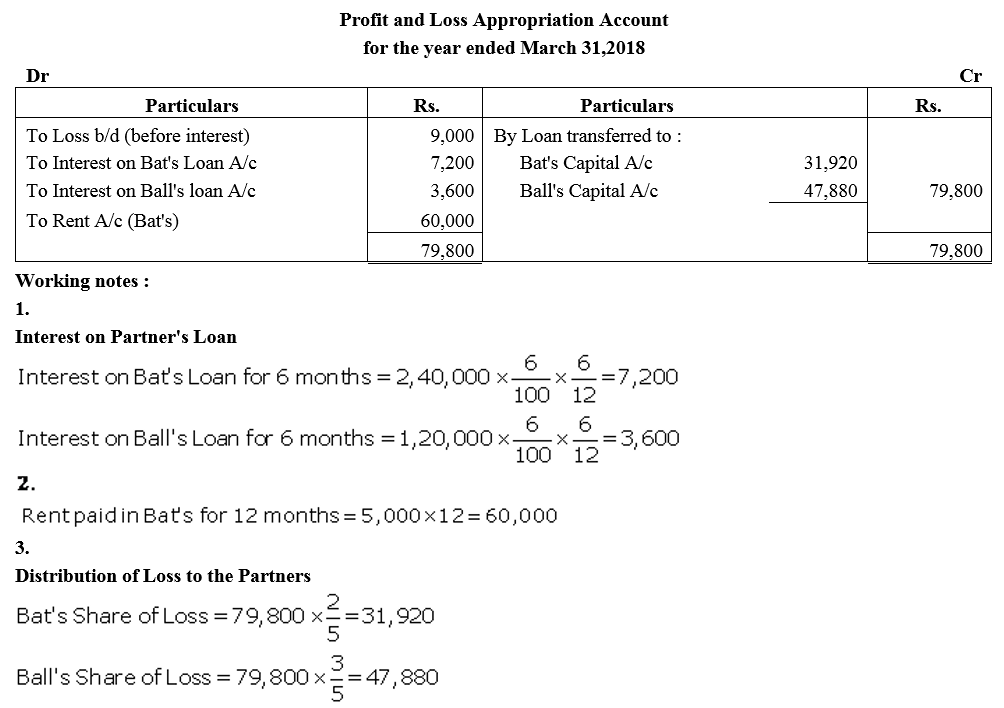
Question 11.
A and B are partners. A’s Capital is ₹ 1,00,000 and B’s Capital is ₹ 60,000. Interest on capital is payable @ 6% p.a. B is entitled to a salary of ₹ 3,000 per month. Profit for the current year before interest and salary to B is ₹ 80,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
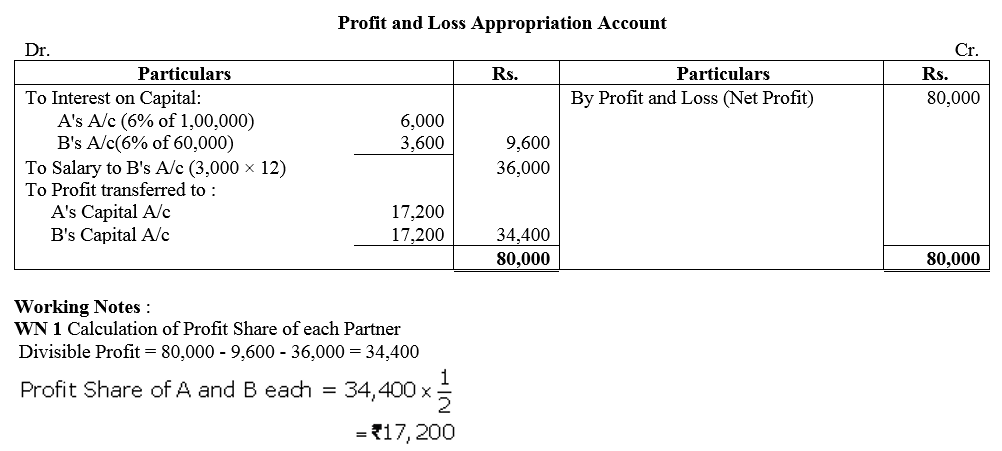
Question 12.
X, Y and Z are partners in a firm sharing profits in 2 : 2 : 1 ratio. The fixed capitals of the partners were : X ₹5,00,000; Y ₹ 5,00,000 and Z ₹ 2,50,000 respectively. The Partnership Deed provides that interest on capital is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. Z is to be allowed a salary of ₹ 2,000 per month. The profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March, 2018 after debiting Z’s salary was ₹ 4,00,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
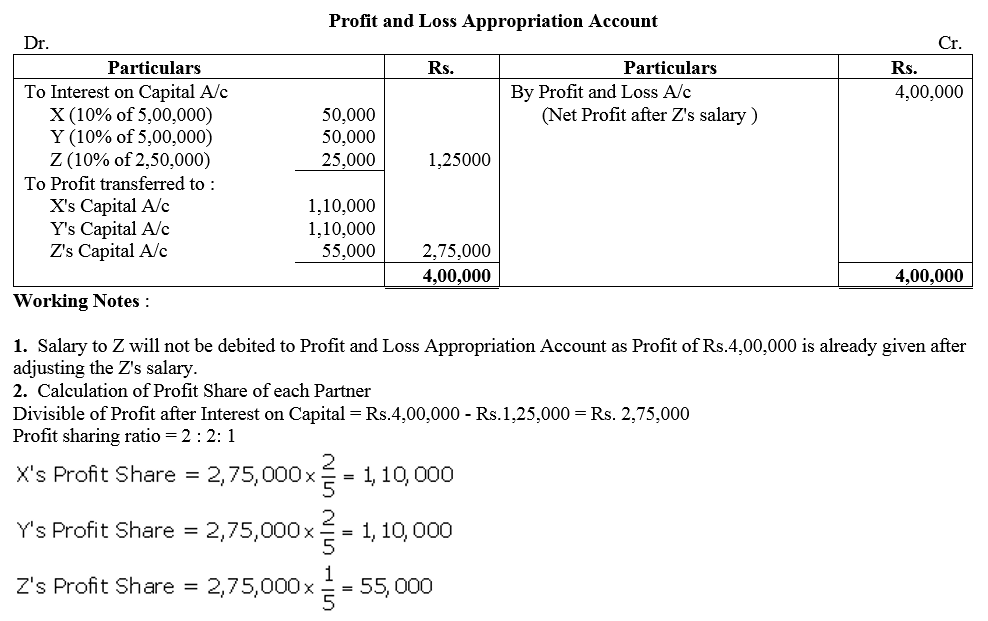
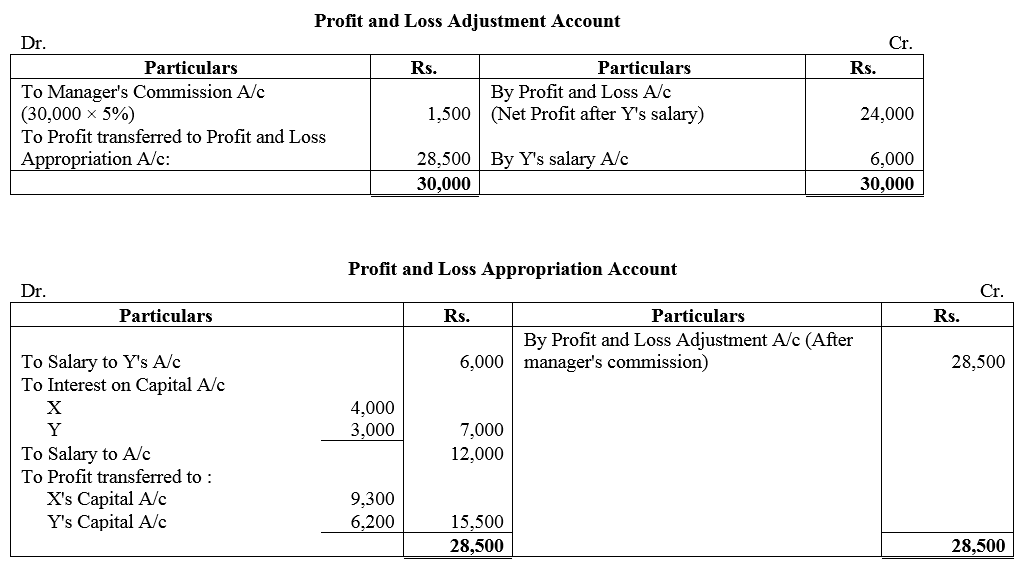
Question 13.
X and Y are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 with capitals of ₹ 80,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively. Interest on capital is agreed @ 5% p.a. Y is to be allowed an annual salary of ₹ 6,000 which has not been withdrawn. Profit for the year ended 31st march, 2018 before interest on capital but after charging Y’s salary amounted to ₹ 24,000. A provision of 5% of the profit is to be made in respect commission to the manager. Prepare an account showing the allocation profits.
Solution:
Question 14.
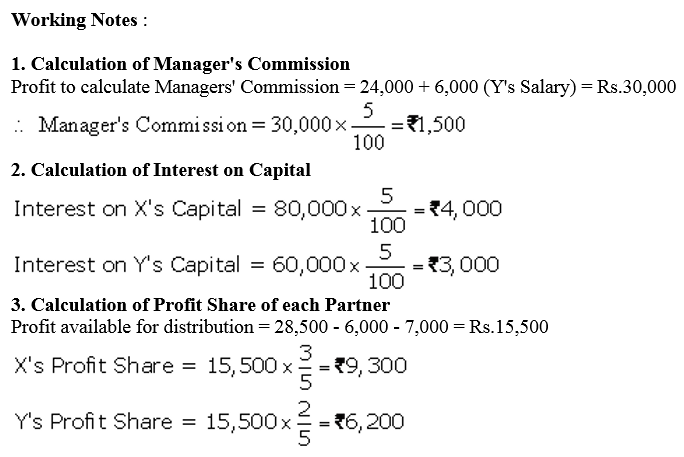
Prem and Manoj are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. The Partnership Deed provided that Prem was to be paid salary of ₹ 2,500 per month and Manoj was to ger a commission of ₹ 10,000 per year. Interest on capital was to be allowed @ 5% p.a. and interest on drawings was to be charged @ 6% p.a. Interest on Prem’s drawings was ₹ 1,250 and on Manoj’s drawings was ₹ 425. Interest on Capitals of the partners were ₹ 10,000 and ₹ 7,500 respectively. The firm earned a profit of ₹ 90,575 for the year ended 31st March, 2018. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account of the firm.
Solution:
Question 15.
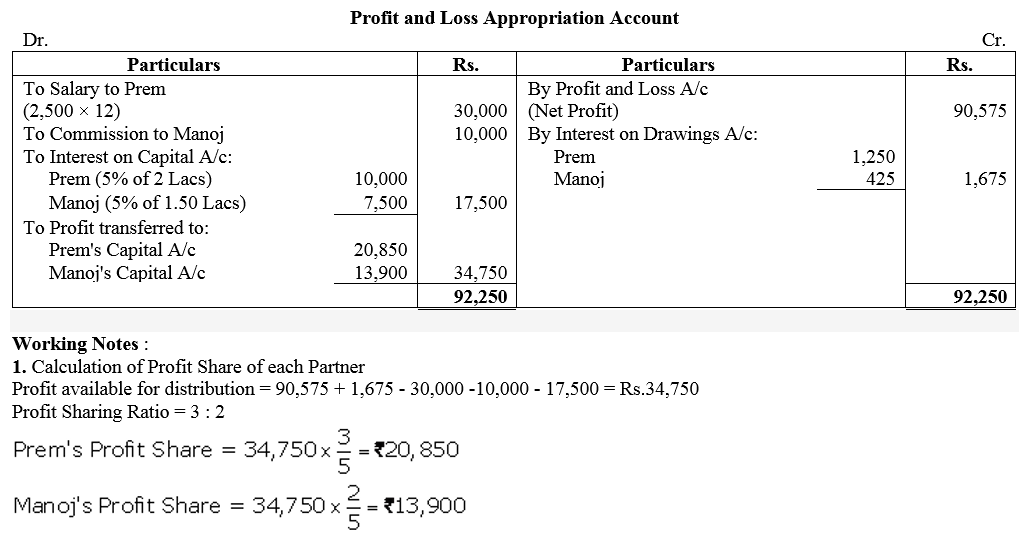
Reema and Seema are partners sharing profits equally. The Partnership Deed provides that both Reema and Seema will get monthly salary of Rs 15,000 each, Interest on Capital will be allowed @ 5% p.a. and Interest on Drawings will be charged @ 10% p.a. Their capitals were Rs 5,00,000 each and drawings during the year were Rs 60,000 each. The firm incurred a loss of Rs 1,00,000 during the year ended 31st March, 2018. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
Question 16.
Bhanu and Partab are partners sharings profits eqully. Their fixed capitals as on 1st April, 2017 are ₹ 8,00,000 and ₹ 10,00,000 respectively. Their drawings the year were ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 1,00,000 respectively. Interest on Capital is a charge and is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. and interest on drawings is to be charged @ 15% p.a. Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 1,20,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
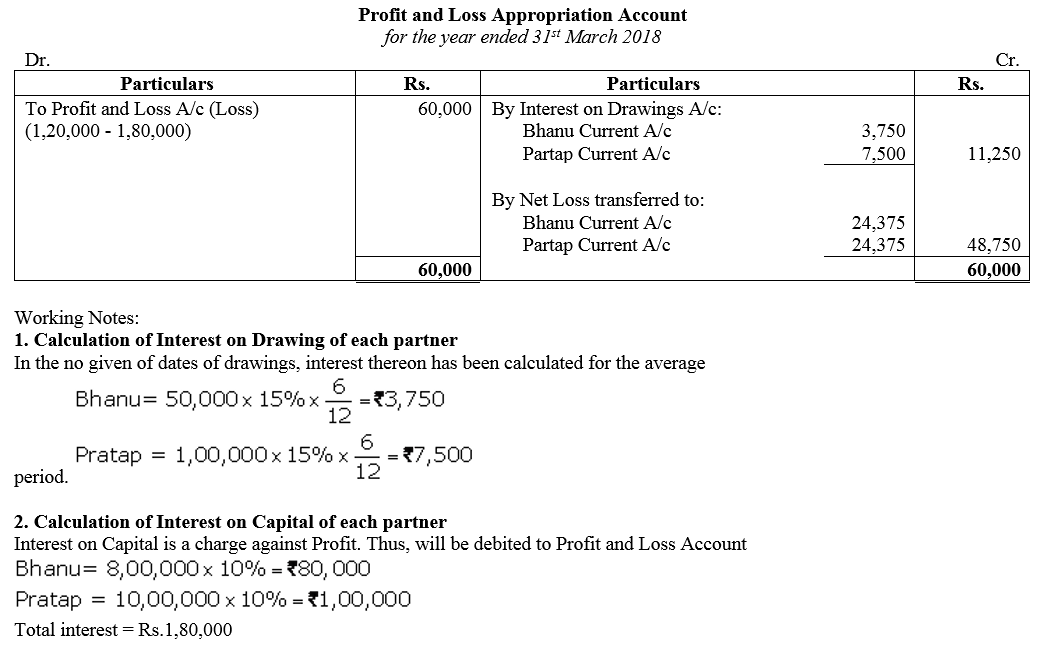
Question 17.
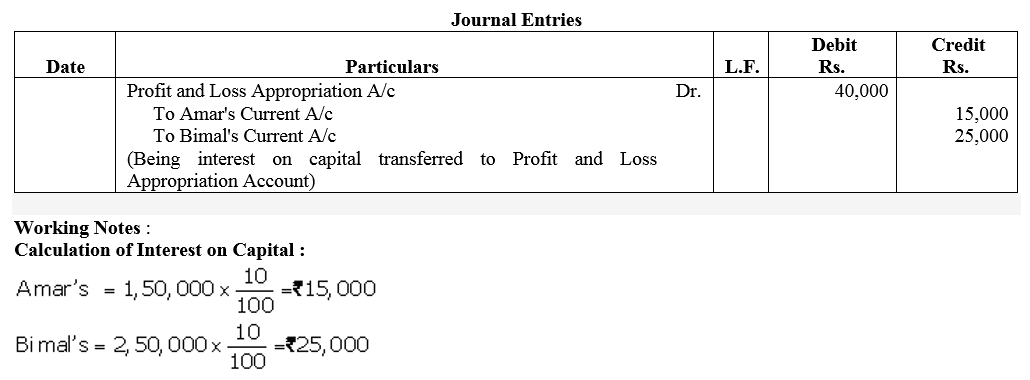
Amar and Bimal entered into partnership on 1st April, 2017 contributing ₹ 1,50,000 and ₹ 2,50,000 respecitvely towards capital. The Partnership Deed provided for interest on capital @ 10% p.a. It also provided that Capital Accounts shall be maintained following Fixed Capital Accounts method. The firm earned net profit of ₹ 1,00,000 for the year ended 31st March 2018. Pass the Journal entry for interest on capital.
Solution:
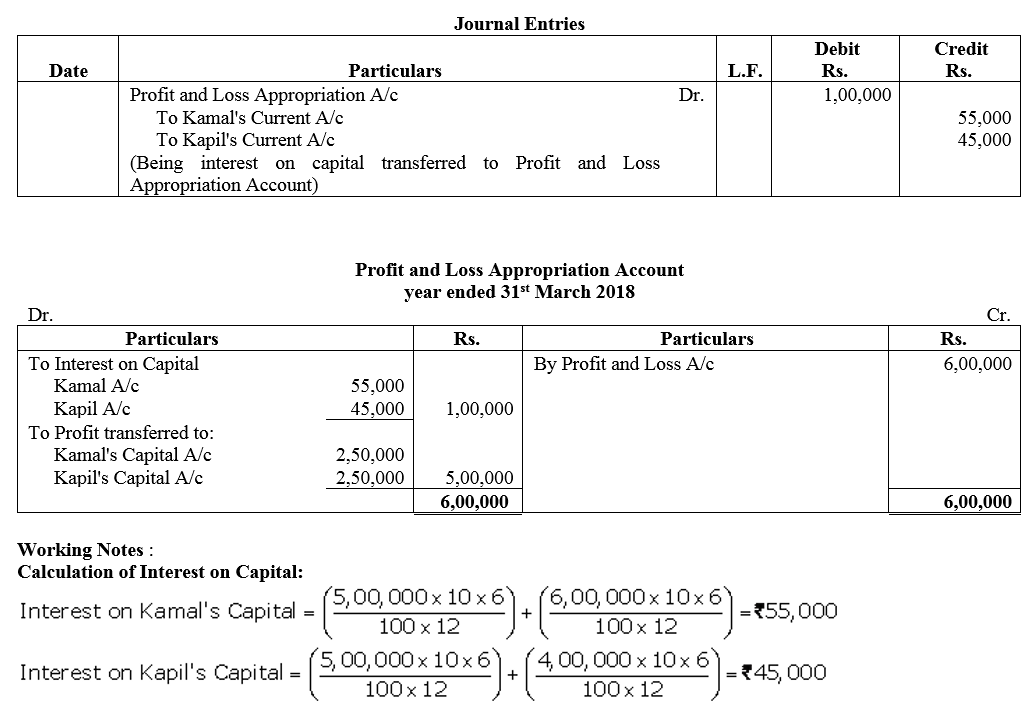
Question 18.
Kamal and Kapil ar partners having fixed capitals of ₹ 5,00,000 each as on 31st March, 2017. Kamal introduced further captial of ₹ 1,00,000 on 1st October, 2017 whereas Kapil withdrew ₹ 1,00,000 on 1st October, 2017 out of capital. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. The firm earned net profit of ₹ 6,00,000 for the year ended 31st March 2018. Pass the Journal entry for interest on capital and prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
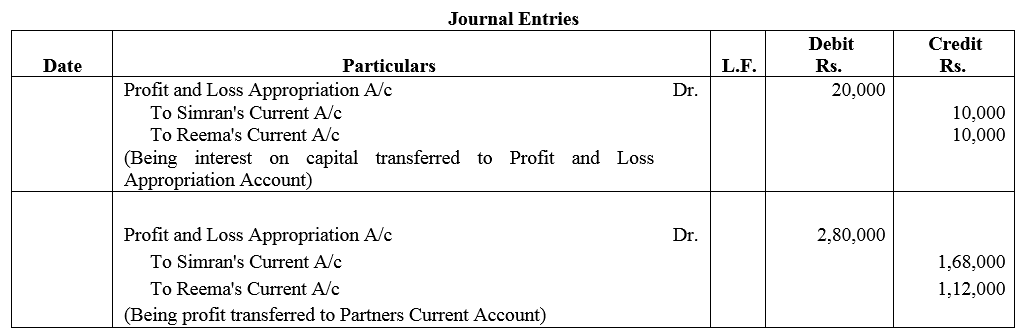
Question 19.
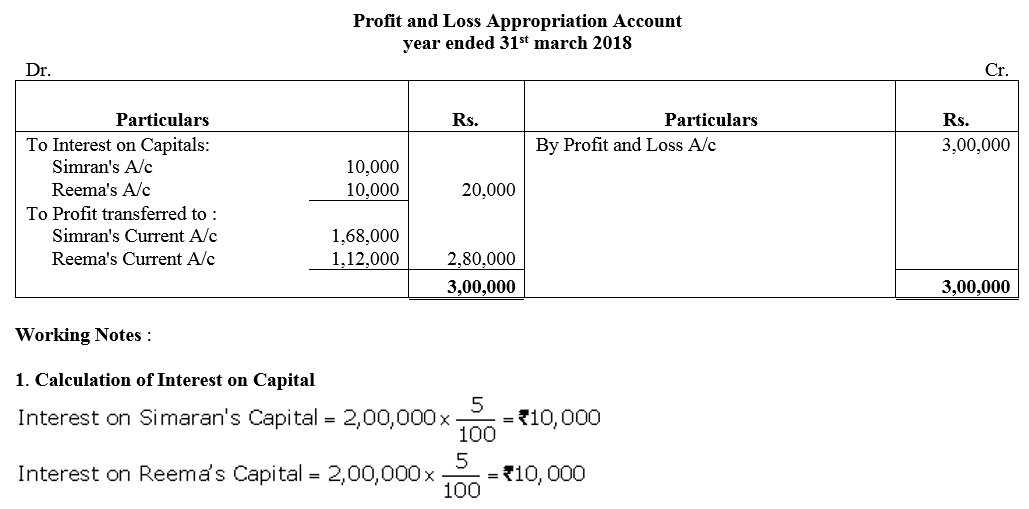
Simran and Reema are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their capitals as on 31st March, 2017 were ₹ 2,00,000 each whereas Current Accounts had balances of ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 25,000 respectively interest is to be allowed @ 5% p.a. on balances in Capital Accounts. The firm earned net profit of ₹ 3,00,000 for the year ended 31st March 2018. Pass the journal entries for interest on capital and distibution of profit. Also prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year.
Solution:
Question 20.
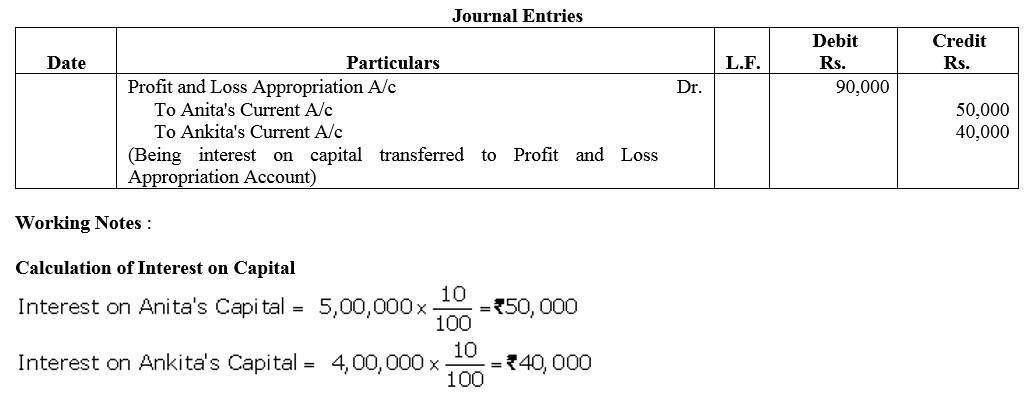
Anita and Ankita are partners sharing profits equally. Their capitals, maintained following Fluctuating Capital Accounts Method, as on 31st March, 2017 were ₹ 5,00,000 and ₹ 4,00,000 respectively. Partnership Deed provided to allow interest on capital @ 10% p.a. The firm earned net profit of ₹ 2,00,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2018. Pass the journal entry for interest on capital.
Solution:
Question 21.
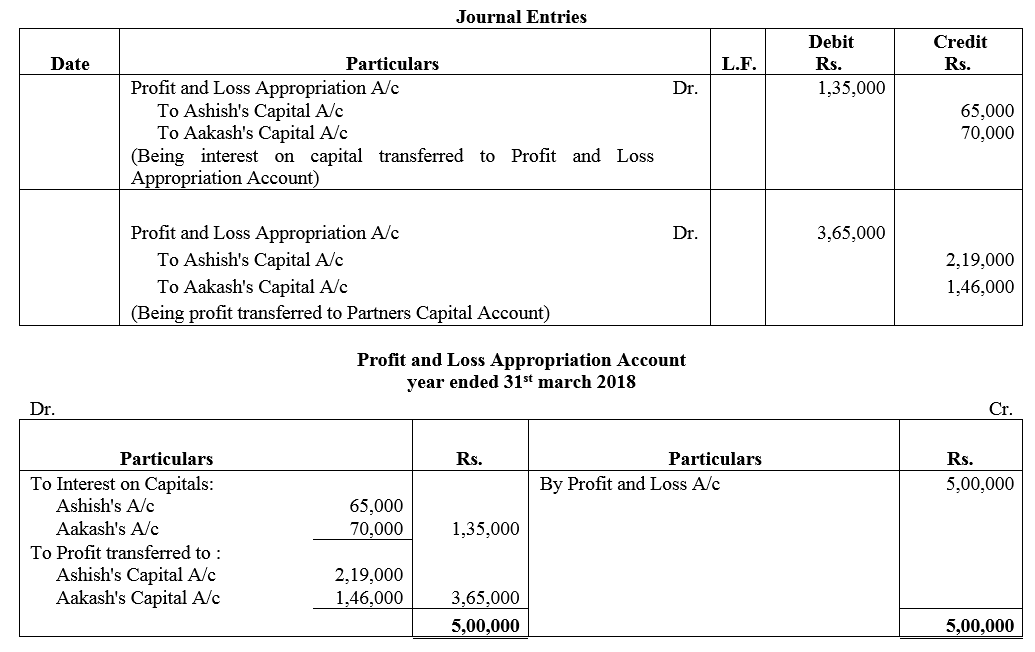
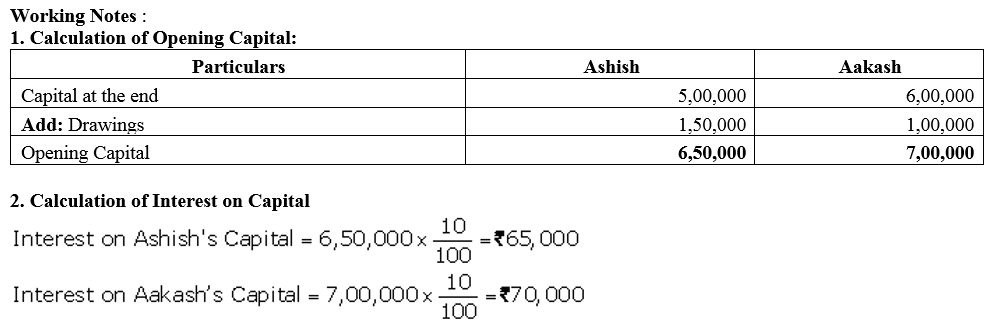
Ashish and Aakash are partners sharing profit in the ratio of 3 : 2. Their Capital Accounts showed a credit balance of ₹ 5,00,000 and ₹ 6,00,000 respectively as on 31st March, 2018 after debit of drawings during the year of ₹ 1,50,000 and ₹ 1,00,000 respectively. Net profit for the year ended 31st March was ₹ 5,00,000. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. Pass the journal entry for interest on capital and prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
Question 22.
Naresh and Sukesh are partners with capitals of ₹ 3,00,000 each as on 31st March, 2018. Naresh had withdrawn ₹ 50,000 against capital on 1st October, 2017 and also ₹ 1,00,000 besides the drawings against capital. Sukesh also had drawings of ₹ 1,00,000. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. Net profit for the year was ₹ 2,00,000, which is yet to be distributed. Pass the journal entries for interest on capital and distribution of profit.
Solution:
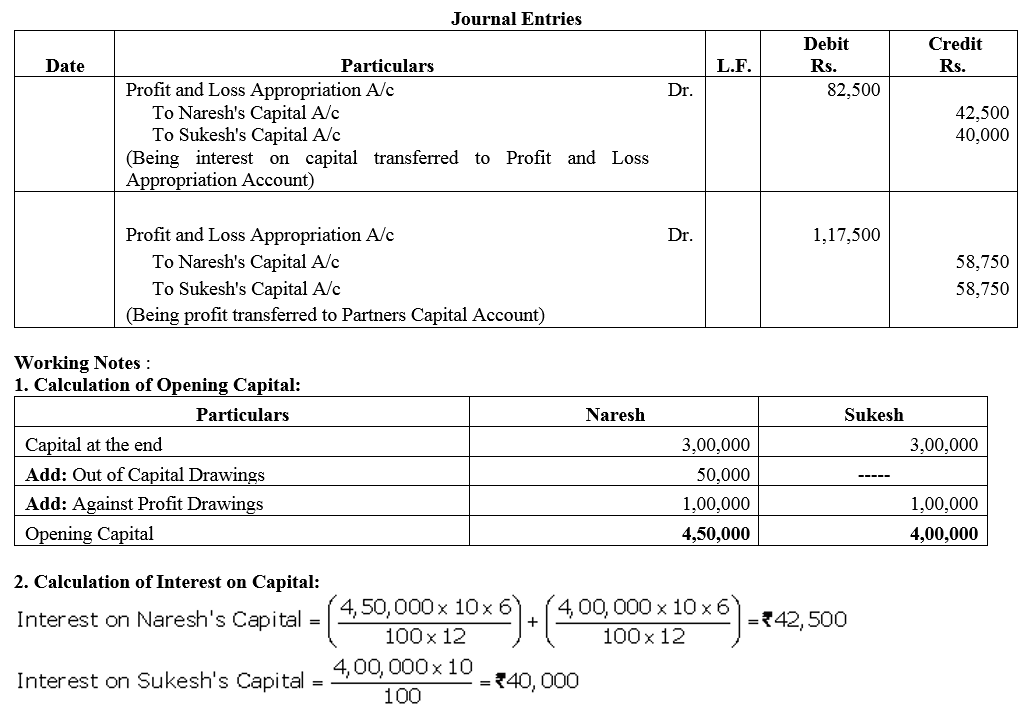
Question 23.
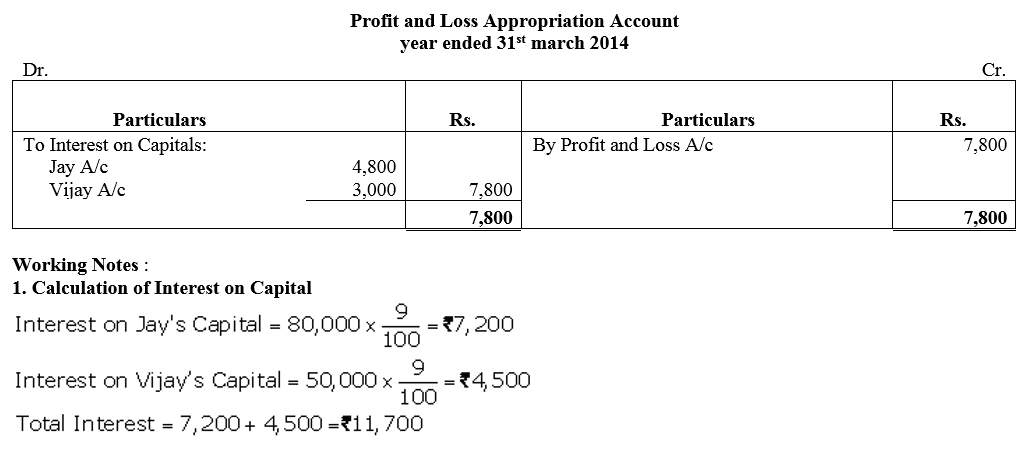
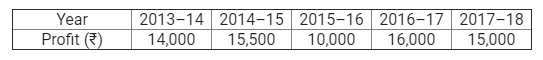
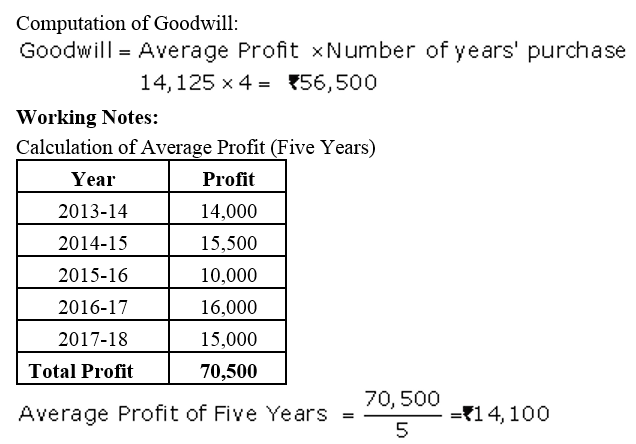
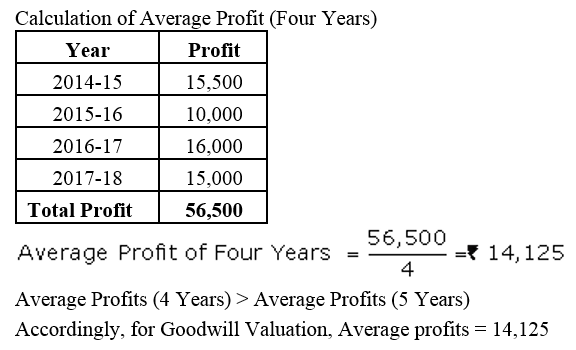
On 1st April, 2013, Jay and Vijay entered into partnership for supplying laboratory equipments to government schools situated in remote and backward areas. They contributed capitals of ₹ 80,000 and ₹ 50,000 respectively and agreed to share the profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. The partnership Deed provided that interest on capital shall be allowed at 9% per annum. During the year the firm earned a profit of ₹ 7,800. Showing your calculations cleary, prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account of Jay and Vijay for the year ended 31st March, 2014.
Solution:

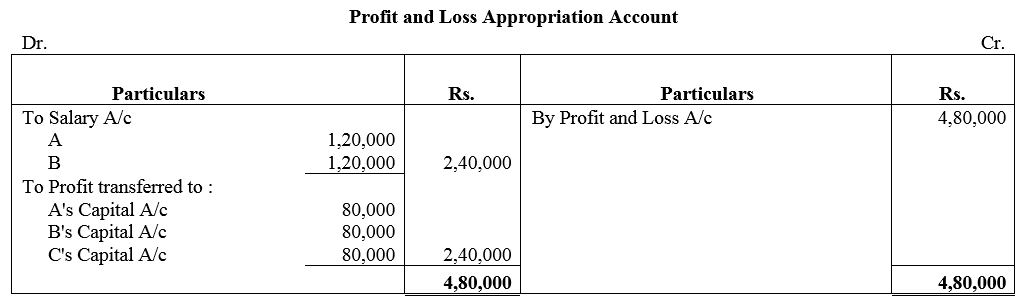
Question 24.
A, B and C are partners in a firm. A and B are to get annual salary of ₹ 1,20,000 p.a. each as they are fully involved in the business. Net profit for the year is ₹ 4,80,000. Determine the share of profit to be credited to each partner.
Solution:
Question 25.
A, B and C are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1 respectively. A is entitled to a commission of 10% on the net profit. Net profit for the year is ₹ 1,10,000. Determine the amount of commission payable to A.
Solution:

Question 26.
X, Y and Z are partners sharing profits and lossed equally. As per partnership Deed, Z is entitled to a commission of 10% on the net profit after charging such commission. The net profit before charging commission is ₹ 2,20,000. Determine the amount of commission payable to Z.
Solution:
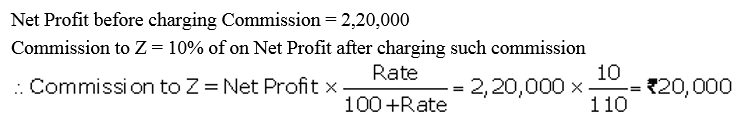
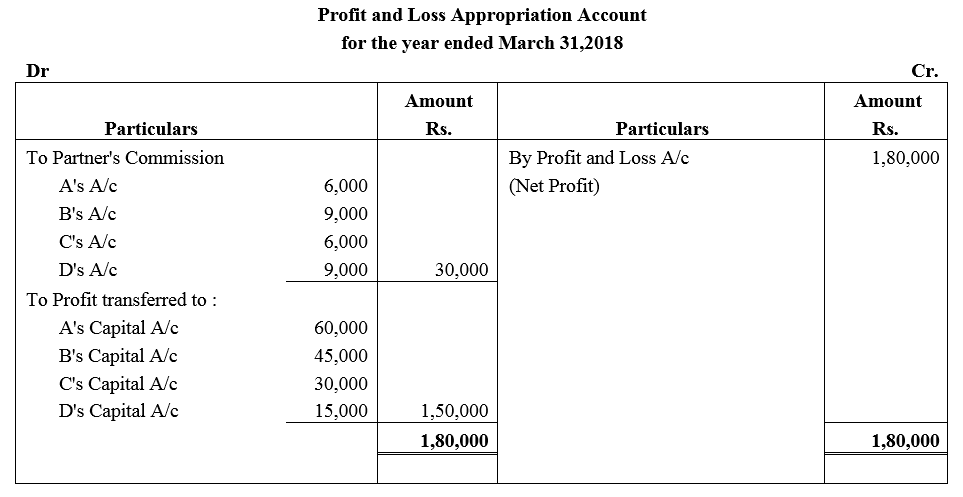
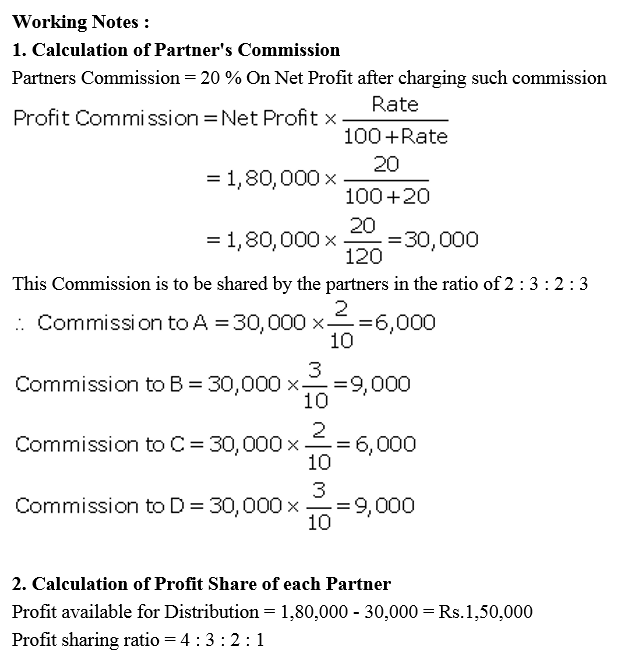
Question 27.
A, B, C, and D are partners in a firm sharing profits as 4 : 3 : 2 : 1 respectively. It earned a profit of ₹ 1,80,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2018. As per the Partnership Deed, they are to charge a commission @ 20% of the profit after charging such commission which they will share as 2 : 3 : 2 : 3. You are required to show appropriation of profits among the partners.
Solution:
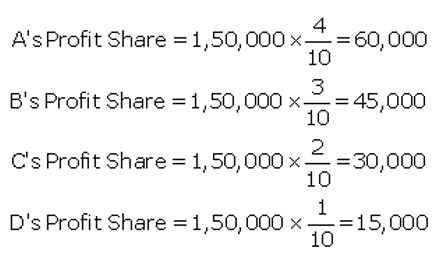
Question 28.
X and Y are partners in a firm. X is entitled to a salary of ₹ 10,000 per month and commission of 10% of the net profit after partners salaries but before charging commission. Y is entitled to a salary of ₹ 25,000 p.a. and commission of 10% of the net profit after chaging all commission and partners salaries. Net profit before providing for partners salaries and commission for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 4,20,000, show distribution of profit.
Solution:
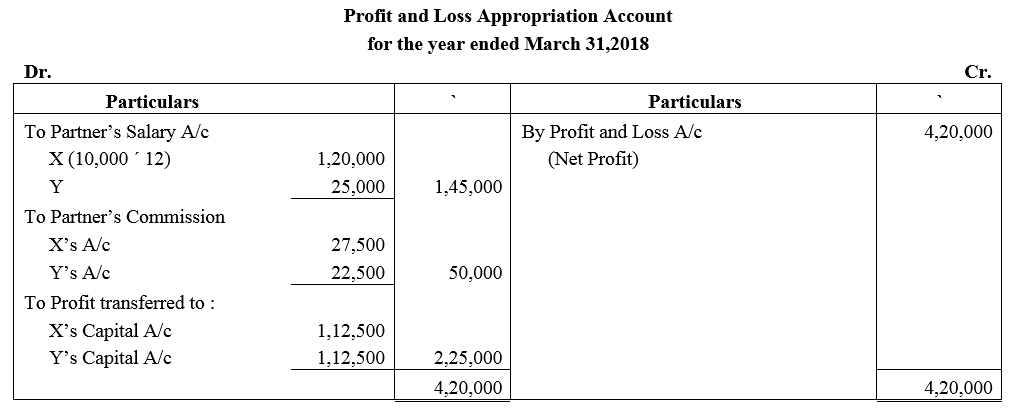
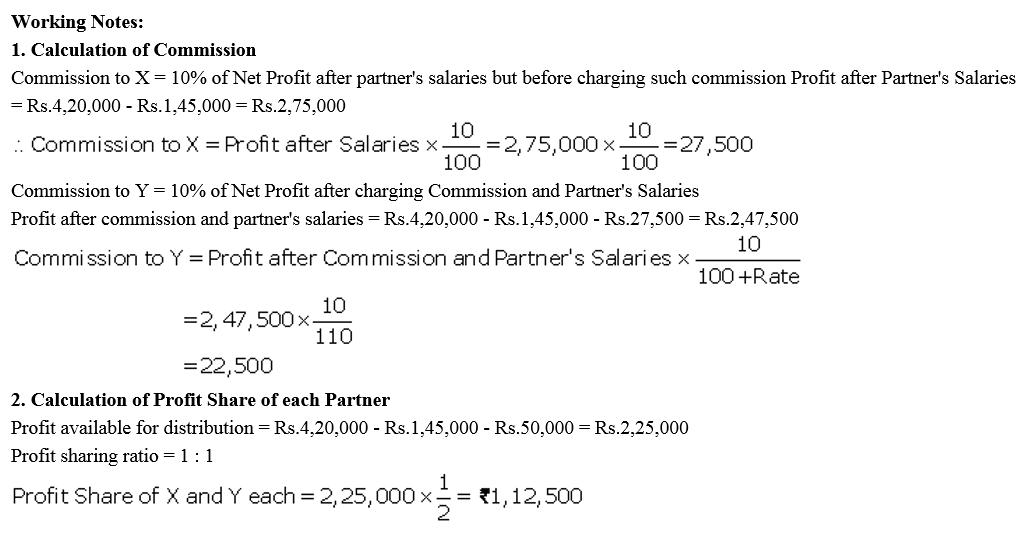
Question 29.
Ram and Mohan, two partners, drew for their personal use ₹ 1,20,000 and ₹ 80,000. Interest is chargeable @ 6% p.a. on the drawings. What is the amount of interest chargeable from each partner?
Solution:
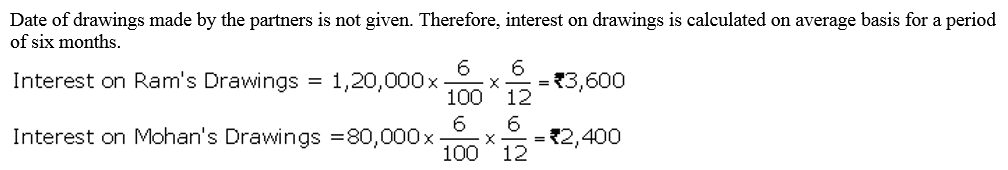
Question 30.
B and M are partners in a firm. They withdrew ₹ 48,000 and ₹ 36,000 respectively during the year evenly in the middle of every month. According to the partnership agreement, interest on drawings is to be charged @ 10% p.a. Calculate interest on drawings of the partners using the appropriate formula.
Solution:
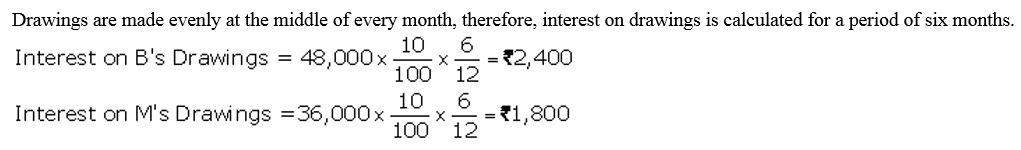
Question 31.
A and B are partners sharing profits equally. A drew regularly ₹ 4,000 in the beginning of every month for six months ended 30th September, 2018. Calculate interest on drawings @ 5% p.a. for a period of six months.
Solution:

Question 32.
A and B are partners sharing profits equally. A drew regularly ₹ 4,000 at the end of every month for six months ended 30th September, 2018. Calculate interest on drawings @ 5% p.a. for a period of six months.
Solution:

Question 33.
Calculate interest on drawings of Mr. Ashok @ 10% p.a. for the year ended 31st March, 2018, in each of the following alternative cases:
Case 1. If he withdrew ₹ 7,500 in the beginning of each quarte.
Case 2. If he withdrew ₹ 7,500 at the end of each quarter.
Case 3. If he withdrew ₹ 7,500 during the middle of each quarter.
Solution:

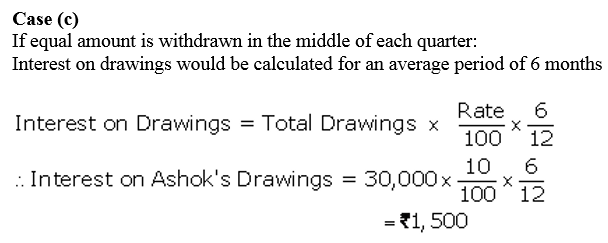
Question 34.
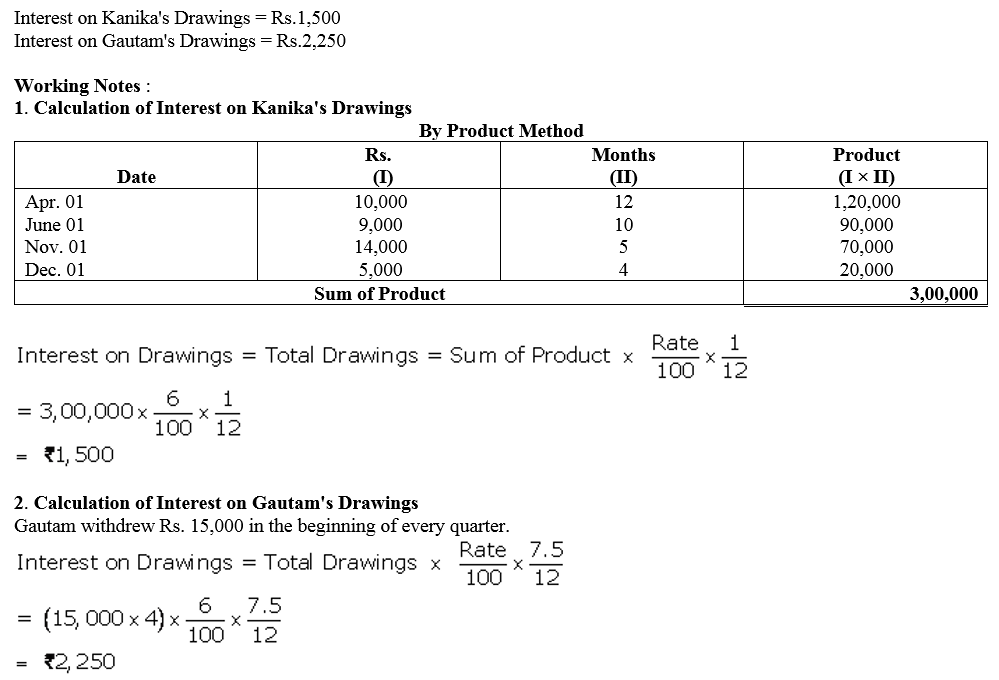
Kanika and Gautam are partners doing a dry cleaning business in Lucknow, sharing profits in the ratio 2 : 1 with capitals ₹ 5,00,000 and ₹ 4,00,000 respectively. Kanika withdrew the following amounts during the year to pay the hostel expenses of her son:
1st April ₹ 10,000
1st June ₹ 9,000
1st November ₹ 14,000
1st December ₹ 5,000
Gautam withdrew ₹ 15,000 on the first day of April, July, October and January to pay rent for the accommodation of his family. He also paid ₹ 20,000 per month as rent for the office of partnership which was in a nearby shopping complex. Calculate interest on drawings @ 6% p.a.
Solution:
Question 35.
A and B are partners sharing Profit and Loss in the ratio 3 : 2 having Capital Account balances of ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 40,000 on 1st April, 2017. On 1st July, 2017, A introduced ₹ 10,000 as his additional capital whereas B introduced only ₹ 1,000. Interest on capital is allowed to partners @ 10% p.a. Calculate interest on capital for the financial year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
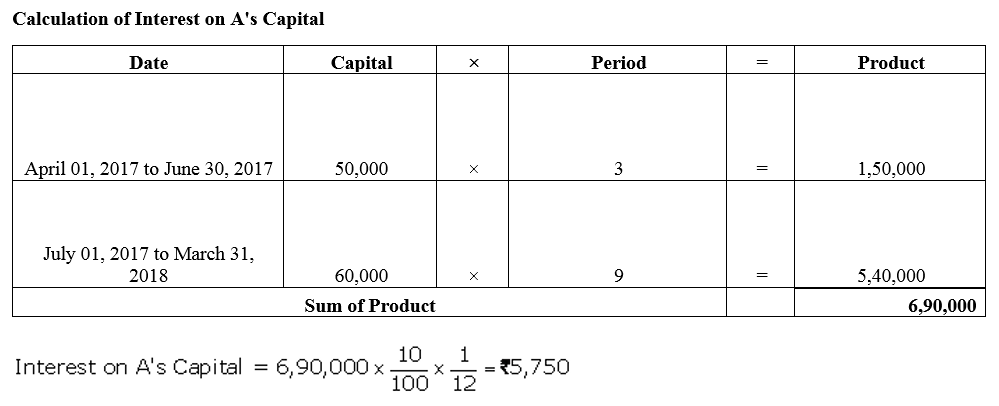
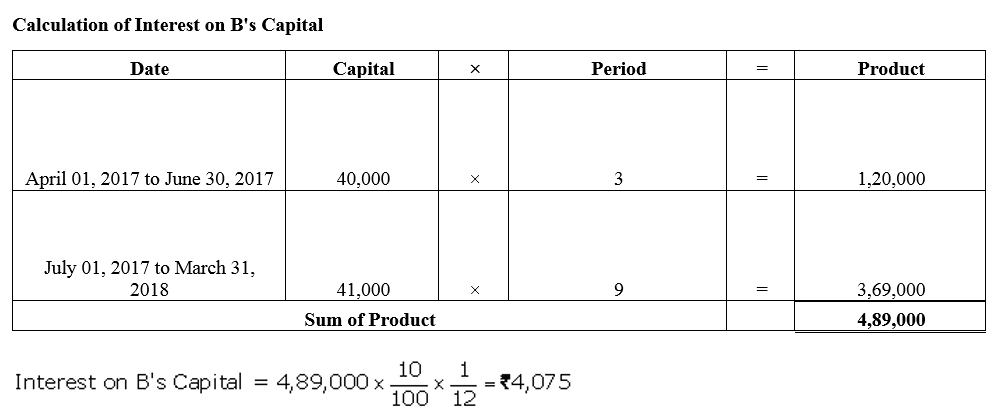
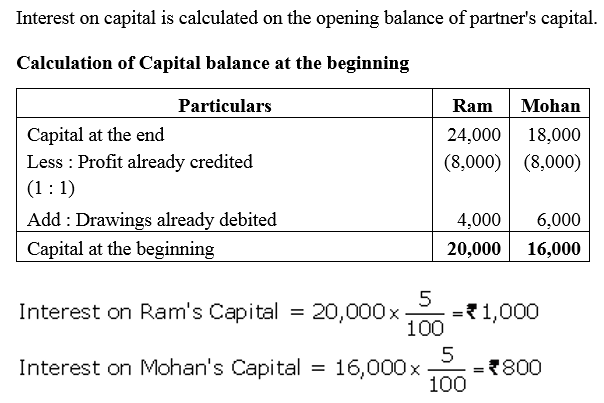
Question 36.
Ram and Mohan are partners in a business. Their capitals at the end of the year were ₹ 24,000 and ₹ 18,000 respectively. During the year, Ram’s drawings and Mohan’s drawings were ₹ 4,000 and ₹ 6,000 respectively. Profit (Before charging interest on capital) during the year was ₹ 16,000. Calculate interest on capital @ 5% p.a. for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
Question 37.
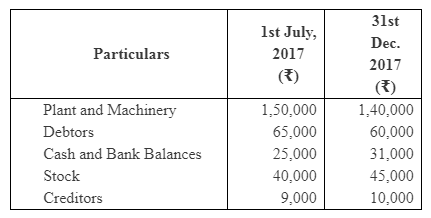
Following is the extract of the Balance Sheet of Neelkant and Mahadev as on 31st March, 2018.
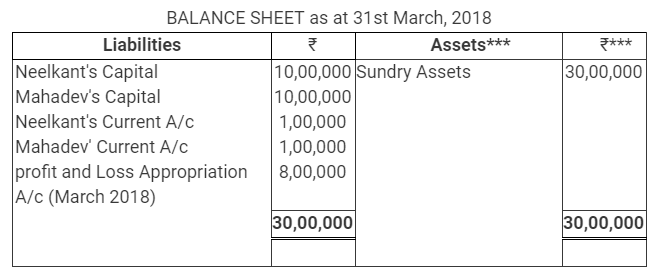
During the year, Mahadev’s drawings were ₹ 30,000. Profits during the year ended 31st March, 2018 is ₹ 10,00,000. Calculate interest on capital @ 5% p.a. for the year ending 31st March, 2018.
Solution:

Question 38.
From the following Balance Sheet of Long and Short, calculate interst on capital @ 8% p.a. for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
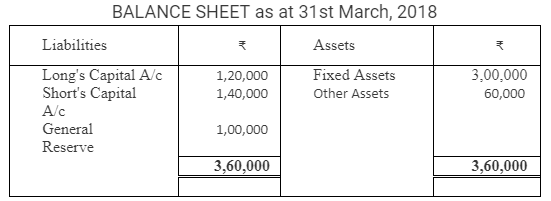
During the year, Long withdrew ₹ 40,000 and Short withdrew ₹ 50,000. Profit for the year was ₹ 1,50,000 out of which ₹ 1,00,000 was transferred to General Reserve.
Solution:
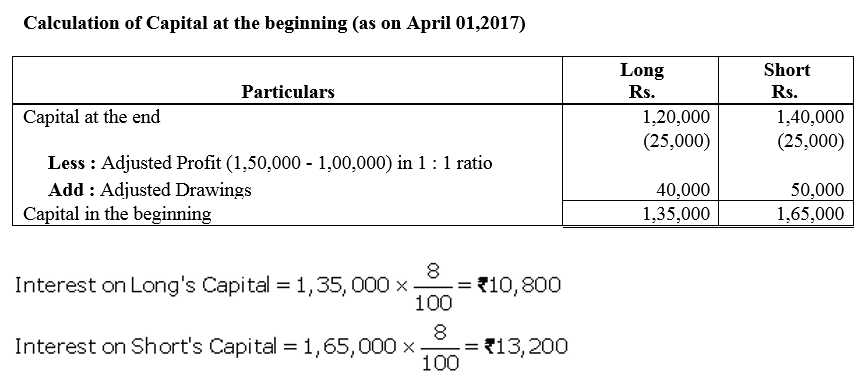
Question 39.
X and Y contribute ₹ 20,000 and ₹ 10,000 respectively towards capital. They decide to allow interest on capital @ 6% p.a. Their respective share of profits is 2 : 3 and the net profit for the year is ₹ 1,500. Show distribution of profits:
(i) where there is no agreement except for interest on capitals; and
(ii) where there is an agreement that the interest on capital as a charge.
Solution:
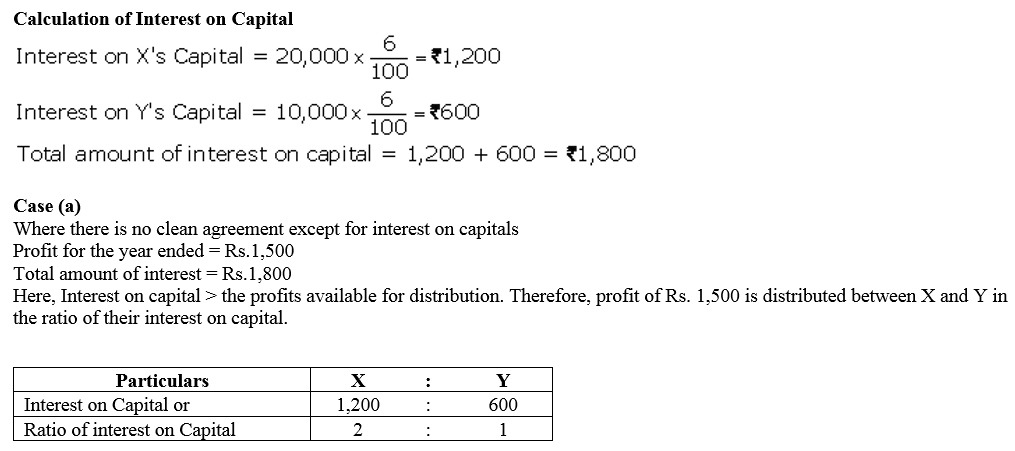
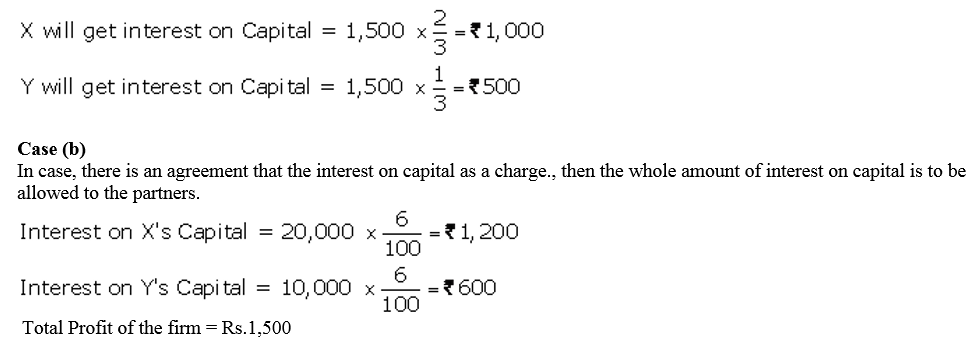
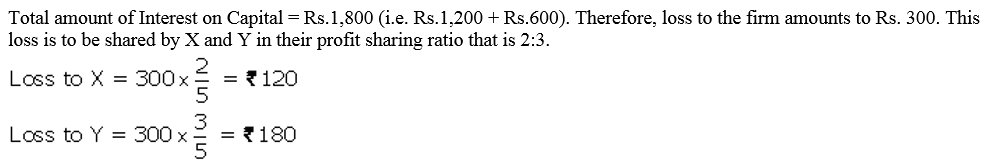
Question 40.
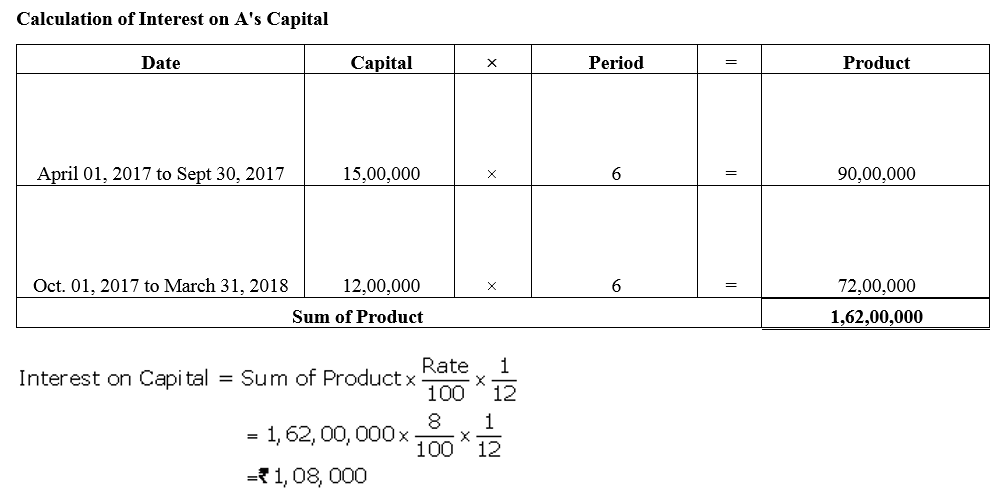
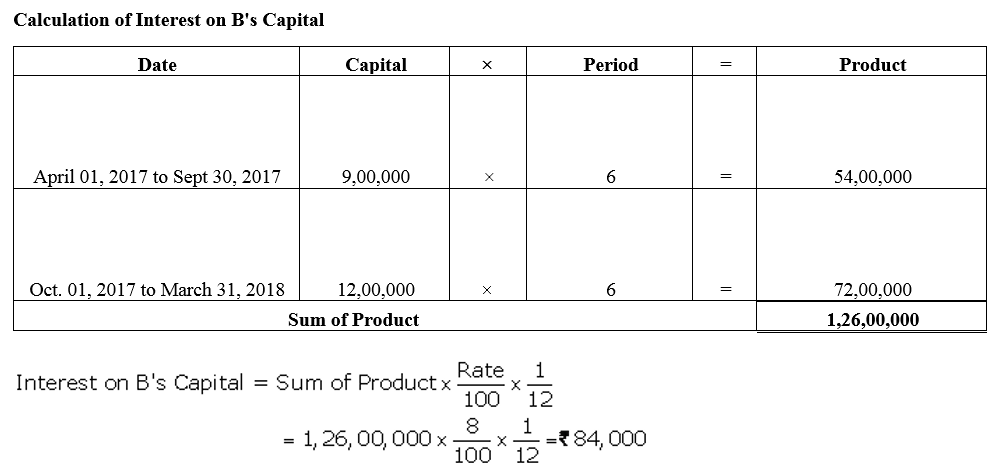
A and B started business on 1st April, 2017 with capitals of ₹ 15,00,000 and ₹ 9,00,000 respectively. On 1st October, 2017, they decided that their capitals should be ₹ 12,00,000 each. The necessary adjustments in capitals were made by introducing or withdrawing by cheque. Interest on capital is allowed @ 8% p.a. Compute interest on capital for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
Question 41.
X and Y are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 . On 31st March, 2018 after closing the books of account, their Capital Accounts stood at ₹ 4,80,000 and ₹ 6,00,000 respectively. On 1st May, 2017, X introduced an additional capital of ₹ 1,20,000 and Y withdrew ₹ 60,000 form his capital.On 1st October, 2017, X withdrew ₹ 2,40,000 from his capital and Y introduced ₹ 3,00,000 . Interest on capital is allowed at 6% p.a. Subsequently, it was discovered that interest on capital @ 6% p.a. had been omitted. The profits for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 2,40,000 and the partners’ drawings had been: X ₹1,20,000 and Y ₹ 60,000. Compute the interest on capital if the capitals are (a) fixed, and (b) fluctuating.
Solution:
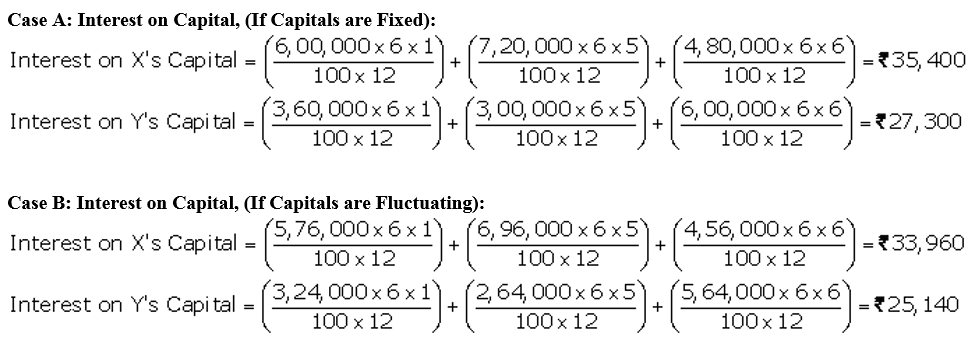
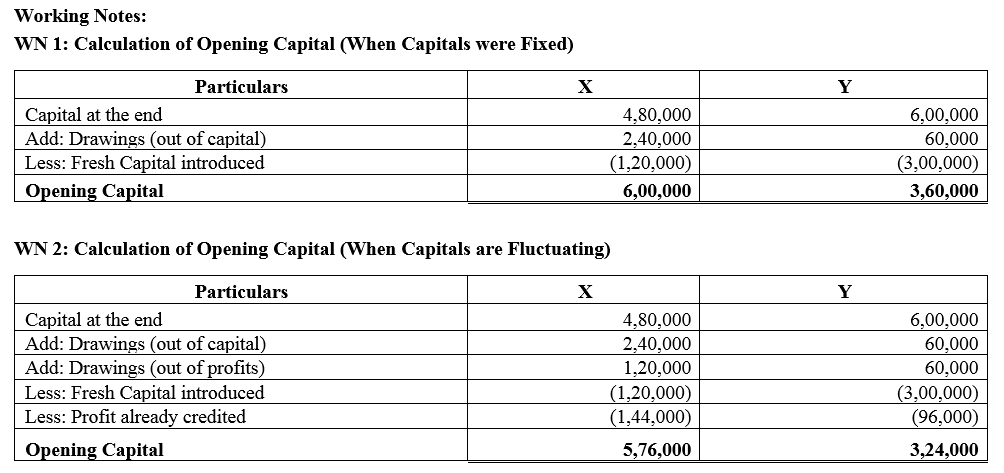
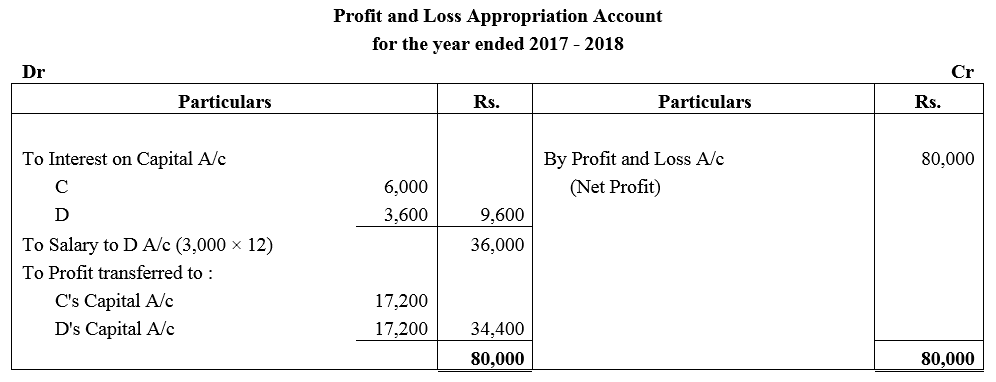
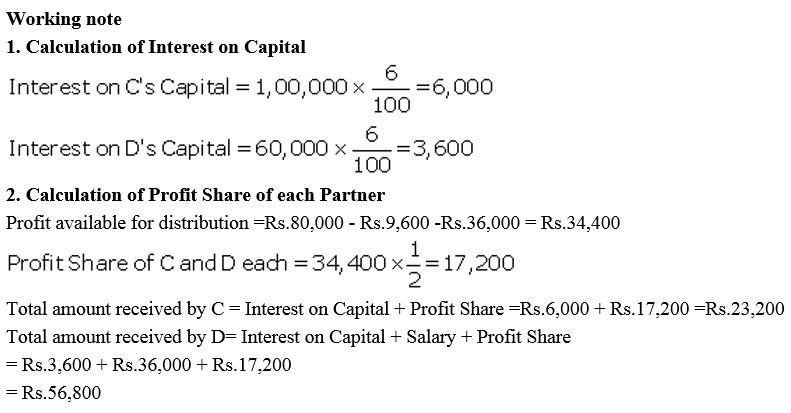
Question 42.
C and D are partners in a firm; C has contributed ₹ 1,00,000 and D ₹ 60,000 as capital. Interest in payable @ 6% p.a. and D is entitled to a salary of ₹ 3,000 per month. In 2017-18, the profit was ₹ 80,000 before interest and salary. Divide the amount between C and D.
Solution:
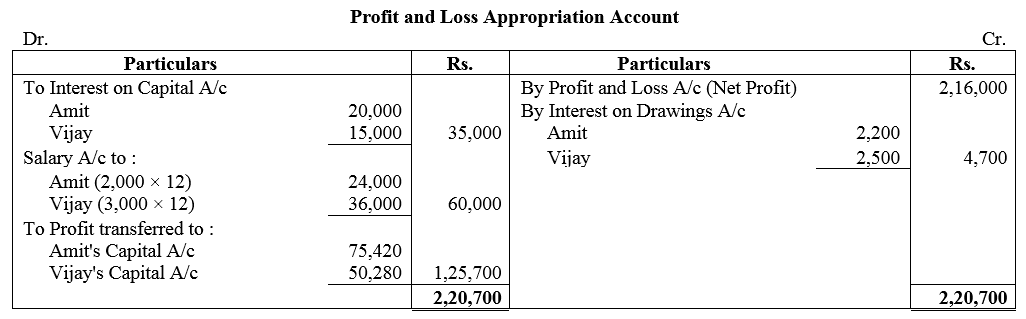
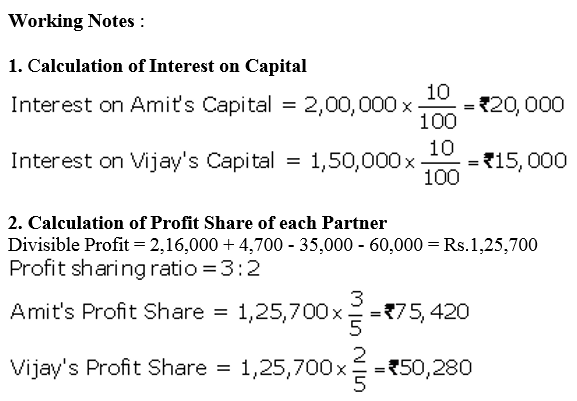
Question 43.
Amit and Vijay started a partnership business on 1st April,2017. Their capital contributions were ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 1,50,000 respectively. The Partnership Deed provided that:
(a) Interest on capital be allowed @ 10% p.a.
(b) Amit to get a salary of ₹ 2,000 per month and Vijay ₹ 3,000 per month.
(c) Profits are to be shared in the ratio of 3 : 2.
Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 befor above appropriations was ₹ 2,16,000. Interest on drawings amounted to ₹ 2,200 for Amit and ₹ 2,500 for Vijay. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
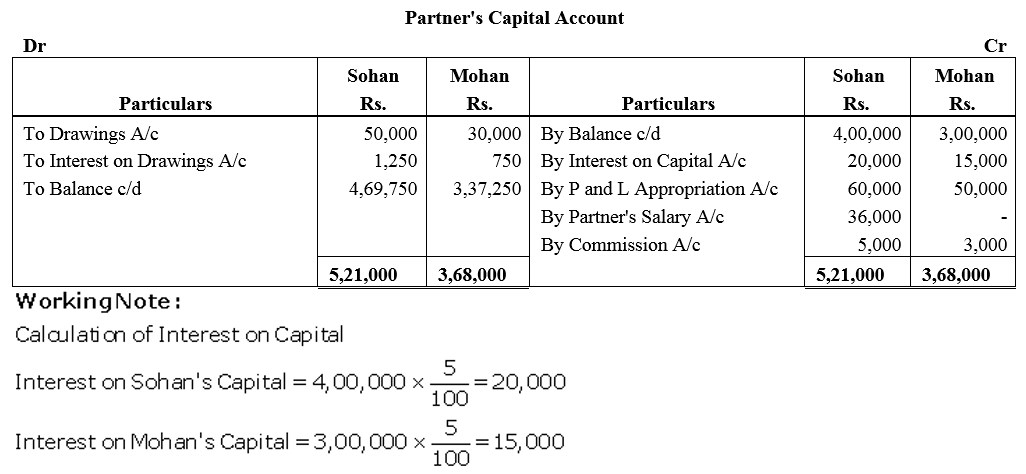
Question 44.
Show how the following will be recorded in the Capital Accounts of the Partners Sohan and Mohan when their capitals are fluctuating:
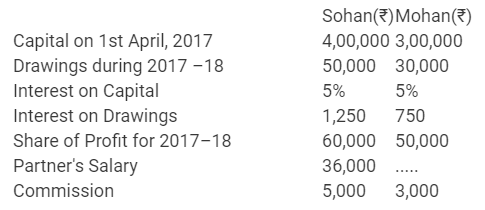
Solution:
Question 45.
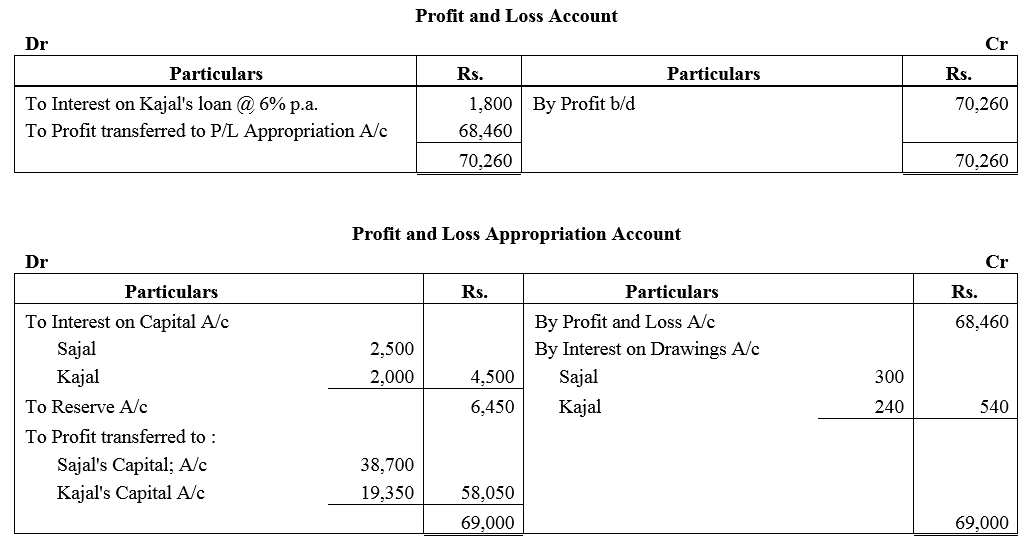
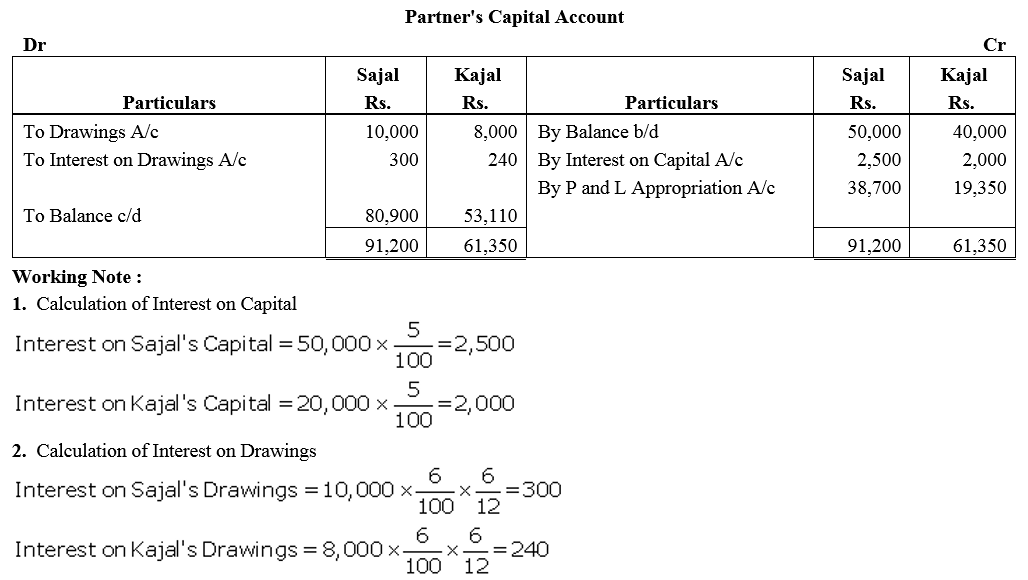
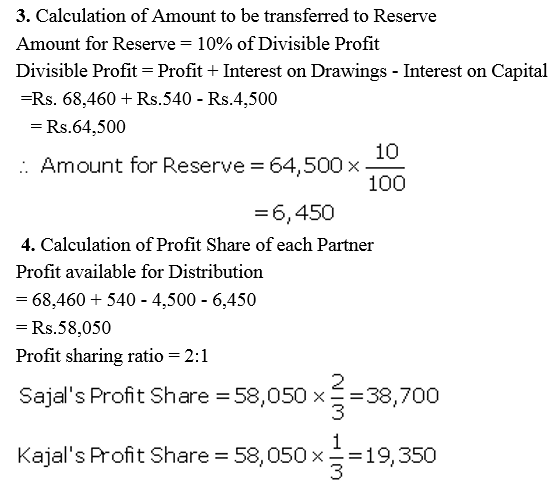
Sajal and Kajal are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 1. On 1st April, 2017 their Capitals were: Sajal ₹ 50,000 and Kajal ₹ 40,000.
Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the Partners Capital Accounts at the end of the year after considering the following items:
(a) Interest on Capital is to be allowed @ 5% p.a.
(b) Interest on the loan advanced by Kajal for the whole year, the amount of loan being ₹ 30,000.
(c) Interest on partners drawings @ 6% p.a. Drawings: Sajal ₹ 10,000 and Kajal ₹ 8,000.
(d) 10% of the divisible profit is to be transferred to Reserve.
The net profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 ₹ 68,460.
Note: Net profit means net profit after debit of interest on loan by the partner.
Solution:
Question 46.
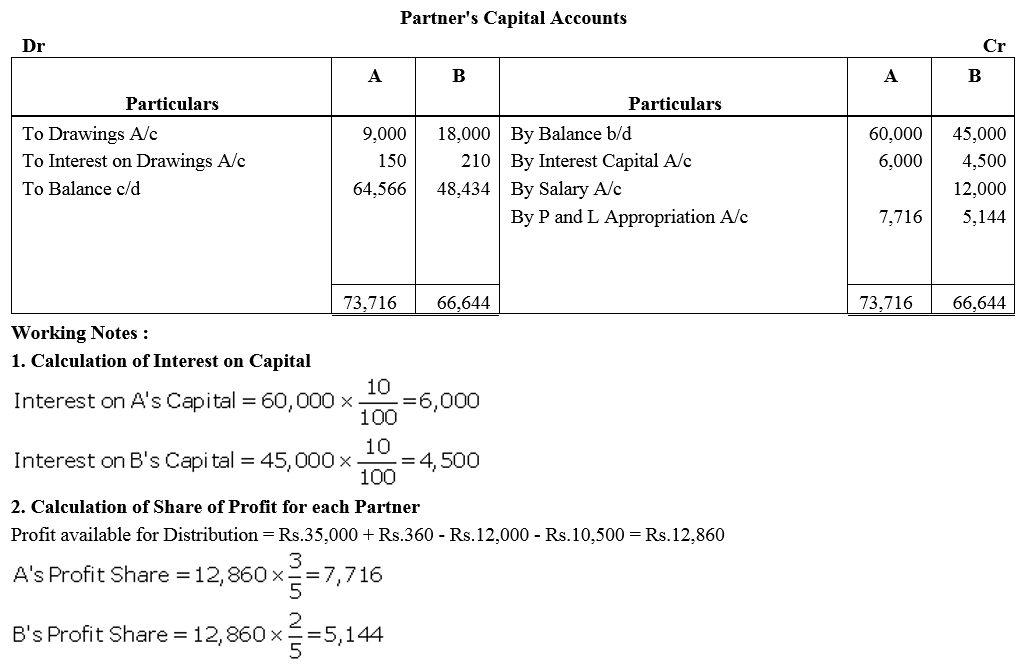
On 1st April, 2017, A and B entered into partnership contributing ₹ 60,000 and ₹ 45,000 respectively. They agreed to share profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. B is allowed salary of ₹ 12,000 per year. Interest on capital is to be allowed @ 10% p.a. During the year, A withdrew ₹ 9,000 and B withdrew ₹ 18,000 as drawings, Interest on drawings paid by A and B were ₹ 150 and ₹ 210 respectively. Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 before the above adjustments was ₹ 35,000. Show distribution of profits by preparing Profit and Loss Appropriation Account of the firm. Prepare Partners Capital Accounts also.
Solution:
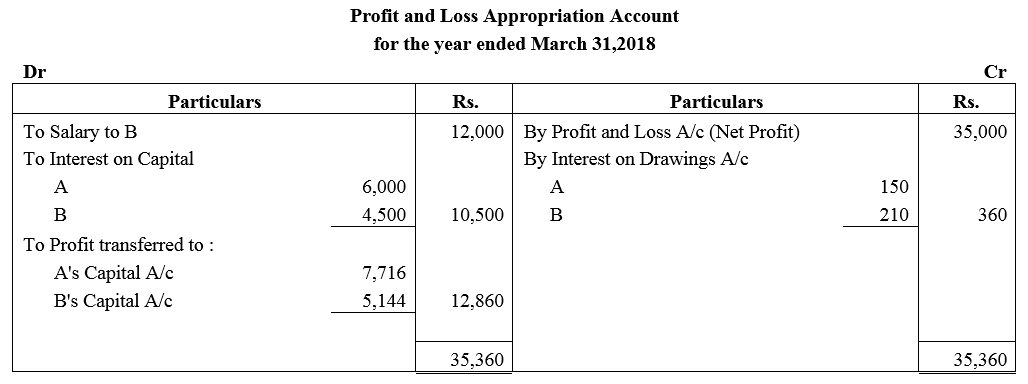
Question 47.
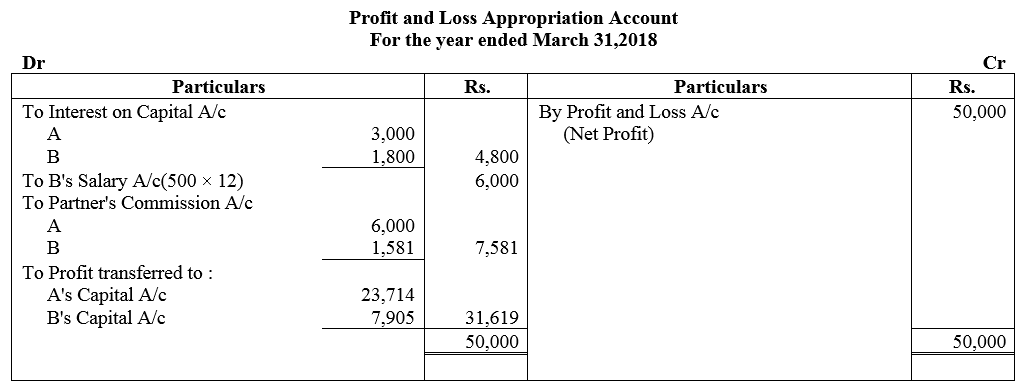
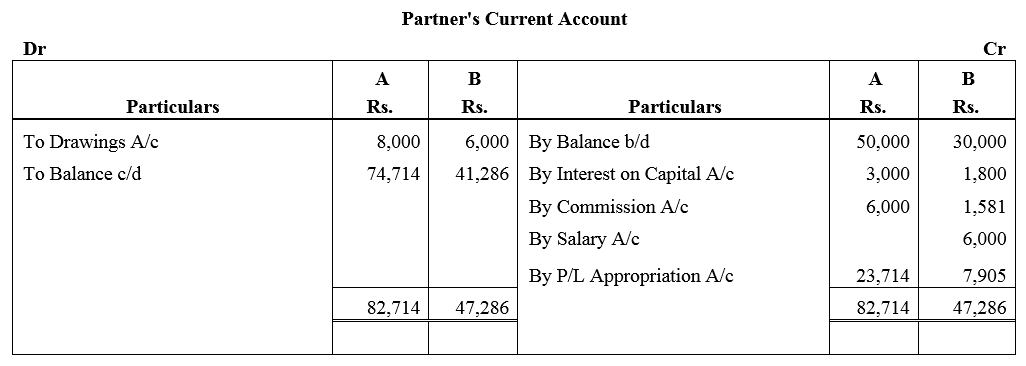
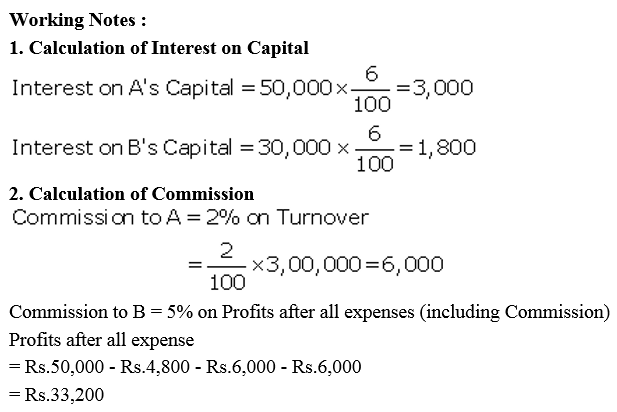
A and B are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 1. On 1st April, 2017, their capitals were: A ₹ 50,000 and B ₹ 30,000. During the year ended 31st March, 2018 they earned a net profit of ₹ 50,000. The terms of partnership are:
(a) Interest on capital is to allowed @ 6% p.a.
(b) A will get a commission @ 2% on turnover.
(c) B will get a salary of ₹ 500 per month.
(d) B will get commission of 5% on profits after deduction of all expenses including such commission.
Partners drawings for the year were: A ₹ 8,000 and B ₹ 6,000. Turnover for the year was ₹ 3,00,000. After considering the above facts, you are required to prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and Partners Capital Accounts.
Solution:
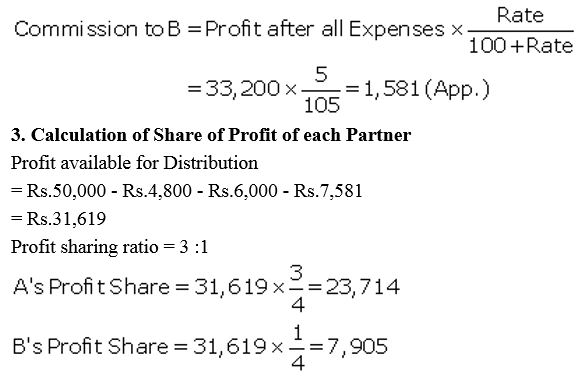
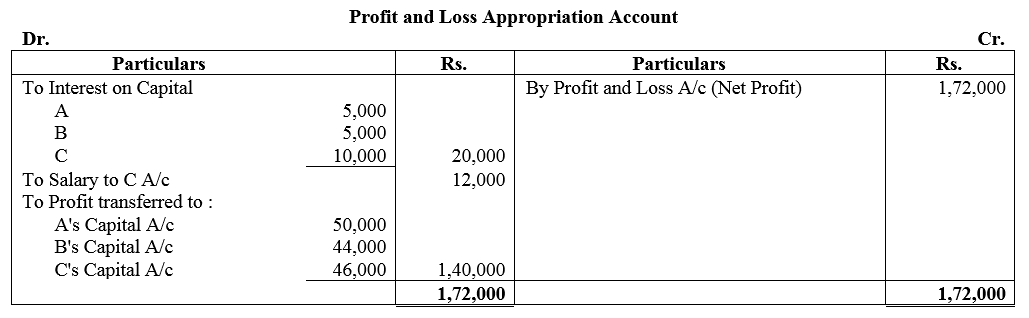
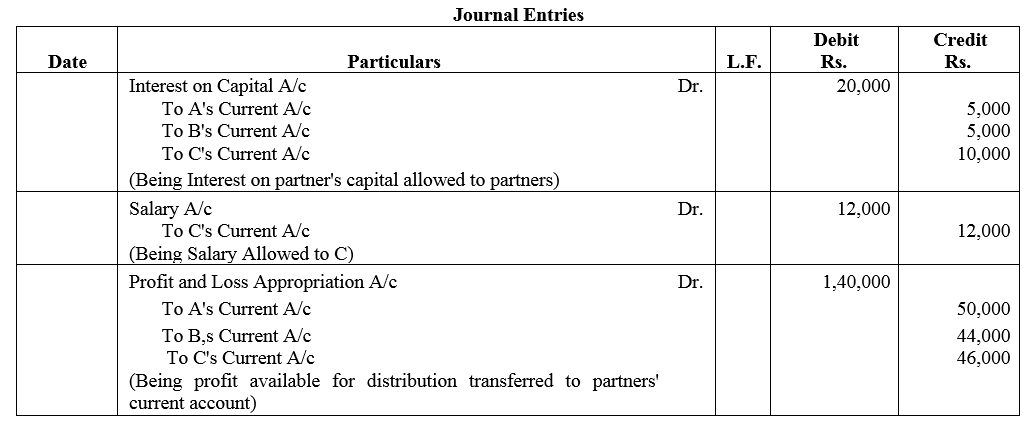
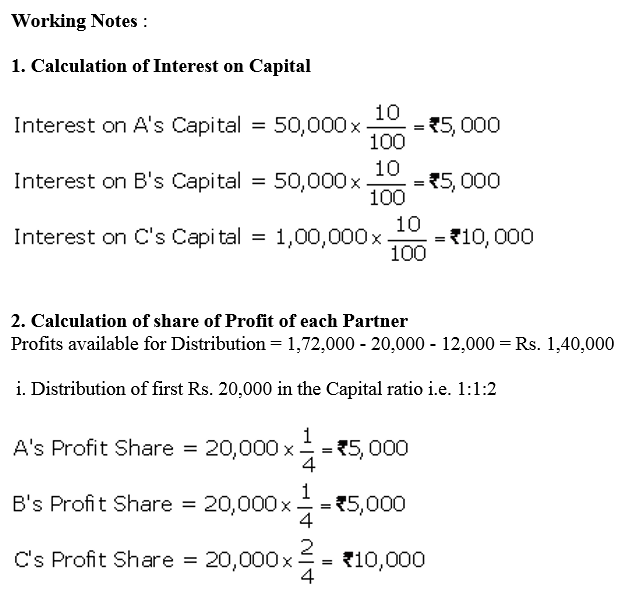
Question 48.
A, B and C were partners in a firm having capitals of ₹ 50,000 ; ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 1,00,000 respectively. Their Current Account balances were A: ₹ 10,000; B: ₹ 5,000 and C: ₹ 2,000 (Dr.). According to the Partnership Deed the partners were entitled to an interest on Capital @ 10% p.a. C being the working partner was also entitled to a salary of ₹ 12,000 p.a. The profits were to be capitals:
(a) The first ₹ 20,000 in proportion to their capitals.
(b) Next ₹ 30,000 in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2.
(c) Remaining profits to be shared equally.
The firm earned net profit of ₹ 1,72,000 before charging any of the above items.
Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and pass necessary Journal entry for the appropriation of profits.
Solution:

Question 49.
A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 with capitals of ₹ 50,000 and ₹ 30,000 respectively. Interest on cpital is agreed @ 6% p.a. B is to be allowed an annual salary of ₹ 2,500. During the year profit prior to interest on capital but after charging B’s salary amounted to ₹ 12,500. A provision of 5% of the profits if to be made in respect of Manager’s Commission.
Solution:
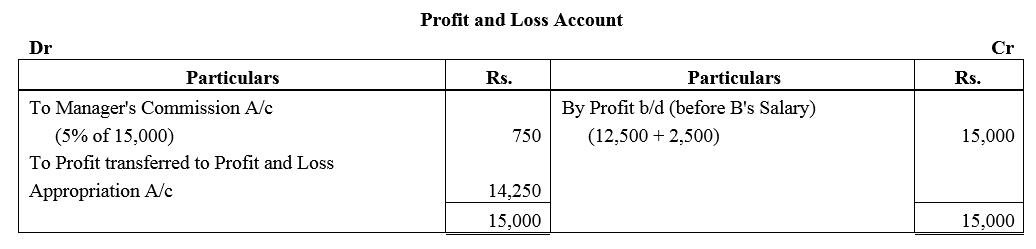
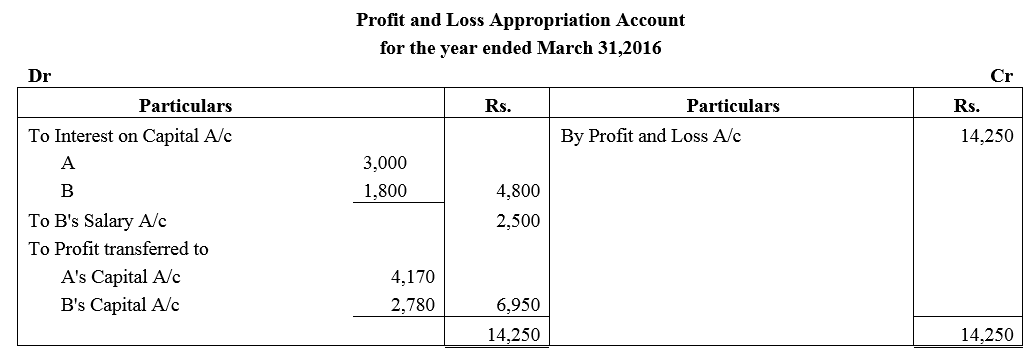
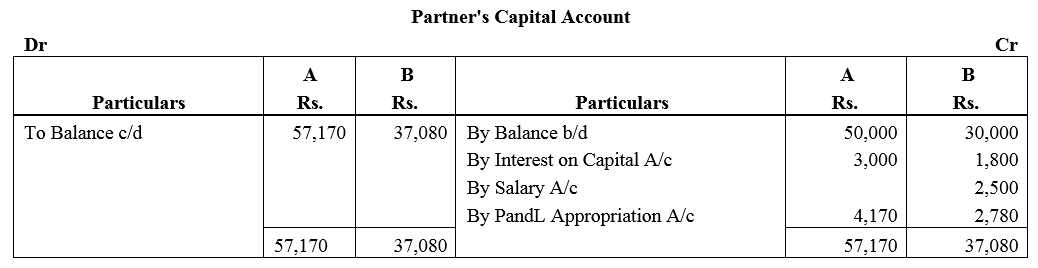
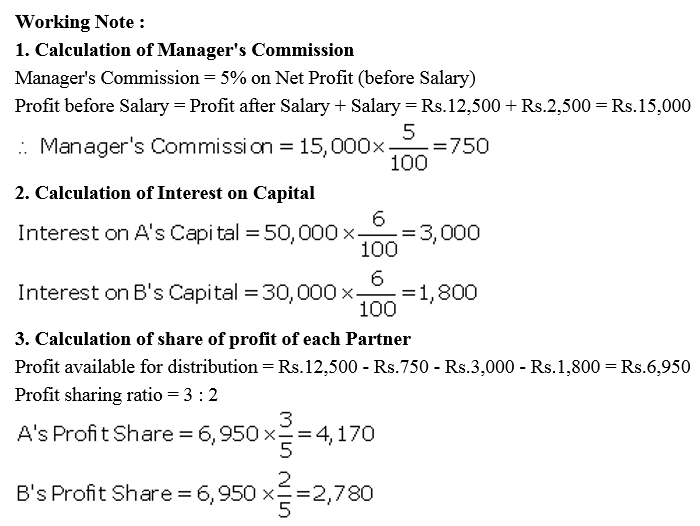
Question 50.
P, Q and R are in a partnership and as at 1st April, 2017 their respective capitals were: ₹ 40,000, ₹ 30,000 and ₹ 30,000. Q is entitled to a salary of ₹ 6,000 and R ₹ 4,000 p.a. payable before division of profits. Interest is allowed on capital @ 5% p.a. and is not charged on drawings. Of the divisible profits, P is entitled to 50% of the first ₹ 10,000, Q to 30% and R to 20%, rest of the profit are shared equally. Profits for the year ended 31st March, 2018, after debiting partners salaries but before charging interest on capital was ₹ 21,000 and the partners had drawn ₹ 10,000 each on account of salaries, interest and profit.
Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 showing the distribution of profit and the Capital Accounts of the partners.
Solution:
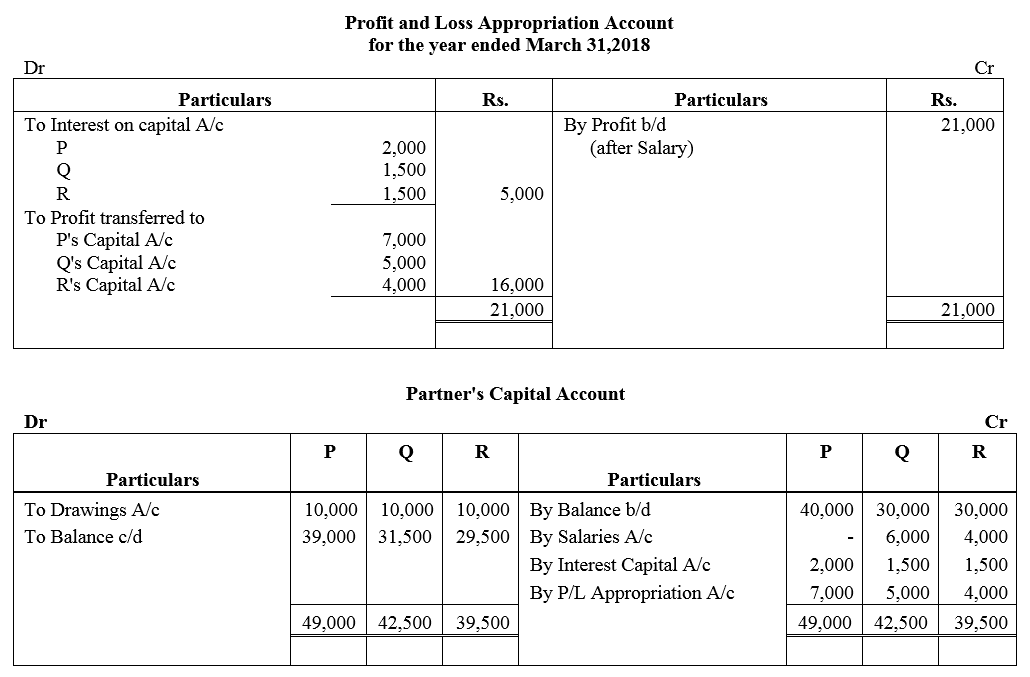
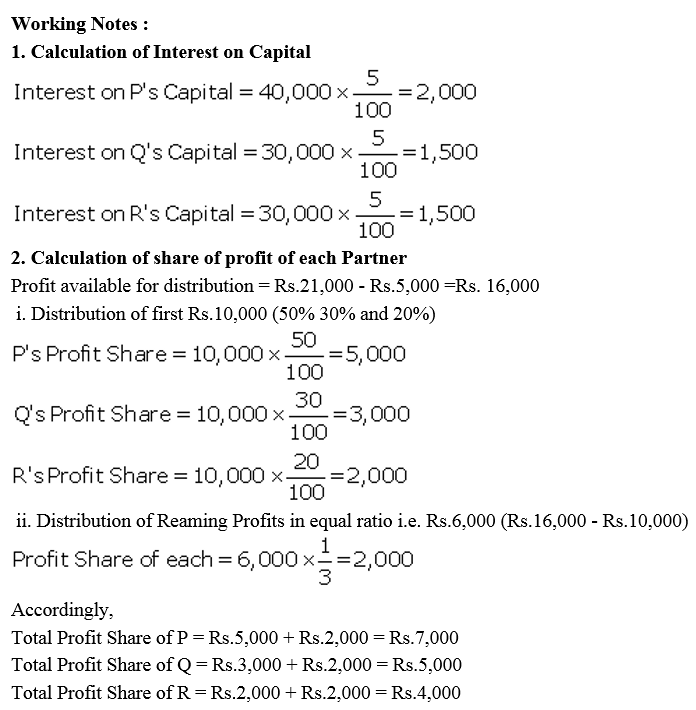
Question 51.
A, B and C are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of A 1/2, B 3/10, C 1/5 after providing for interest @ 5% on their respective capitals, viz., A ₹ 50,000; B ₹ 30,000 and C ₹ 20,000 and allowing B and C a salary of ₹ 5,000 each per annum. During the year ended 31st March, 2018, A has drawn ₹ 10,000 and B and C in addition to their salaries have drawn ₹ 2,500 and ₹ 1,000 respectively. The Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018 showed a net profit of ₹ 45,000 before charging (a) interest on capital and (b) partners salaries. On 1st April, 2017, the balances in the current Account of the partners were A (cr.) ₹ 4,500; B (Cr.) ₹ 1,500 and C (Cr.) ₹ 1,000. Interest is not charged on Drawings or Current Account balances. Show Partners Capital and Current Accounts as at 31st March, 2018 after division of profits in accordance with the partnership agreement.
Solution:
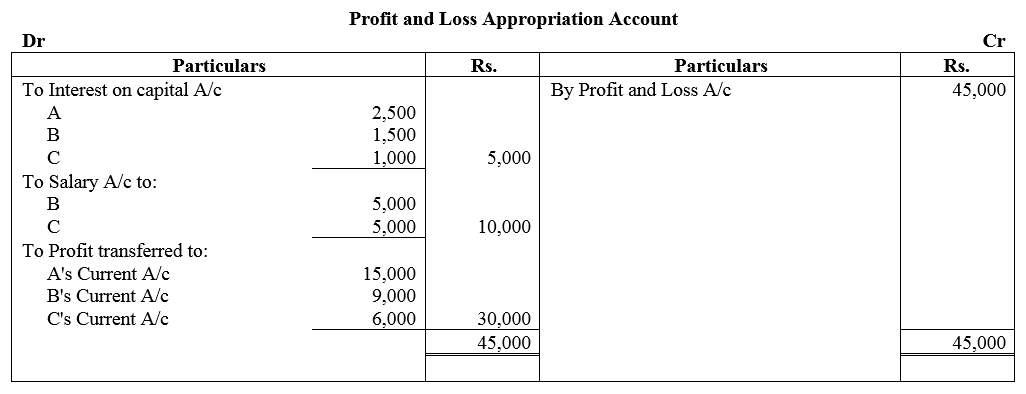
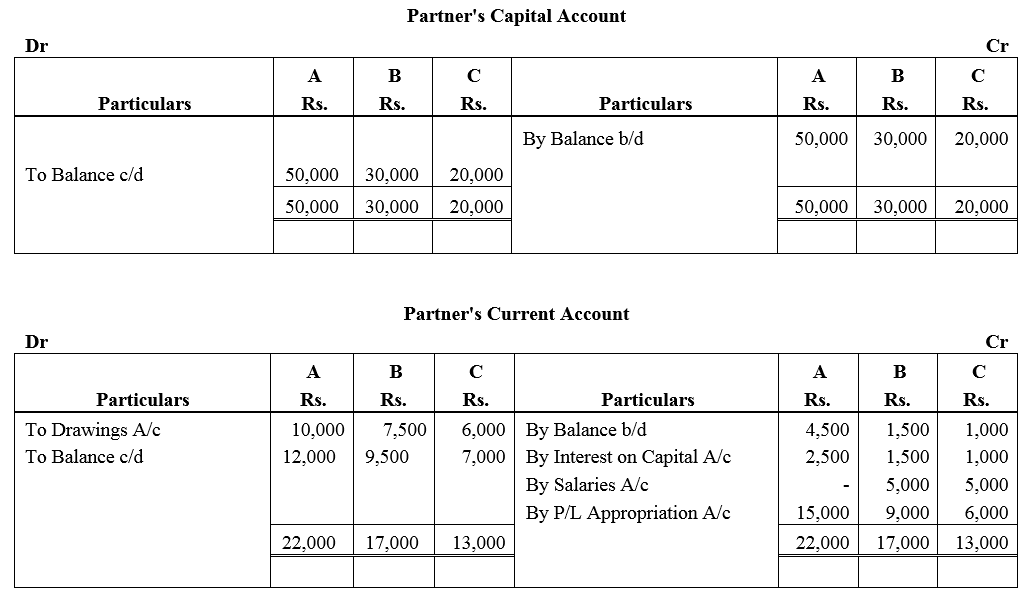
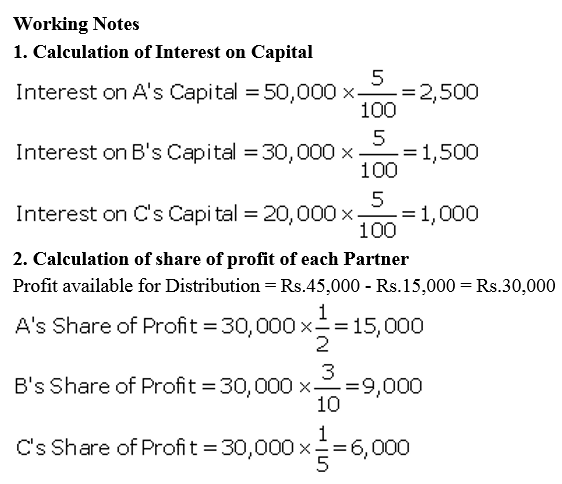
Question 52.
Ali the Bahadur are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses as Ali 70% and Bahadur 30%. Their respective capitals as at 1st April, 2017 stand as Ali ₹ 25,000 and Bahadur ₹ 20,000. The partners are allowed interest on capitals @ 5% p.a. Drawings of the partners during the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 3,500 and ₹ 2,500 respectively. Profit for the year, before charging interest on capital and annual salary of Bahadur @ ₹ 3,000, amounted to ₹ 40,000, 10% of divisible profit is to be transferred to Reserve. You are asked to show Partners Current Account and Capital Accounts recording the above transactions.
Solution:
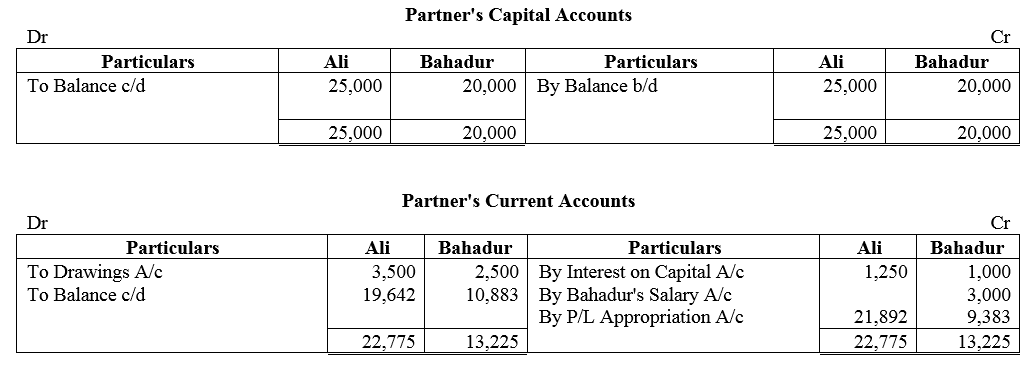
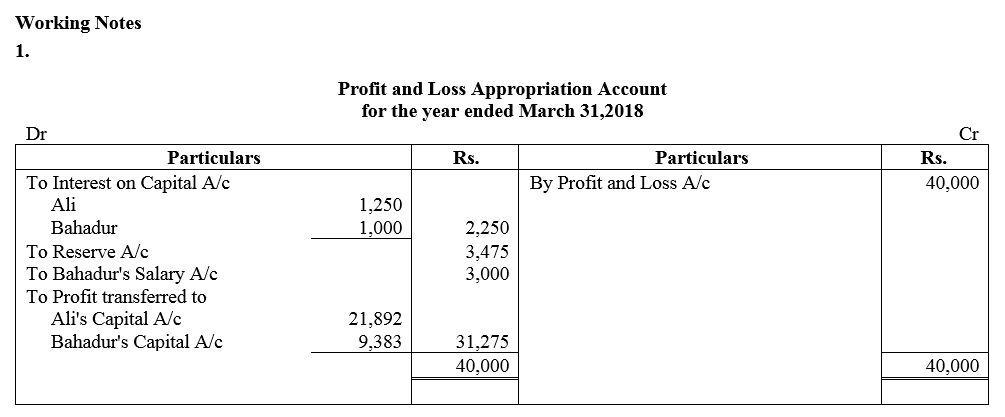
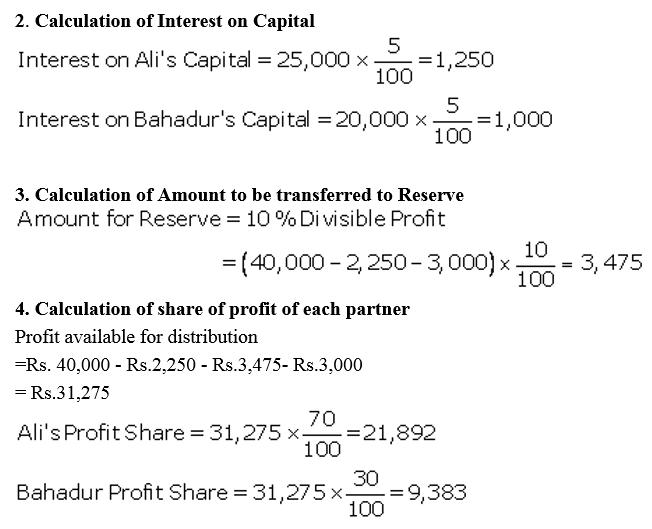
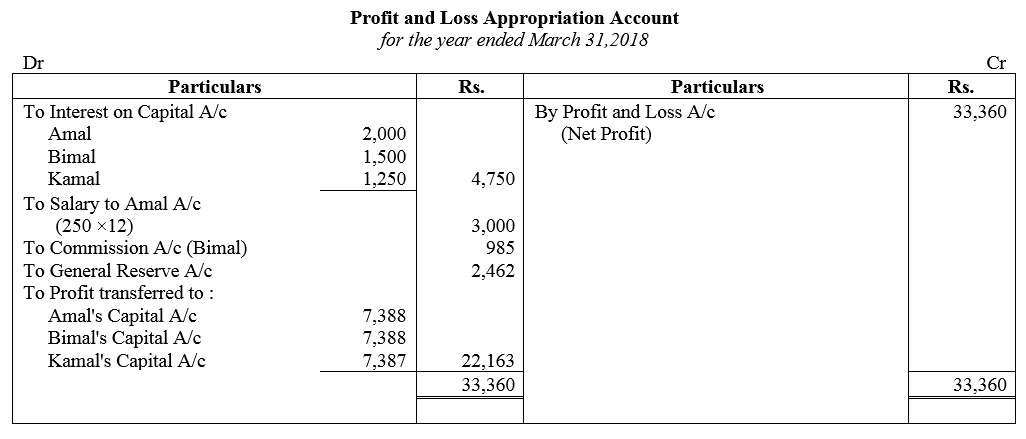
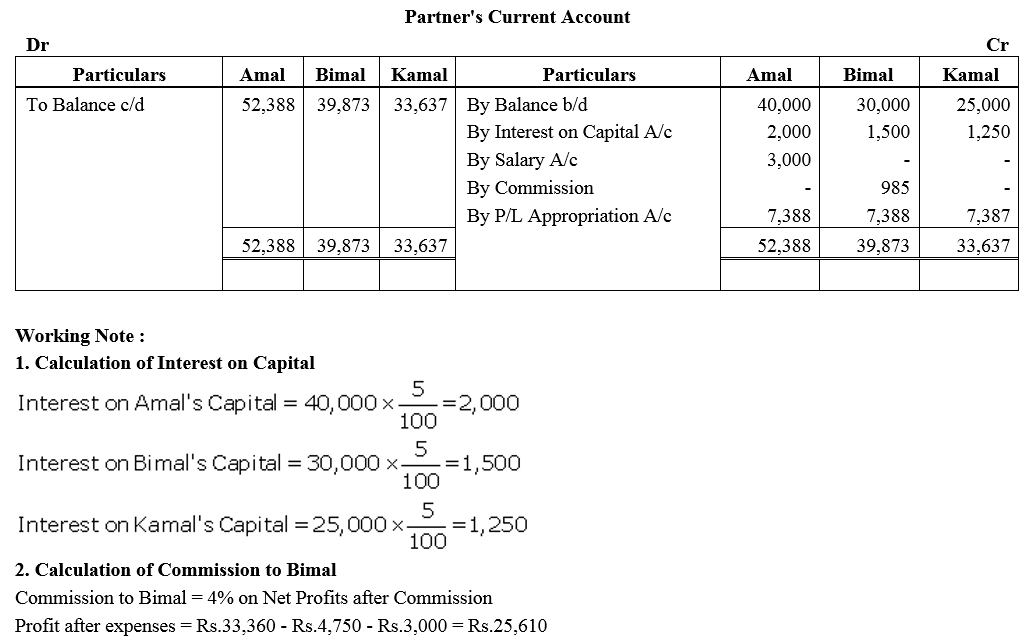
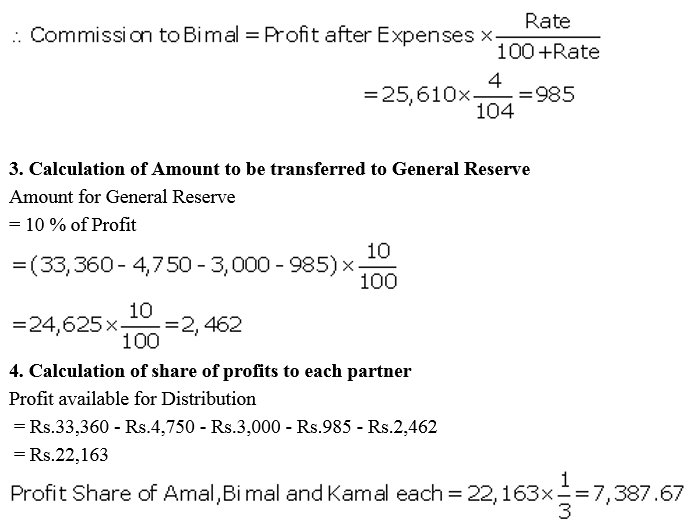
Question 53.
Amal, Bimal and kamal are three partners. On 1st April, 2017, their Capitals stood as: Amal ₹ 40,000, Bimal ₹ 30,000 and Kamal ₹ 25,000. It was decided that:
(a) they would receive interest on Capital @ 5% p.a.
(b) Amal would get a salary of ₹ 250 per month.
(c) Bimal would receive commission @ 4% on net profit after deducting commission, interest on capital and salary, and
(d) After deducting all of these 10% of the profit should be transferred to the General Reserve.
Before the above items were taken into account, the profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 33,360. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the Capital Accounts of the Partners.
Solution:
Question 54.
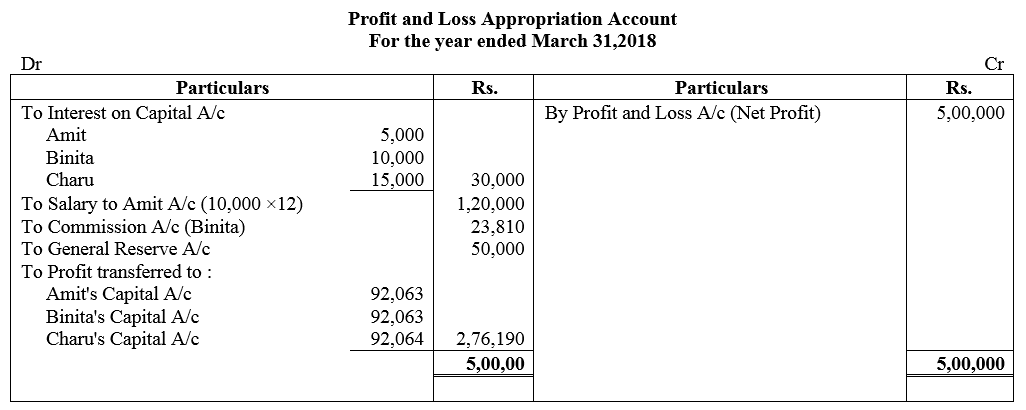
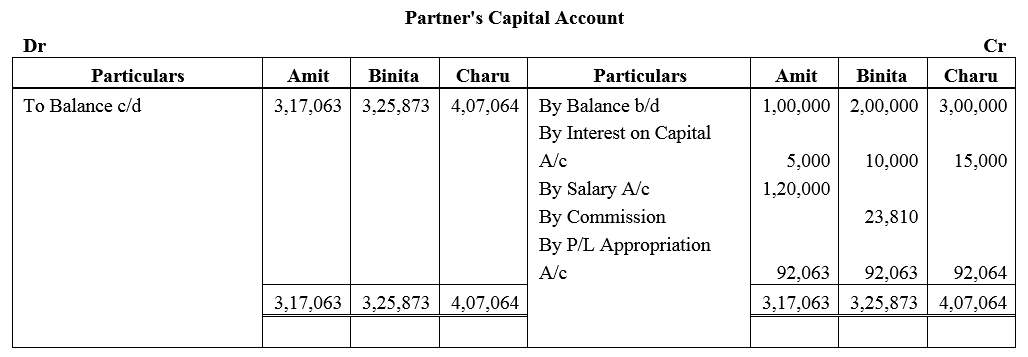
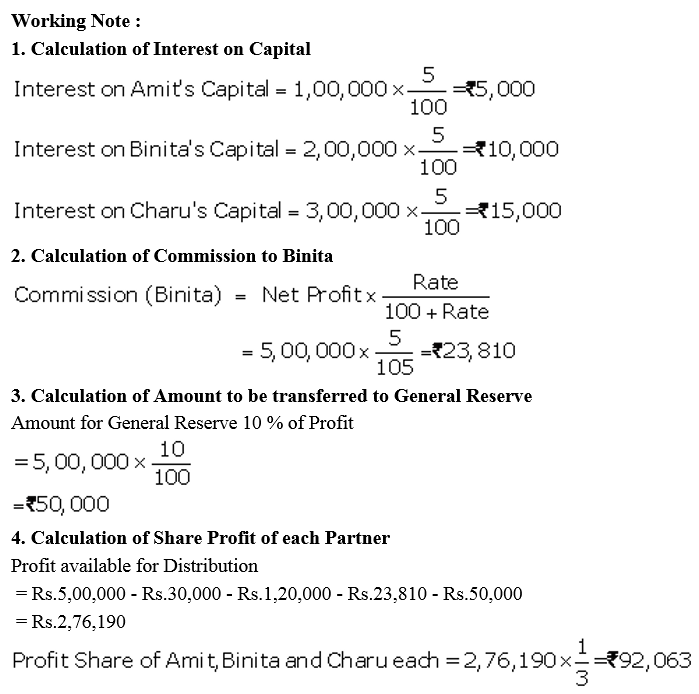
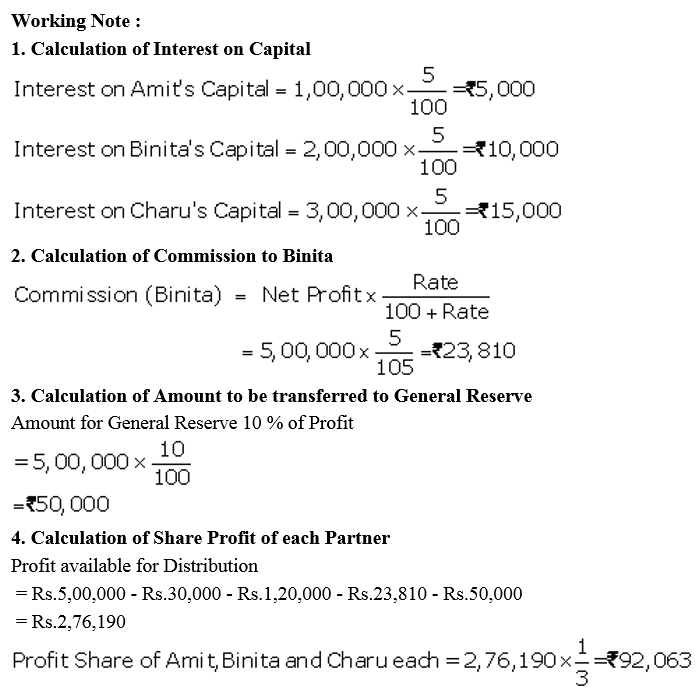
Amit, Binita and Charu are three partners. On 1st April, 2017, their Capitals stood as: Amit ₹ 1,00,000, Binita ₹ 2,00,000 and Charu ₹ 3,00,000. It was decided that:
(a) they would receive interest on Capital @ 5% p.a.
(b) Amit would get a salary of ₹ 10,000 per month.
(c) Binita would receive commission @ 5% of net profit after deduction of commission, and
(d) 10% of the net profit would be transferred to the General Reserve.
Before the above items were taken into account, the profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 5,00,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the Capital Accounts of the partners.
Solution:
Question 55.
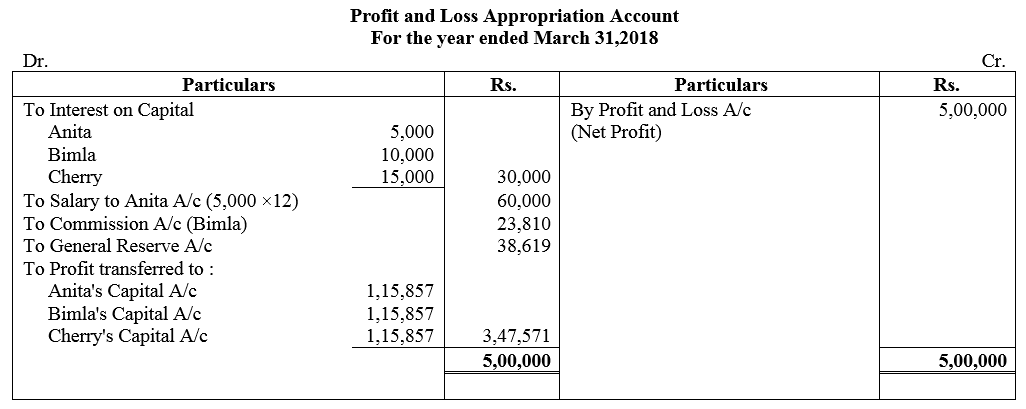
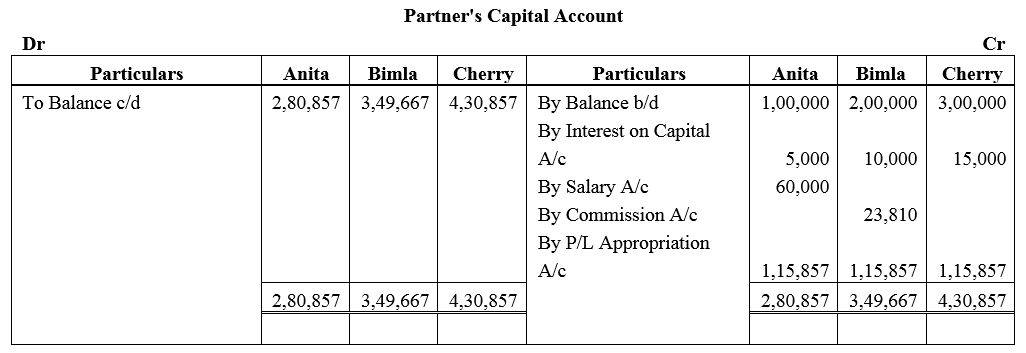
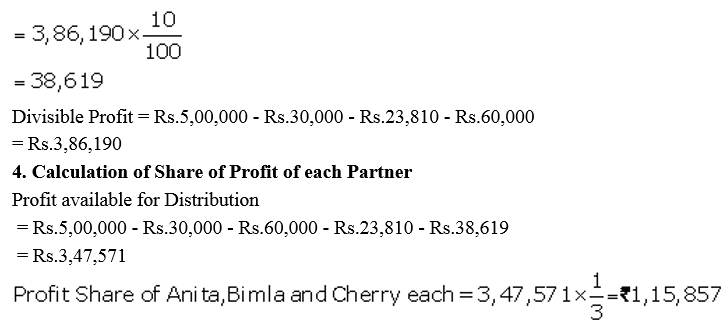
Anita, Bimla and Cherry are three partners. On 1st April, 2017, their Capitals stood as: Anita ₹ 1,00,000, Bimla ₹ 2,00,000 and Cherry ₹ 3,00,000. It was decided that:
(a) they would receive interest on Capital @ 5% p.a.
(b) Anita would get a salary of ₹ 5,000 per month.
(c) Bimla would receive commission @ 5% of net profit after deduction of commission, and
(d) 10% of the net divisible profit would be transferred to the General Reserve.
Before the above items were taken into account, the profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 5,00,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the Capital Accounts of the partners.
Solution:
Question 56.
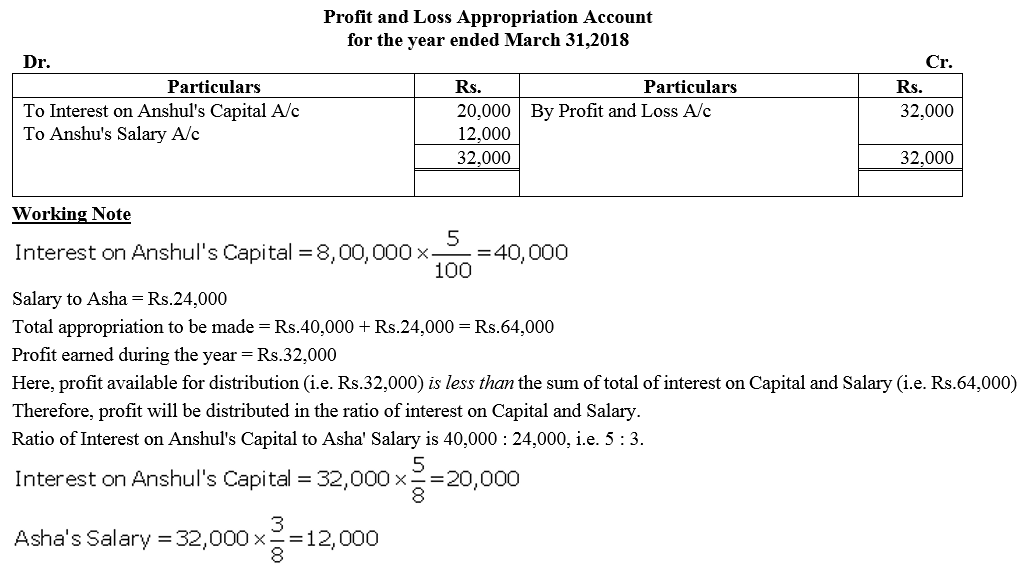
Anshul and Asha are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Anshul being a non-working partner contributed ₹ 8,00,000 as her capital. Asha being a working partner did not contribute capital. The partnership Deed provides for interest on capital @ 5% and salary to every working partner @ ₹ 2,000 per month. Net profit before providing for interest on capital and partner’s salary for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 32,000.
Solution:
Question 57.
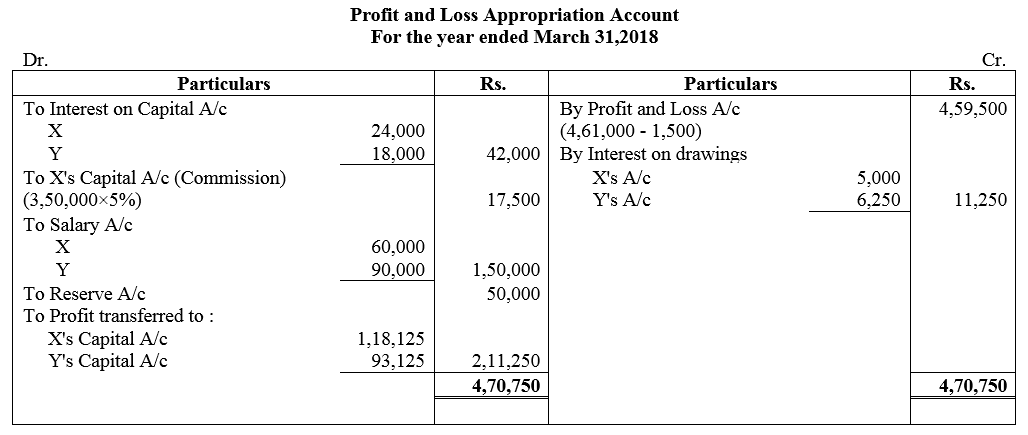
X and Y entered into partnership on 1st April, 2017 and contributed ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 1,50,000 respectively as their capitals. On 1st October, 2017, X provided ₹ 50,000 as loan to the firm. As per the provisions of the partnership Deed:
(i) 20% of Profits before charging interest on Drawings but after making appropriations to be transferred to General Reserve.
(ii) Interest on capital at 12% p.a. and Interest on Drawings @ 10% p.a.
(iii) X to ger monthly salary of ₹ 5,000 and Y to get salary of ₹ 22,500 per quarter.
(iv) X is entitled to a commission of 5% on sales. Sales for the year were ₹ 3,50,000.
(v) Profit and Loss to be shared in the ratio of their capital contribution up to ₹ 1,75,000 and above ₹ 1,75,000 equally.
The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 before providing for any interest was ₹ 4,61,000. The drawings of X and Y were ₹ 1,00,000 and ₹ 1,25,000 respectively. Pass the necessary Journal entries relating to appropriation our of profit and Loss Appropriation Account and the Partners Capital Accounts.
Solution:
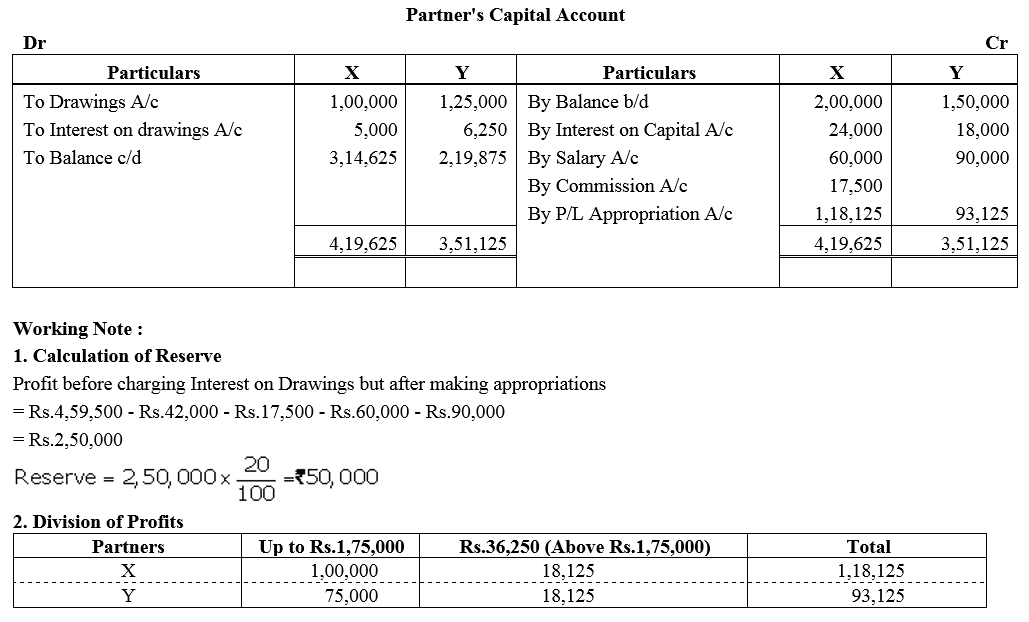
Question 58.
P and Q were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses equally. Their fixed capitals were ₹ 2,00,000 and ₹ 3,00,000 respectively. The Partnership Deed provided for interest on capital @ 12% per annum. For the year ended 31st March, 2016, the profits of the firm were distributed without providing interest on capital. Pass necessary adjustment entry to rectify the error.
Solution:
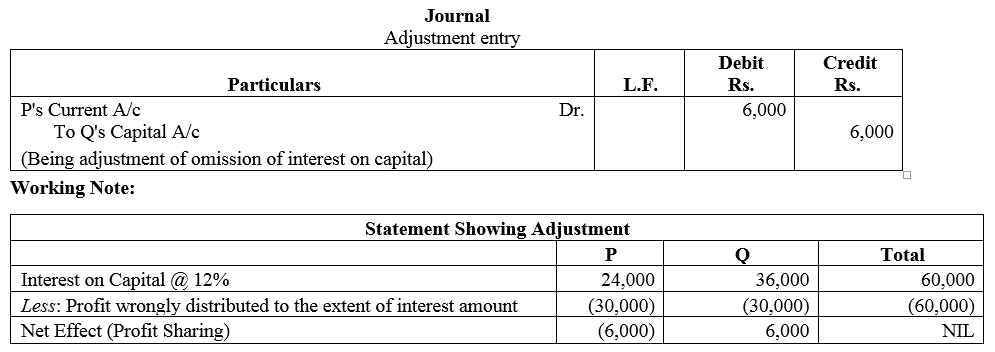
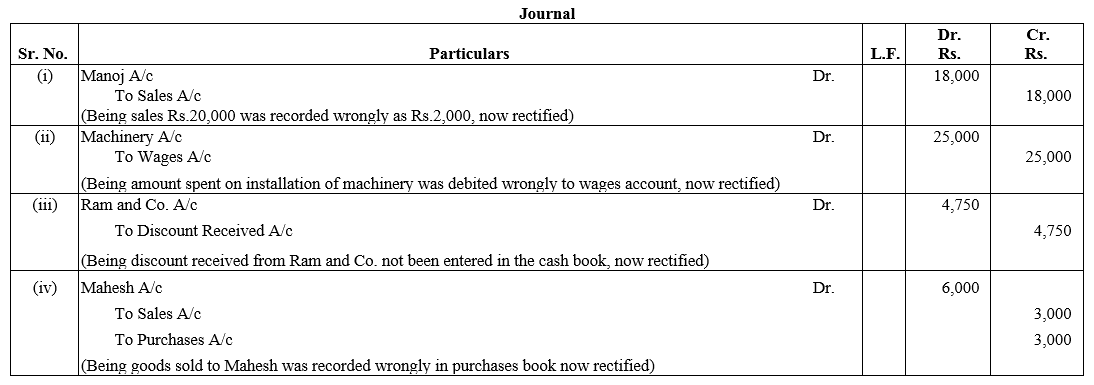
Question 59.
Reya, Mona and Nisha shared profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. The profits for the last three year were ₹ 1,40,000; ₹ 84,000 and ₹ 1,06,000 respectively. These profits were by mistake shared equally for all the give necessary Journal entry for the same.
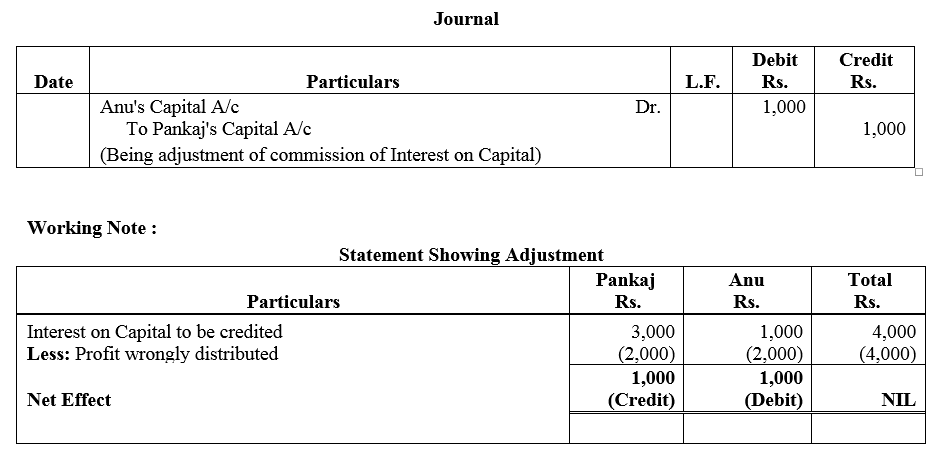
Solution:
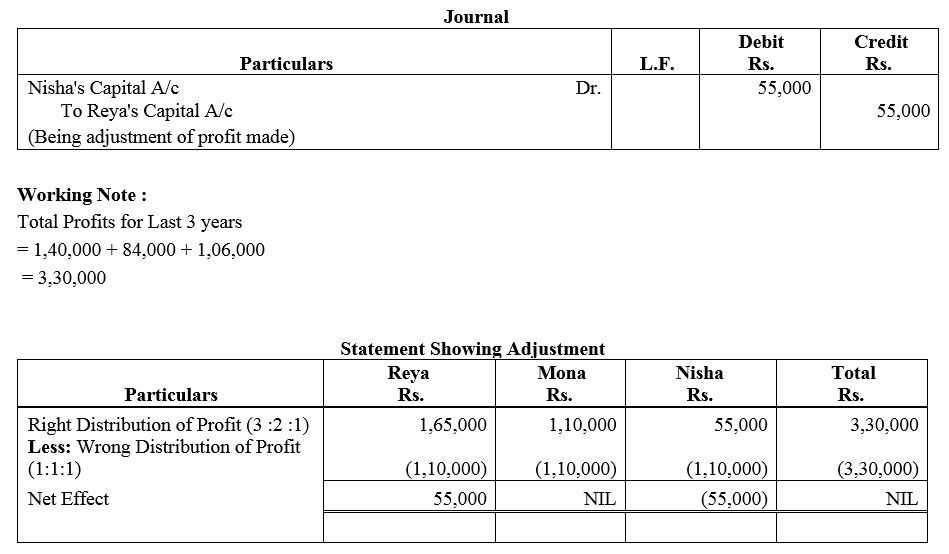
Question 60.
Profits earned by a partnership firm for the year ended 31st March, 2017 were distributed equally between the partners Pankaj and Anu without allowing interest on capital. Interest due on capital was Pankaj ₹ 3,000 and Anu ₹ 1,000.
Solution:
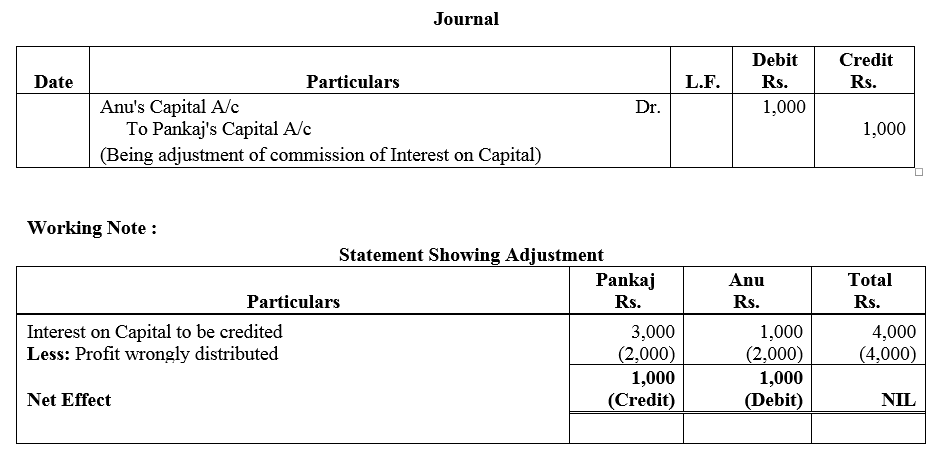
Question 61.
Azad and Benny are equal partners. Their capitals are ₹ 40,000 and ₹ 80,000 respectively. After the accounts for the year have been prepared, it is discovered that interest @ 5% p.a. as provided in the partnership agreement has not been credited to the Capital Accounts before distribution of profits. It is decided t make an adjustment entry in the beginning of the next year. Record the necessary journal entry.
Solution:
Question 62.
Ram and Mohan are equal partners. Their capitals are ₹ 4,000 and ₹ 8,000 respectively. After the accounts for the year are prepared it is discovered that interest @ 5% p.a. on capital as provided in the Partnership Deed has not been credited to the Capital Accounts before distribution of profits. It is decided to make an adjusting entry in the beginning of the next year. Give necessary adjustment entry.
Solution:
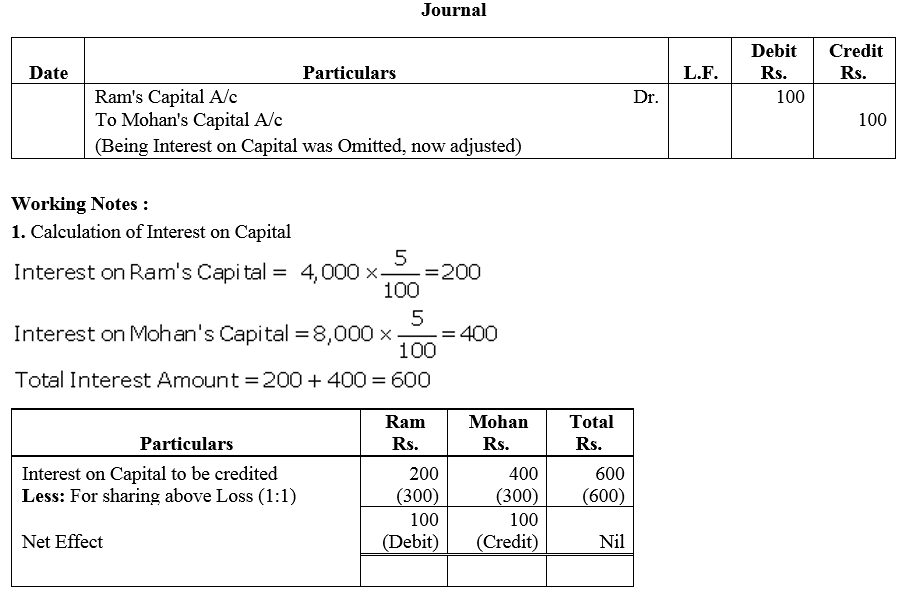
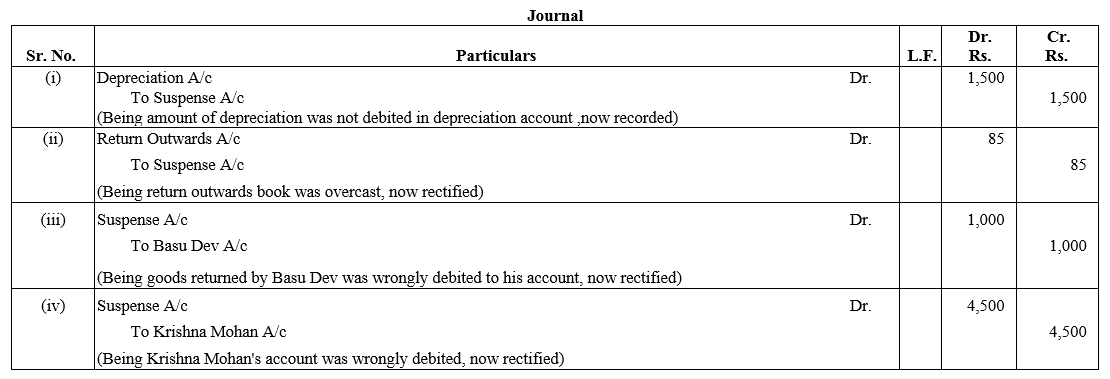
Question 63.
Ram, Mohan and Sohan sharing profits and losses equally have capitals of ₹ 1,20,000, ₹ 90,000 and ₹ 60,000. For the year ended 31st March, 2018, interest was credited to them @ 6% instead of 5%. Give adjustment Jounral entry.
Solution:
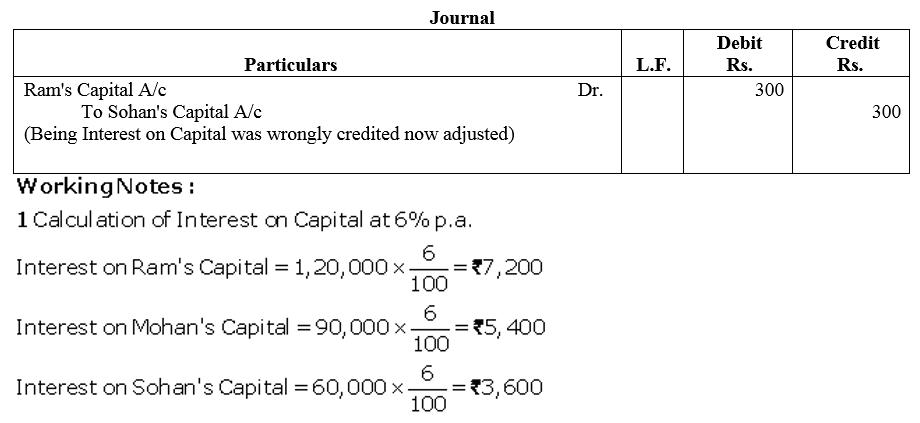
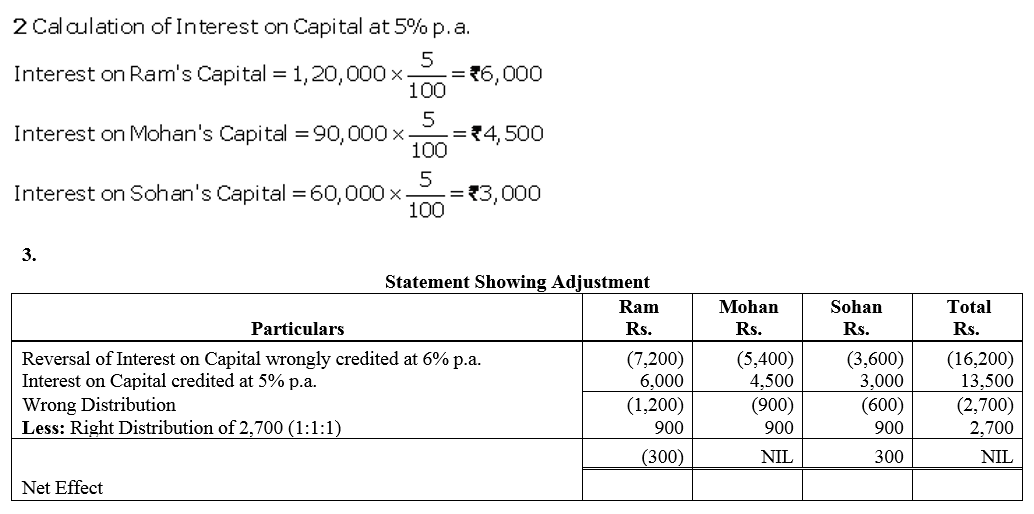
Question 64.
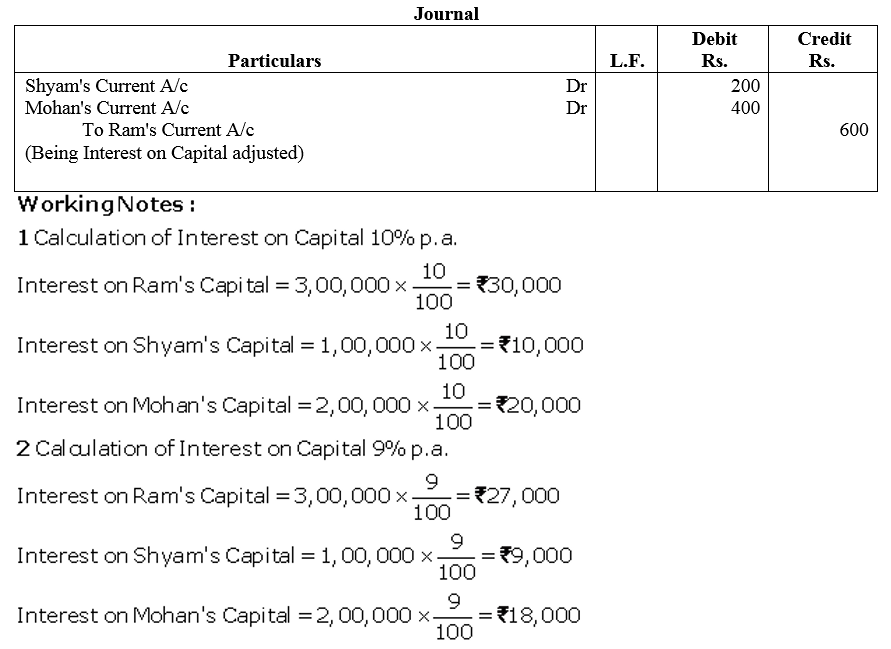
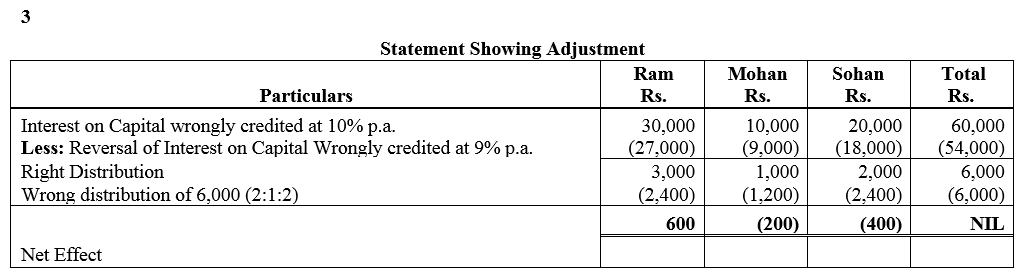
Ram, Shyam and Mohan were partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 2 : 1 : 2. Their capitals were fixed at ₹ 3,00,000, ₹ 1,00,000, ₹ 2,00,000. For the year ended 31st March, 2018, interest on capital was credited to them @ 9% instead of 10% p.a. The profit for the year before charging interest was ₹ 2,50,000. Show your working notes clearly and pass necessary adjustment entry.
Solution:
Question 65.
Mita and Usha are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 3. Their Capital Accounts as on 1st April, 2015 showed balances of ₹ 1,40,000 and ₹ 1,20,000 respectively. The drawings of mita and Usha during the year 2015-16 were ₹ 32,000 and ₹ 24,000 respectively. Both the amounts were withdrawn on 1st January 2016. It was subsequently found that the following items had been omitted while preparing the final accounts for the year ended 31st March, 2016:
(a) Interest on Capital @ 6% p.a.
(b) Interest on Drawings @ 6% p.a.
(c) Mita was entitled to a commission of ₹ 8,000 for the whole year.
Showing your working clearly, pass a rectifying entry in the books of the firm.
Solution:
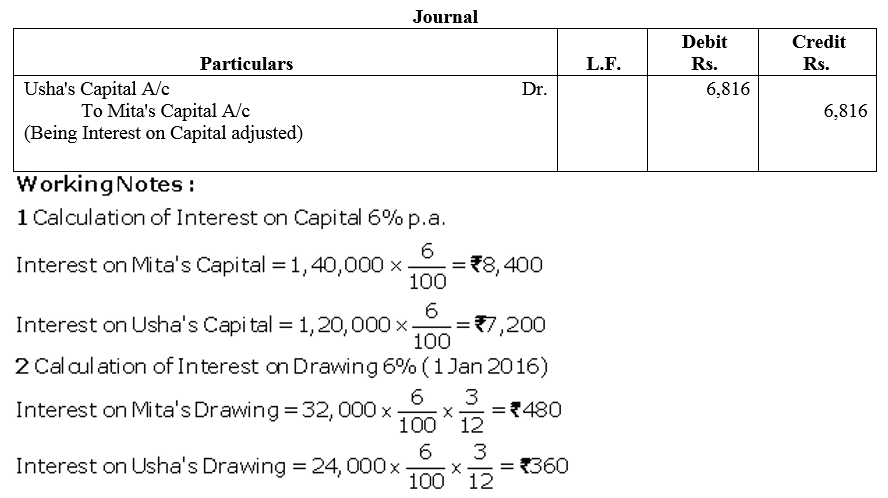
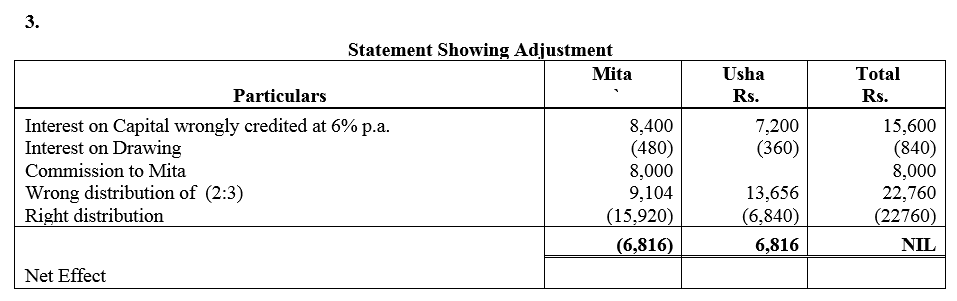
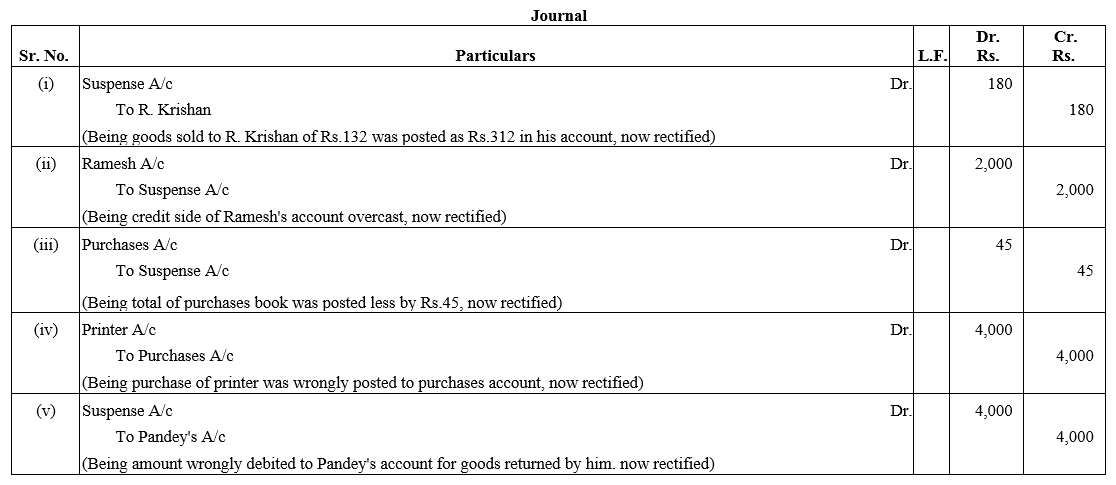
Question 66.
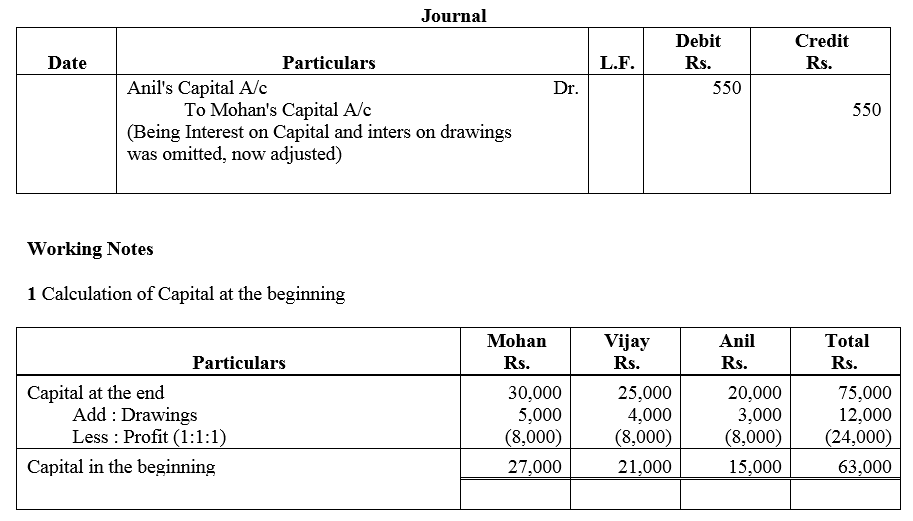
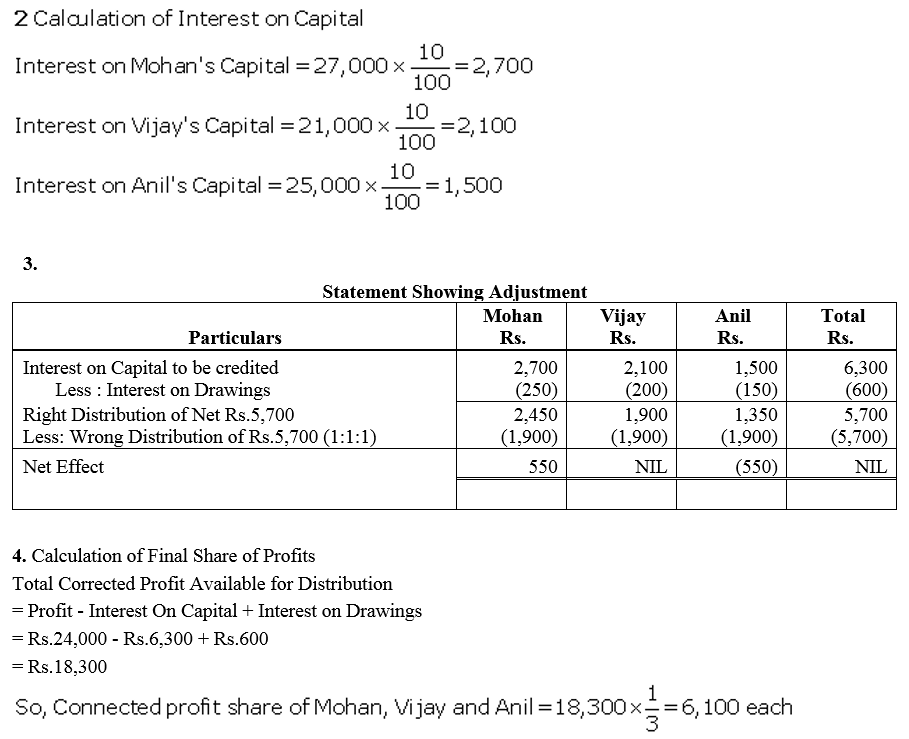
Mohan, Vijay and Anil are partners, the balances of their Capital Accounts being ₹ 30,000, ₹ 25,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively. In arriving at these figures, the profits for the year ended 31st March, 2016, ₹ 24,000 had already been credited to partners in the proportion in which they shared profits. Their drawings were ₹ 5,000 (Mohan), ₹ 4,000 (Anil) during the year. Subsequently, the following omissions were noticed and it was decided to bring them into account:
(a) Interest on capital @ 10% p.a.
(b) Interest on drawings: Mohan ₹ 250, Vijay ₹ 200 and Anil ₹ 150.
Make necessary corrections through a Journal entry and show your workings clearly.
Solution:
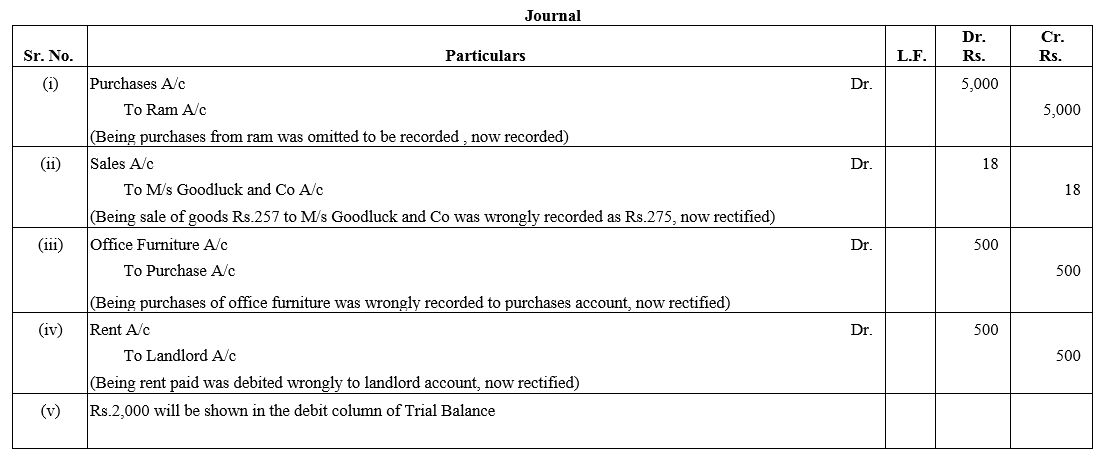
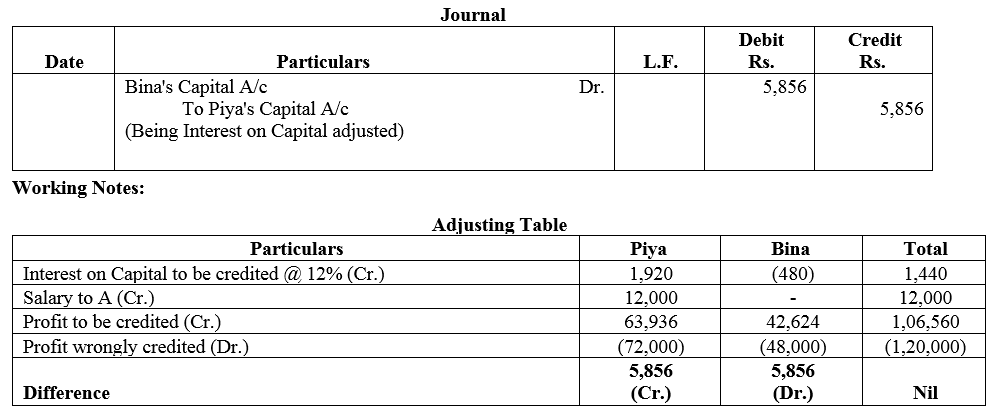
Question 67.
Piya and Bina are partners in a firm sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. Following was the Balance Sheet of the firm as on 31st March, 2016:
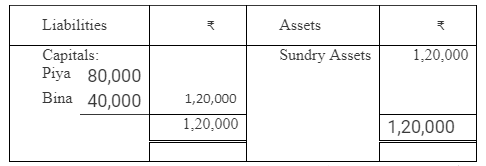
The profits ₹ 30,000 for the year ended 31st March, 2016 were divided between the partners without allowing interest on capital @ 12% p.a. salary to Piya @ ₹ 1,000 per month. During the year Piya withdrew ₹ 8,000 and Bina withdrew ₹ 4,000. Showing your working notes clearly, pass the necessary rectifying entry.
Solution:

Question 68.
The firm of Harry, Porter and Ali, who have been sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1, have existed for same years. Ali wants that he should get equal share in the profits with Harry and Porter and he further wishes that the change in
the profit-sharing ratio should come into effect retrospectively were for the three years. Harry and Porter have agreement on this account. The profits for the last three years were:
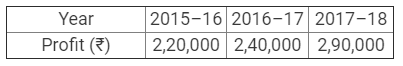
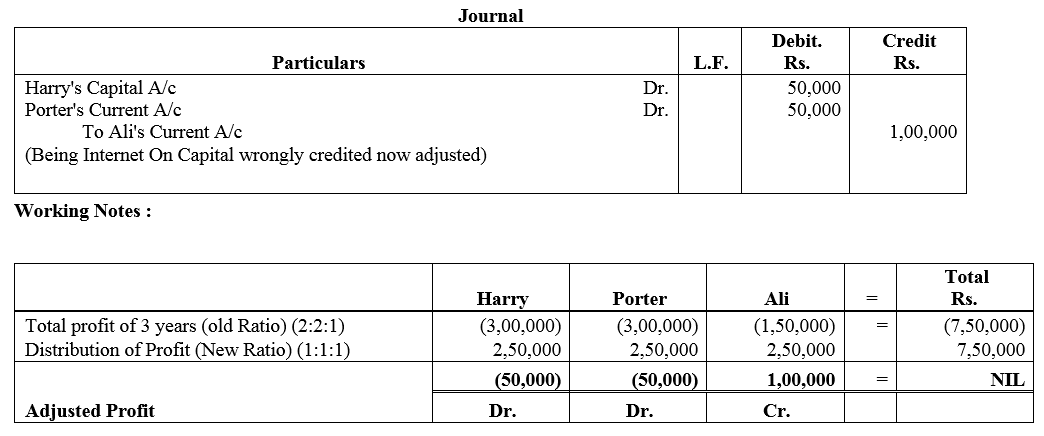
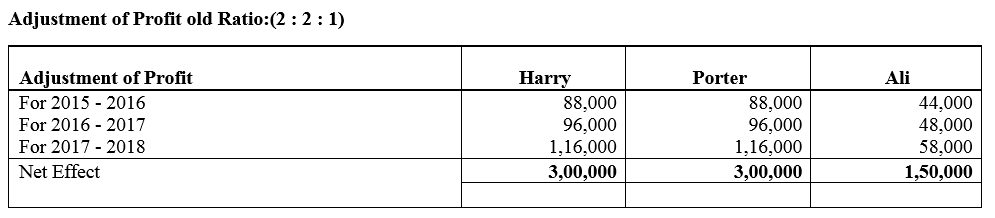
Show adjustment of profits by means of a single adjustment Journal entry.
Solution:
Question 69.
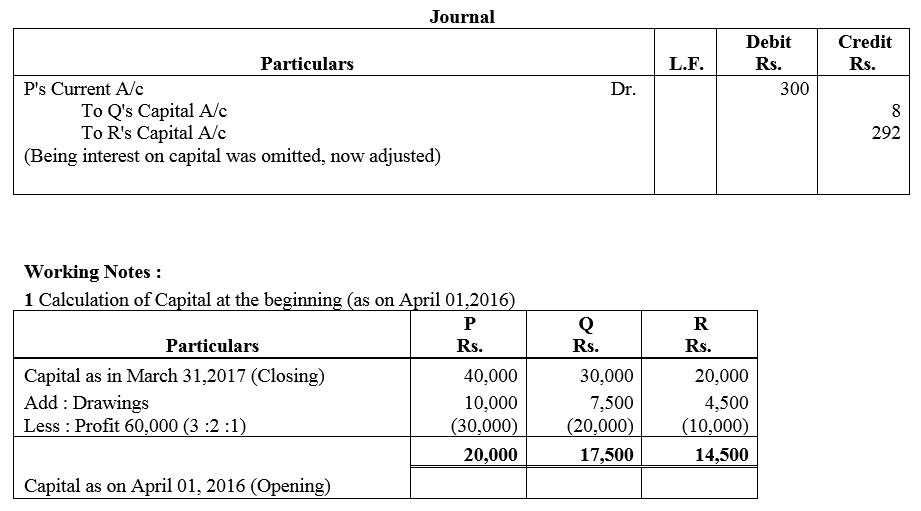
On 31st March, 2018, after the closing of the accounts, the Capital Accounts of P, Q and R stood in the books of the firm at ₹ 40,000; ₹ 30,000 and ₹ 20,000 respectively. Subsequently, it was discovered that interest on capital @ 5% had been omitted. Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 60,000 and the partners drawings had been P ₹ 10,000, Q ₹ 7,500 and R ₹ 4,500. The profit-sharing ratio of P, Q and R is 3 : 2 : 1. Give necessary adjustment entry.
Solution:
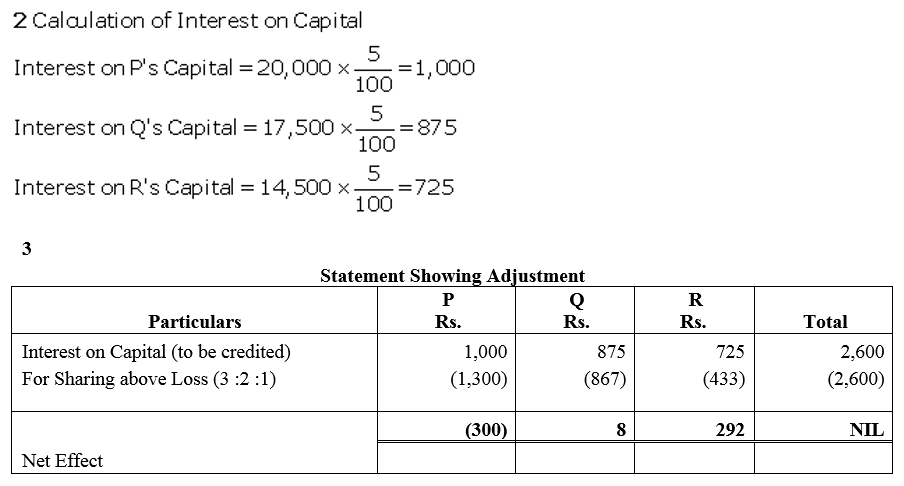
Question 70.
A, B and C were partners. Their capitals were A ₹ 30,000; B ₹ 20,000 and C ₹ 10,000 respectively. According to the Partnership Deed, they were entitled to an interest on capital @ 5% p.a. In addition, B was also entitled to draw a salary of ₹ 500 per month. C was entitled to a commission of 5% on the profits after charging the interest on capital, but before charging the salary payable to B. The net profit for the year were ₹ 30,000 distributed in the ratio of capitals without providing for any of the above adjustments. The profits were to be shared in the ratio of 5 : 3 : 2.
Pass necessary adjustment entry showing the workings clearly.
Solution:
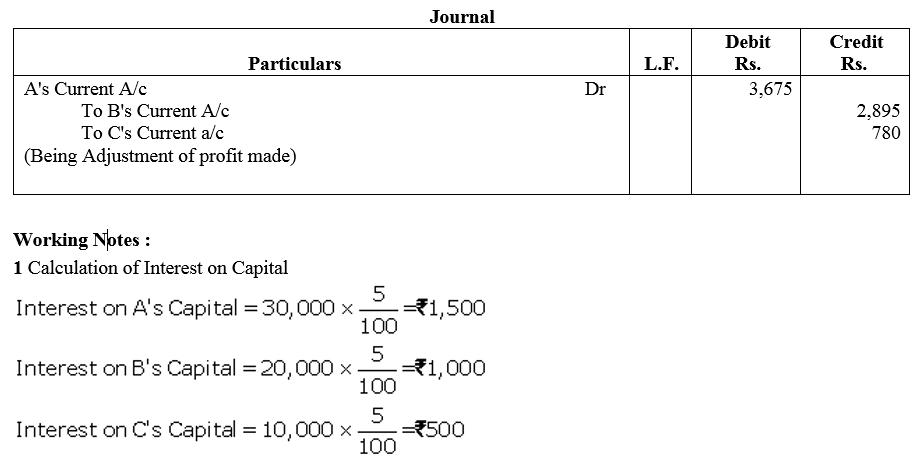
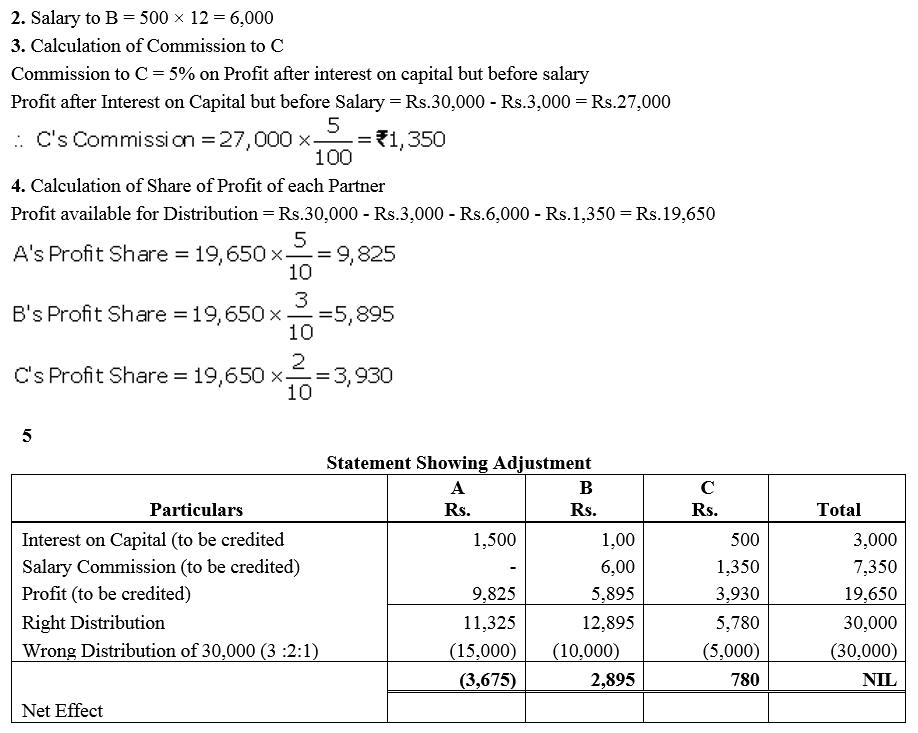
Question 71.
Mannu and shristhi are partners in a firm sharing profit in the ratio of 3 : 2. Following is the balance sheet of the firm as on 31st March 2018:
Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 5,000 which was divided in the agreed ratio, but interest @ 5% p.a. on capital and @ 6% p.a. on drawings was inadvertently enquired. Adjust interest on drawings on an average basis for 6 months. Give the adjustment entry.
Solution:
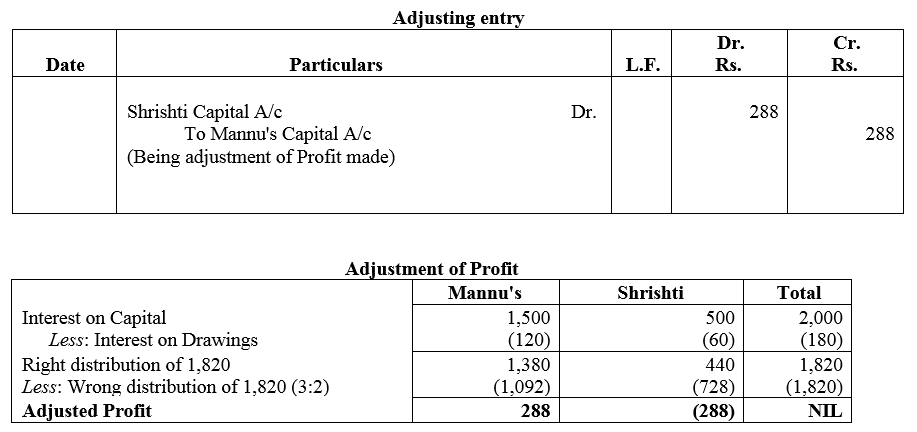
Question 72.
A, B and C are partners in a firm. Net profit of the firm for the year ended 31st march, 2018 is ₹ 30,000, which has been duly distributed among the partners, in their agreed ratio of 3 : 1 : 1 respectively. It is discovered on 10th April, 2018 that the undermentioned transactions were not passed through the books of account of the firm for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
(a) Interest on Capital @ 6% per annum, the capital of A, B and C being ₹ 50,000; ₹ 40,000 and ₹ 30,000 respectively.
(b) Interest on drawings: A ₹ 350; B ₹ 250; C ₹ 150.
(c) Partners’ Salaries: A ₹ 5,000; B ₹ 7,500.
(d) Commission due to A (for some special transaction) ₹ 3,000.
You are required to pass a Journal entry, which will not affect Profit and Loss Account of the firm and rectify the position of partners.
Solution:
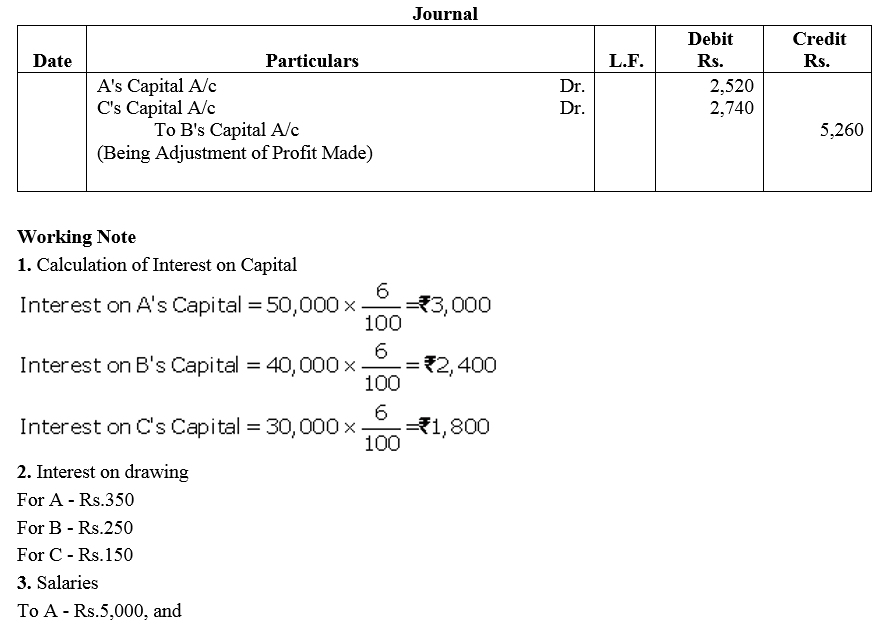
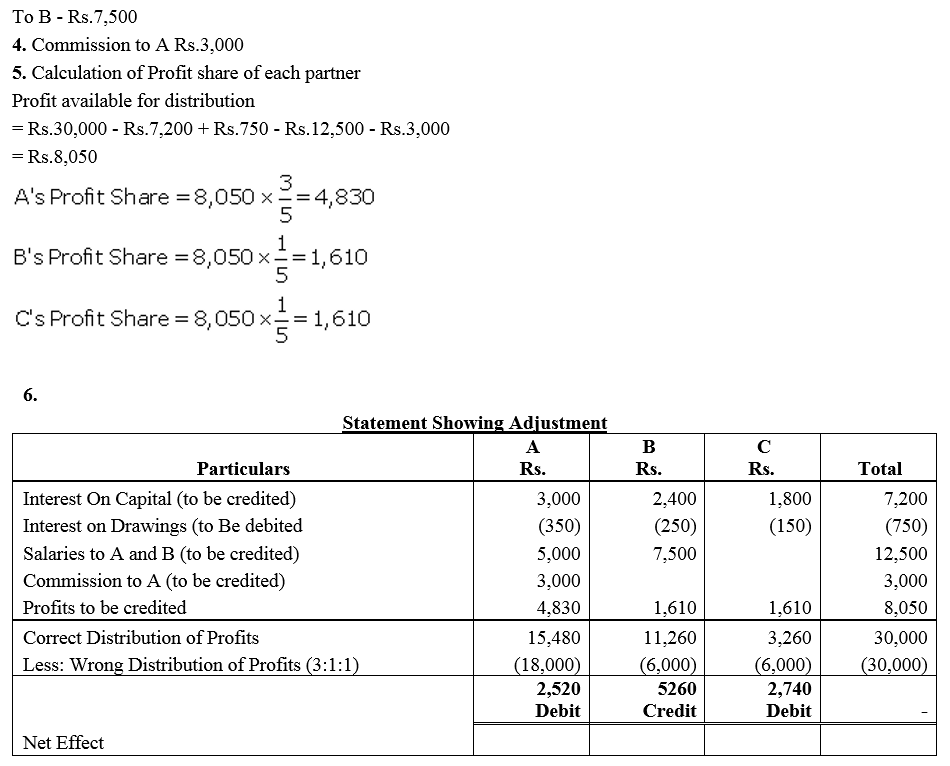
Question 73.
On 31st March, 2014, the balances in the Capital Accounts of Saroj, Mahinder and Umar after making adjustments for profits and drawings, etc., were ₹ 80,000, ₹ 60,000, ₹ 40,000 respectively. Subsequently, it was discovered that the interest on capital and drawings has been omitted.
(a) The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2014 was ₹ 80,000.
(b) During the year Saroj and Mahinder each withdrew a sum of ₹ 24,000 in equal instalments in the end of each month and Umar withdrew ₹ 36,000.
(c) The interest on drawings was to be charged @ 5% p.a. and interest on capital was to be allowed @ 10% p.a.
(d) The profit-sharing ratio among partners was 4 : 3 : 1.
Showing your workings clearly, pass the necessary rectifying entry.
Solution:
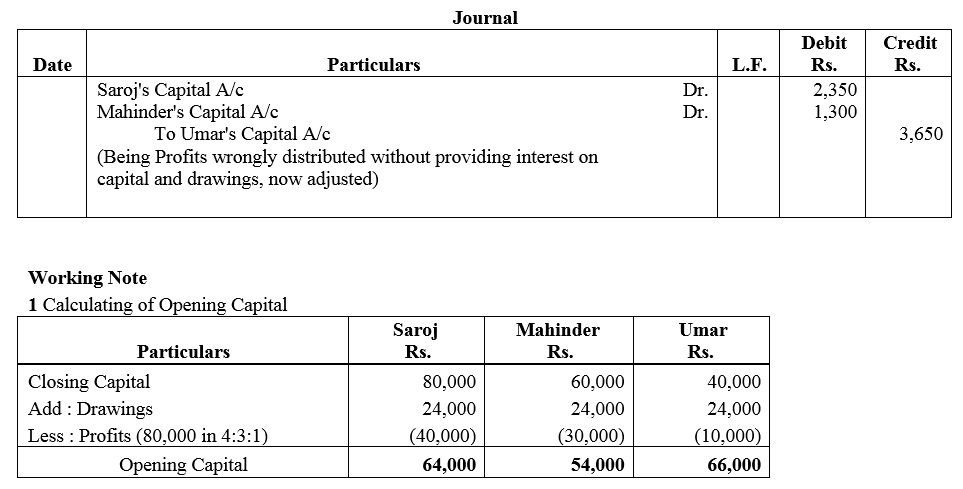
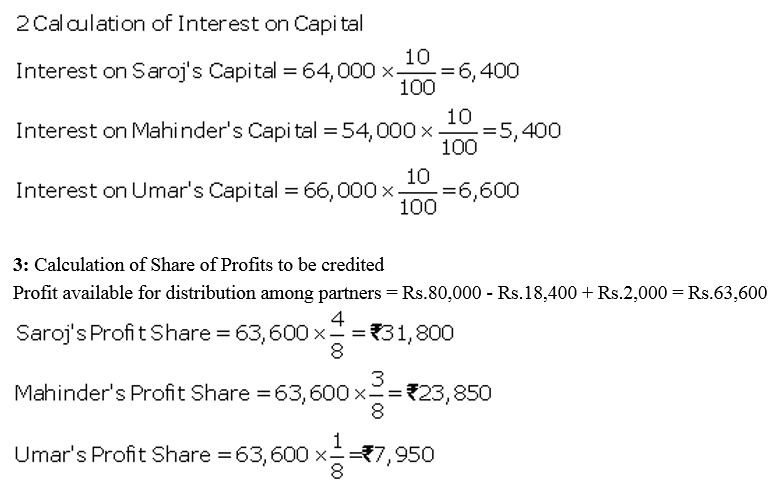
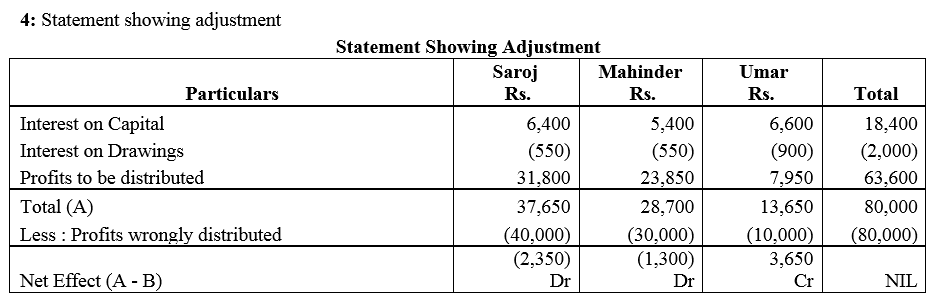
Question 74.
The Capitals of A, B and C as on 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 90,000, ₹ 3,30,000 and ₹ 6,60,000 respectively. The profits amounting ₹ 1,80,000 for the year 2017-18 were distributed in the ratio of 4 : 1 : 1 after allowing interest on Capital @ 10% p.a. During the year, each partner withdrew ₹ 3,60,000. The Partnership Deed was silent as to profit-sharing ratio but provided for interest on capital @ 12%.
Pass the necessary adjustment entry showing the working clearly.
Solution:

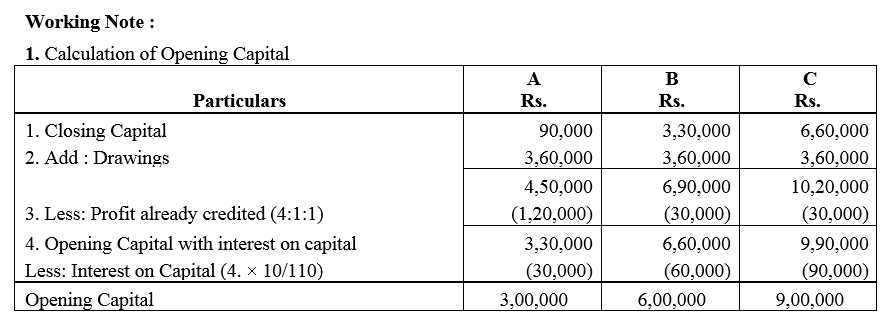
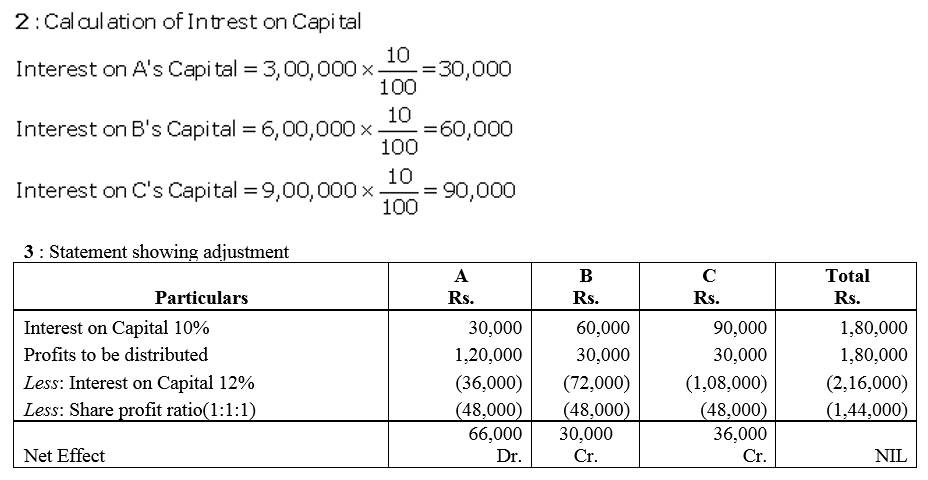
Question 75.
The Capital Accounts of A and B stood at ₹ 4,00,000 and ₹ 3,00,000 respectively after necessary adjustments in respect of the drawings and the net profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018. It was subsequently discovered that 5% p.a. interest on capital and also drawings were not taken into account in arriving at the distributable profit. The drawings of the partners had been: A–₹ 12,000 drawn at the end of each quarter and B–₹ 18,000 drawn at the end of each half year. The profit for the year as adjusted amounted to ₹ 2,00,000. The partners share profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. You are required to pass Journal entries and show adjusted Capital Accounts of the partners.
Solution:
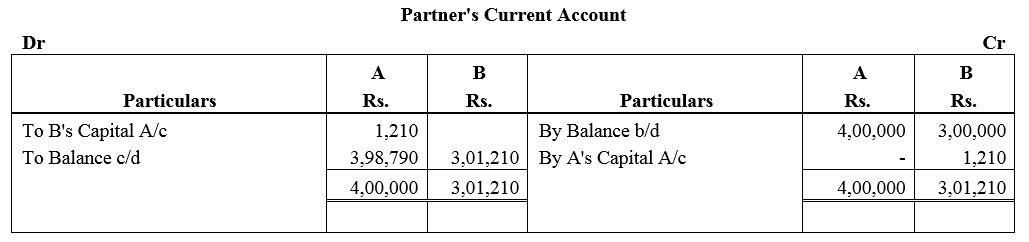
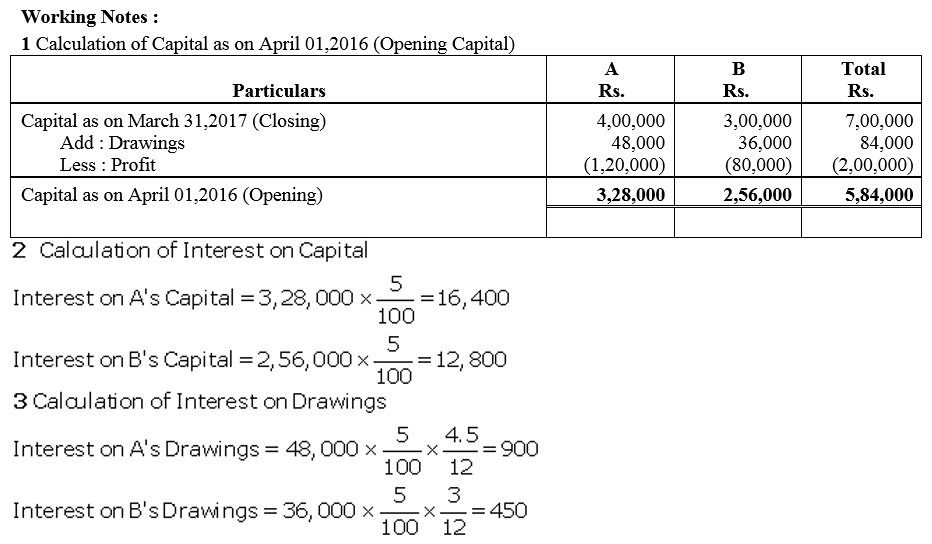
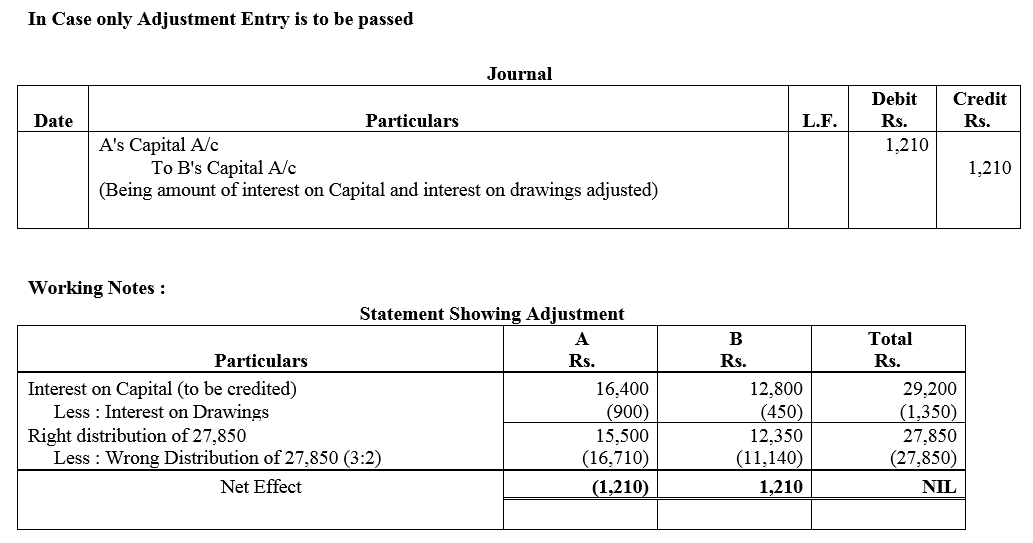
Question 76.
X and Y are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. They employed Z as their Manager to whom they paid a salary of ₹ 7,500 per month. Z had deposited ₹ 2,00,000 on which interest was payable ₹ 9% p.a. At the end off the accounting year (i.e., 31st March, 2018) 2017-18 (after division of the year’s profits), it was decided that Z should be treated as a partner with effect from 1st April, 2014 with 1/6th share of profits, his deposit being considered as capital carrying interest @ 6% p.a. like capitals of other partners. The firm’s profits and losses after allowing interest on capitals were 2014-15:
Profit ₹ 5,90,000; 2015-16: Profit ₹ 6,26,000; 2016-17: Loss ₹ 40,000 and 2017-18: Profit ₹ 7,80,000.
Record necessary Journal entries to give effect to the above.
Solution:
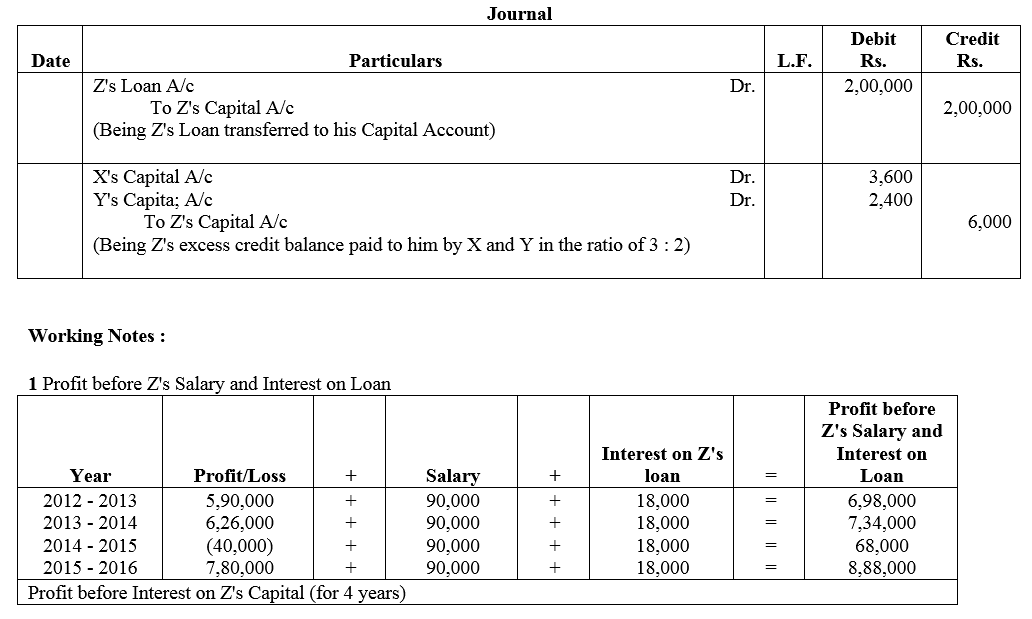
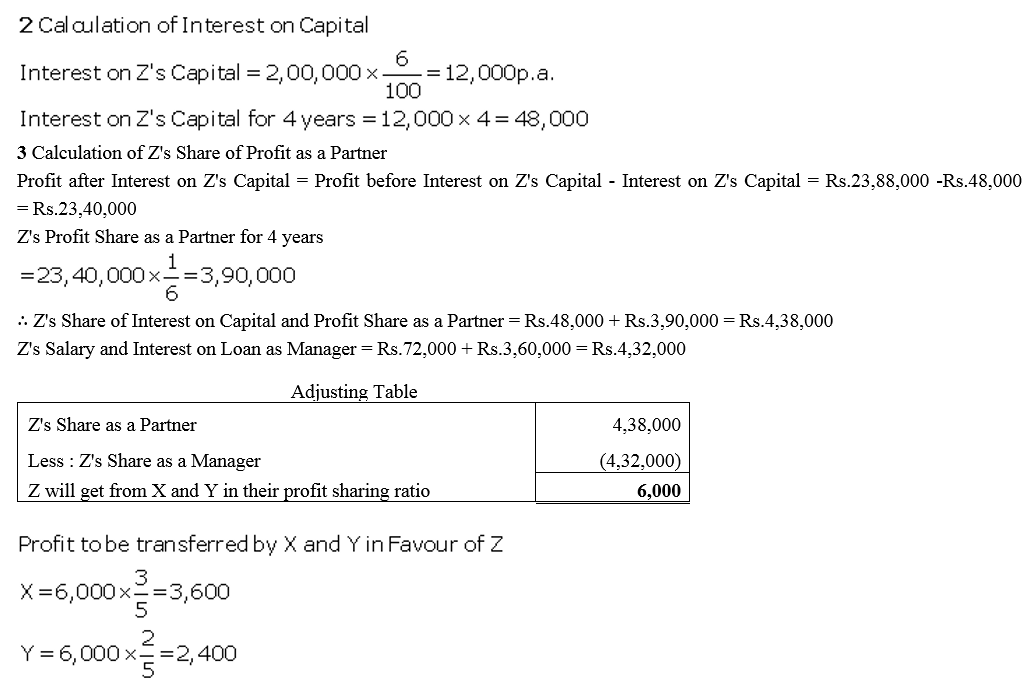
Question 77.
A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 2 : 1. They decided to admit C, their manager, as a partner form 1st April, 2017, giving him 1/5th share of profit. C, while a manager, was getting a salary of ₹ 50,000 p.a. plus a commission of 10% of the net profit after charging such salary and commission. It was also agreed that any excess amount which C receives as a partner (over his salary and commission) will be borne by A. Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 6,44,000, before payment of salary and commission. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
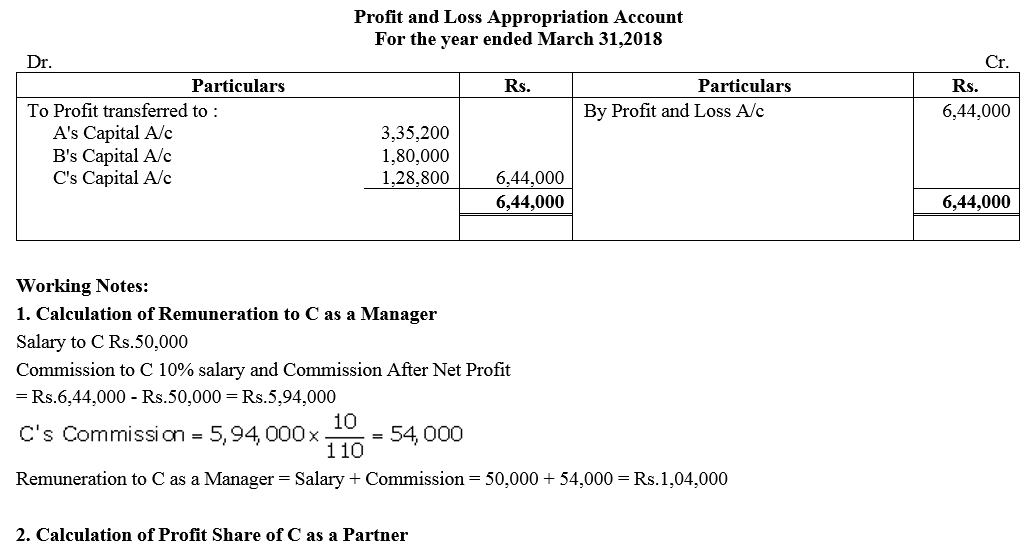

Question 78.
X and Y are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. The have a manager, Z, who gets ₹ 10,000 p.m. salary plus commission of 5% of the profit after charging his salary and commission, Now, they decide to admit Z as a partner, giving him 1/5th share in the profits of the firm. Any excess amount which Z receives as a partner (over his salary and commission) will be borne by X. The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 8,40,000 after charging Z’s salary. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account showing the division of profit for the year.
Solution:
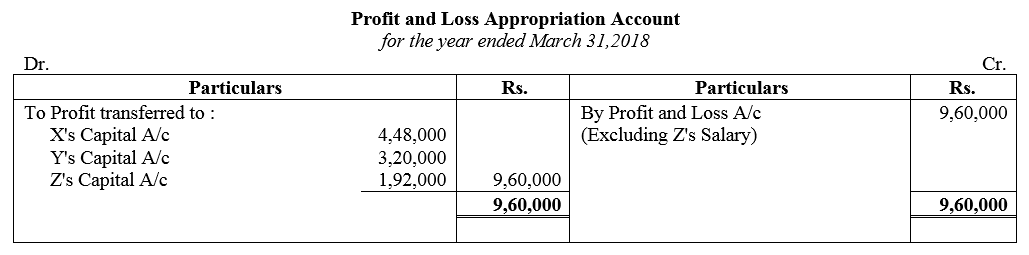
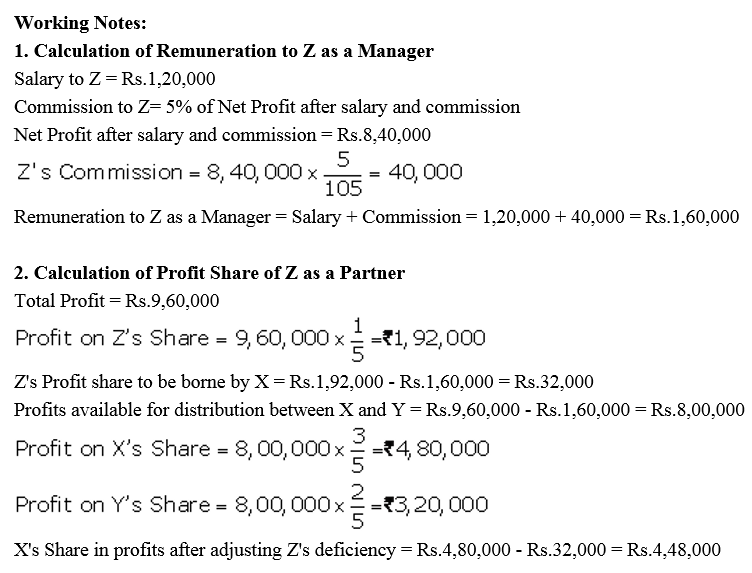
Question 79.
A, B and C were in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 2 : 1 respectively. It was provided that C’s share in profit for a year would not be less then ₹ 7,500. The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 31,500. You are required to show the appropriation among the partners. The profit and Loss Appropriation Account is not required.
Solution:
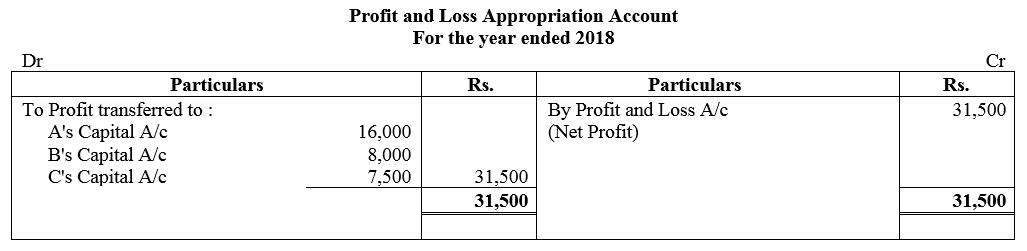

Question 80.
A and B are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. C was admitted for 1/6th share of profit with a minimum guaranteed amount of ₹ 10,000. At the close of the first financial year the firm earned a profit of ₹ 54,000. Find out the share of profit which A, B and C will get.
Solution:
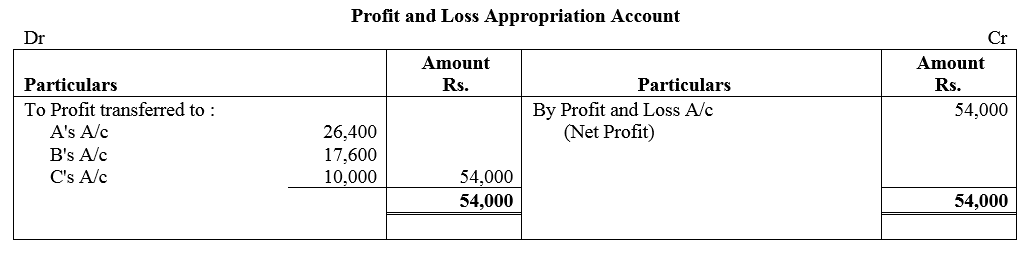

Question 81.
X, Y and Z entered into partnership on 1st October, 2017 to share profits and losses in the ratio of 4 : 3 : 3. X, personally guaranteed that Z’s share of profit after charging interest on capital @ 10% p.a. would not be less then ₹ 80,000 in any year. The capital contributions were: X ₹ 3,00,000, Y ₹ 2,00,000 and Z ₹ 1,50,000.
The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 1,60,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
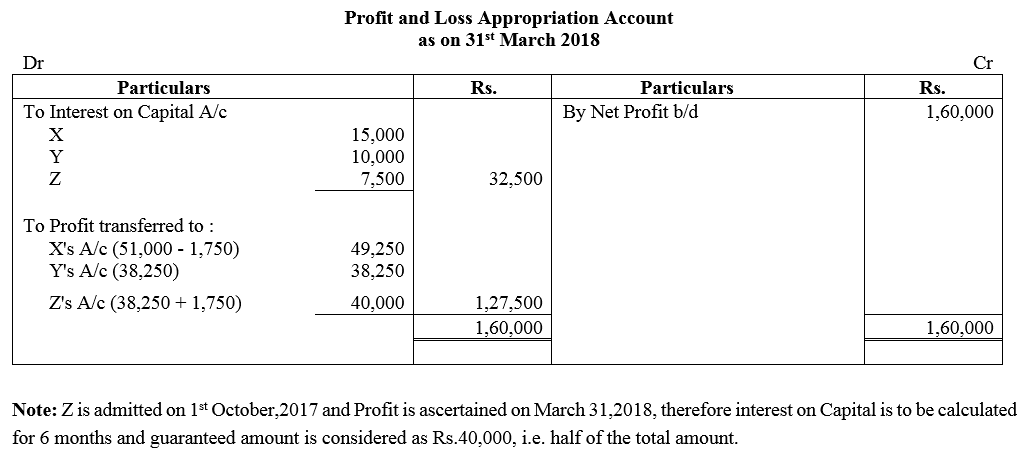
Question 82.
A, B and C are partners in a firm. Their profit-sharing ratio is 2 : 2 : 1. C is guaranteed a minimum amount of ₹ 10,000 as share of profit every year. Any deficiency arising on that amount shall be met by B. The profits for the two years ended 31st March, 2017 and 2018 were ₹ 40,000 and ₹ 60,000 respectively. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the two years.
Solution:
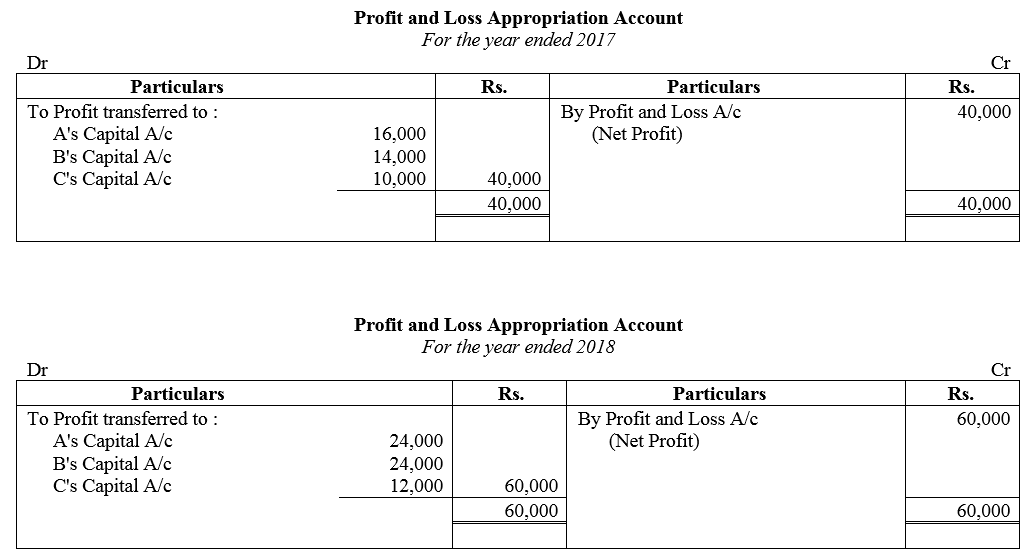
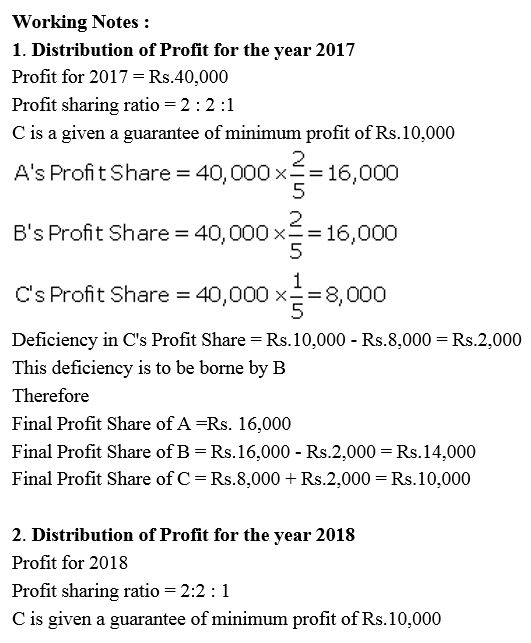
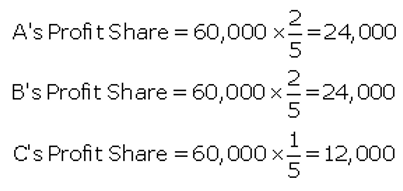
Question 83.
A, B and C are partners sharing profits in the ratio of 5 : 4 : 1. C is given a guarantee that his minimum share of profit in any given year would be at least ₹ 5,000. Deficiency, if any, would be borne by A and B equally. The profit for the year 2017-18 amounted to ₹ 40,000.
Pass necessary Journal entries in the books of the firm.
Solution:
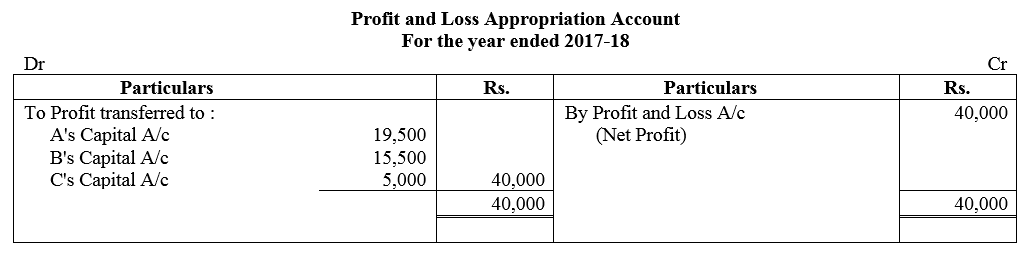
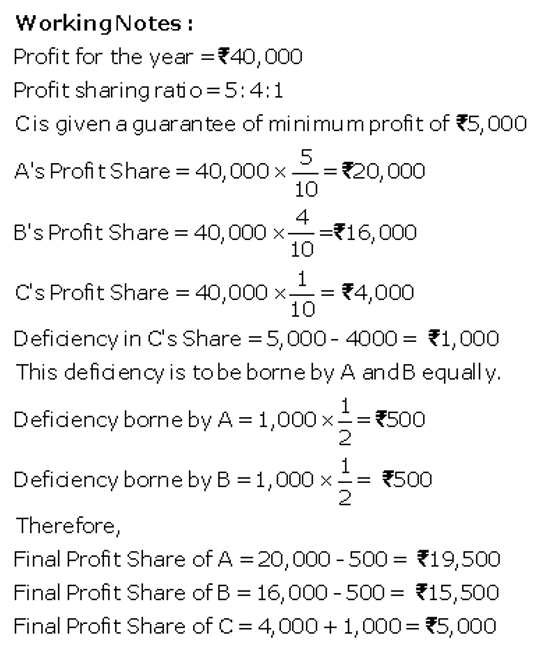
Question 84.
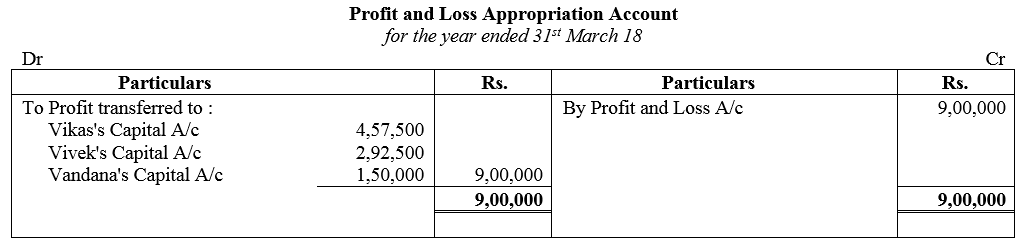
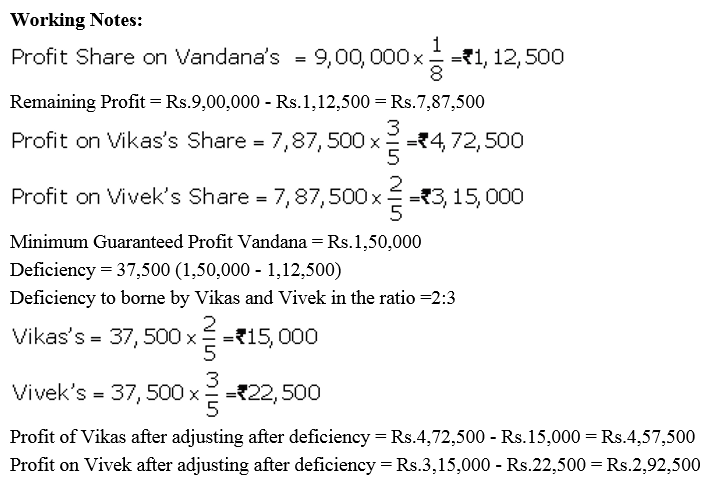
Vikas and Vivek were partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2. On 1st April, 2017, they admitted Vandana as a new partner for 1/8th share in the profits with a guaranteed profit of ₹ 1,50,000. The new profit-sharing ratio between Vikas and Vivek will remain same but they decided to bear any deficiency on account of guarantee to Vandana in the ratio 3 : 2. The profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March, 2018 was ₹ 9,00,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account of Vikas, Vivek and Vandana for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
Question 85.
Pranshu and Himanshu are partners sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2 respectively. They admit Anshu as partner with 1/6 share in the profits of the firm. Pranshu personally guaranteed that Anshu’s share of profit would not be less than ₹ 30,000 in any year. The net profit of the firm for the ear ending 31st March, 2013 was ₹ 90,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Solution:
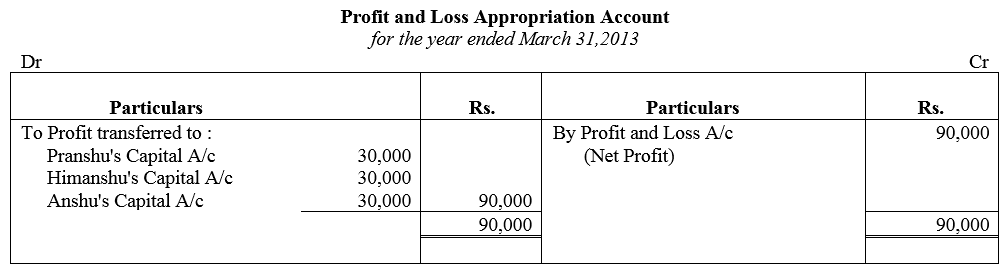

Question 86.
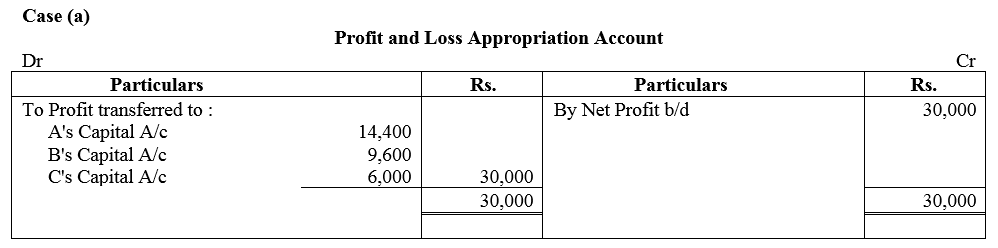
A, B and C are partners in a firm sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1. They earned a profit of ₹ 30,000 during 2017-18. Distribute profit among A, B and C if:
(a) C’s share of profit is guaranteed to be ₹ 6,000 Minimum.
(b) Minimum profit payable to C amounting to ₹ 6,000 is guaranteed by A.
(c) Guaranteed minimum profit of ₹ 6,000 payable to C is guaranteed by B.
(d) Any deficiency after making payment of guaranteed ₹ 6,000 will be borne by A and B in the ratio of 3 : 1.
Solution:

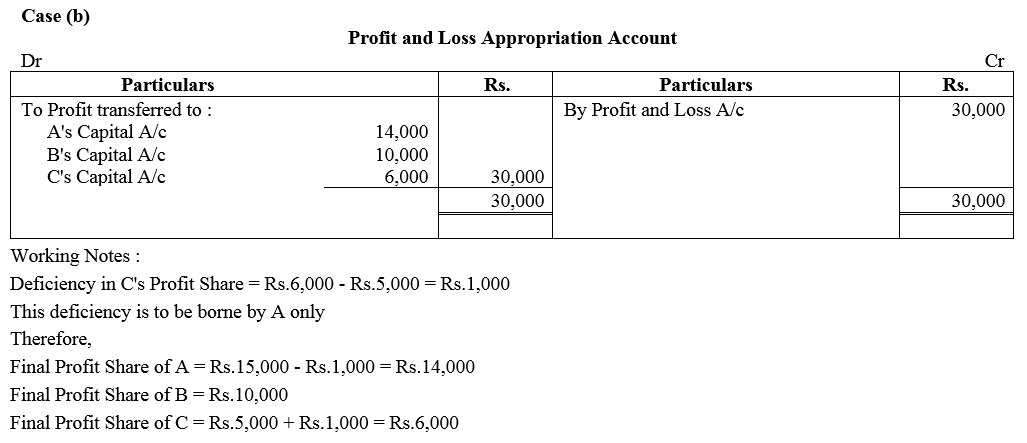
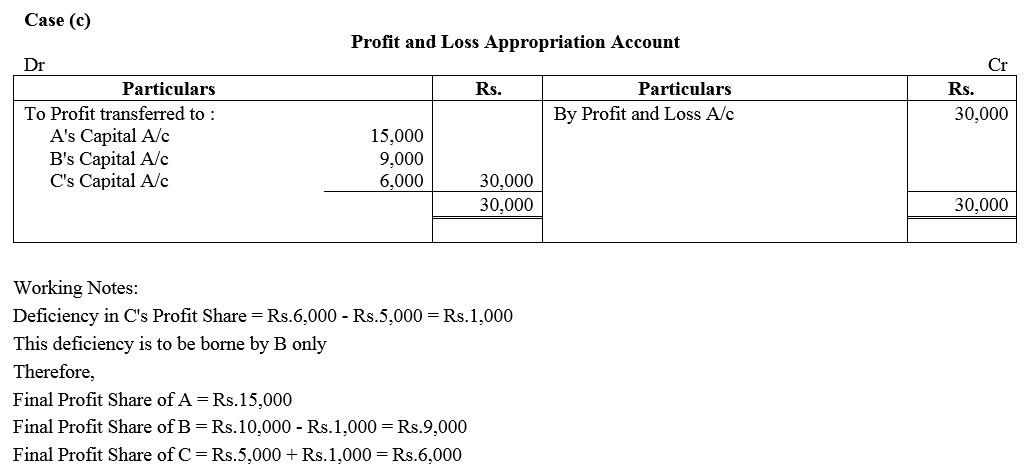
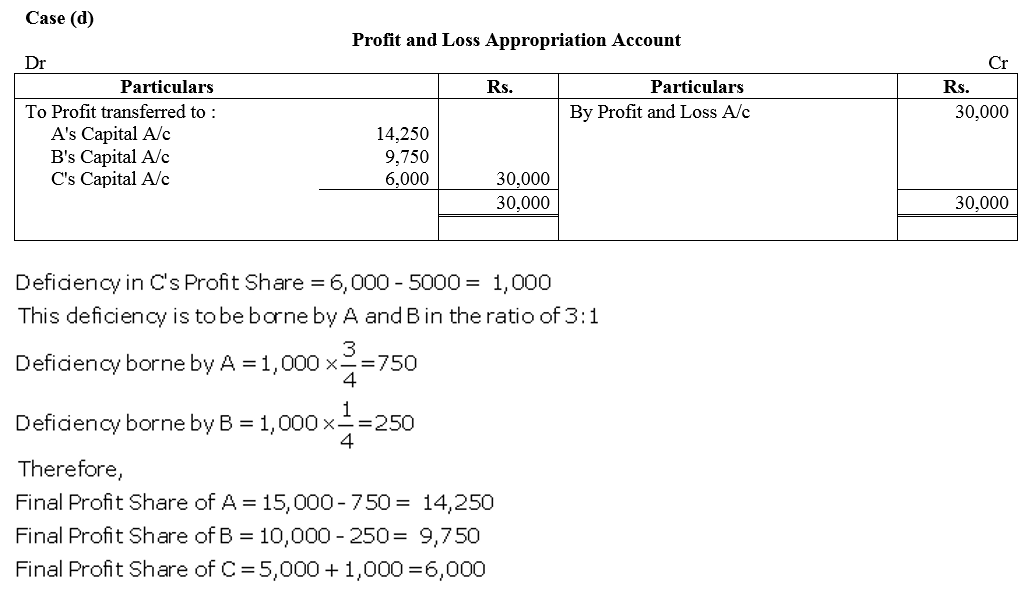
Question 87.
A and B are in partnership sharing profits and losses in the ratio of 3 : 2. They decided to admit C, their Manager, as a partner with effect from 1st April, 2017, giving him 1/4th share of profits.
C, while a Manager, was in receipt of a salary of ₹ 27,000 p.a. and a commission of 10% of the net profits after charging such salary and commission.
In terms of the Partnership Deed, and excess amount, which C will be entitled to receive as a partner over the amount which would have been due to him if he continued to be the manager, would have to be personally borne by A out of his share of profit. Profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 2,25,000. You are required to show Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31at March, 2018.
Solution:
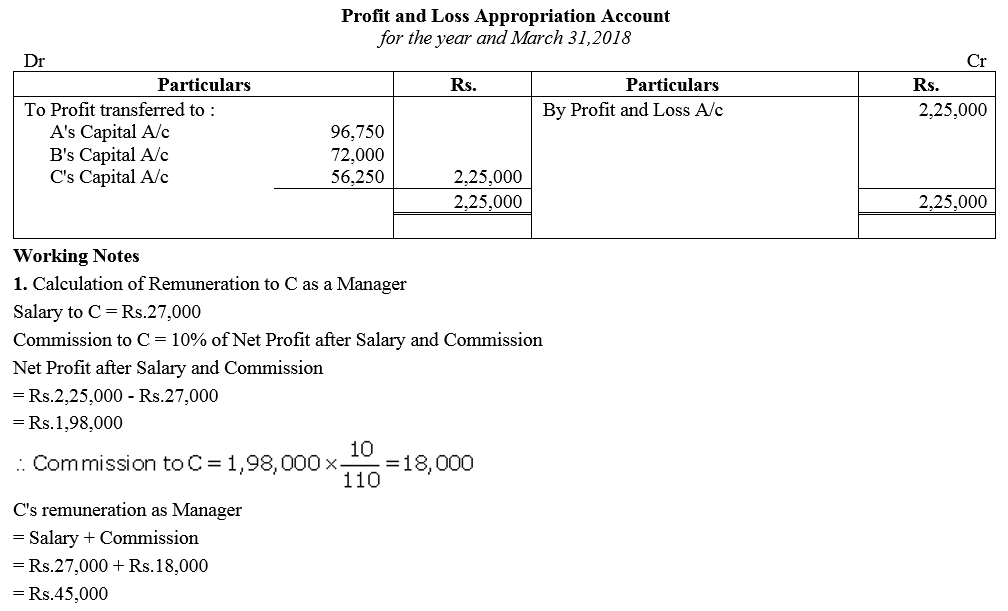
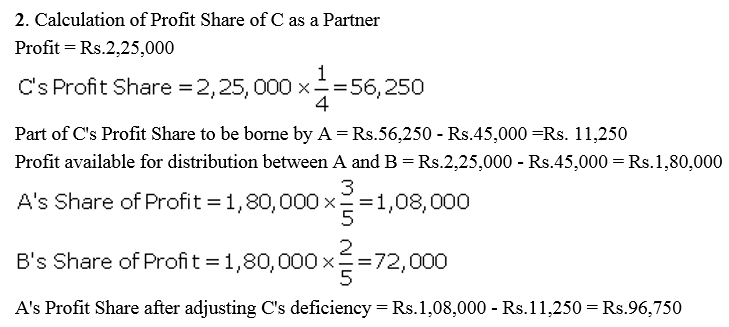
Question 88.
Asgar, Chaman and Dholu are partners in a firm. Their Capital Accounts stood at ₹ 6,00,000; ₹ 5,00,000 and ₹ 4,00,000 respectively on 1st April, 2017. They shared Profits and Losses in the proportion of 4 : 2 : 3. Partners are entitled to interest on capital @ 8% per annum and salary to Chaman and Dholu @ ₹ 7,000 per month and ₹ 10,000 per quarter respectively as per the provision of the Partnership Deed. Sholu’s share of profit ( excluding interest on capital but including salary) is guaranteed at a minimum of ₹ 1,10,000 p.a. Any deficiency arising on that account shall be met by Asgar. The profit for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 4,24,000.
Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
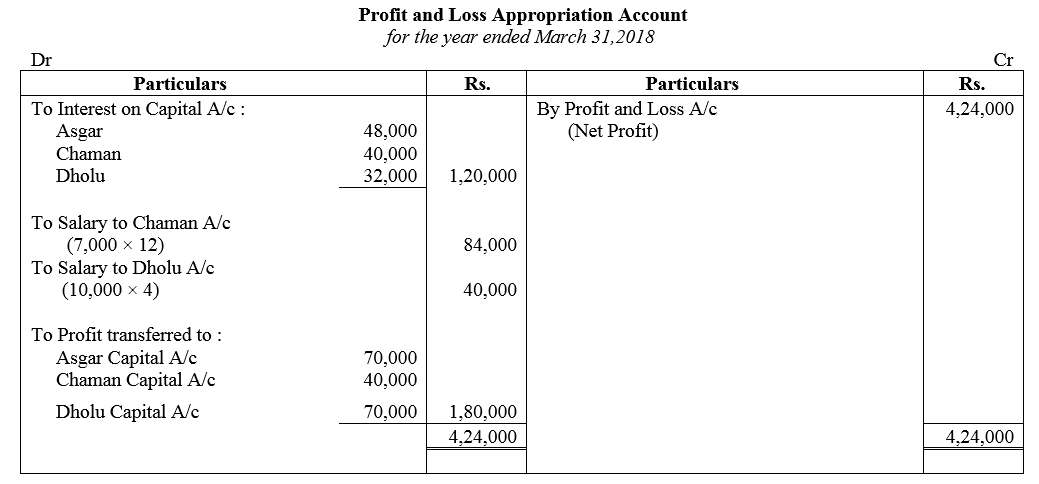
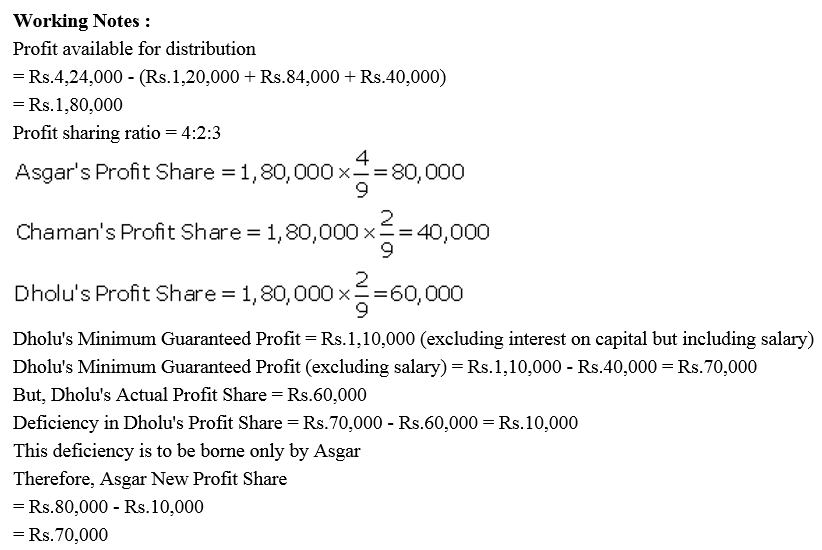
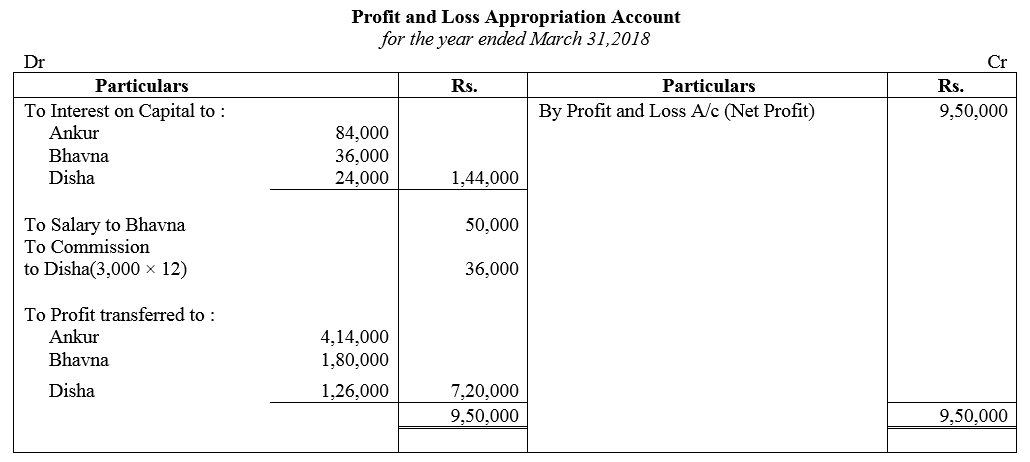
Question 89.
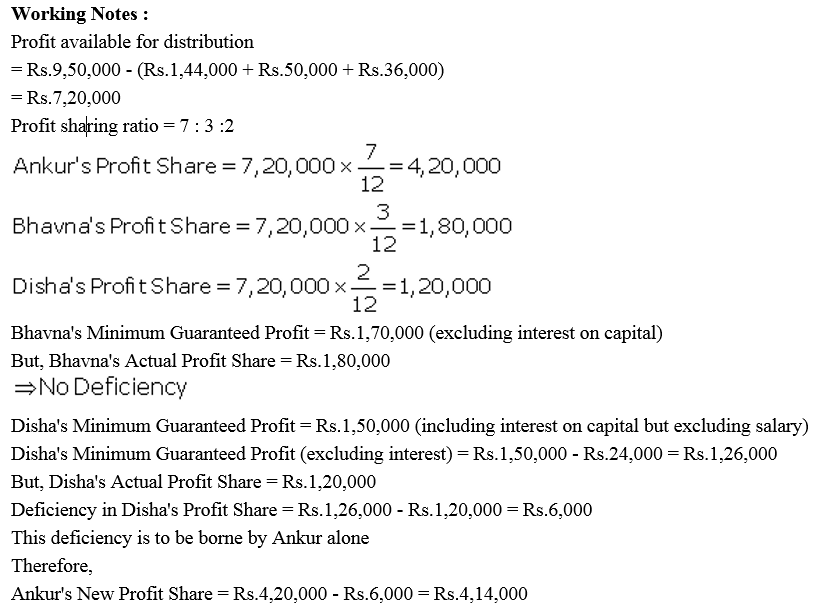
Ankur, Bhavns and Disha are partners in a firm. On 1st April, 2017, the balance in their Capital Accounts stood at ₹ 14,00,000, ₹ 6,00,000 and ₹ 4,00,000 respectively. They shared profits in the proportion of 7 : 3 : 2 respectively. Partners are entitled to interest on capital @ 6% per annum and salary to Bhavna @ ₹ 50,000 p.a. and a commission of ₹ 3,000 per month to Disha as per the provisions of the partnership Deed. Bhavna’s share of profit (excluding interest on capital) is guaranteed at not less than ₹ 1,70,000 p.a. Disha’s share of profit (including interest on capital but excluding commission) is guaranteed at not less than ₹ 1,50,000 p.a. Any deficiency arising on that account shall be met by Ankur. The profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March, 2018 amounted to ₹ 9,50,000. Prepare Profit and Loss Appropriation Account for the year ended 31st March, 2018.
Solution:
Question 90.
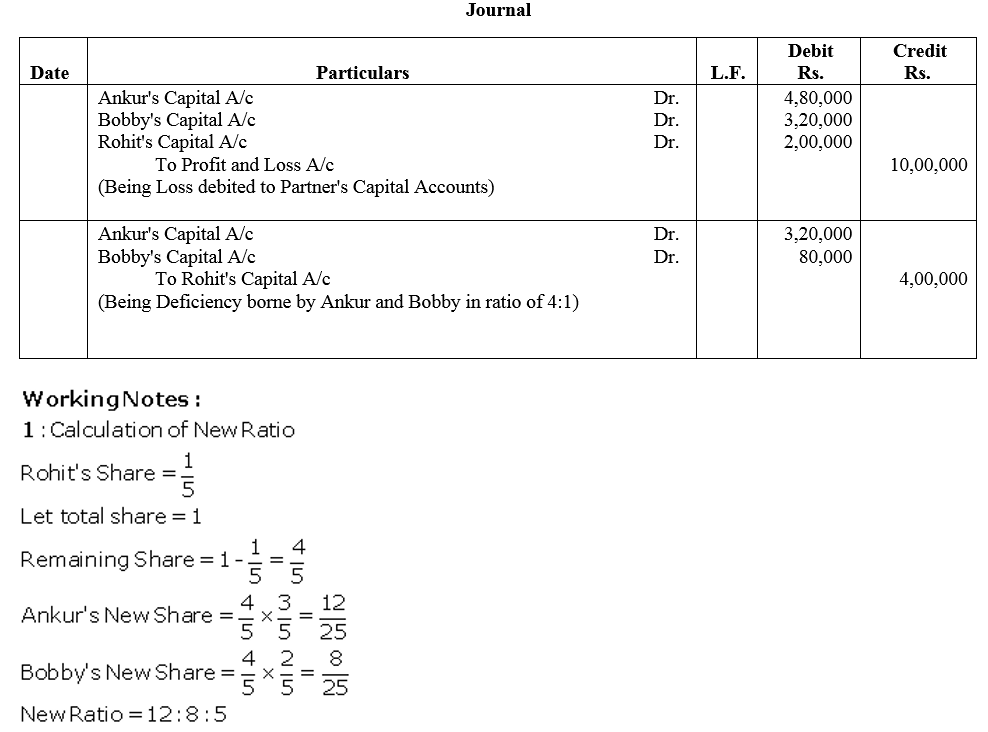
Ankur and Bobby were into the business of providing software solutions in India. They were sharing profits and losses in the ratio 3 : 2. They admitted Rohit for a 1/5 share in the firm. Rohit, an alumni or IIT, Chennai would help them to expand their business to various South African countries where he had been working earlier. Rohit is guaranteed a minimum profit of ₹ 2,00,000 for the year. Any deficiency in Rohit’s share is to be borne by Ankur and Bobby in the ratio 4 : 1. Loss for the year was ₹ 10,00,000. Pass the necessary Journal entries.
Solution:
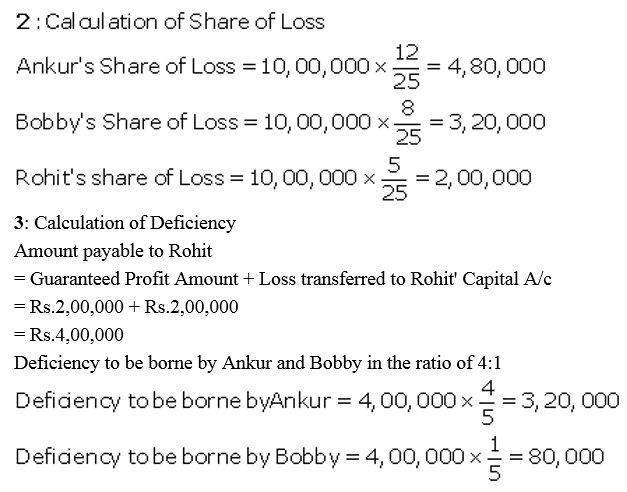
Question 91.
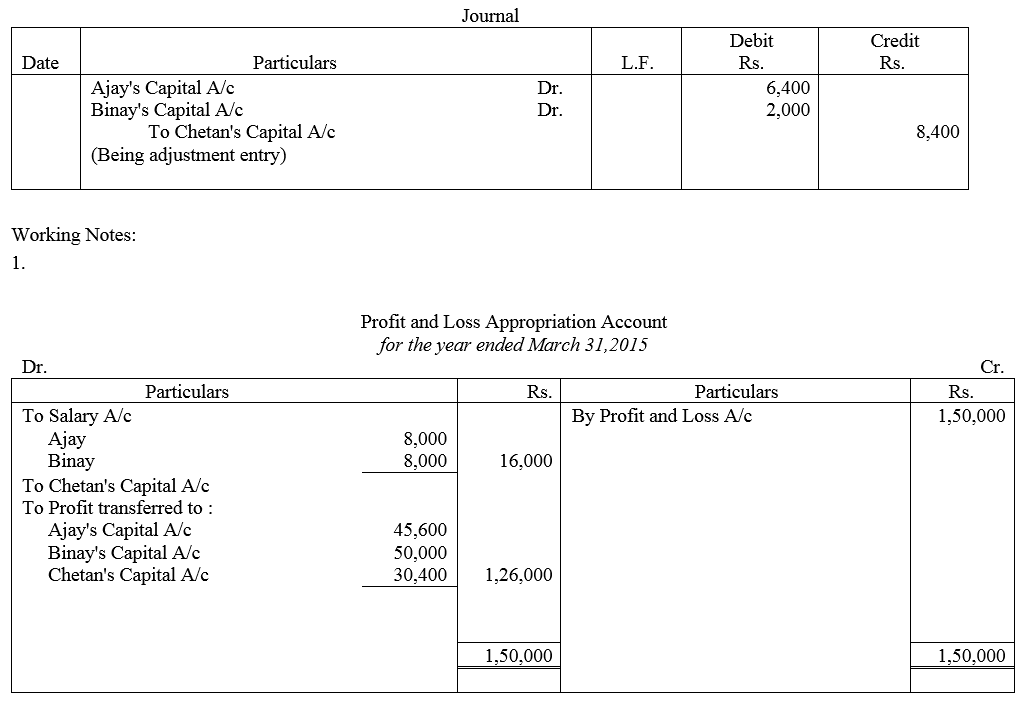
Ajay, Binay and Chetan were partners sharing profits in the ratio of 3 : 3 : 2. The Partnership Deed provided for the following:
(i) Salary of ₹ 2,000 per quarter to Ajay and Binay.
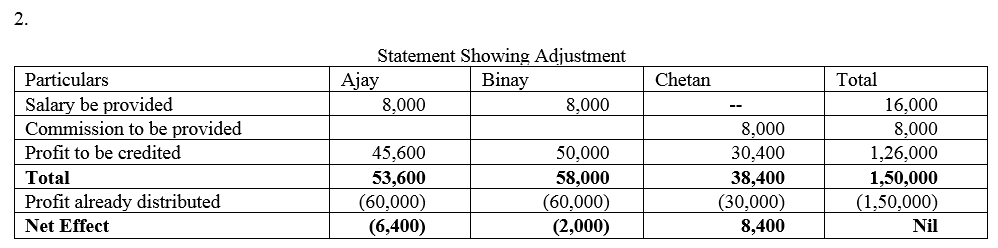
(ii) Chetan was entitled to a commission of ₹ 8,000.
(iii) Binay was guaranteed a rofit of ₹ 50,000 p.a.
The profit of the firm for the year ended 31st March, 2015 was ₹ 1,50,000 which was distributed among Ajay, Binay and Chetan in the ratio of 2 : 2 : 1, without taking into consideration the provisions of Partnership Deed. Pass necessary rectifying entry for the above adjustments in the books of the firm. Show your workings clearly.
Solution:
Question 92.
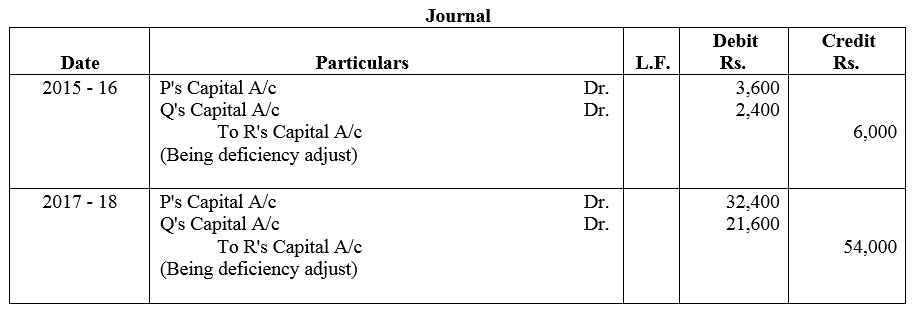
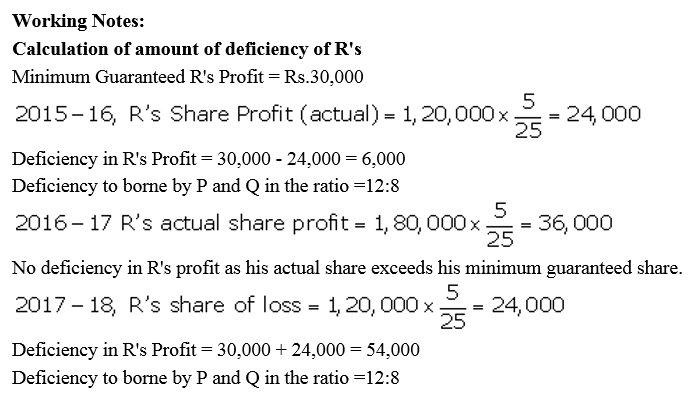
P, Q and R entered into partnership on 1st April, 2015 to share profits and losses in the ratio of 12 : 8 : 5. It was provided that in no case R’s share in profit be less then ₹ 30,000 p.a. The profits and losses for the period ended 31st March were: 2015-16 Profit ₹ 1,20,000 2016-17 Profit ₹ 1,80,000; 2017-18 Loss ₹ 1,20,000.
Pass the necessary Journal entries in the books of the firm.
Solution:
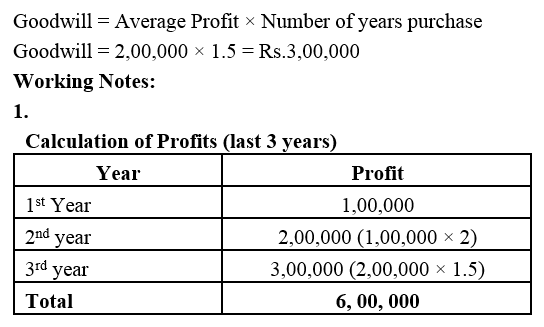
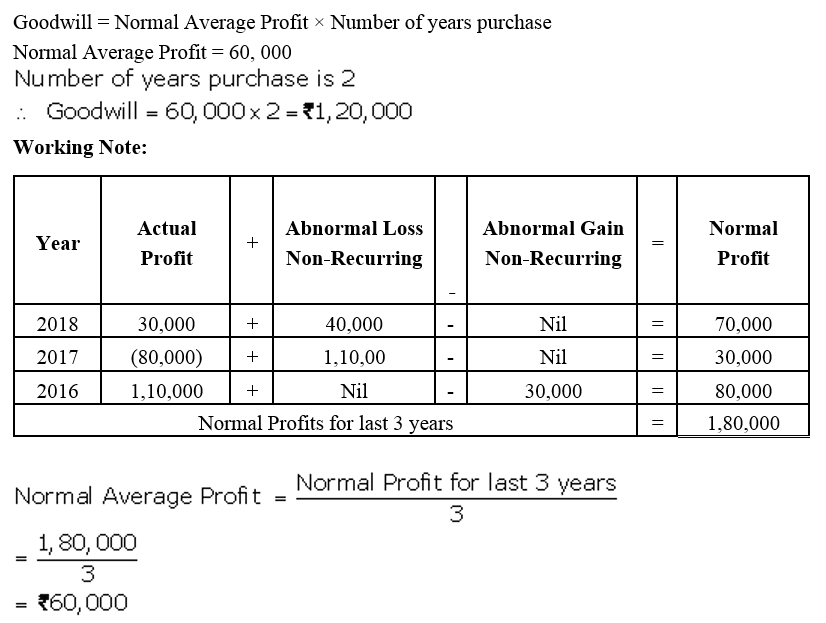
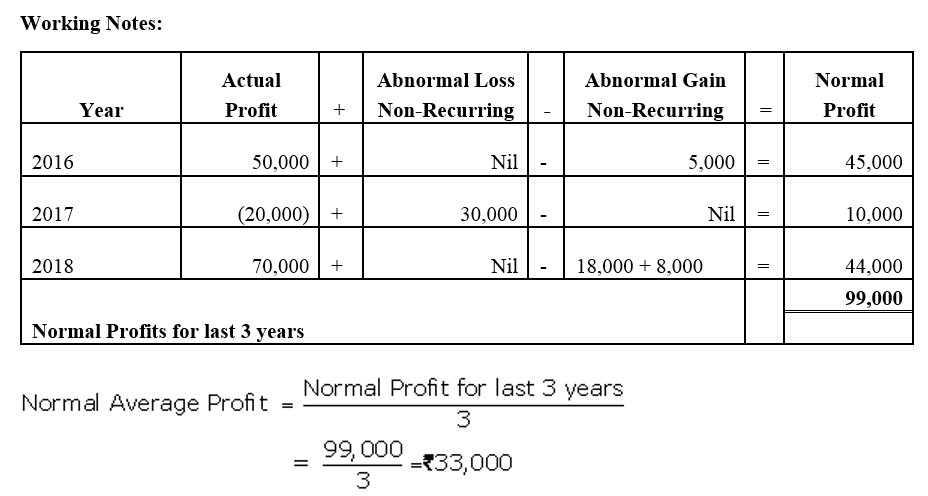
 ]
]
Question 93.
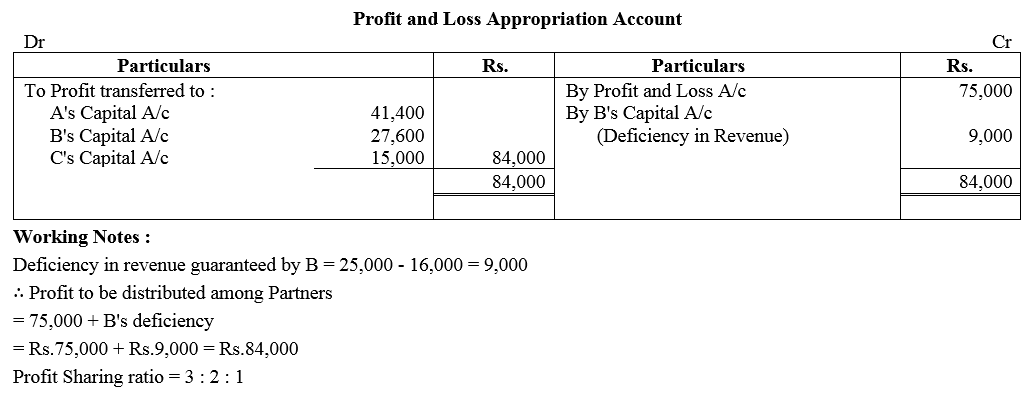
Three Chartered Accountants A, B and C form a partnership, profits being shared in the ratio of 3 : 2 : 1 subject to the following:
(a) C’s share of profit guaranteed to be not less than ₹ 15,000 p.a.
(b) B gives a guarantee to the effect that gross fee earned by him for the firm shall be equal to his average gross fee of the preceeding five years when he was carrying on profession alone, which on an average works out at ₹ 25,000.
The profit for the first year of the partnership are ₹ 75,000. The gross fee earned by B for the firm is ₹ 16,000. You are required to show Profit and Loss Appropriation Account after giving effect to the above.
Solution:

We hope the TS Grewal Accountancy Class 12 Solutions Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals help you. If you have any query regarding TS Grewal Accountancy Class 12 Solutions Chapter 1 Accounting for Partnership Firms – Fundamentals, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.
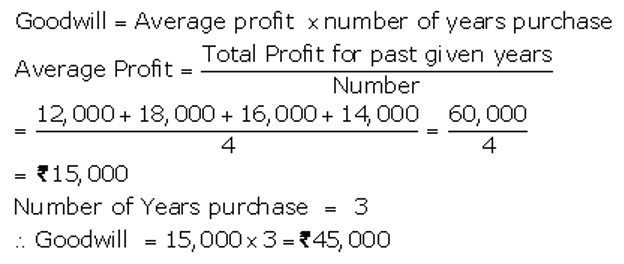
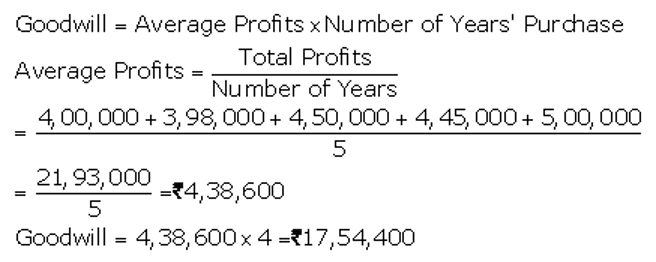
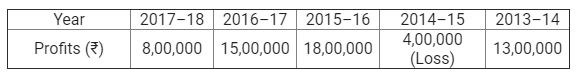
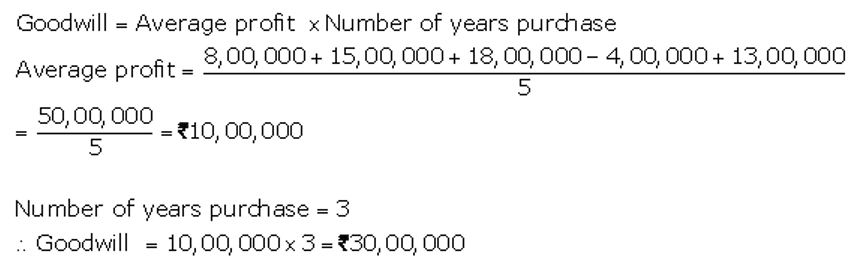

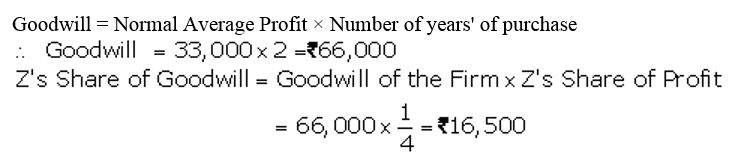
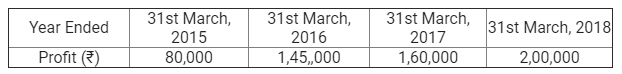
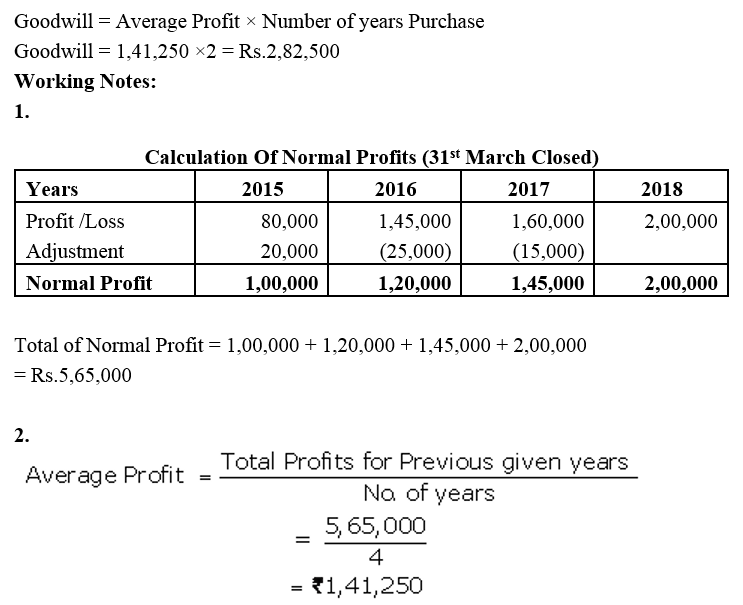
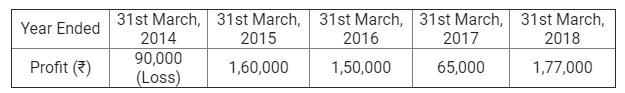
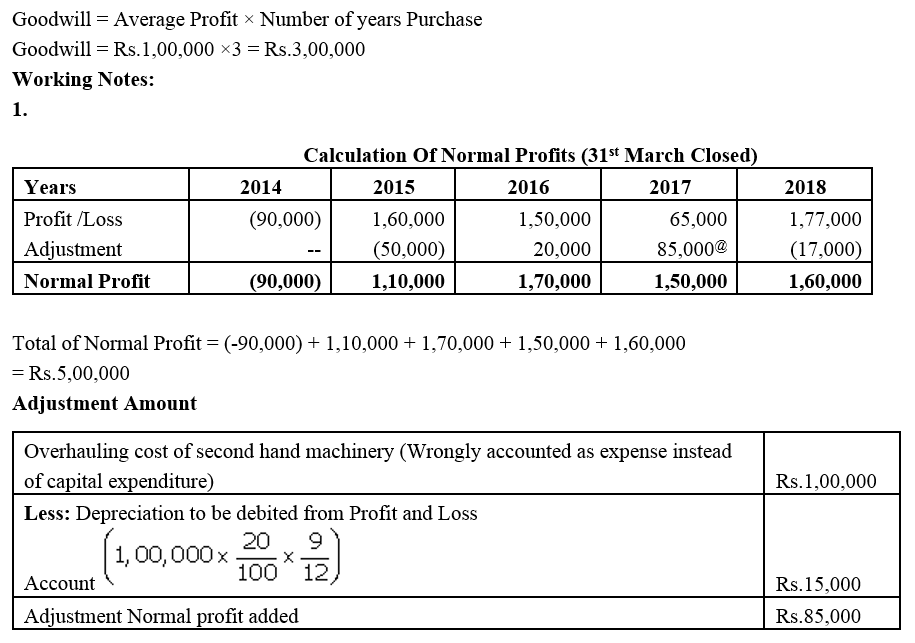
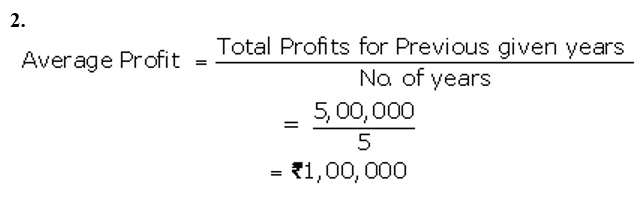
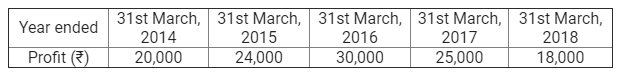
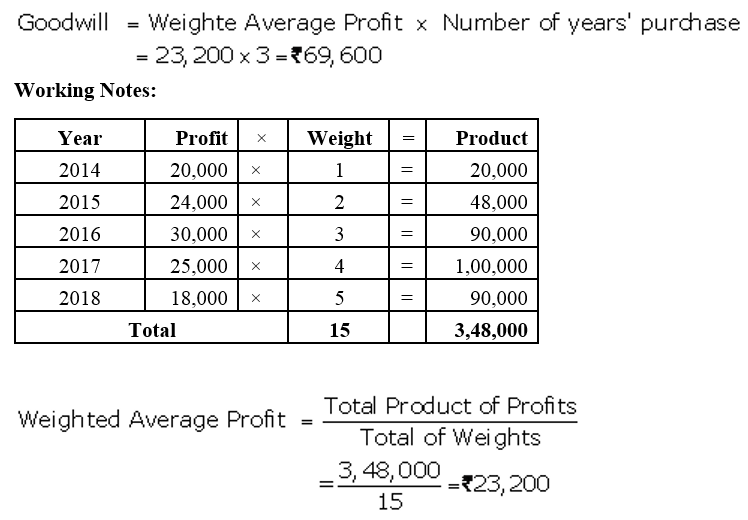
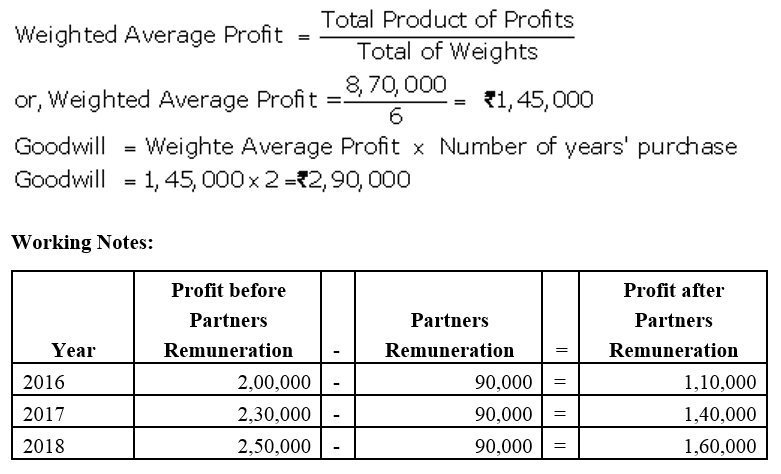
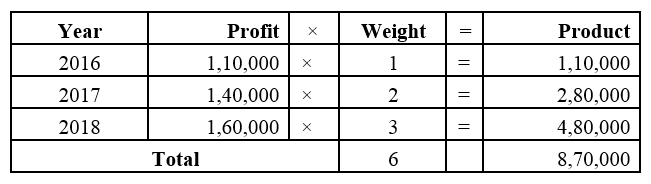
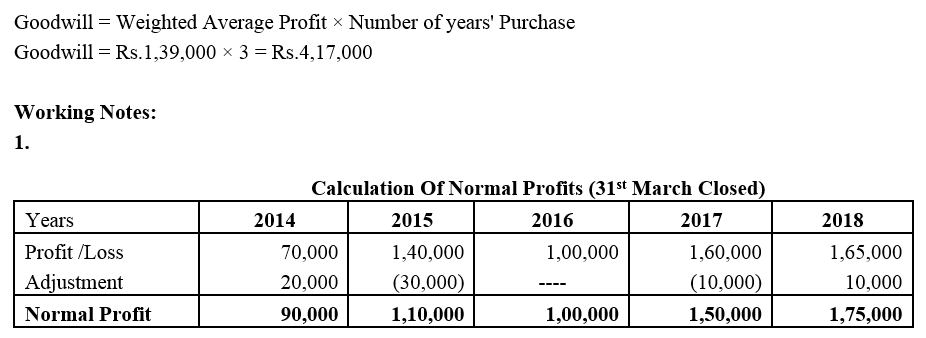
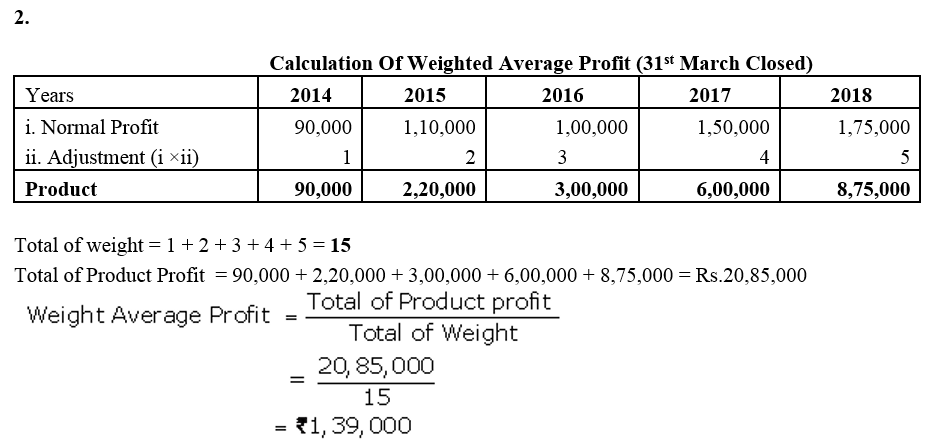
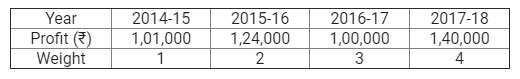
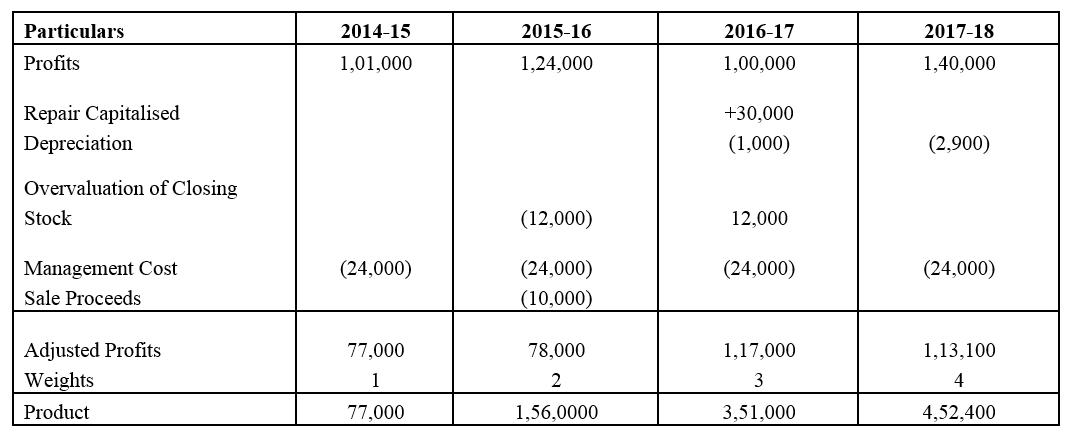

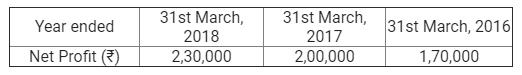
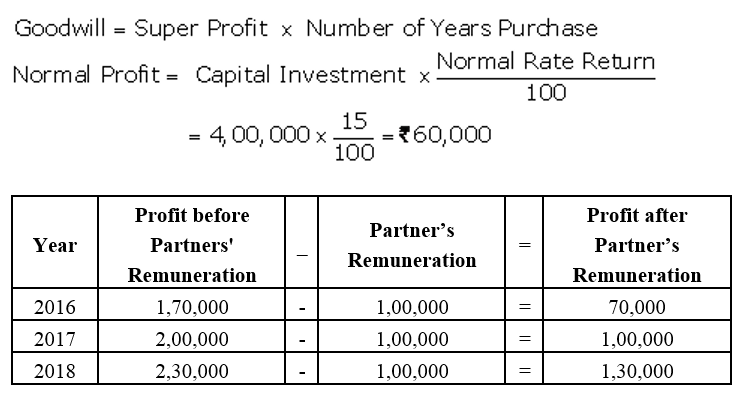
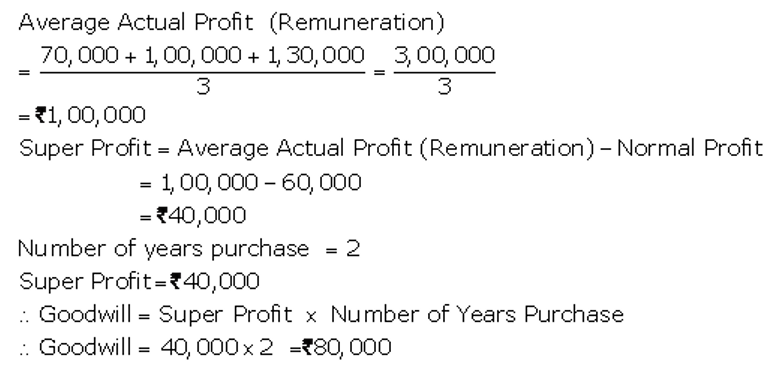
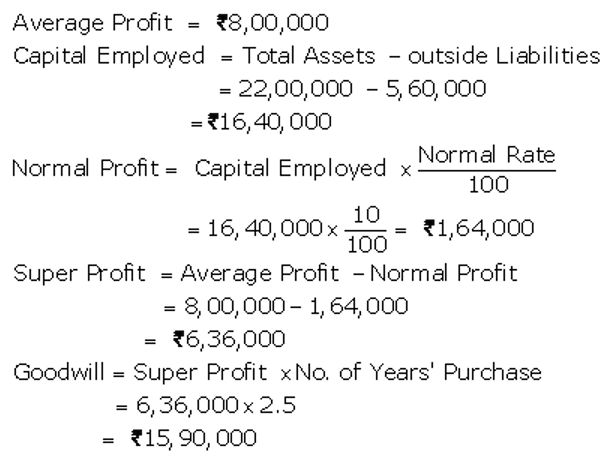
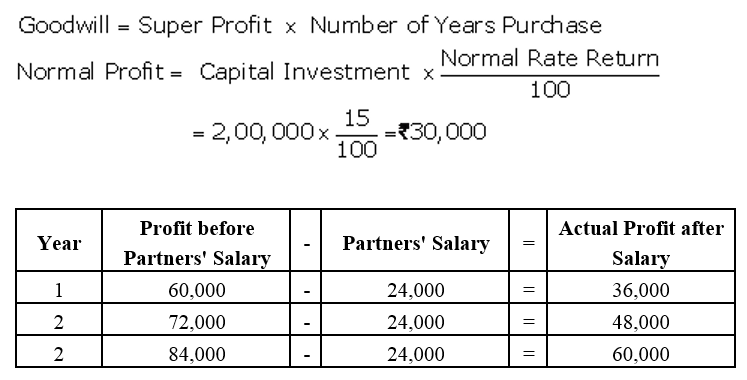
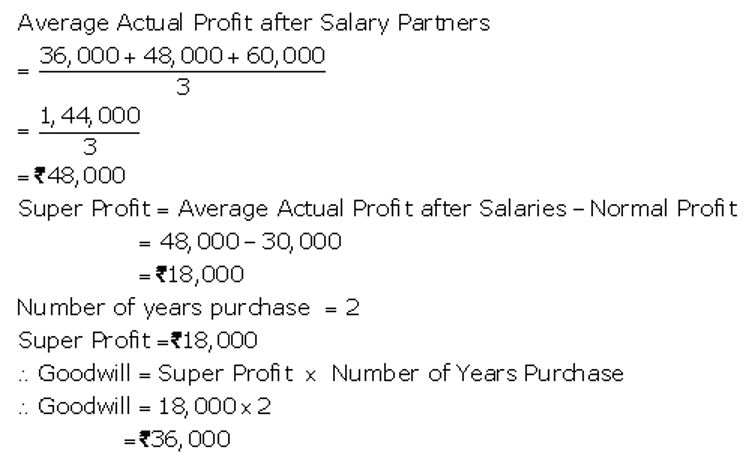
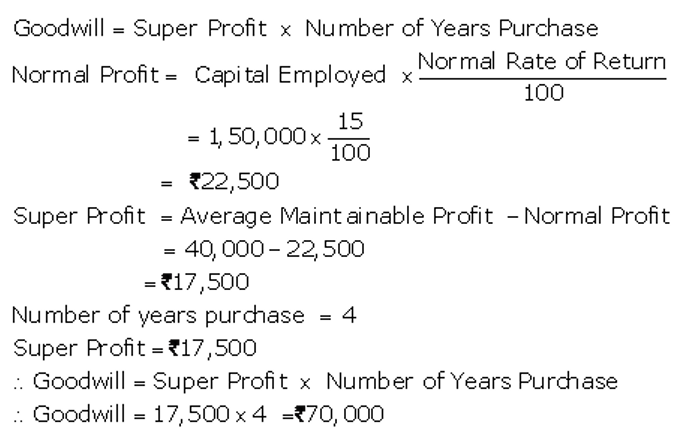
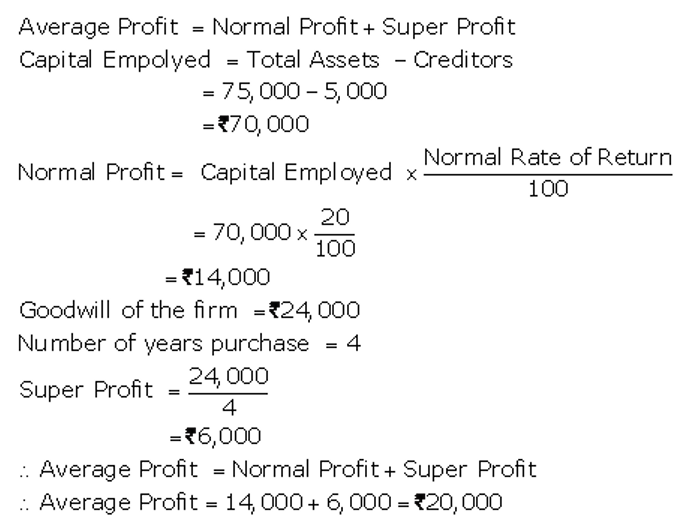
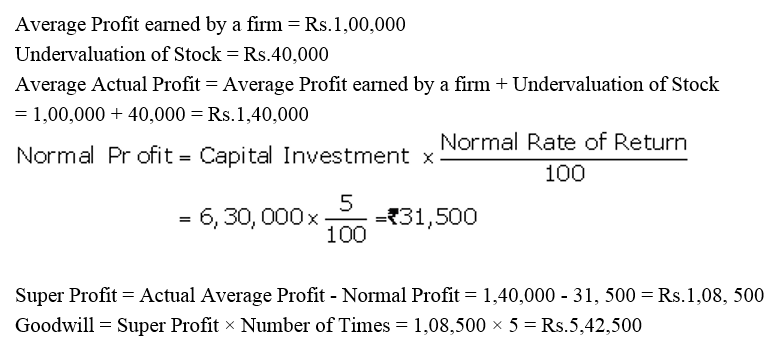
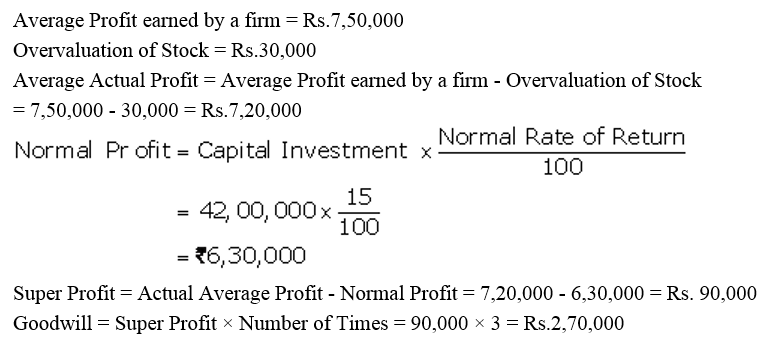
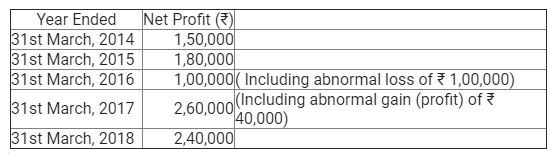
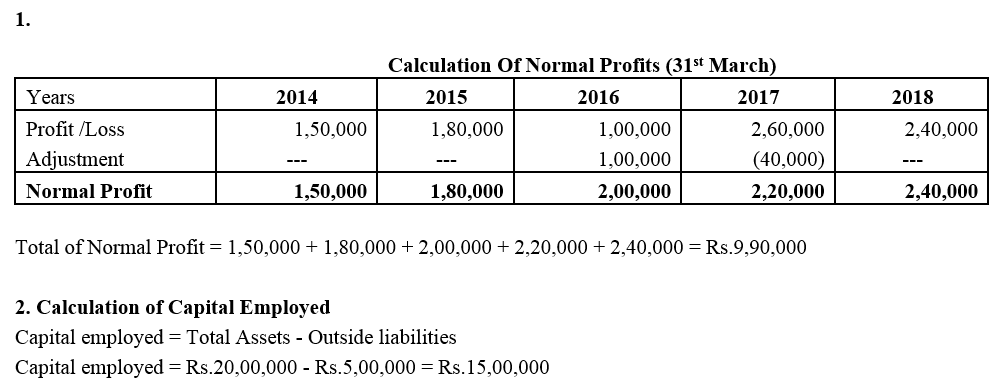
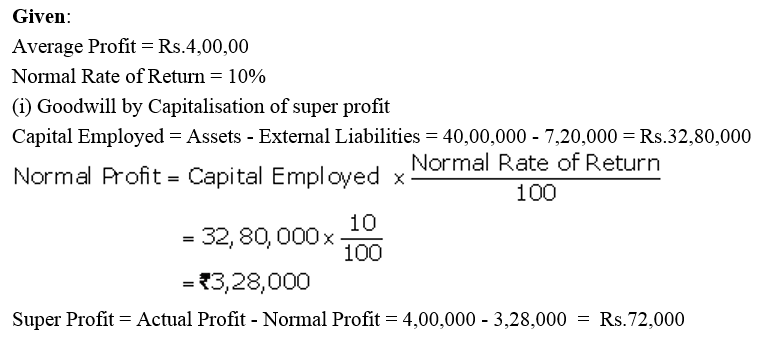
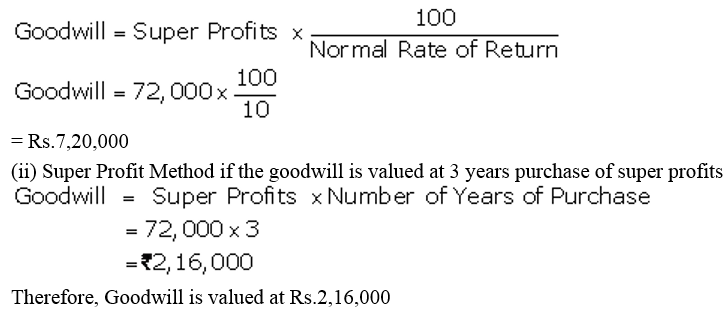
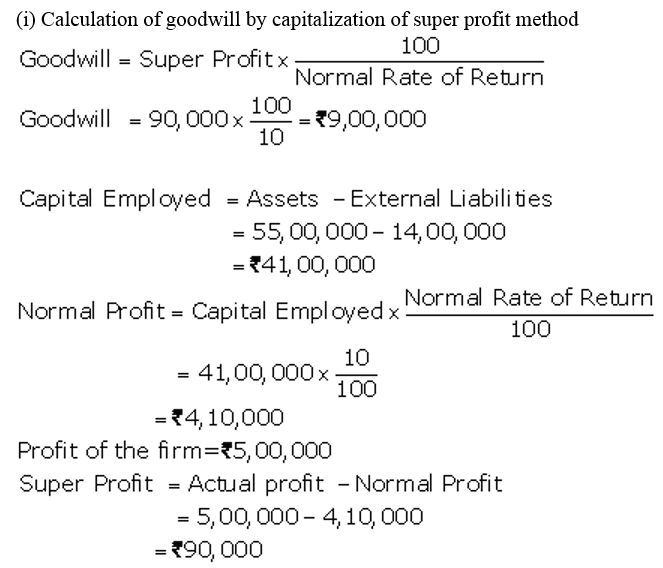
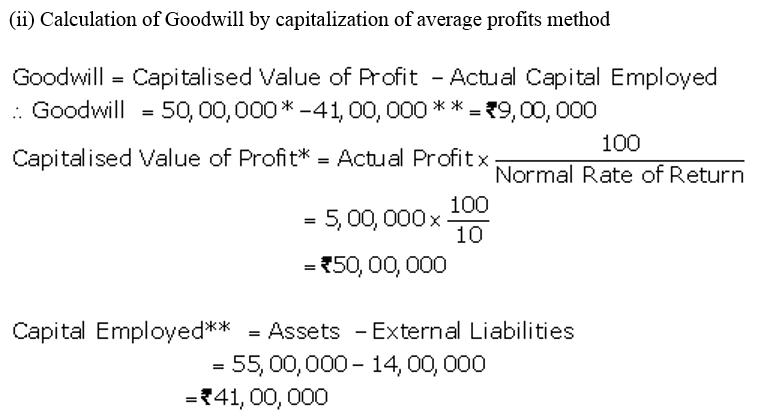
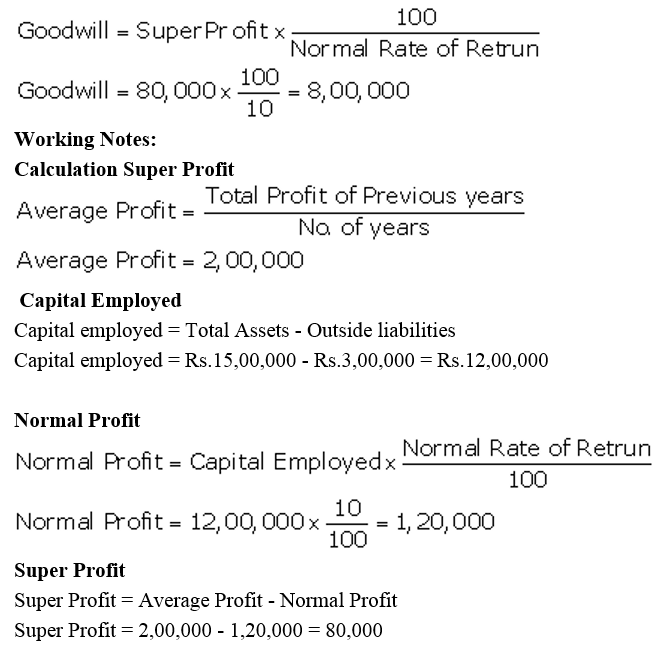
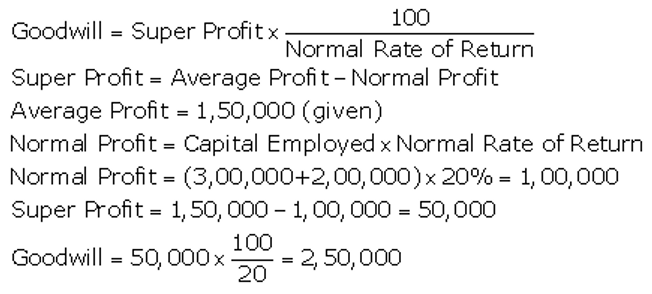
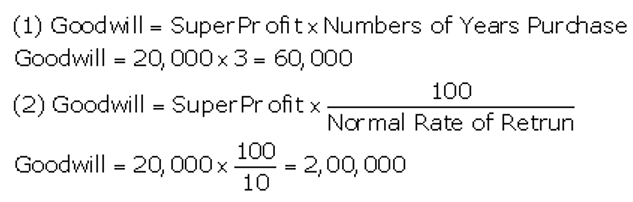
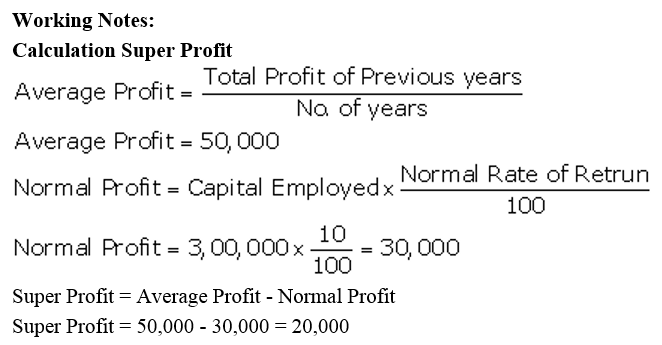
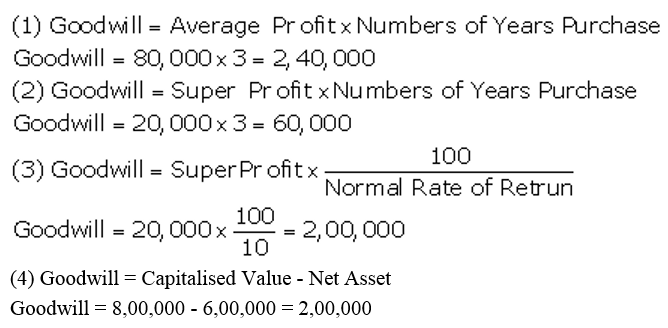
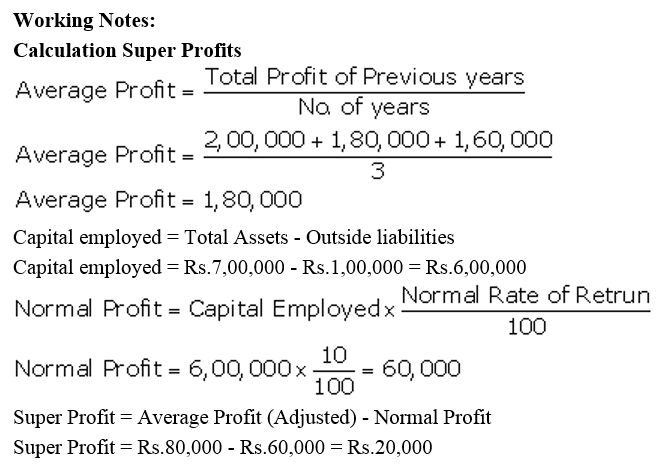



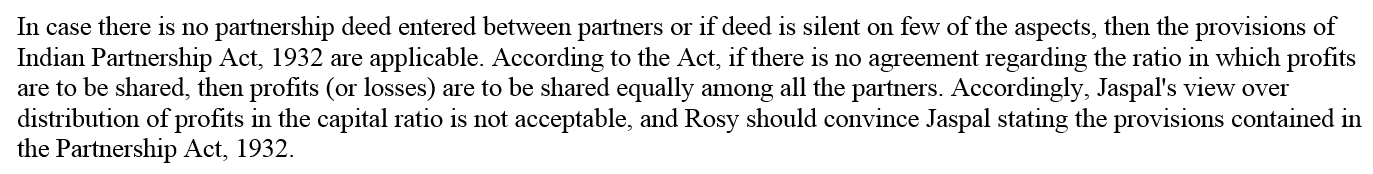




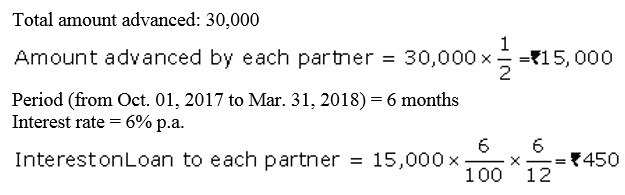

























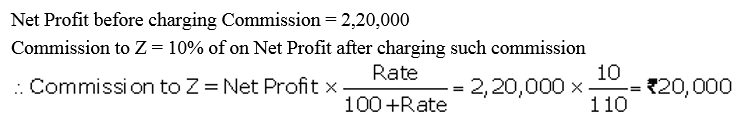


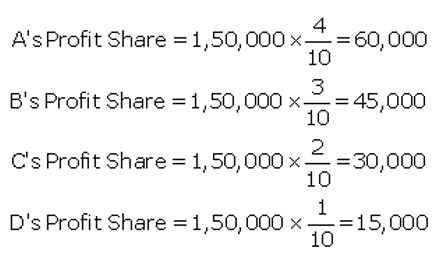


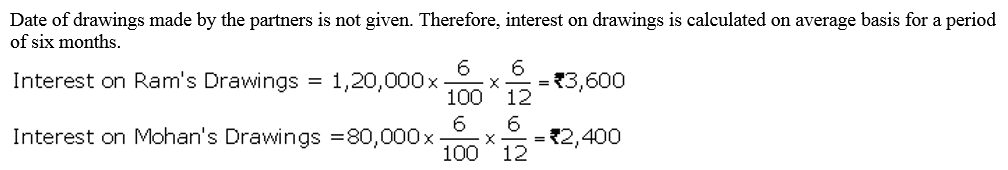
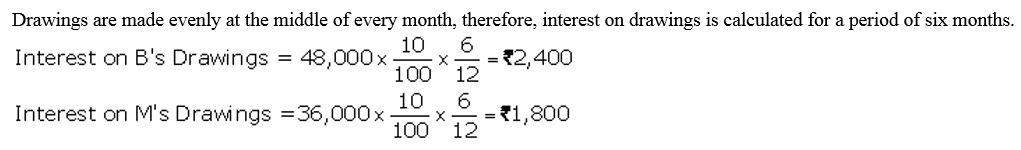



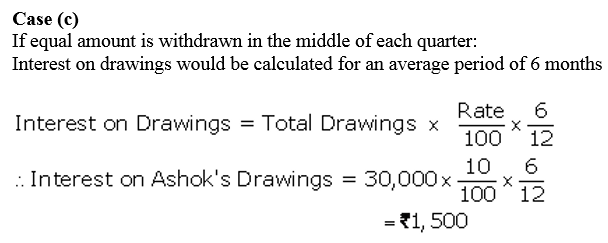









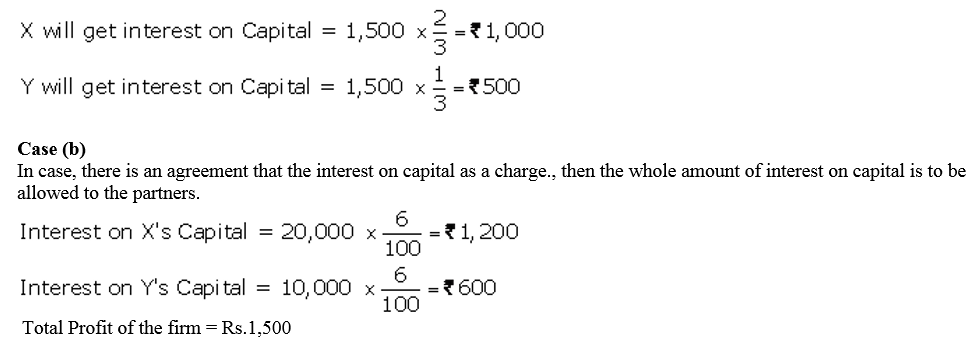
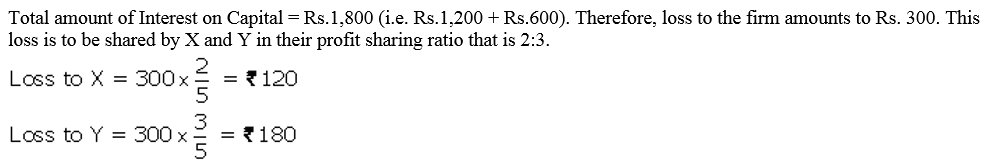
































































































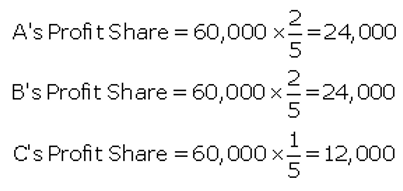




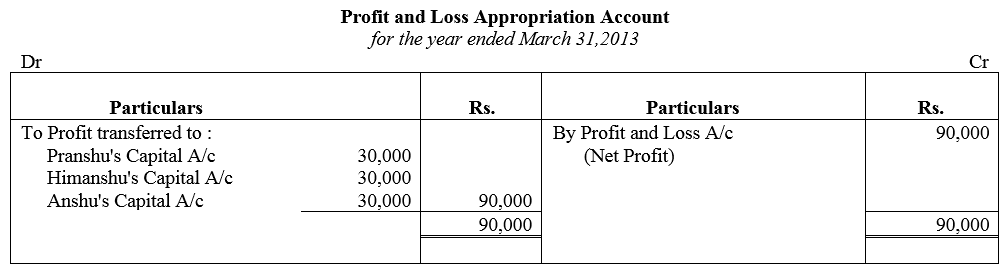













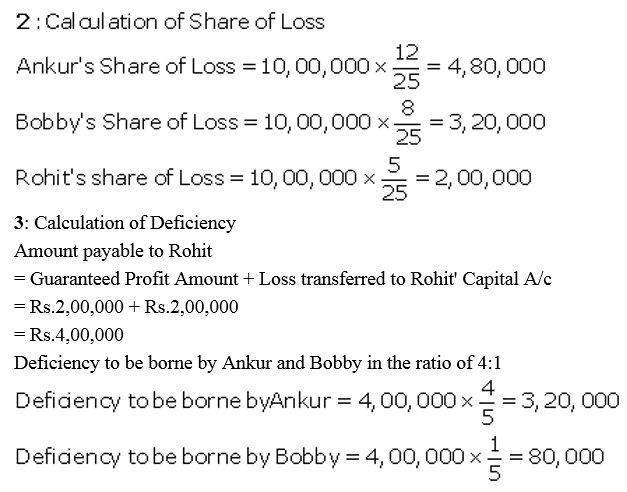



 ]
]

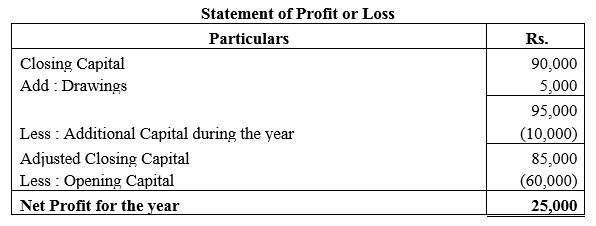
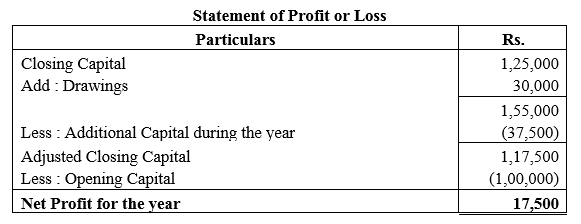
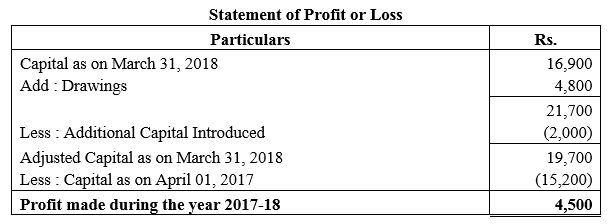
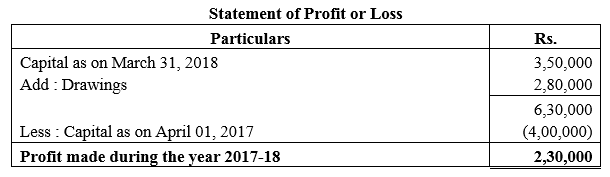
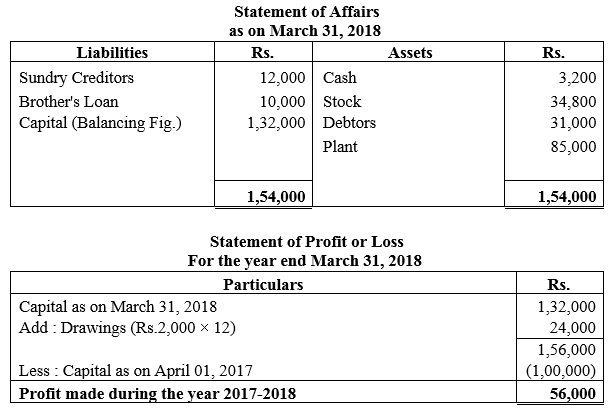
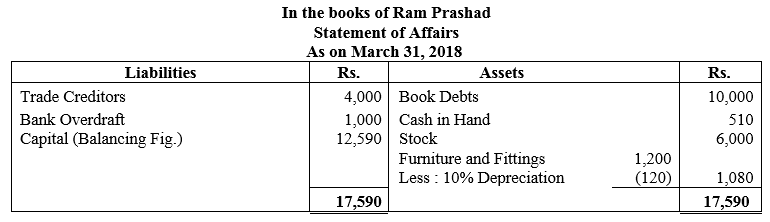
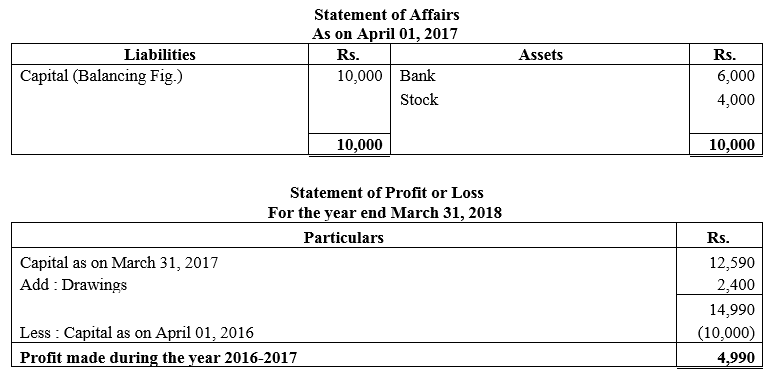

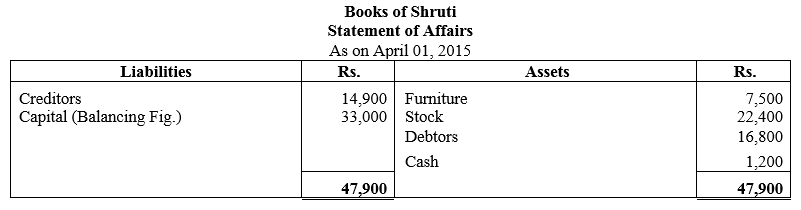
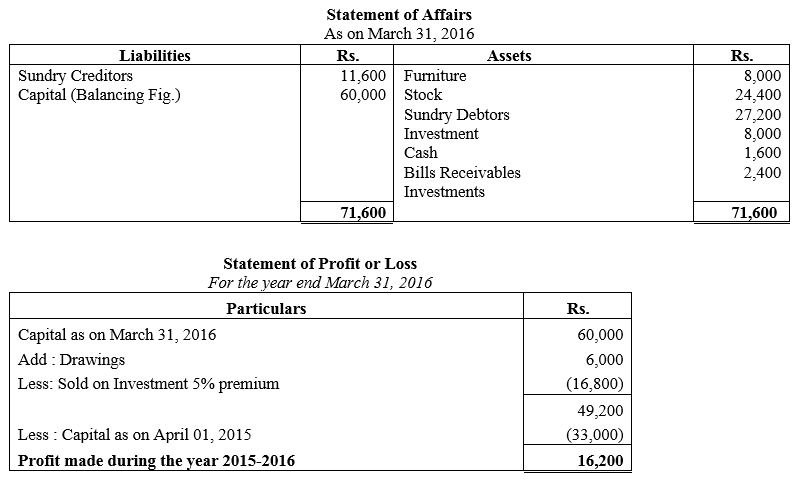

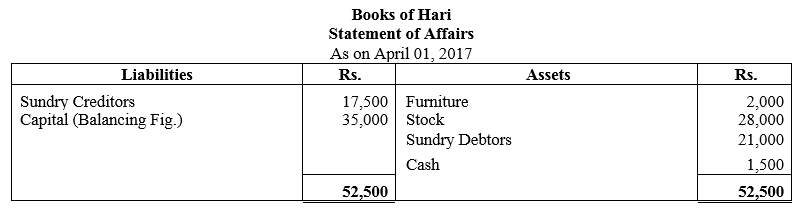
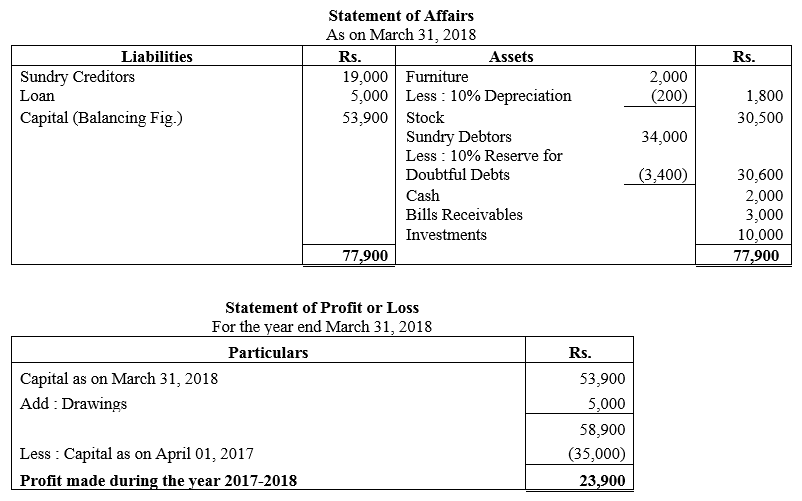
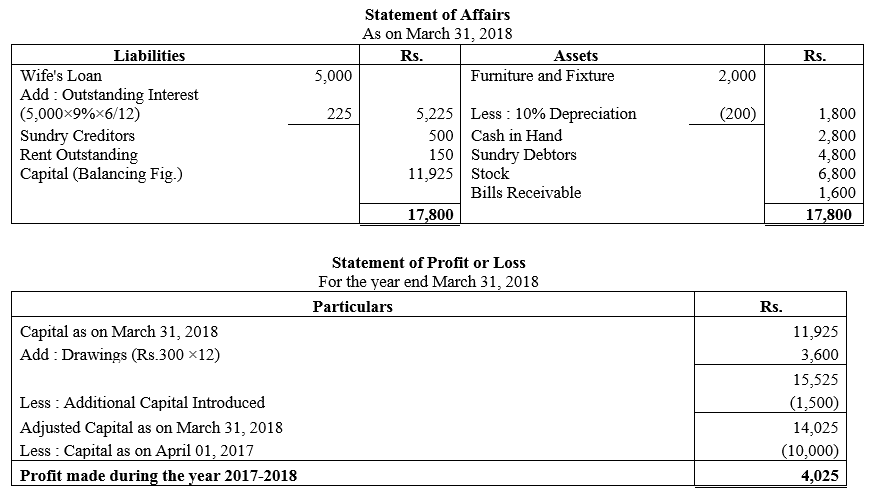

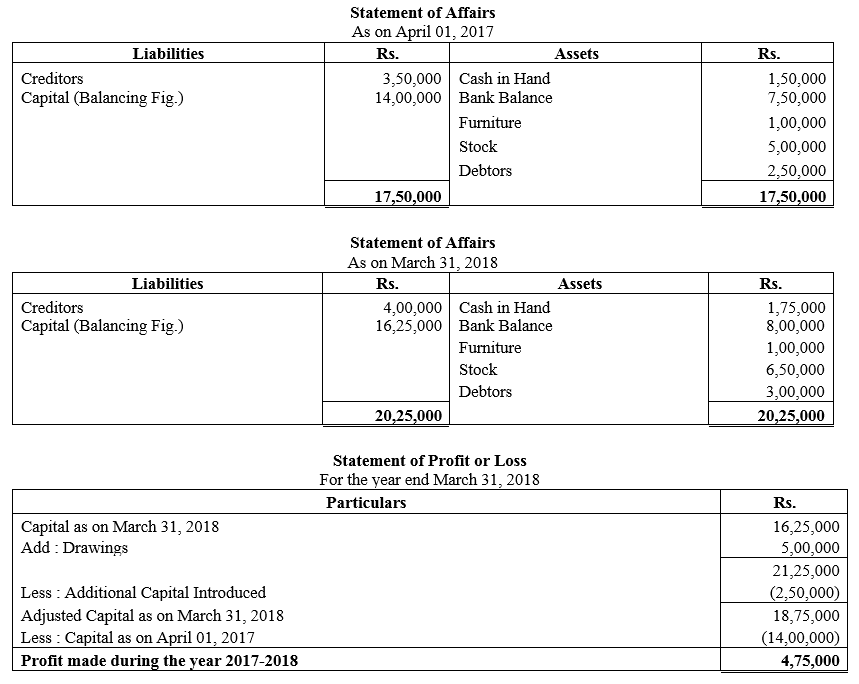
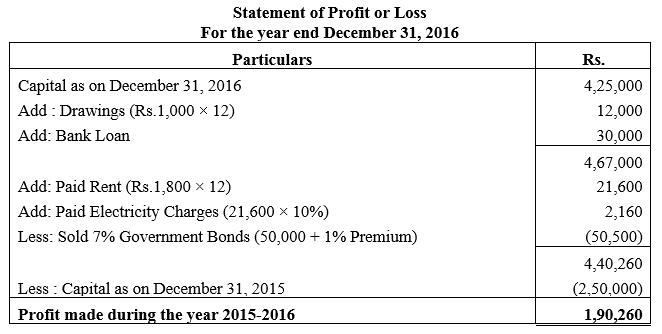
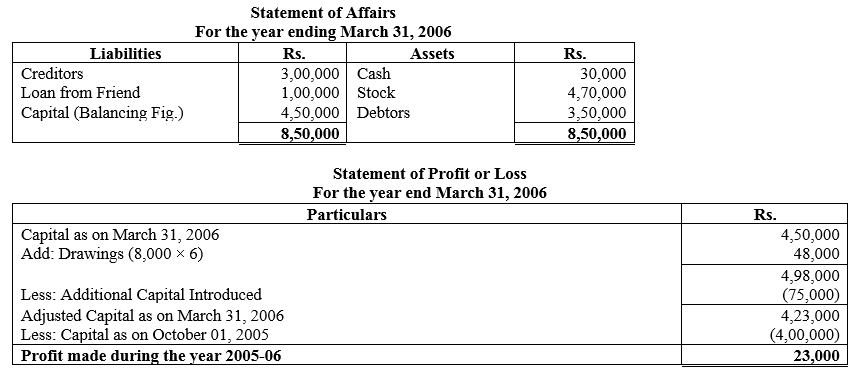
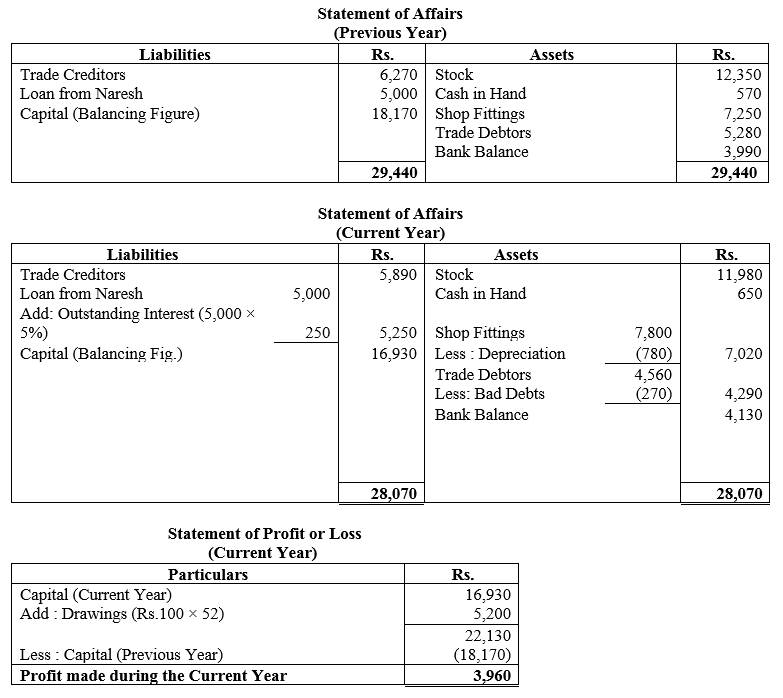
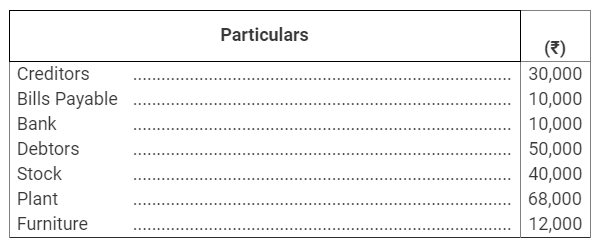
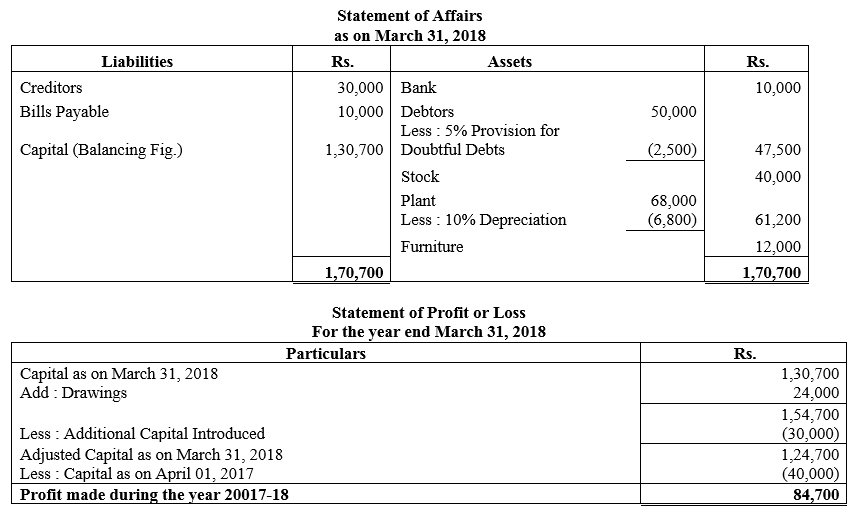
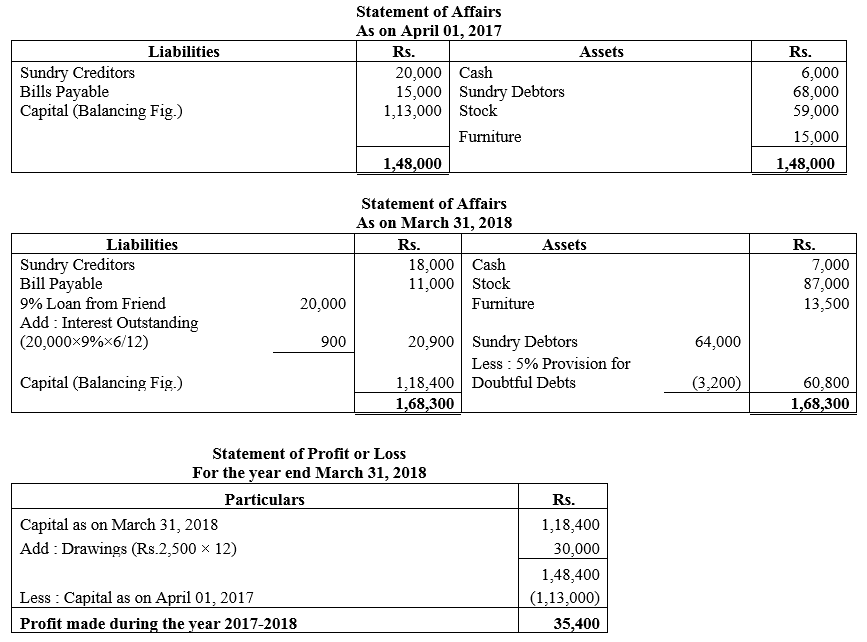
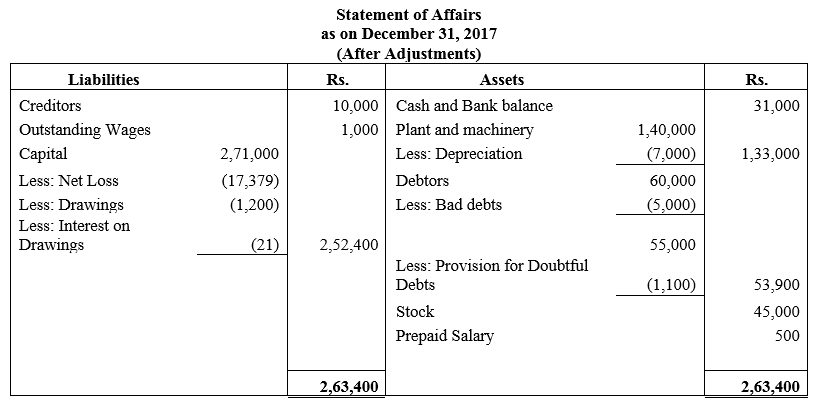
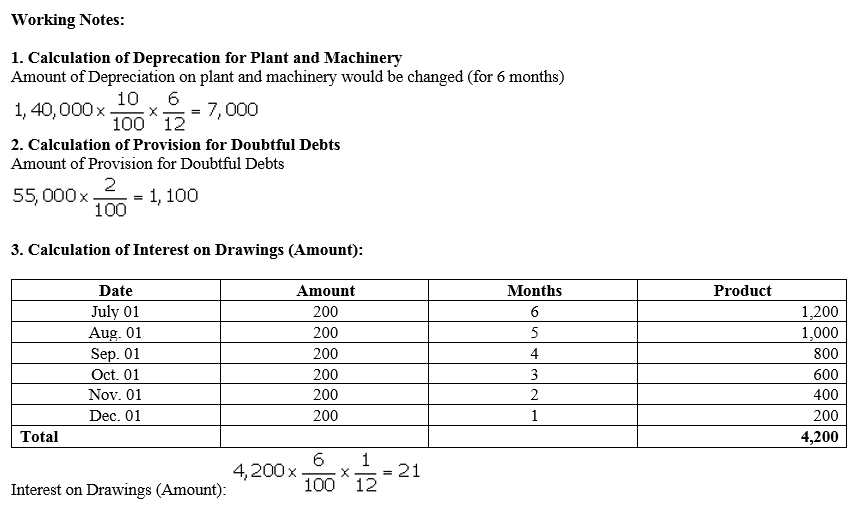
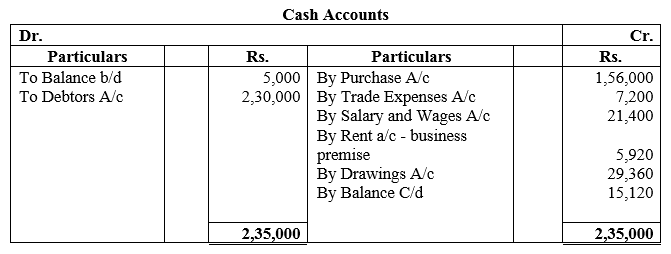
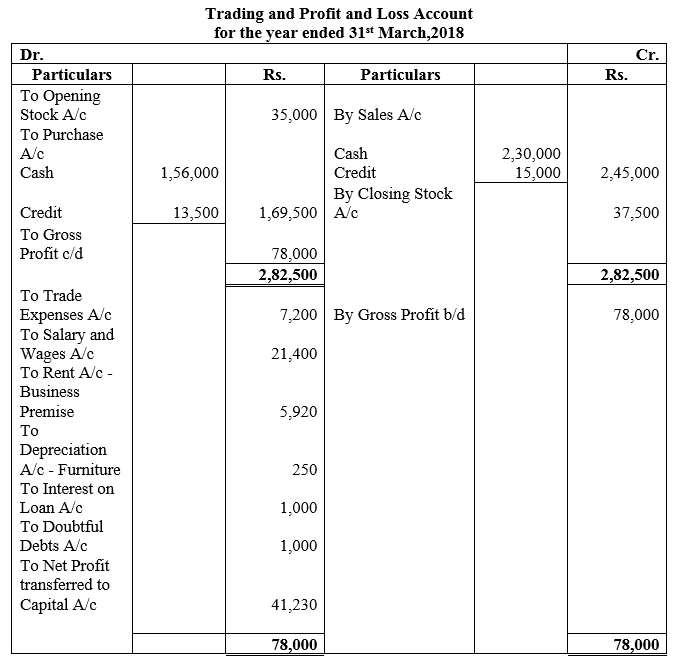
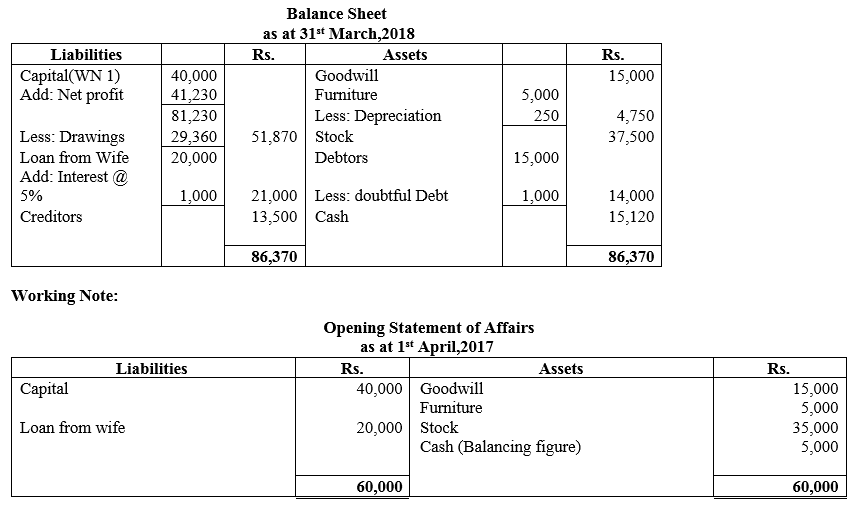
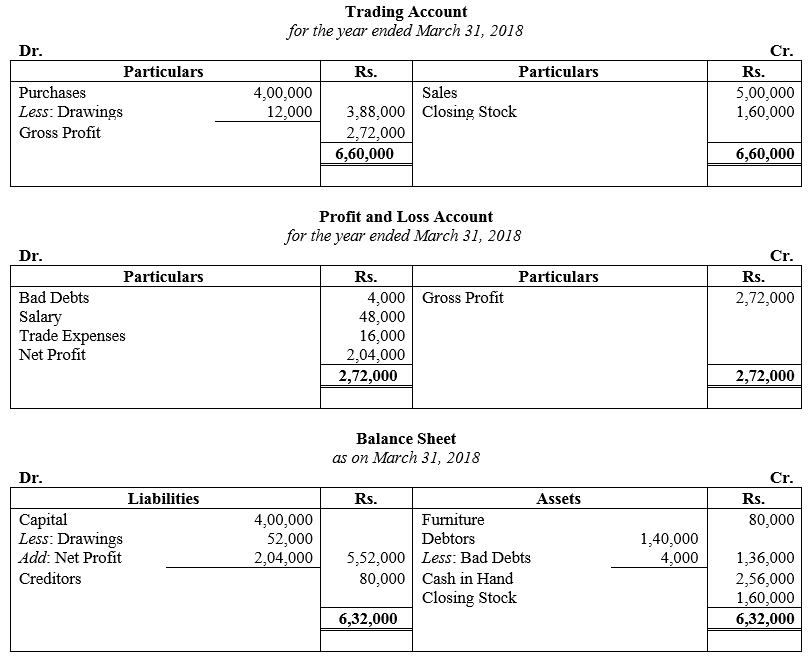
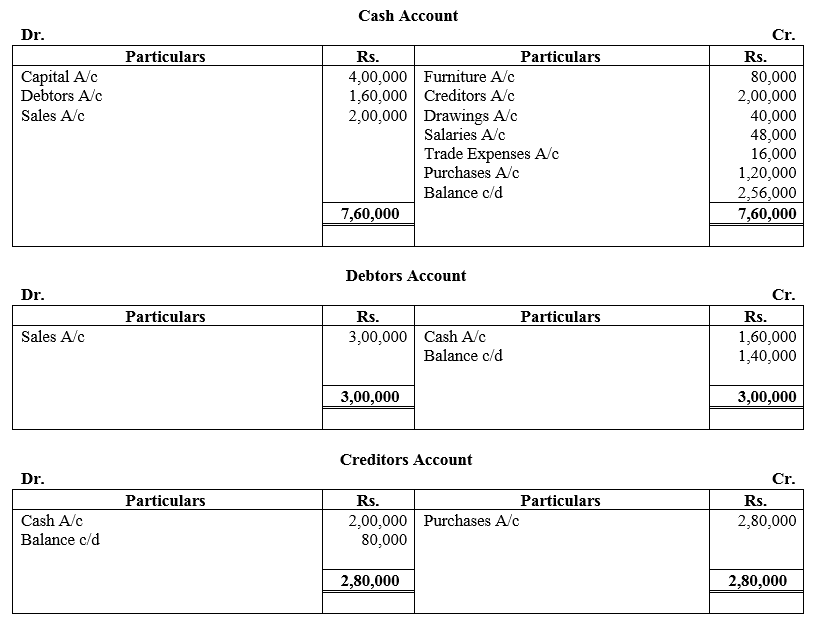
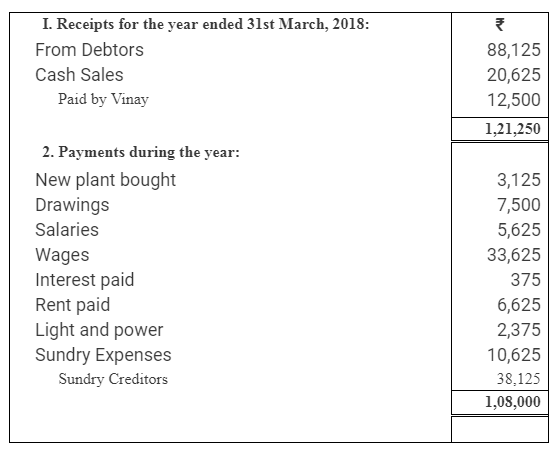
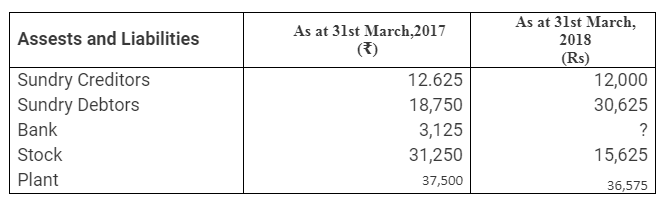
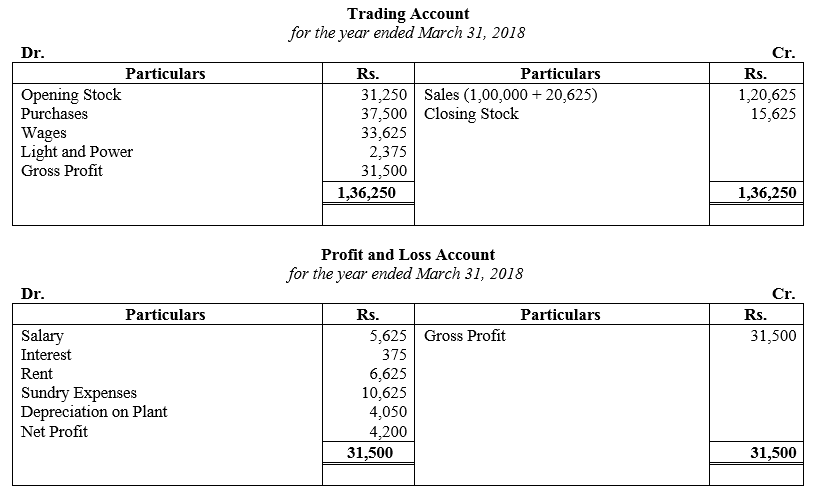
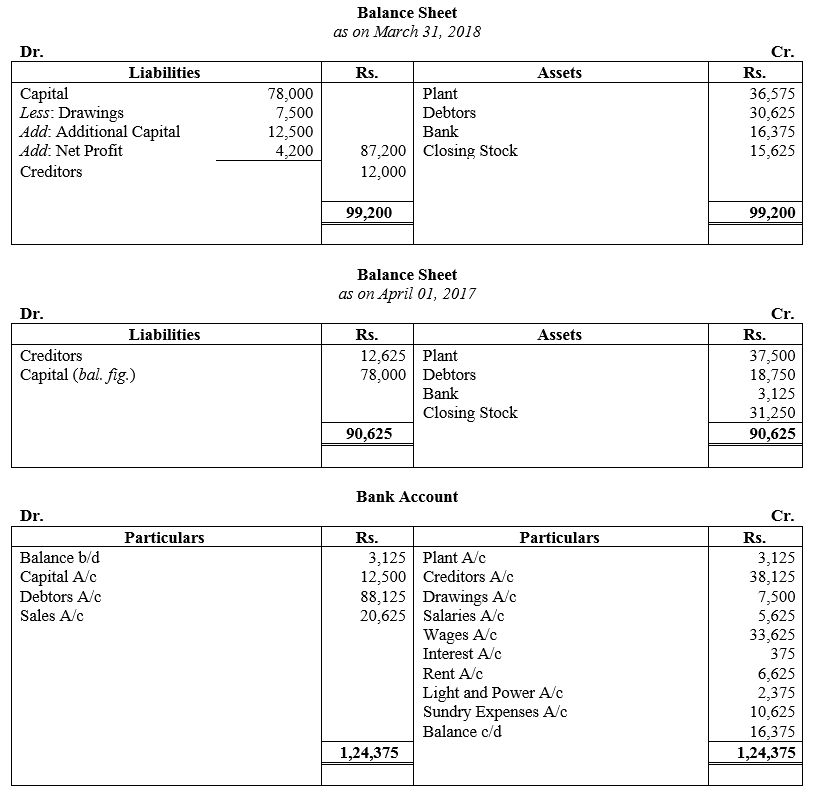
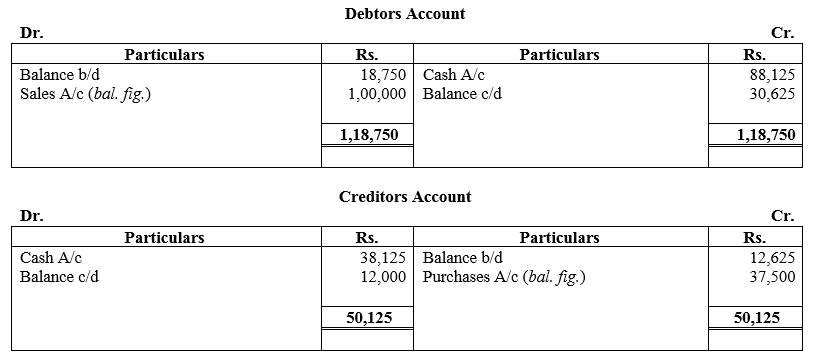
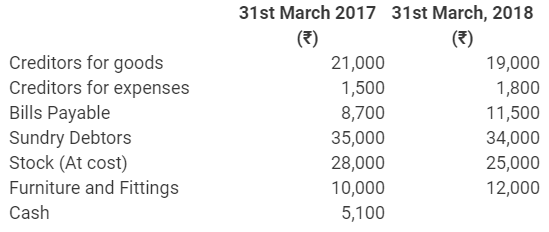
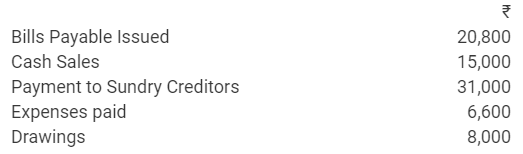
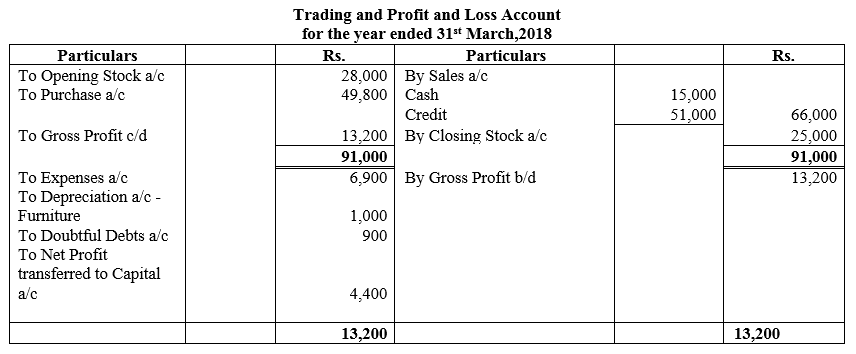
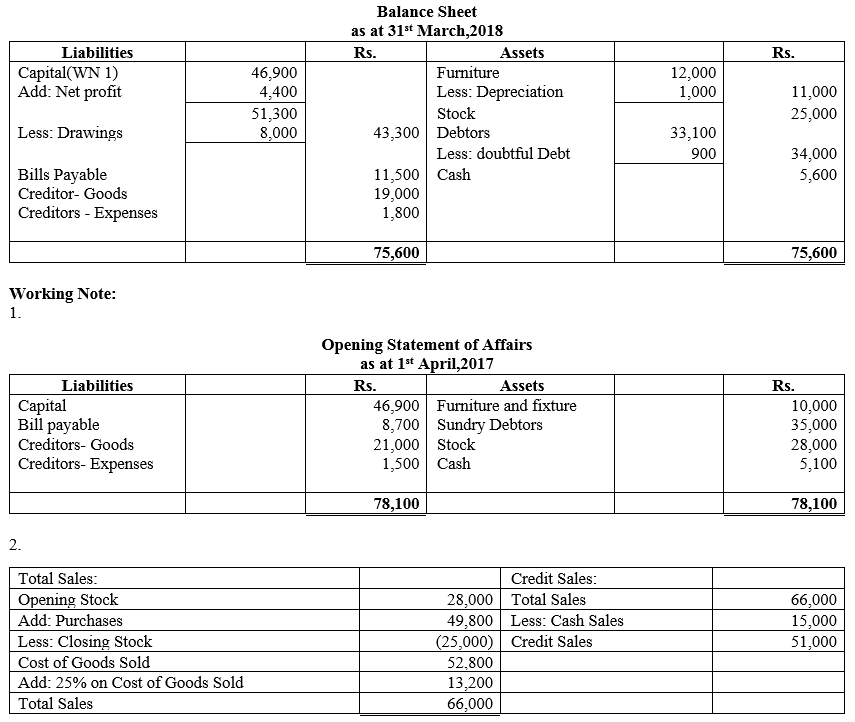
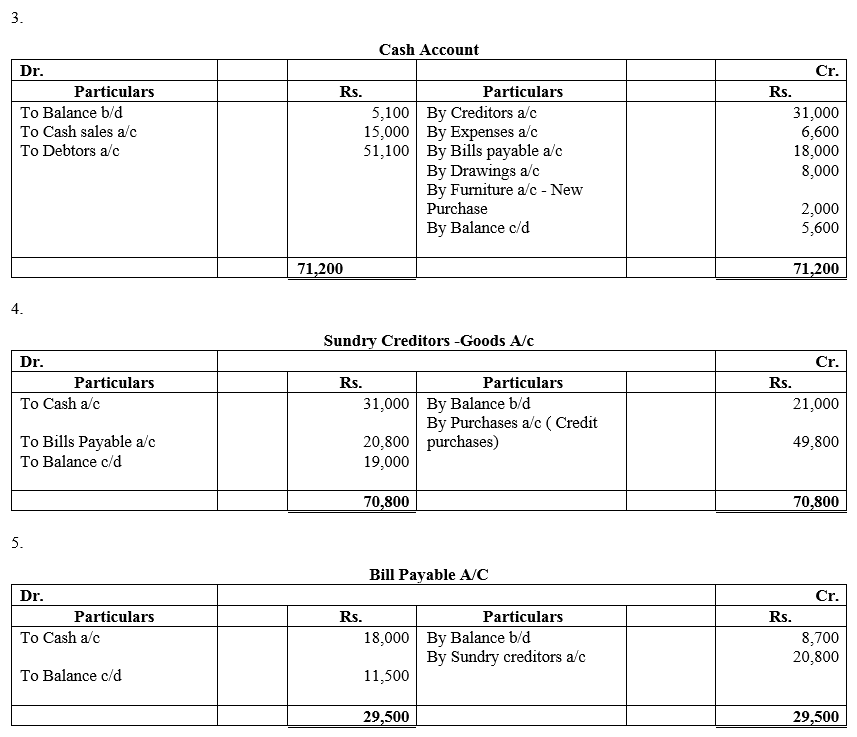
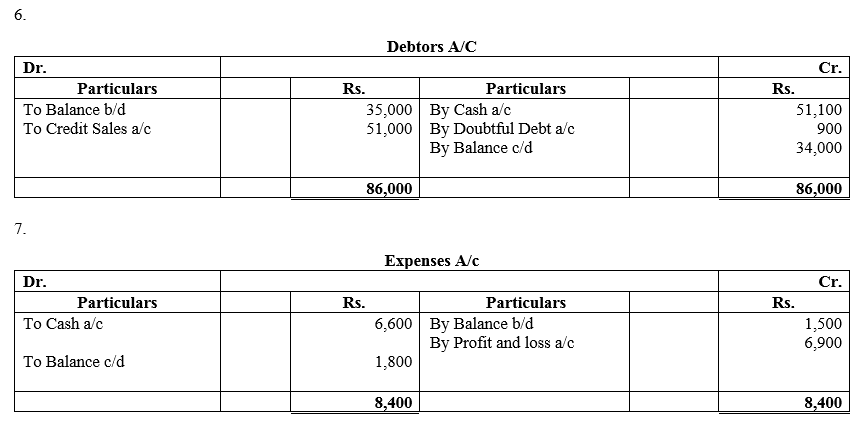
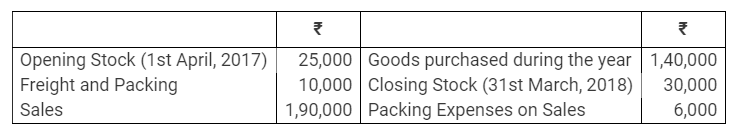
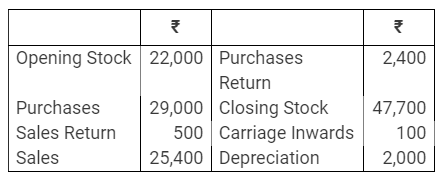
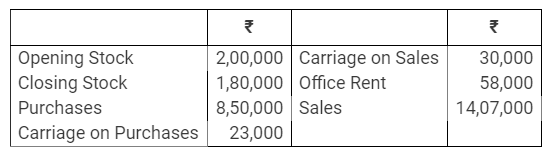
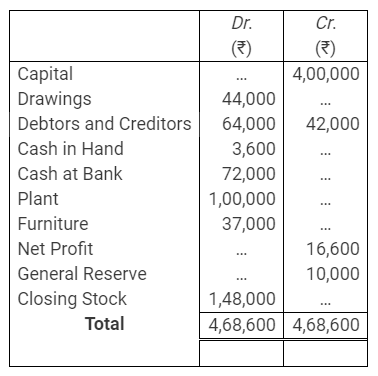
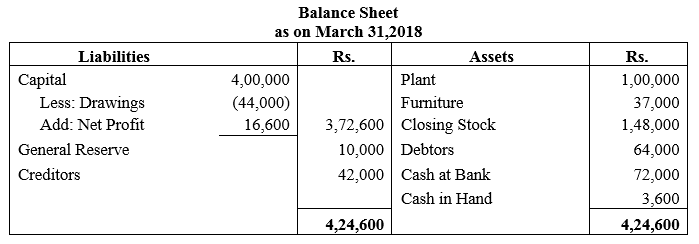
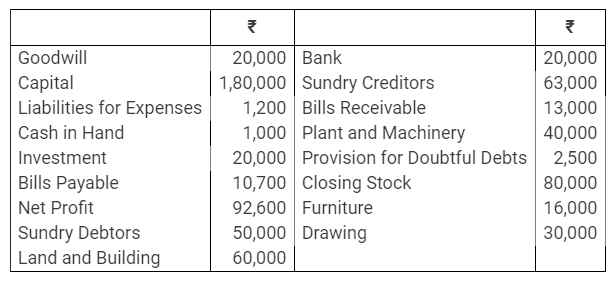
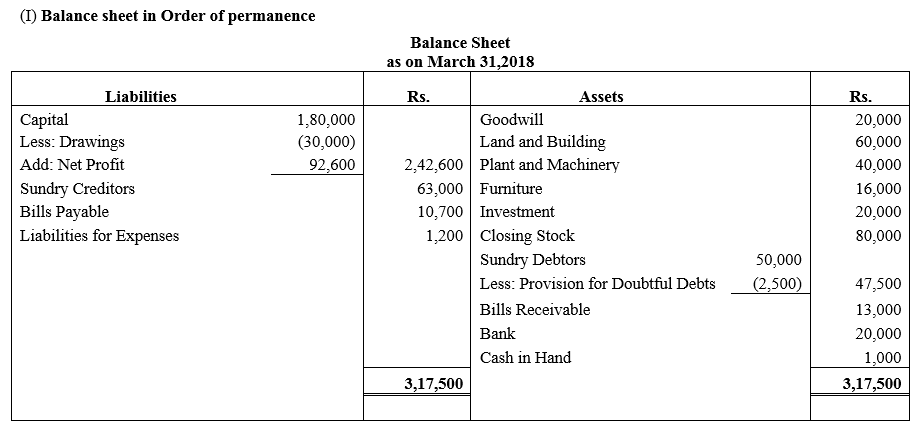
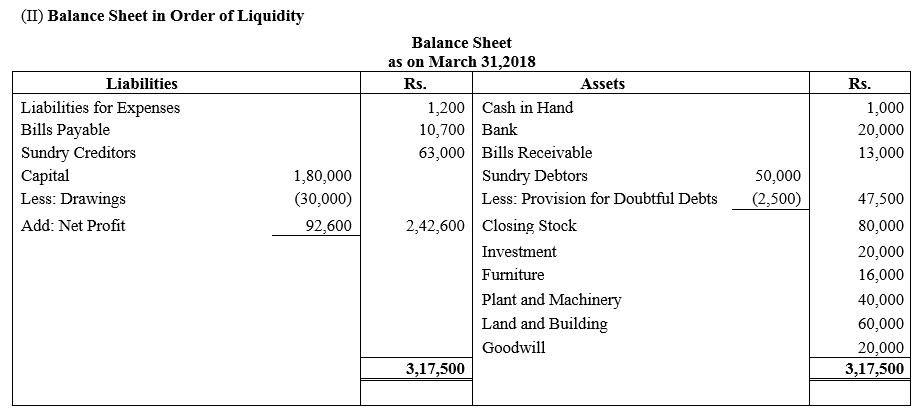
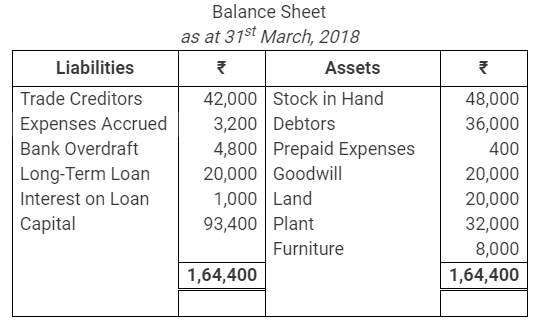
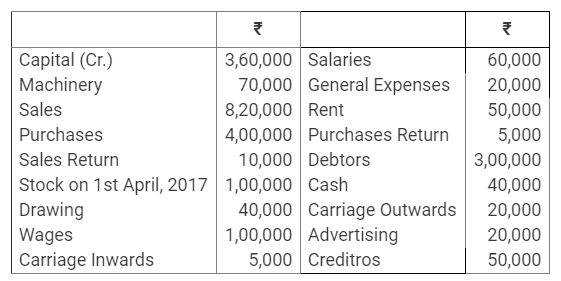
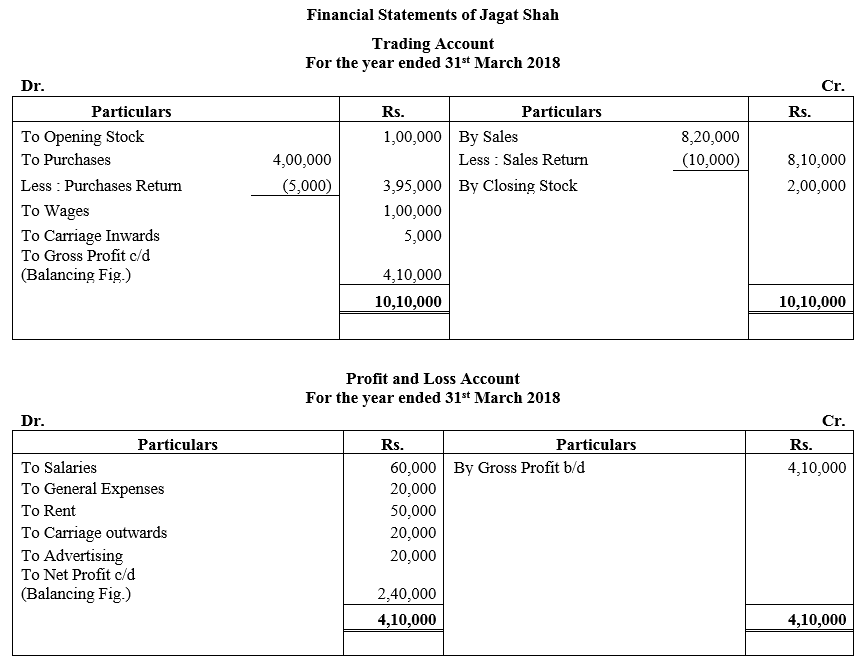
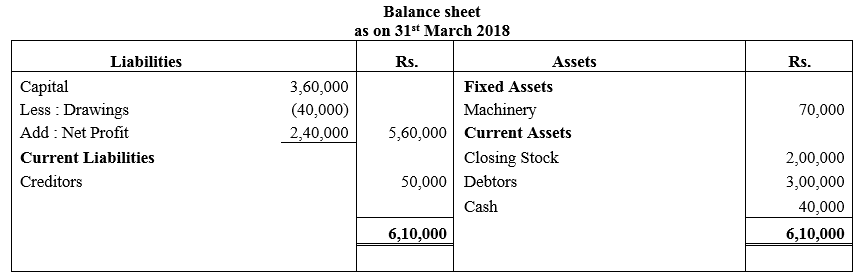
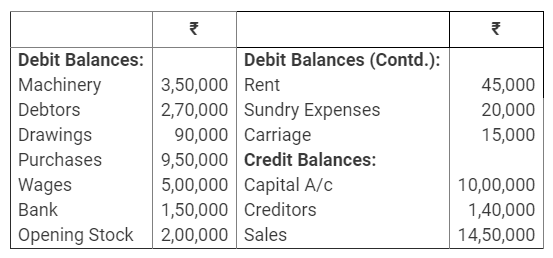
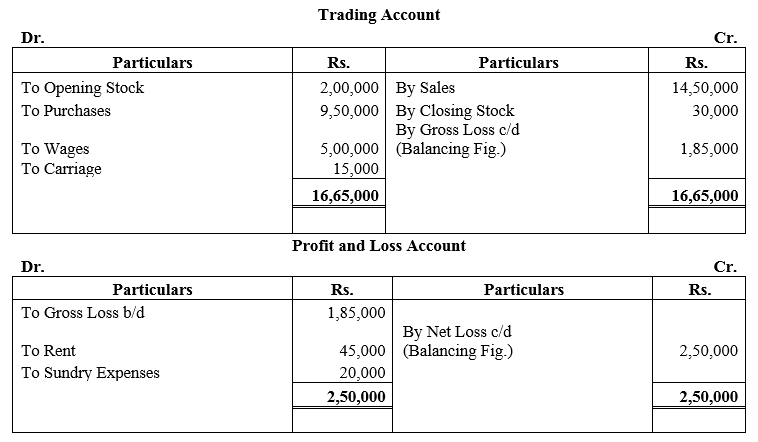
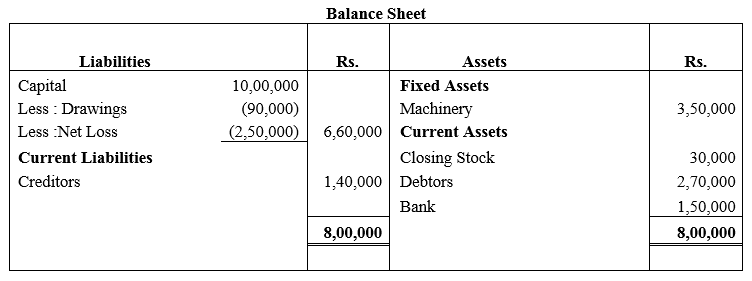
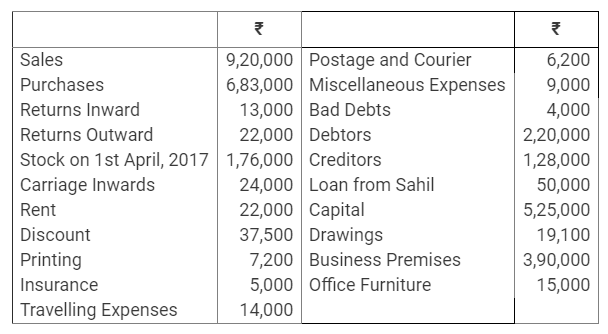
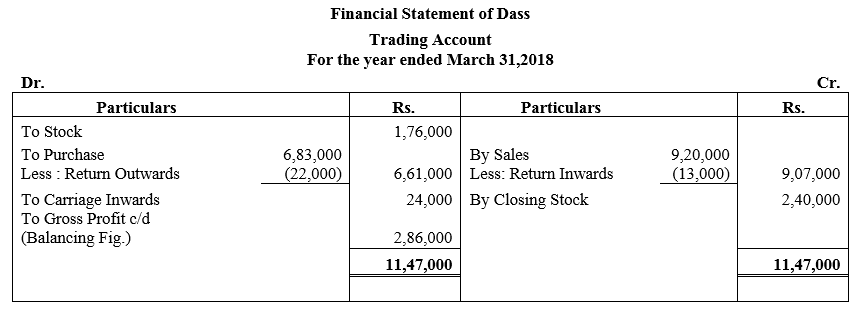
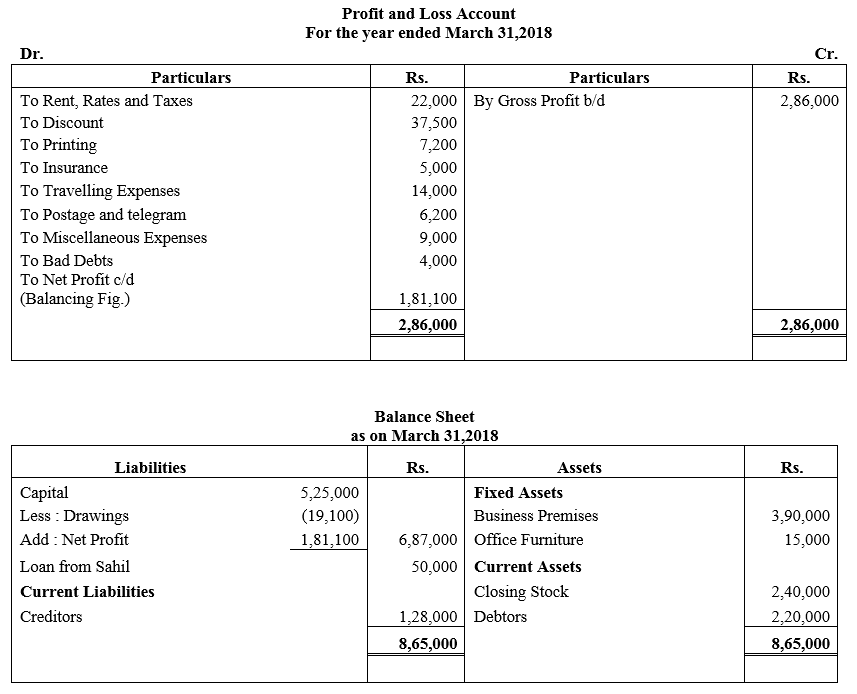
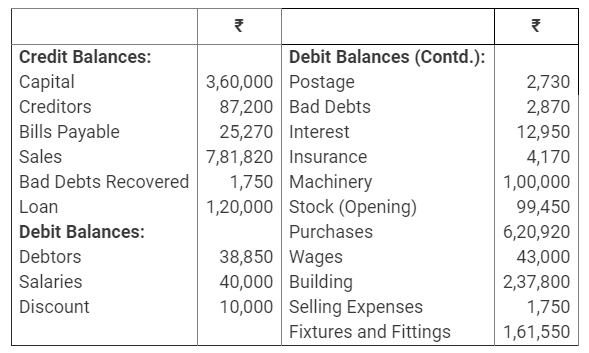
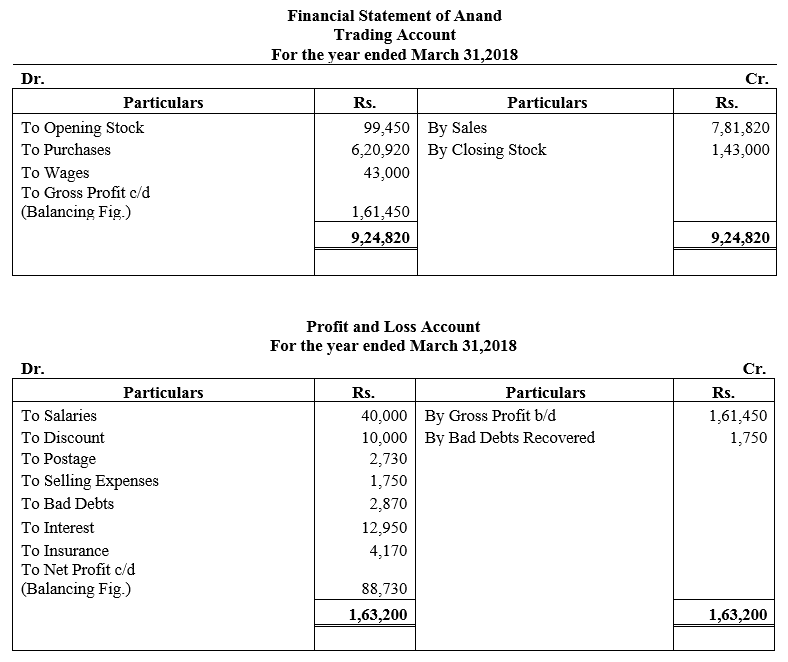
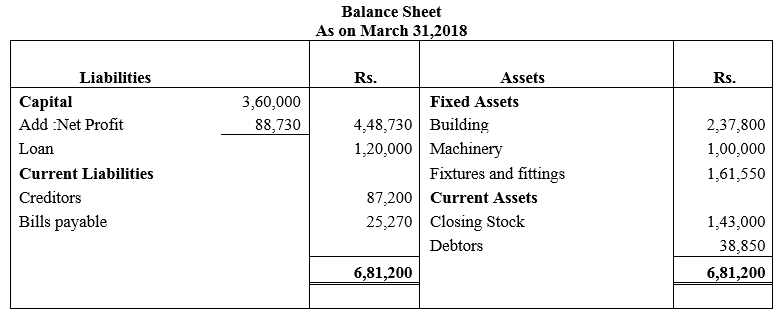
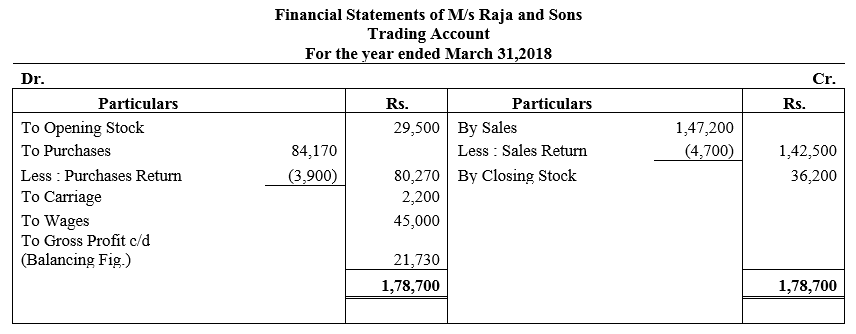
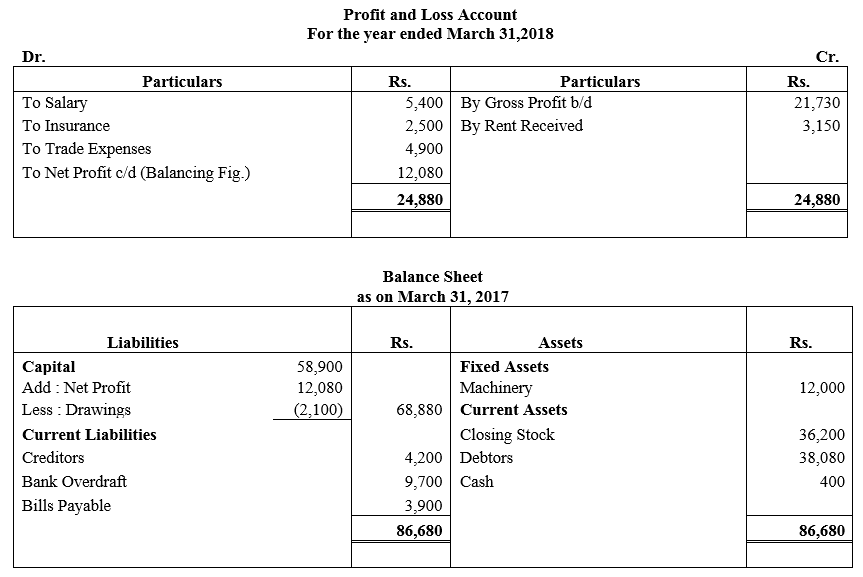
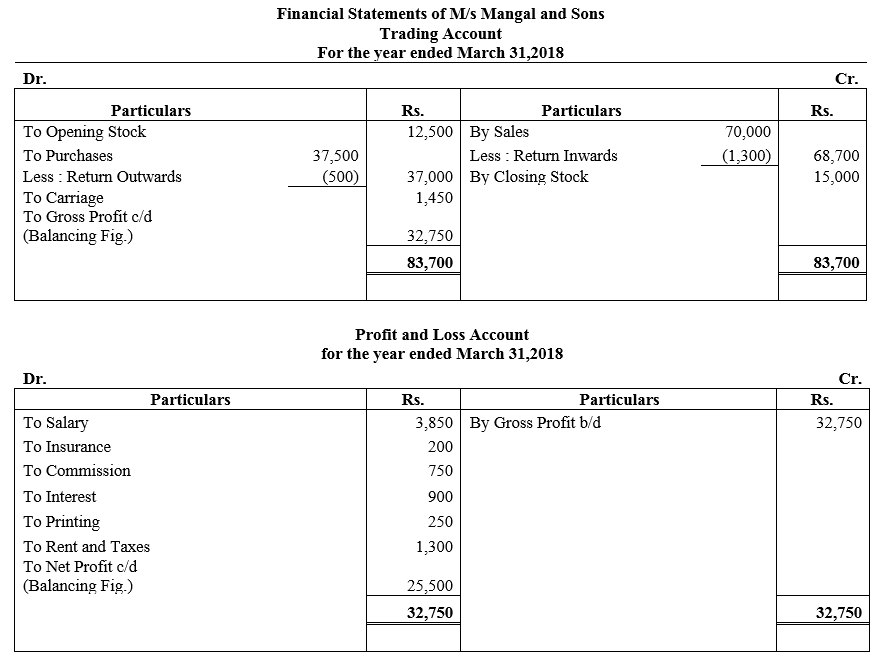
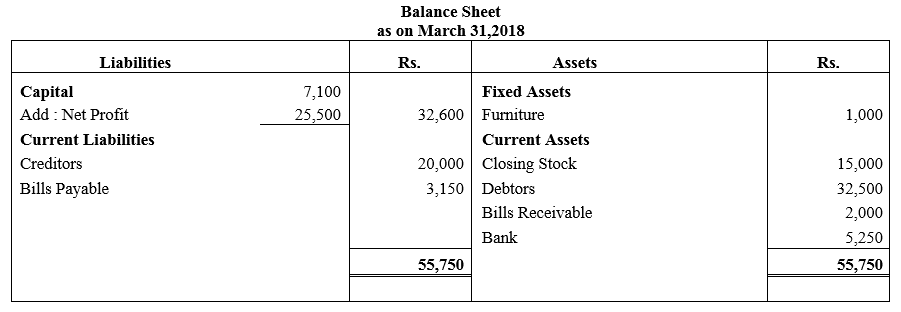
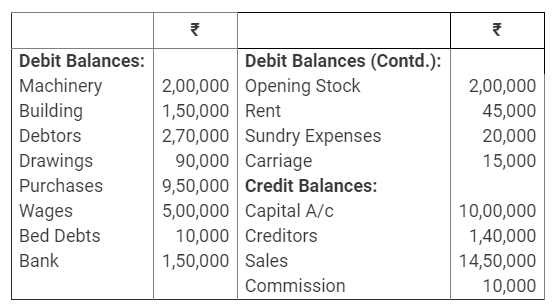
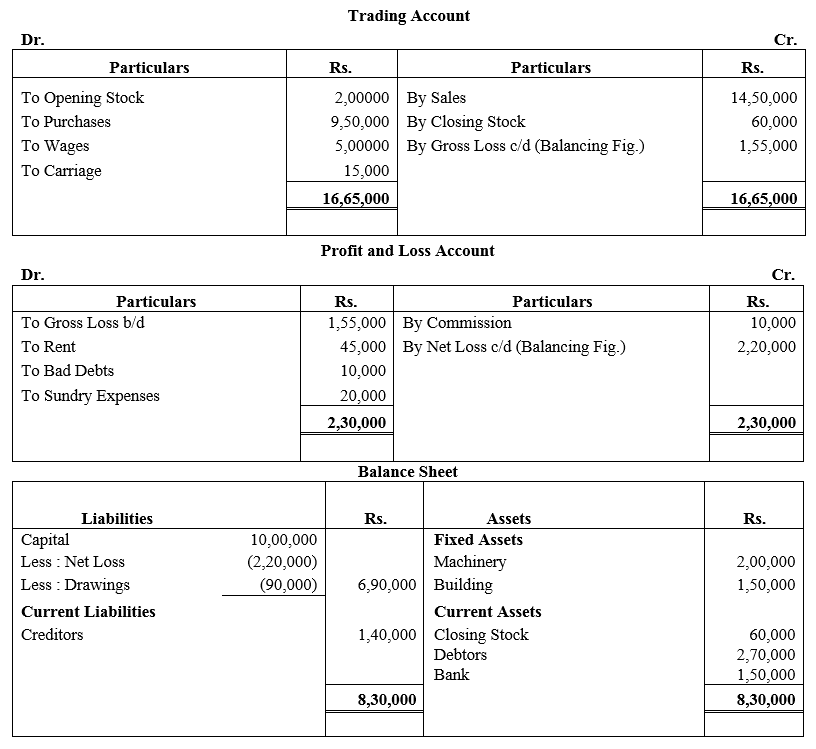
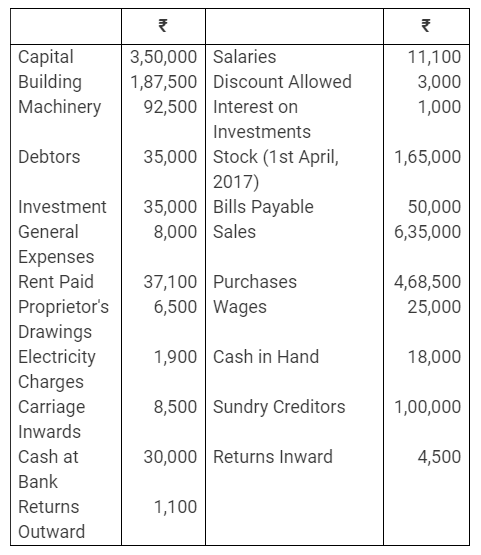
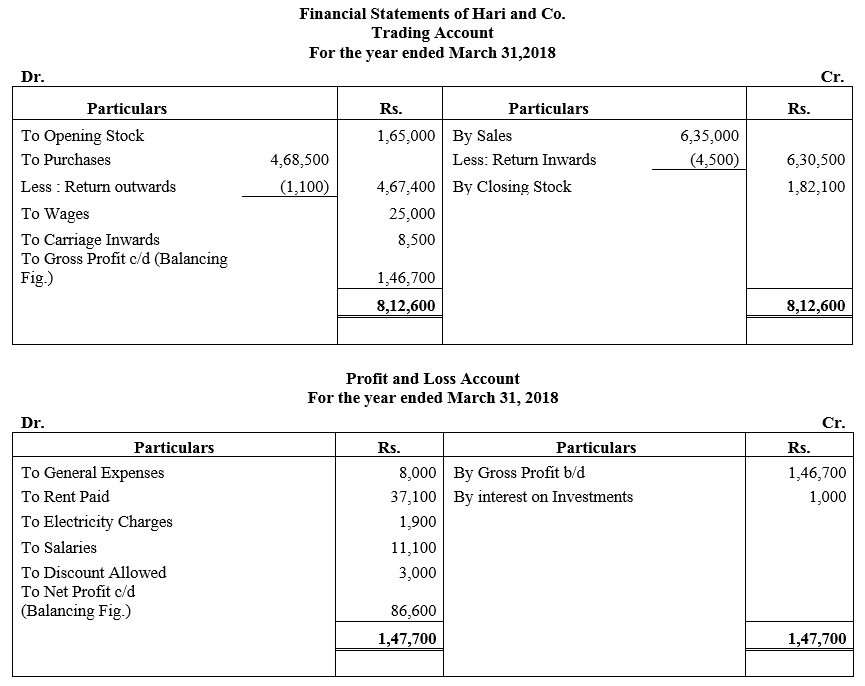
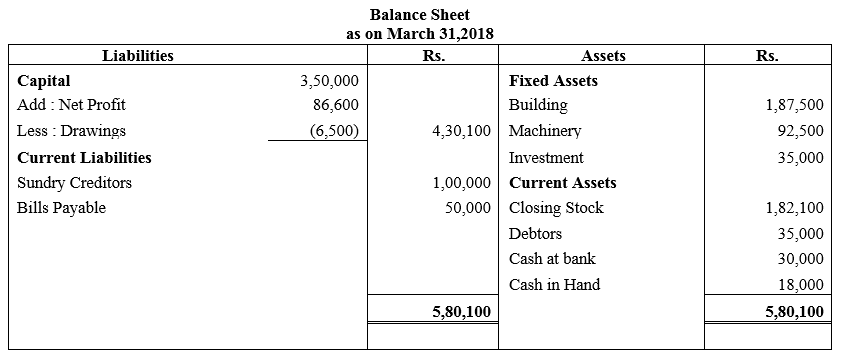
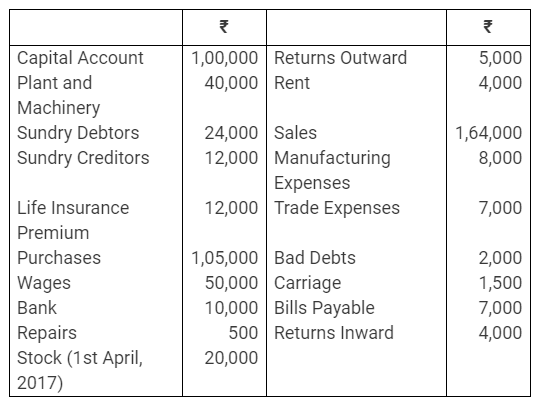
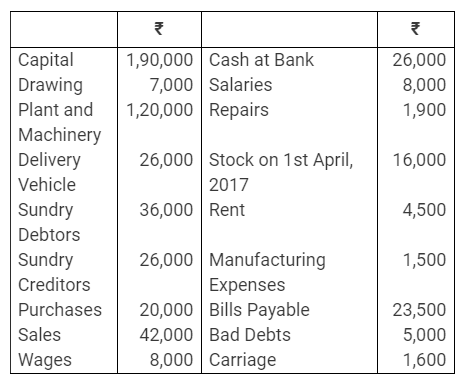
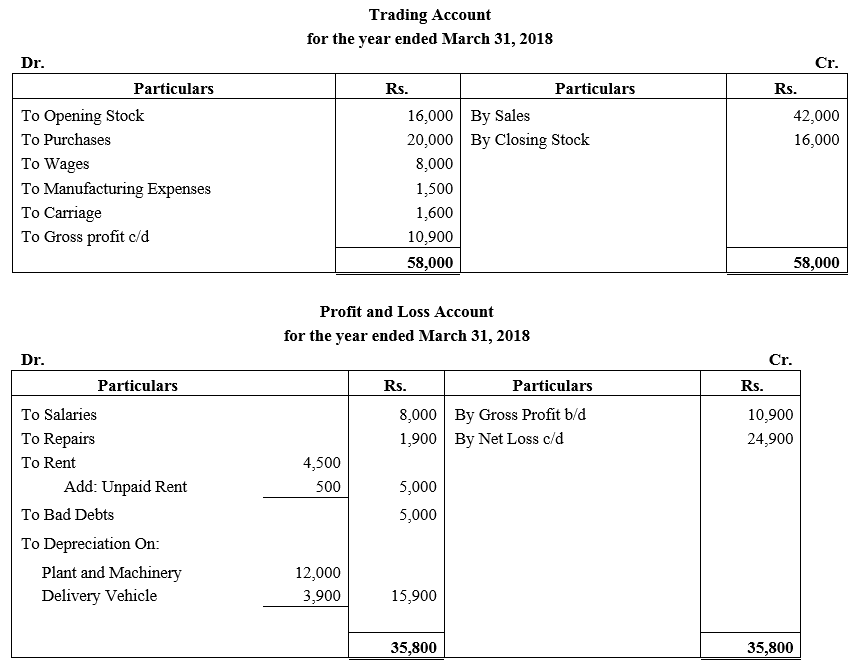
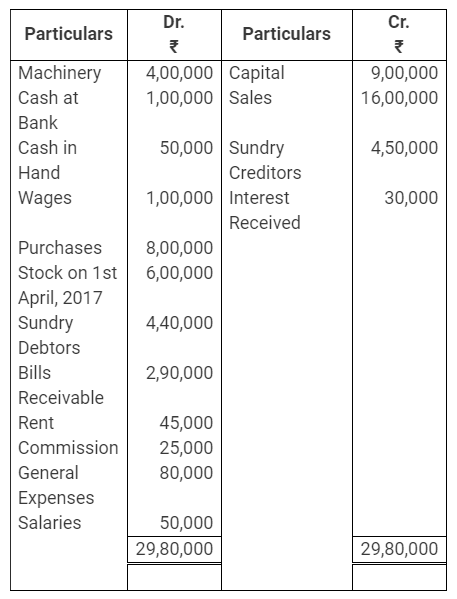
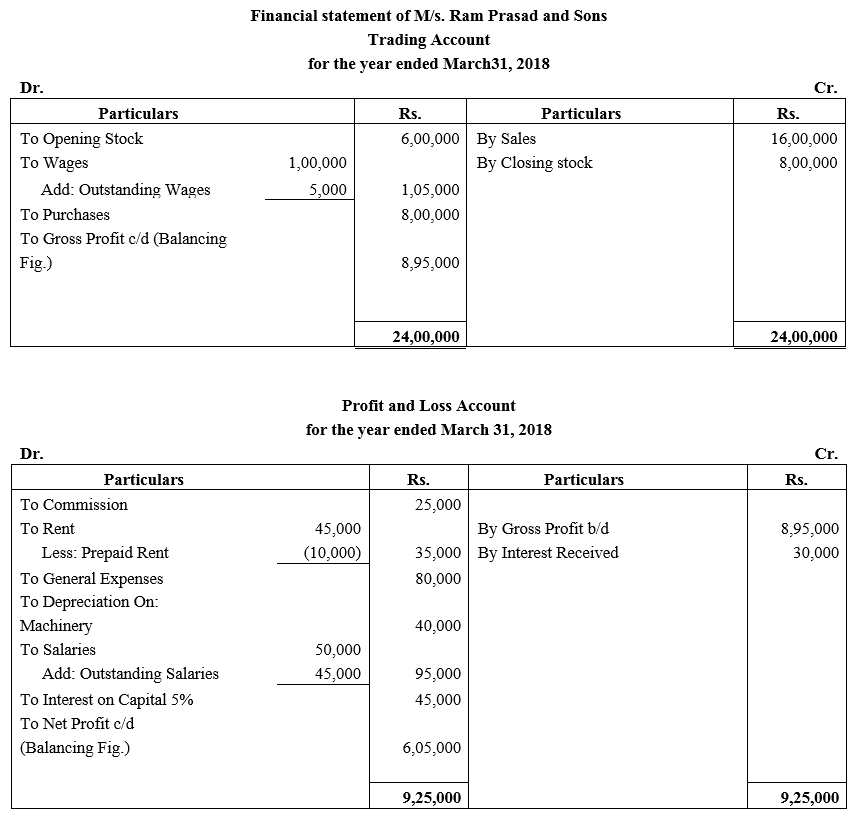
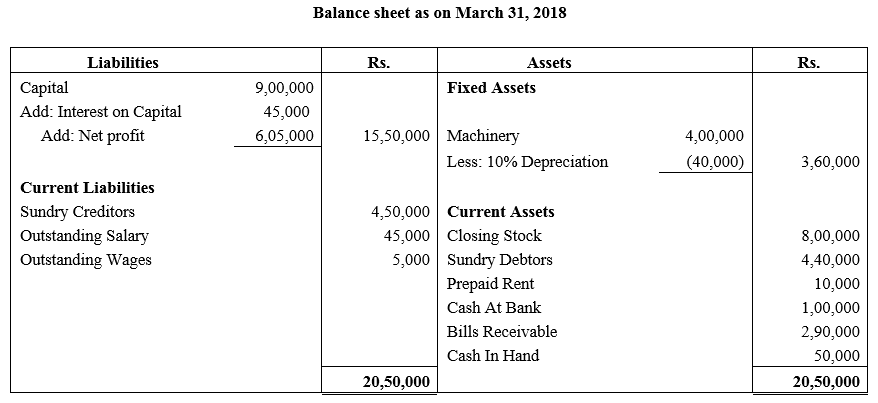
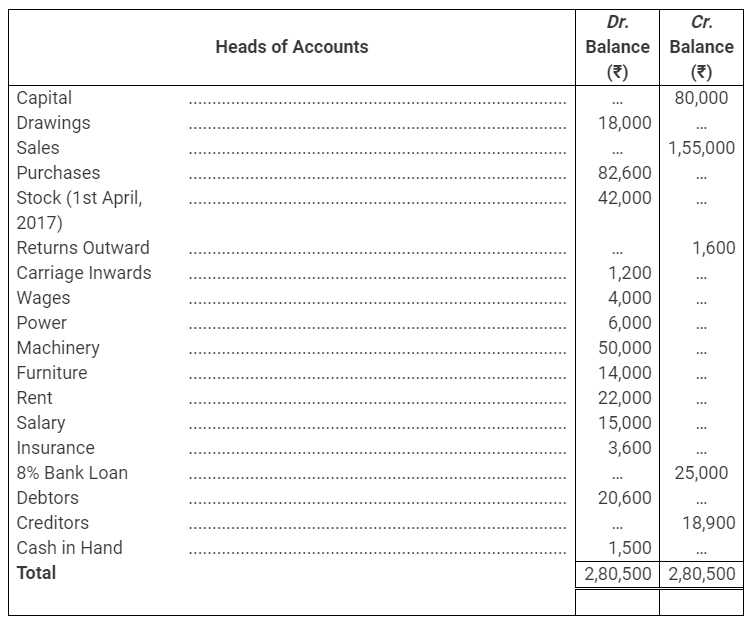
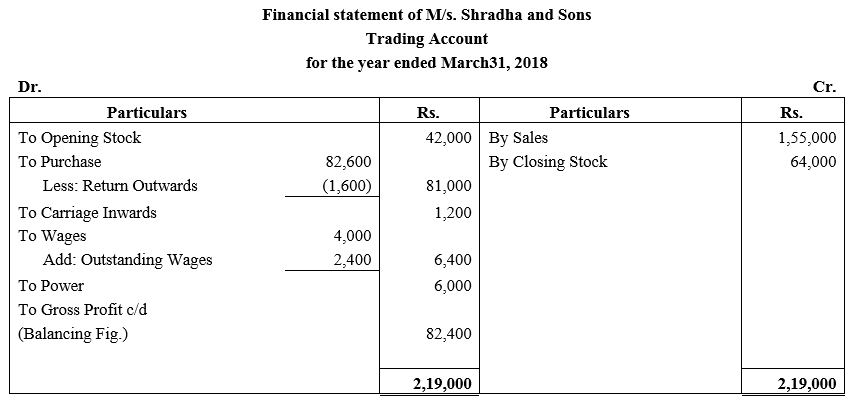
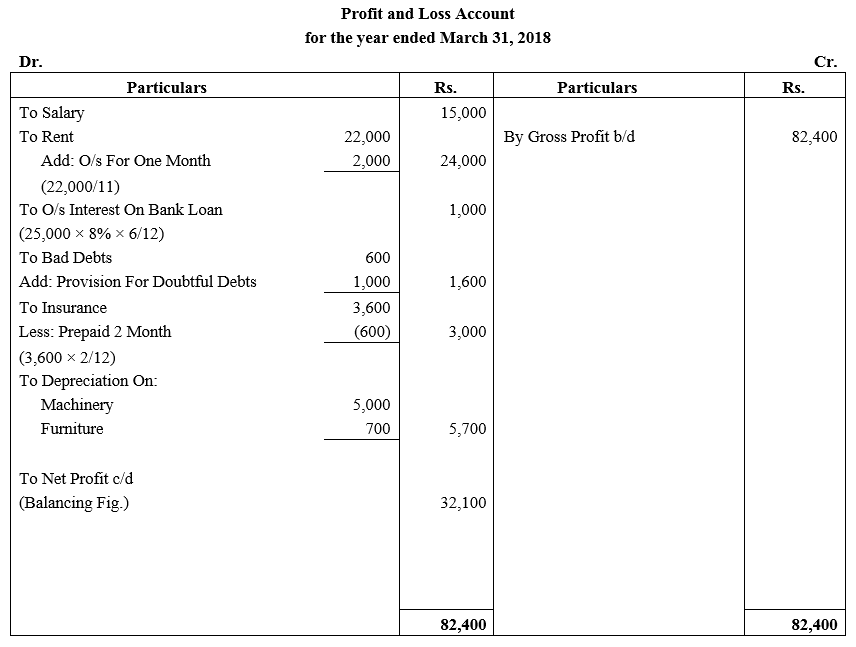
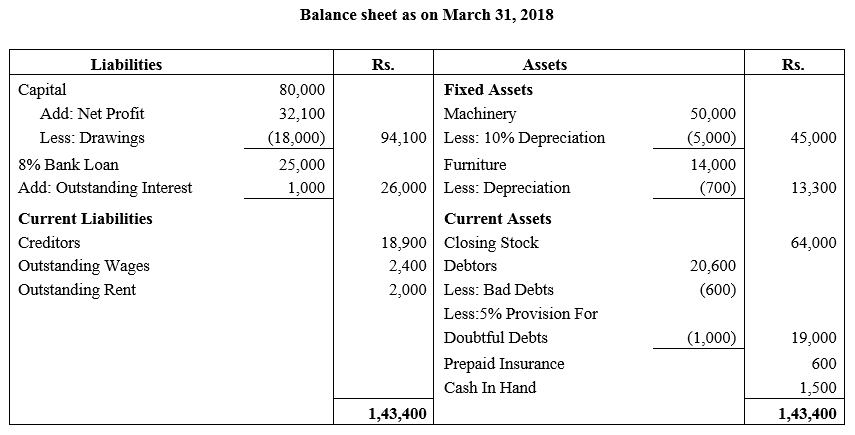
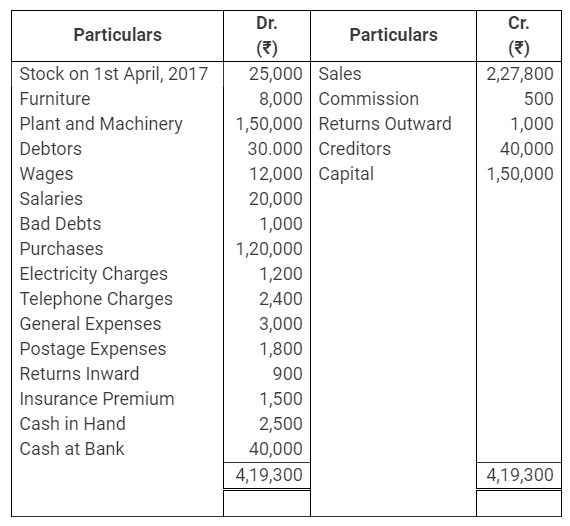
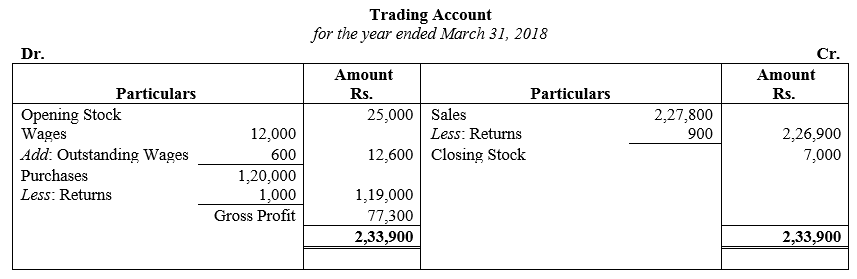
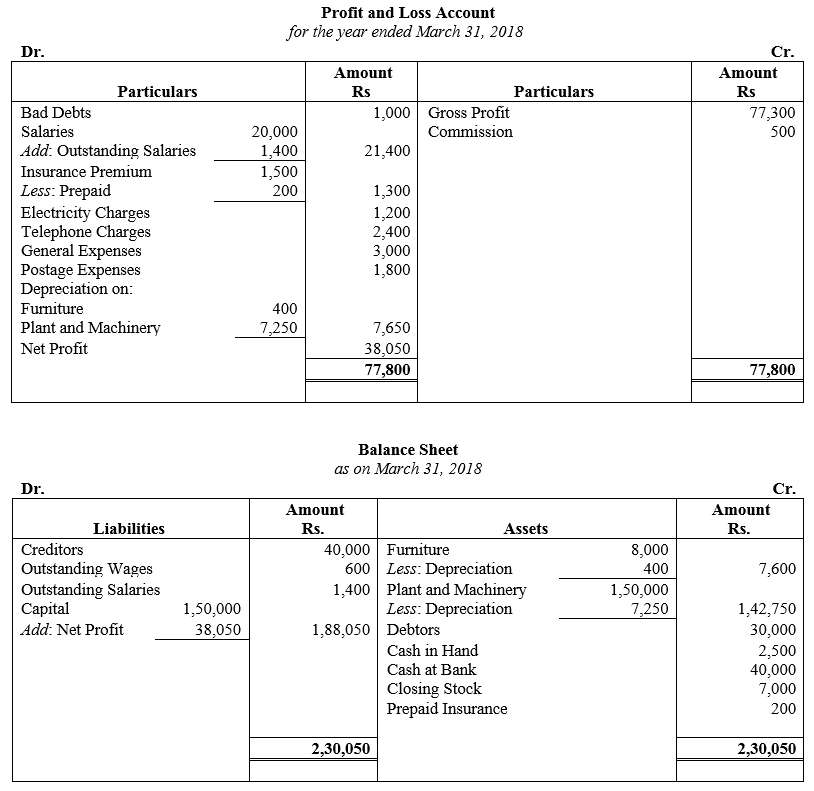
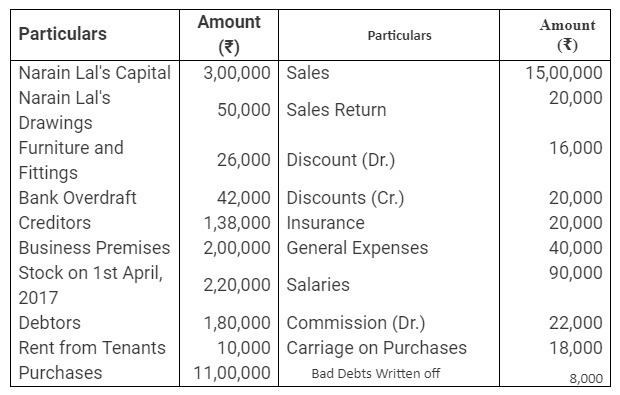
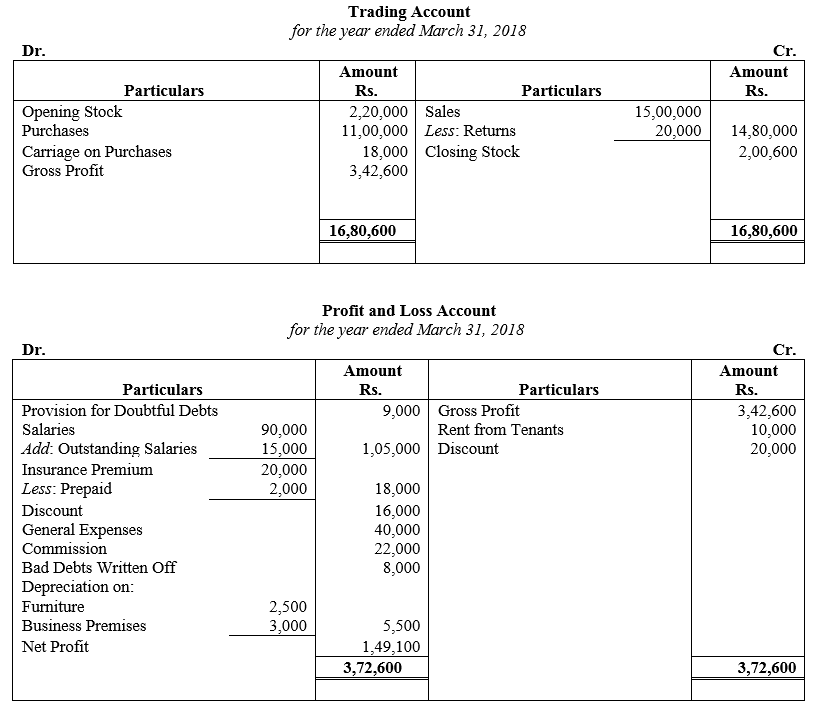
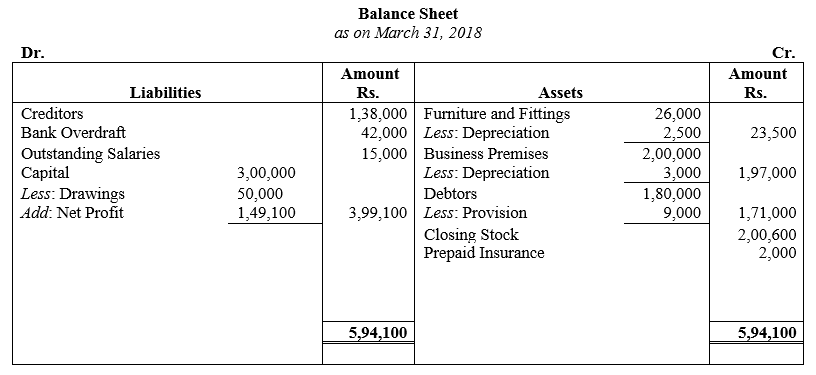
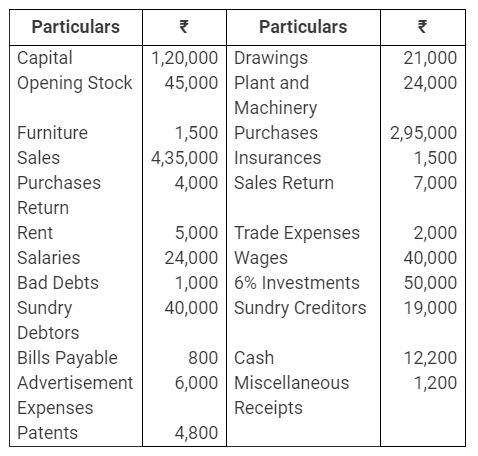
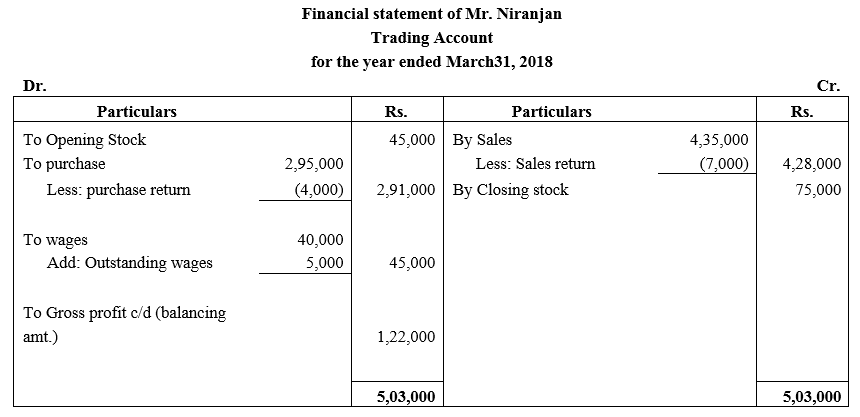
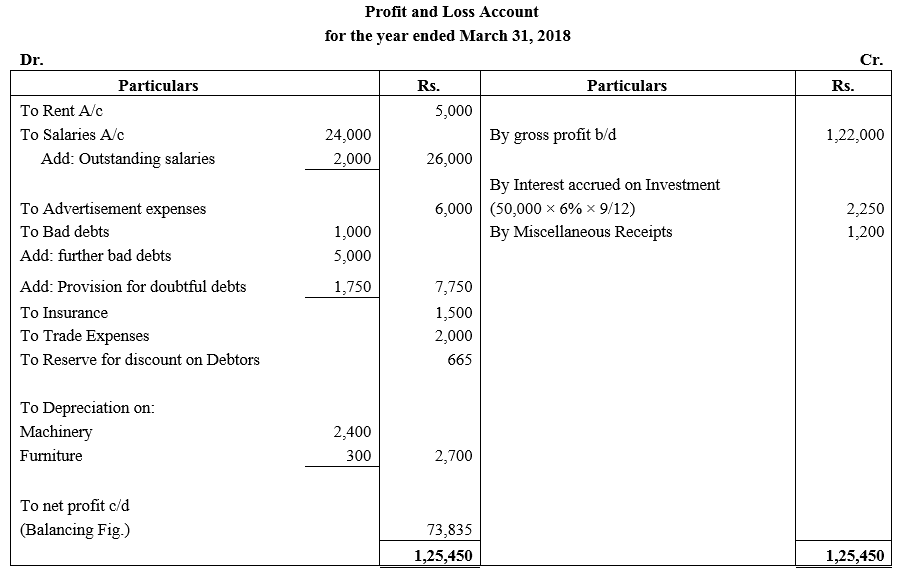
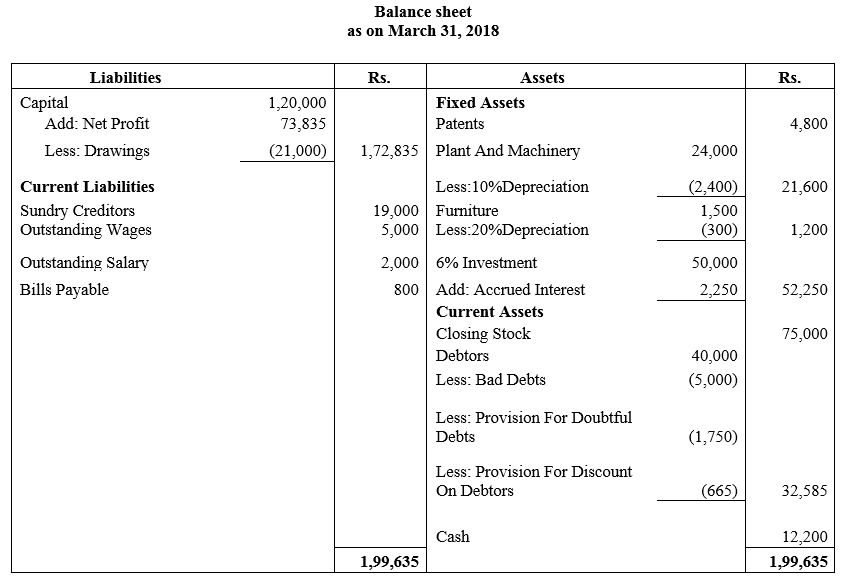
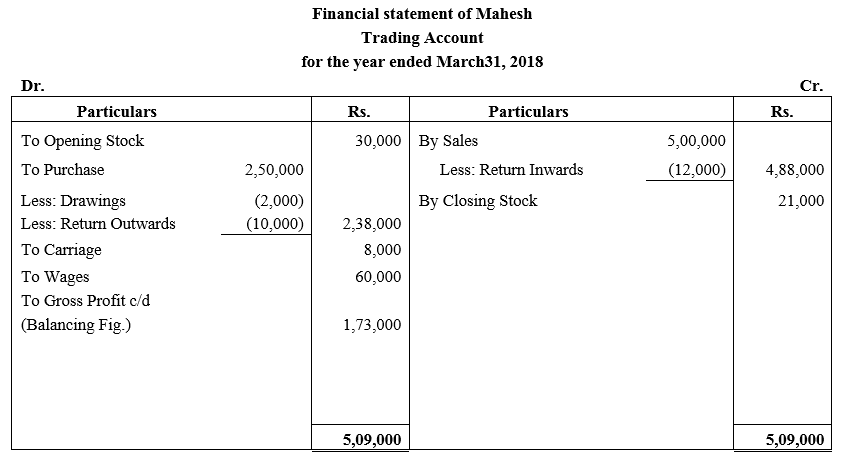
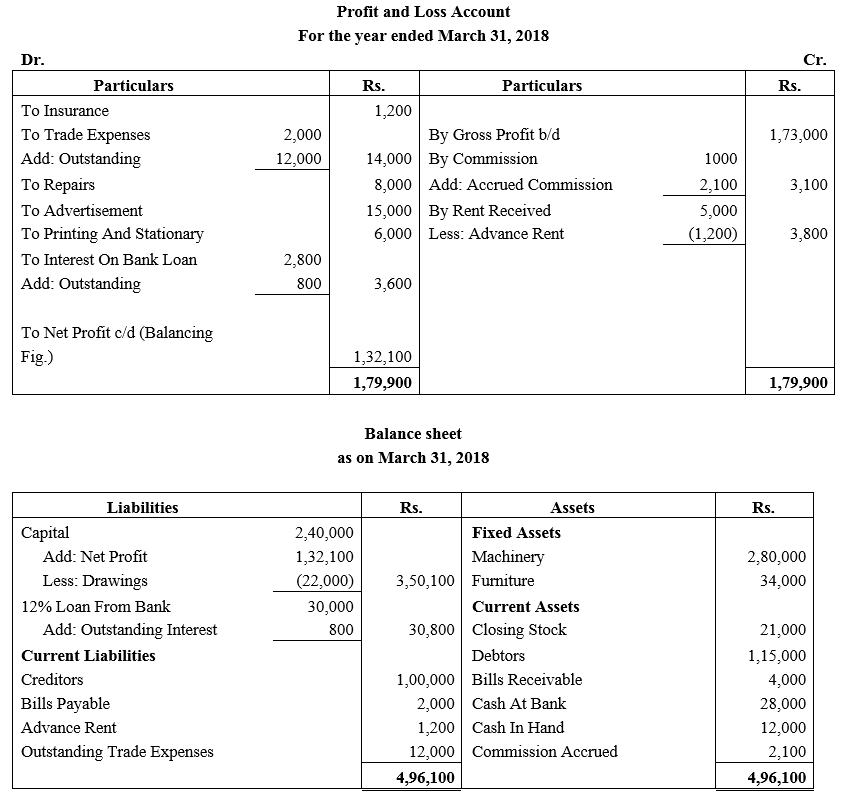
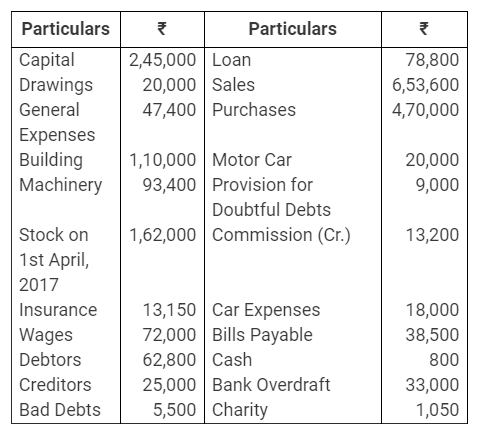
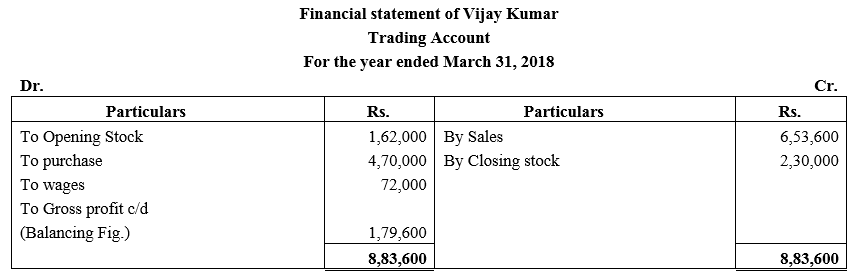
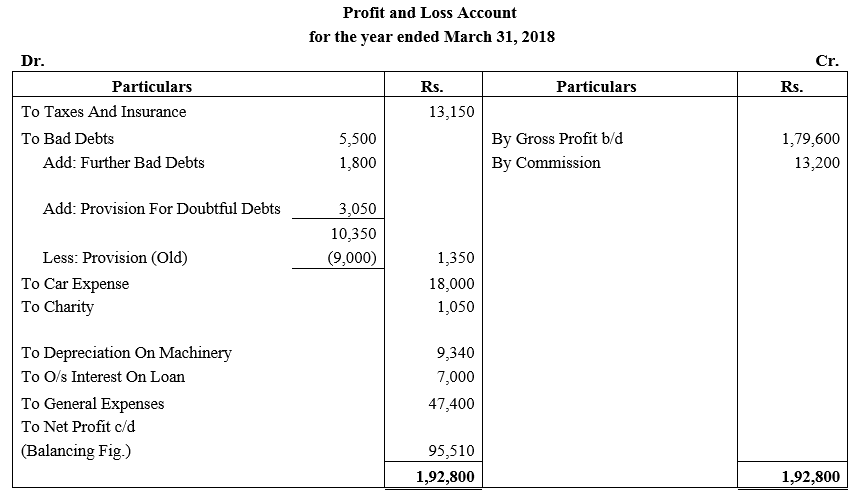
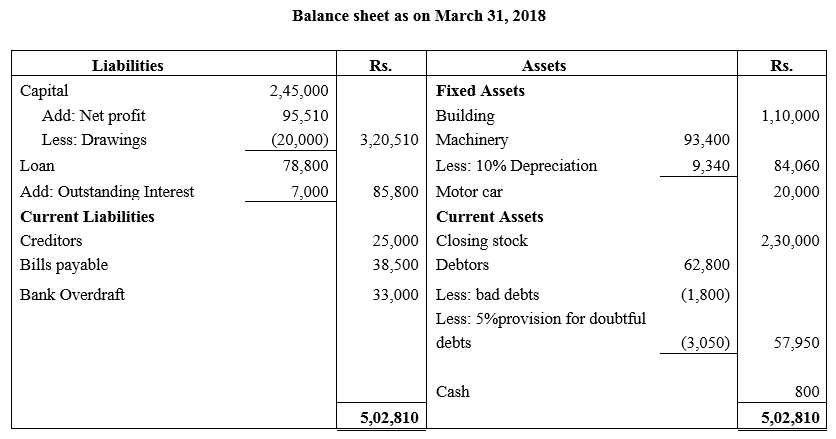
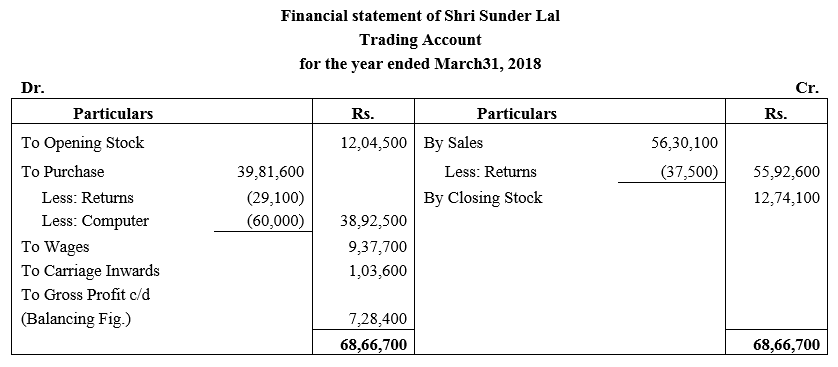
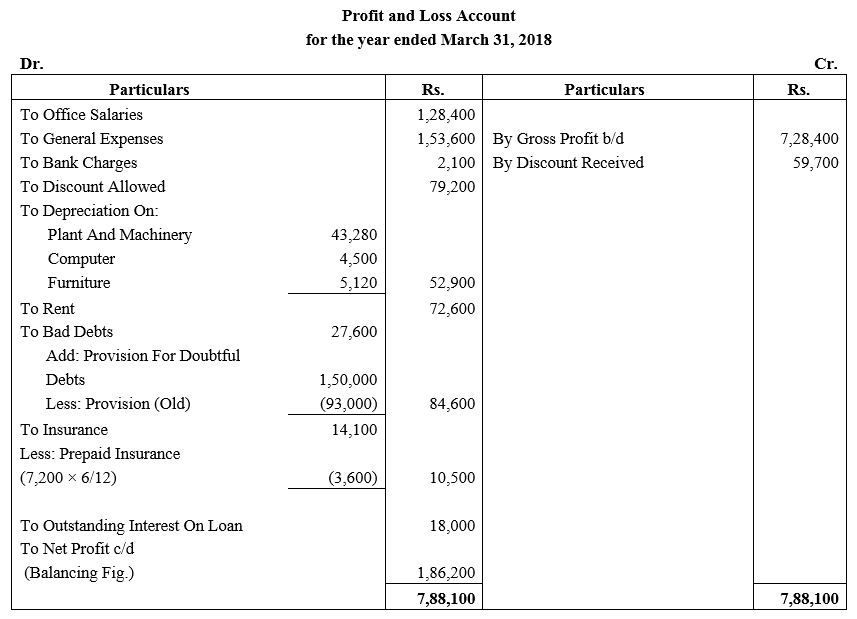
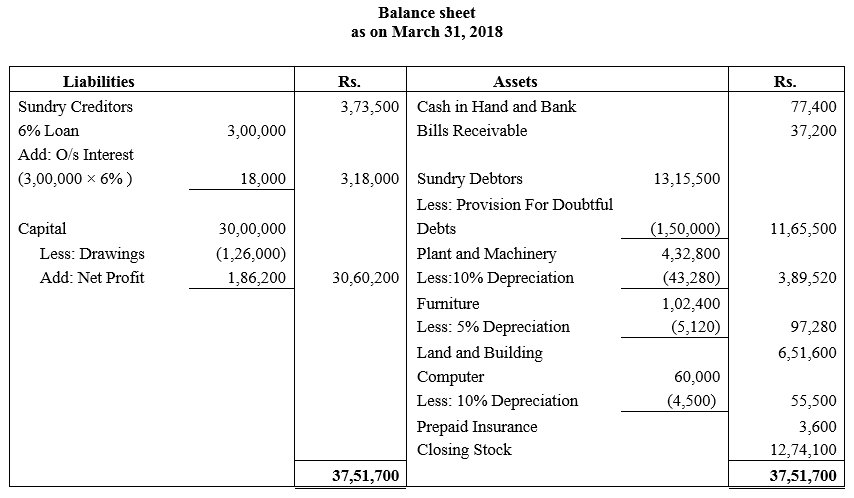
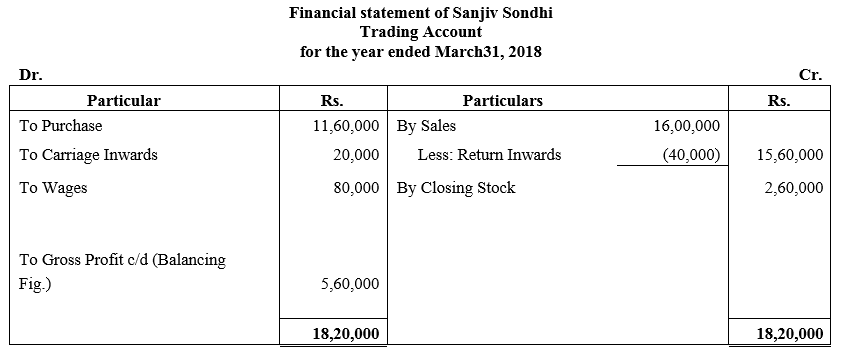
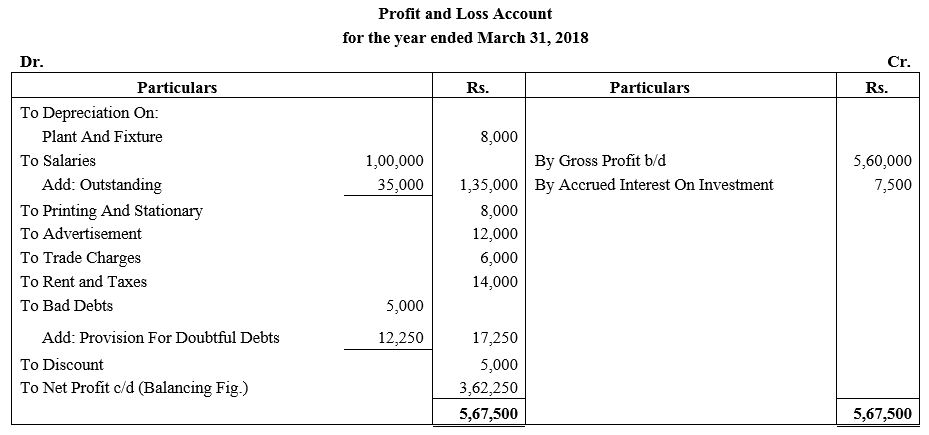
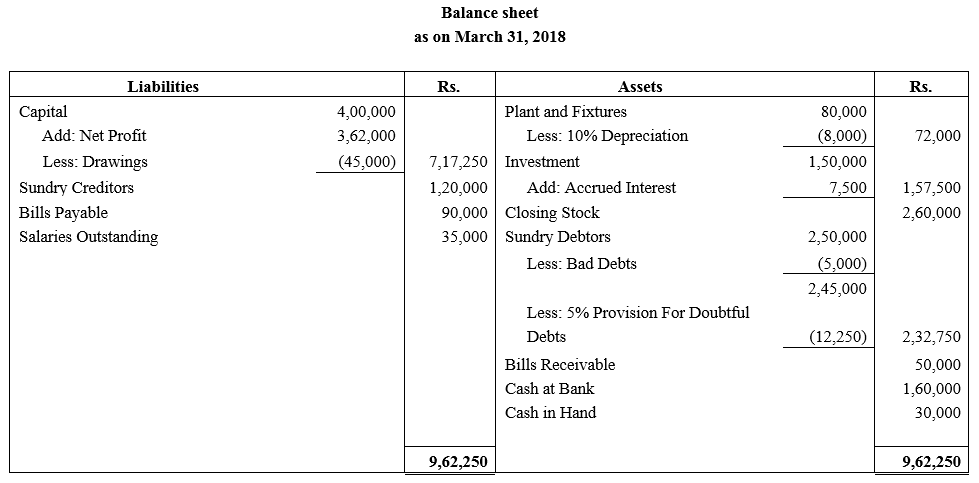
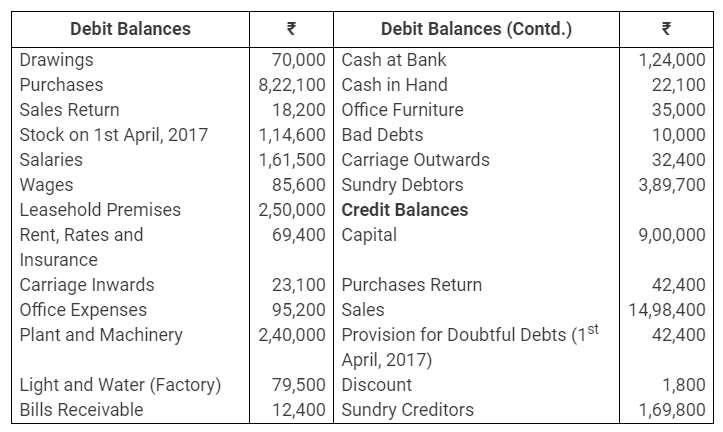
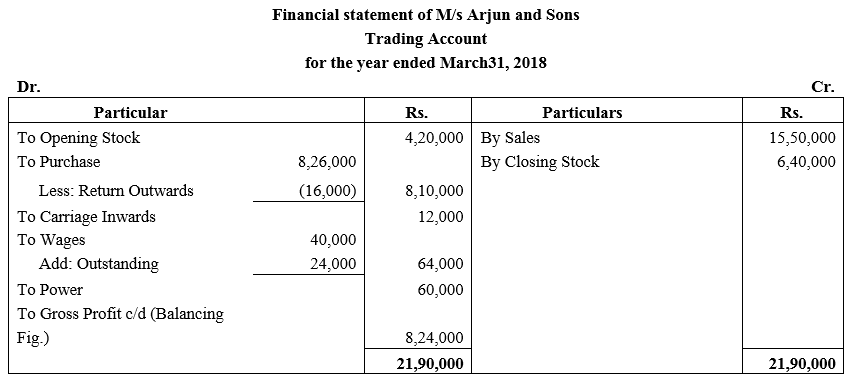
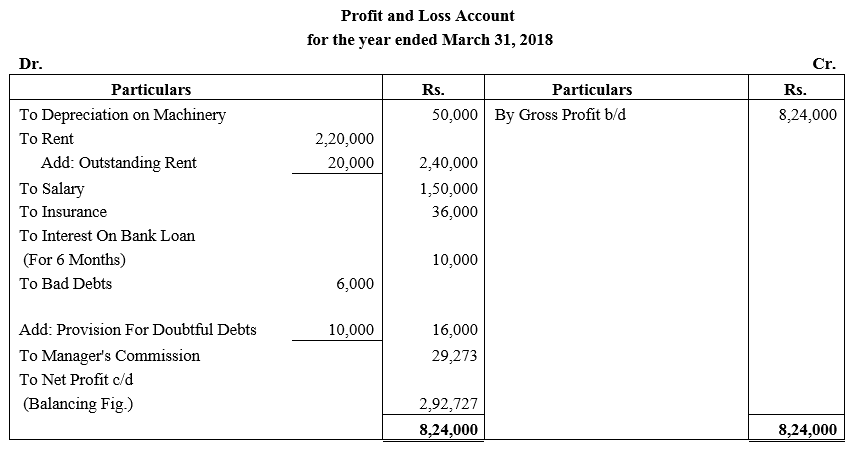
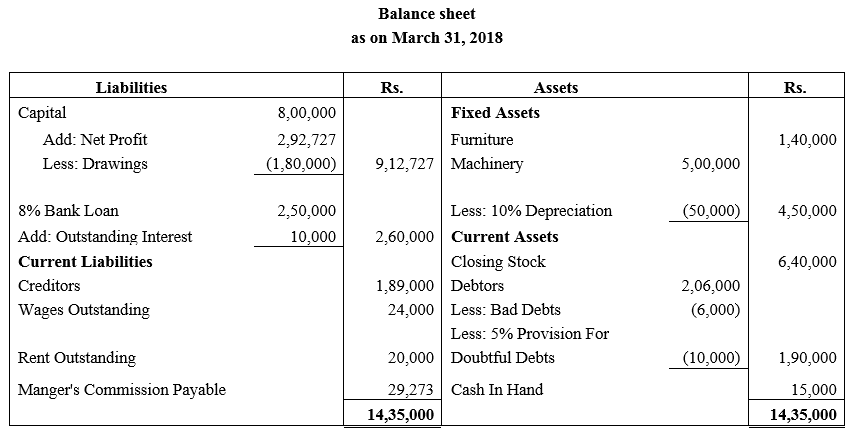
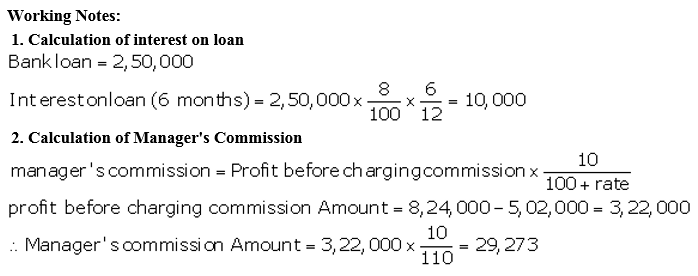
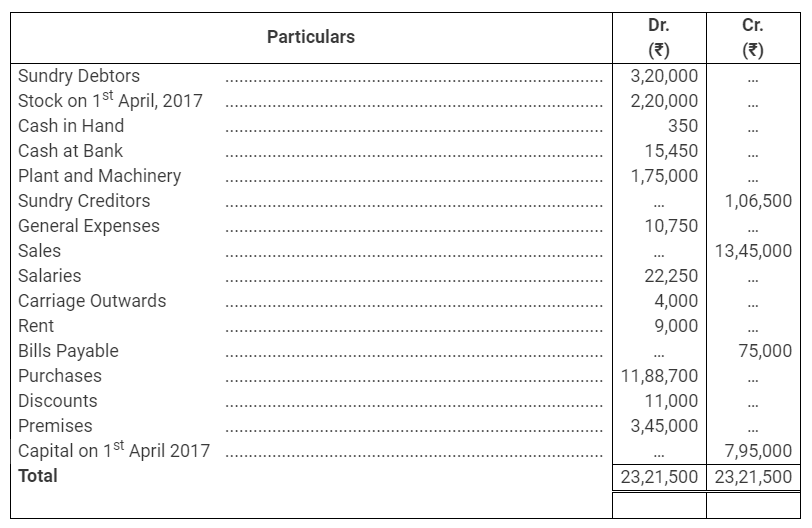
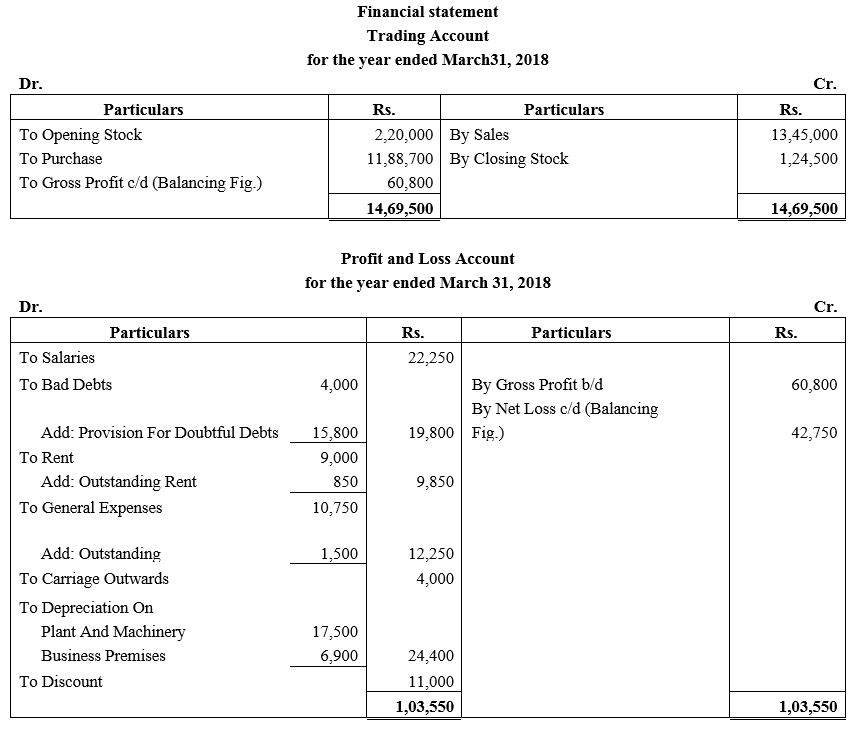
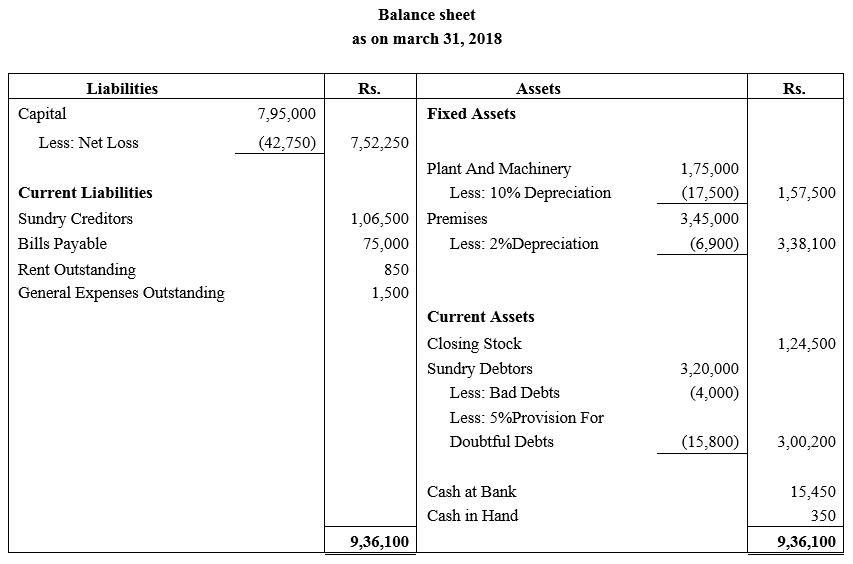
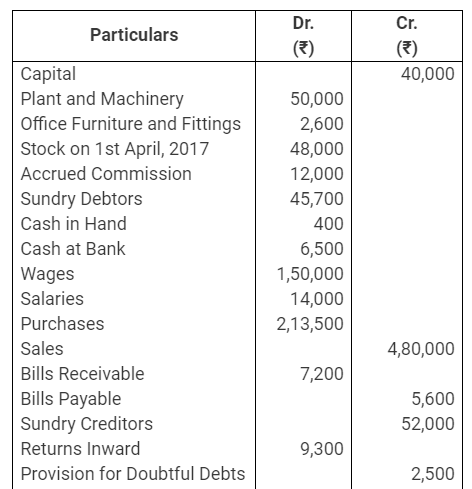
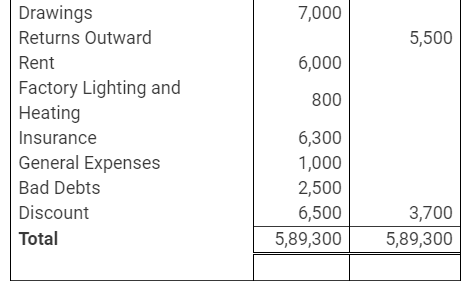
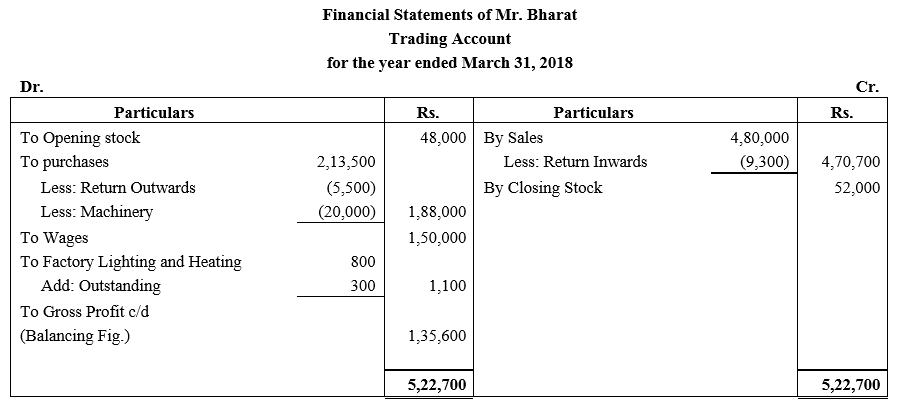
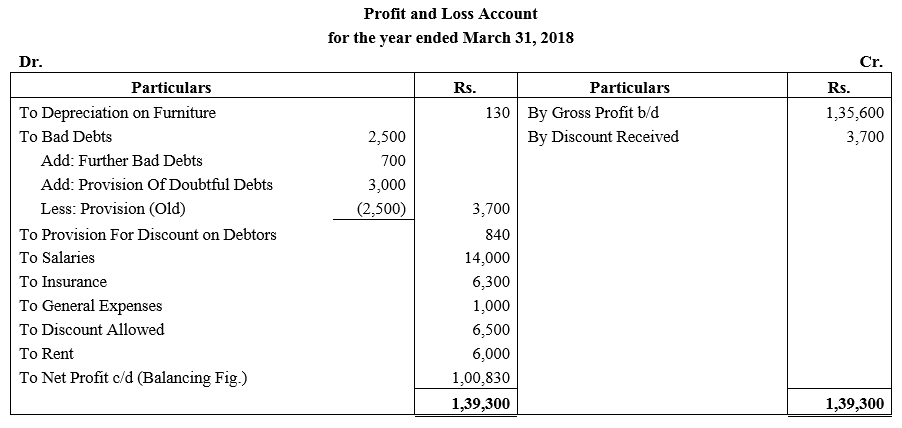
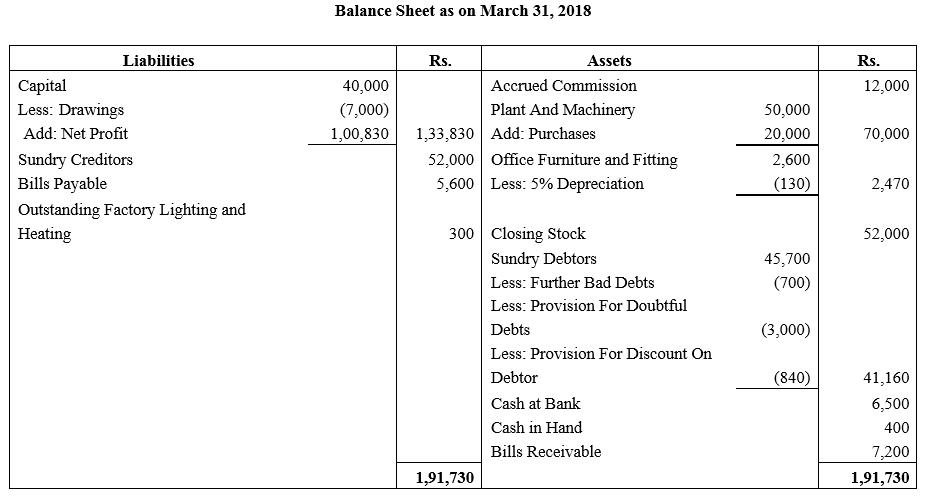
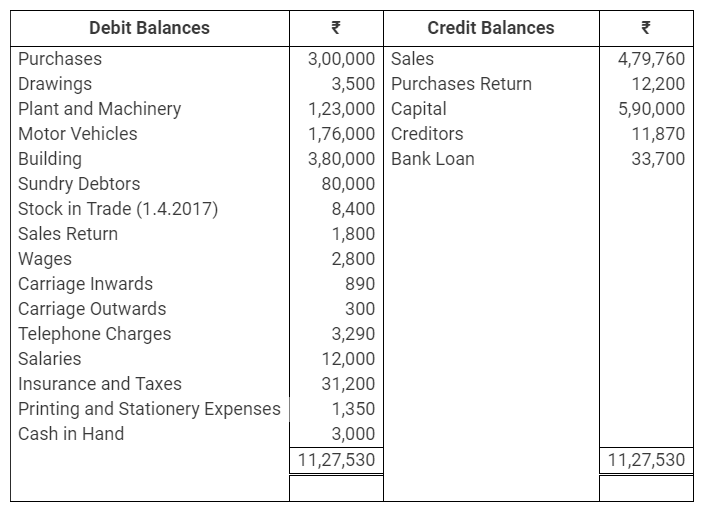
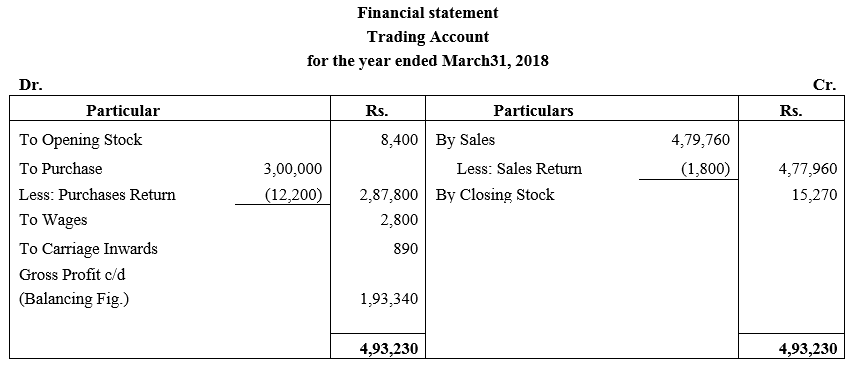
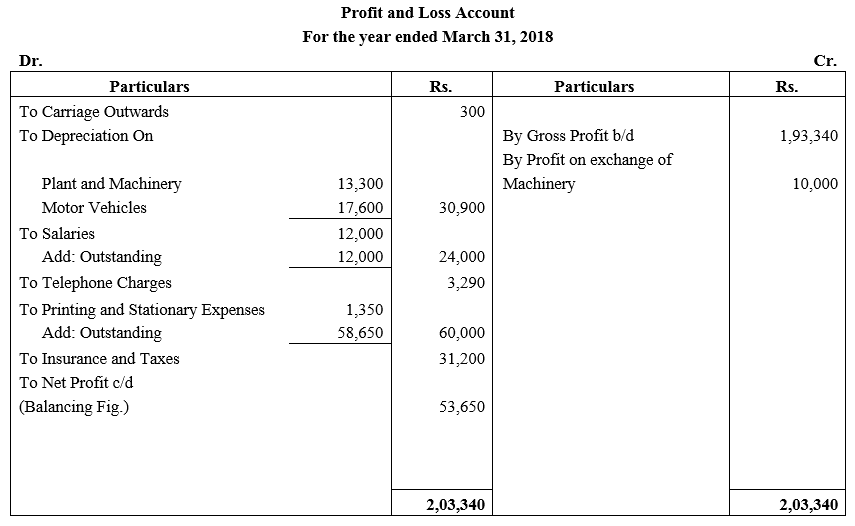
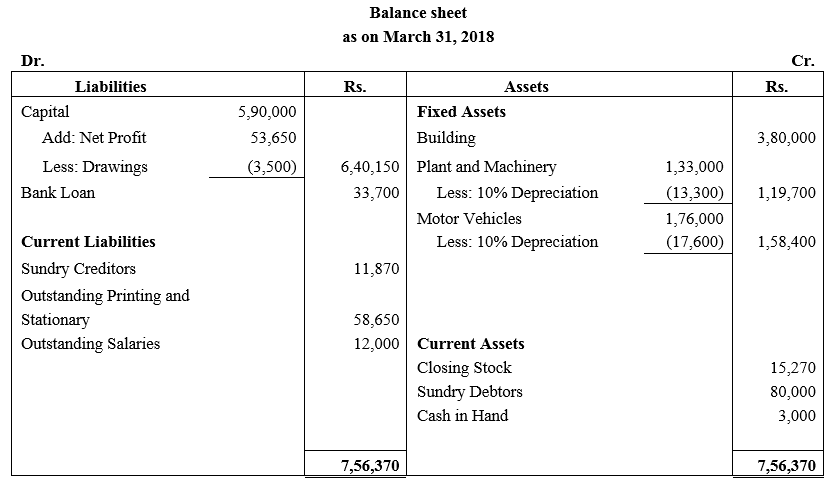
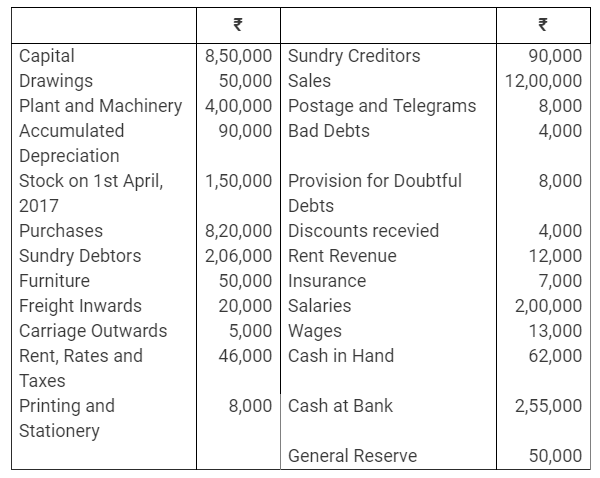
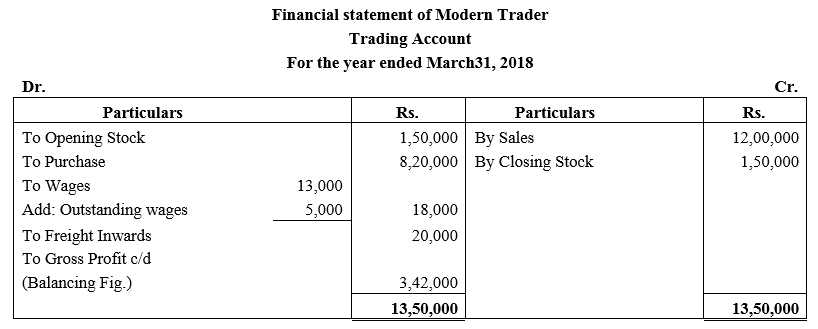
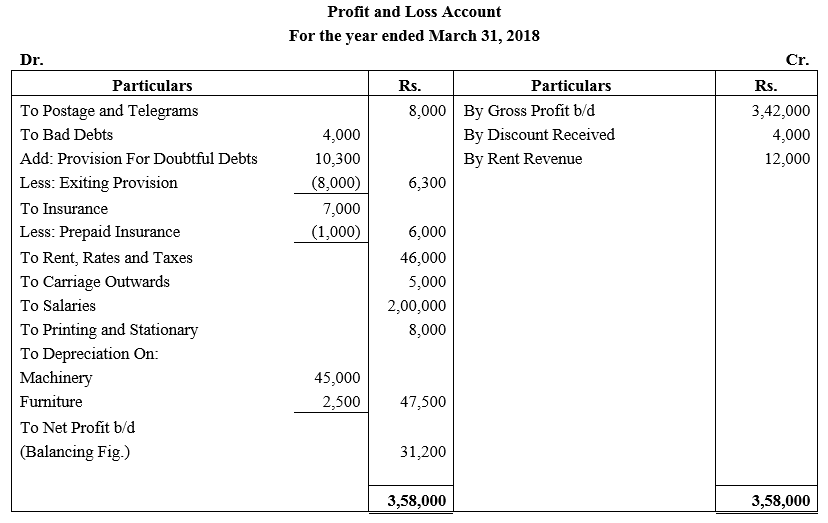
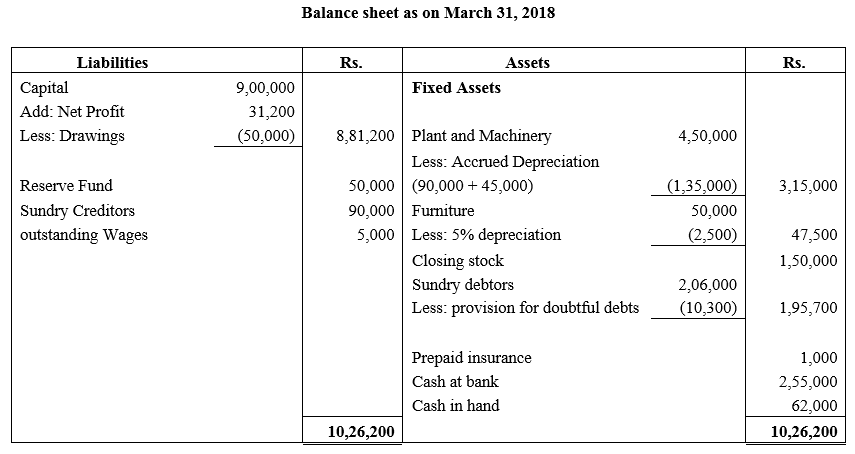
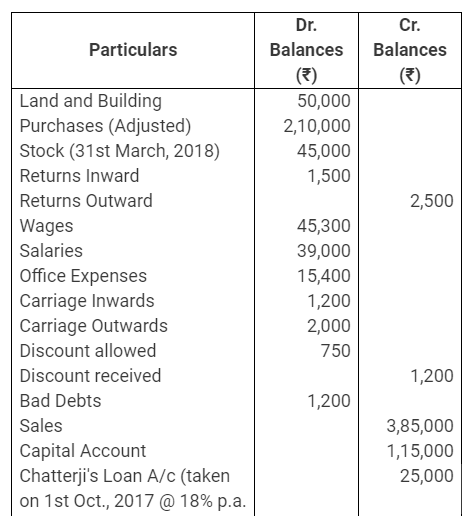
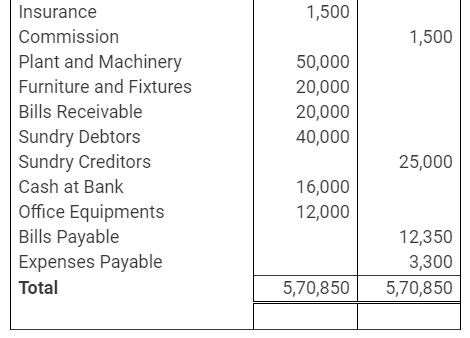
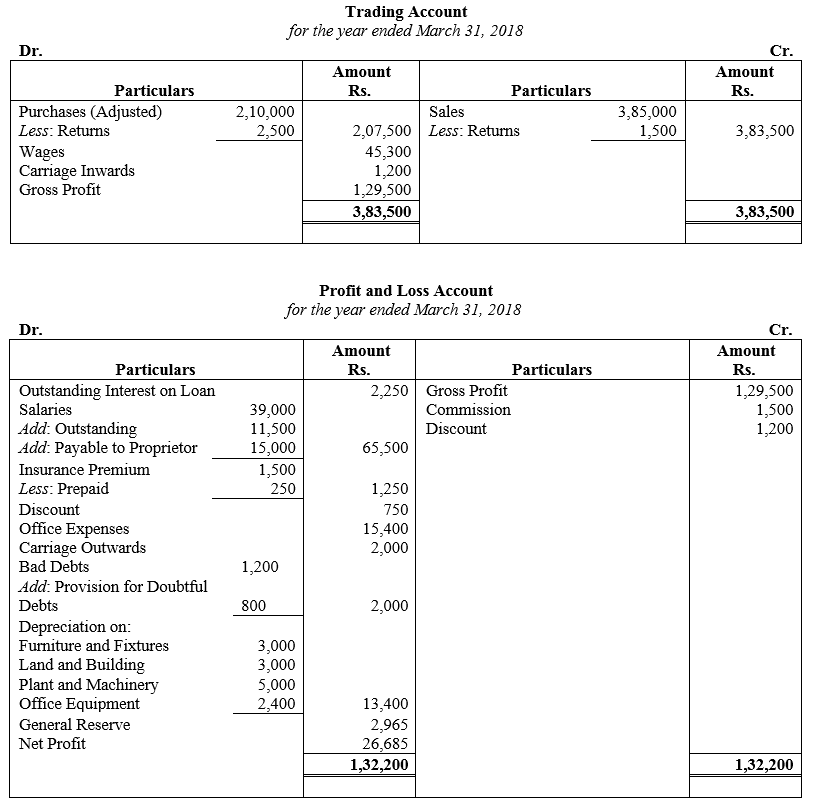
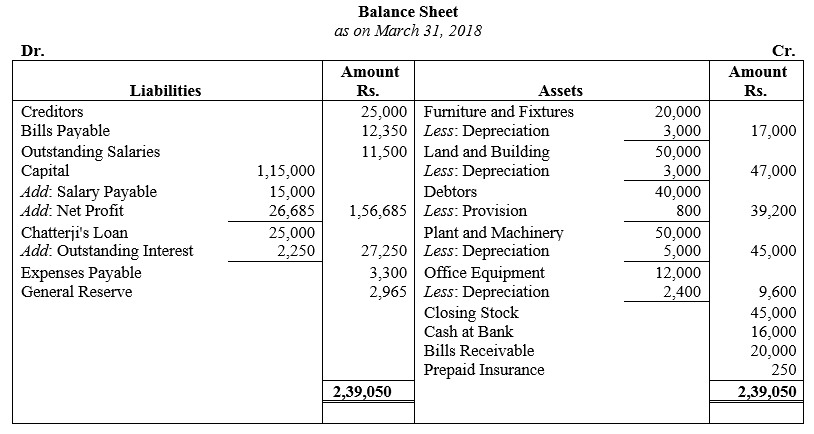
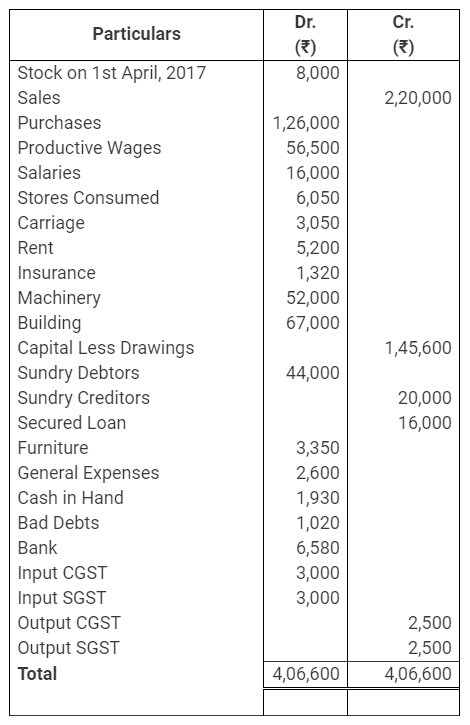
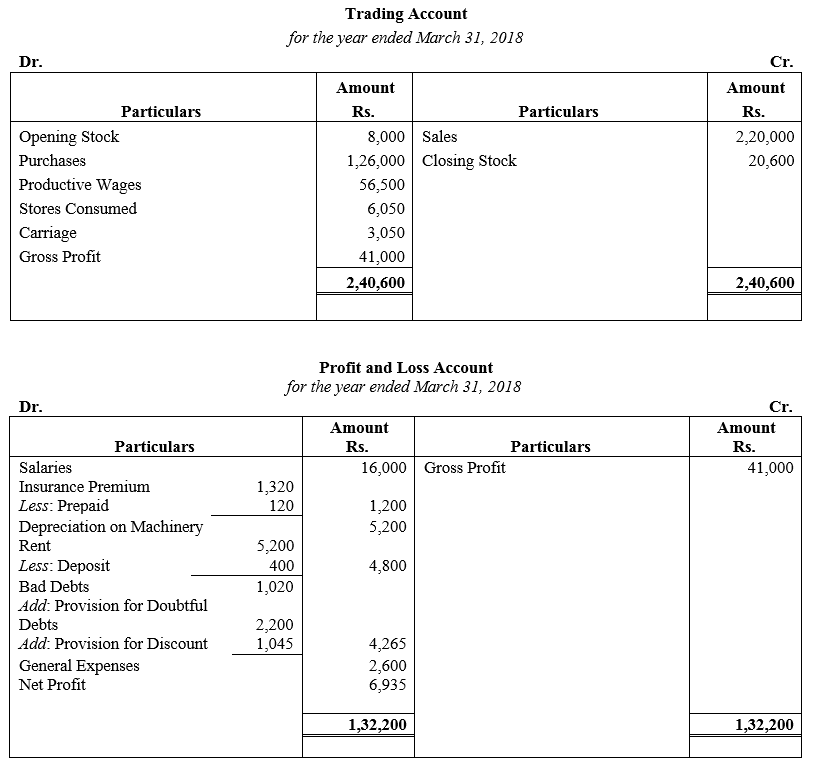
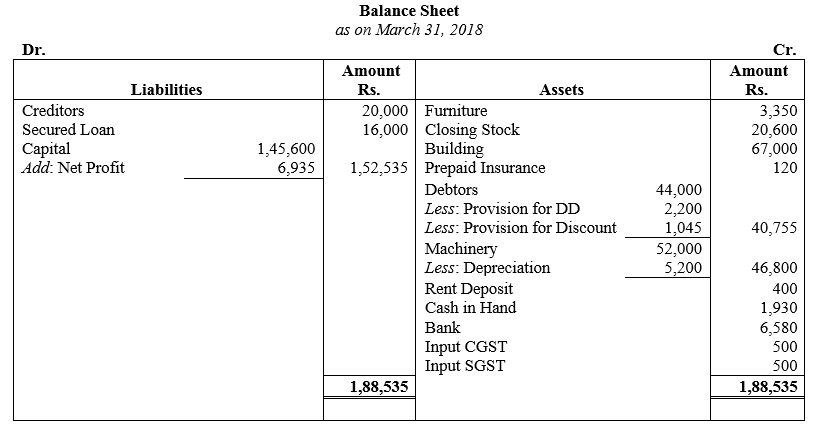
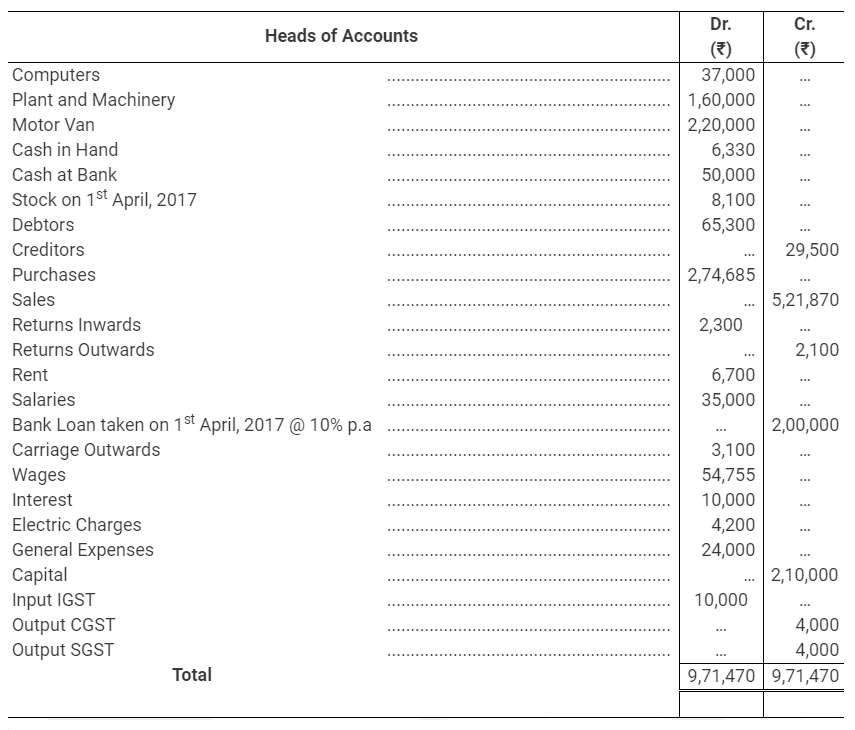
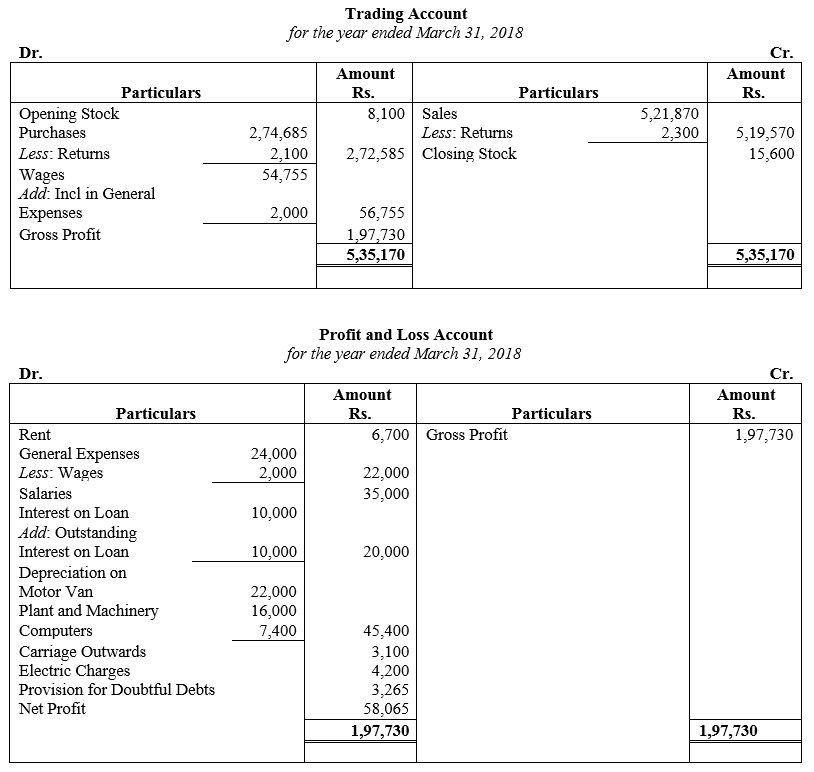
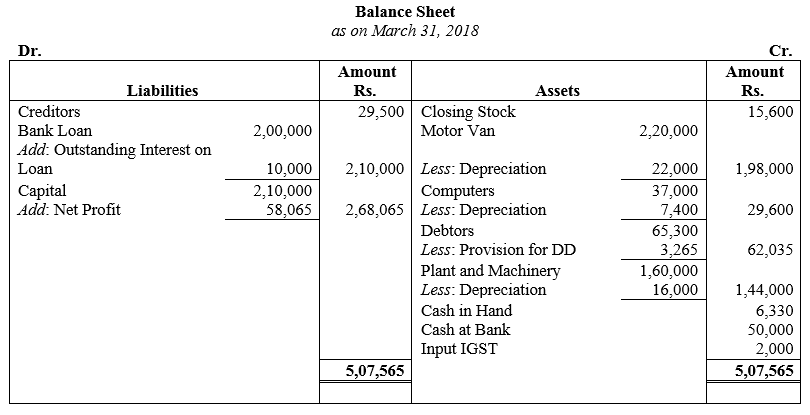
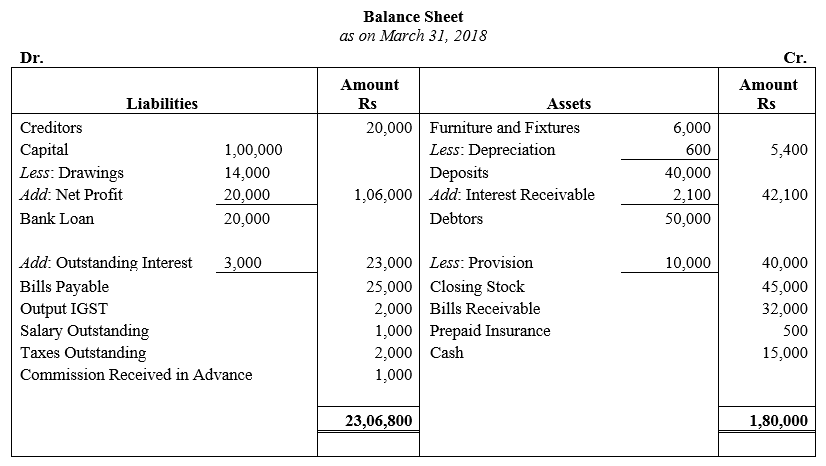
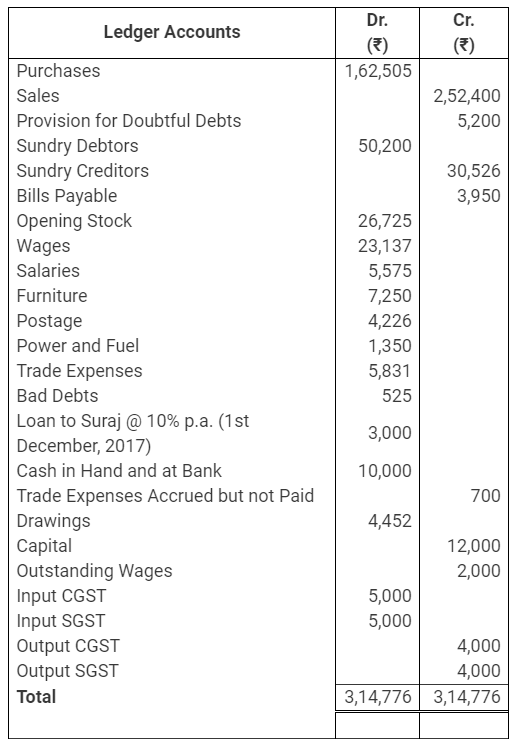
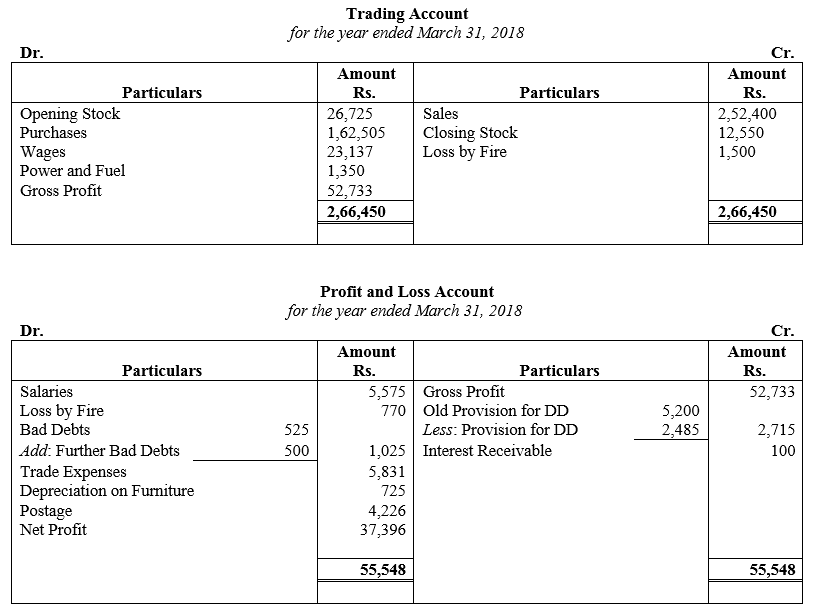
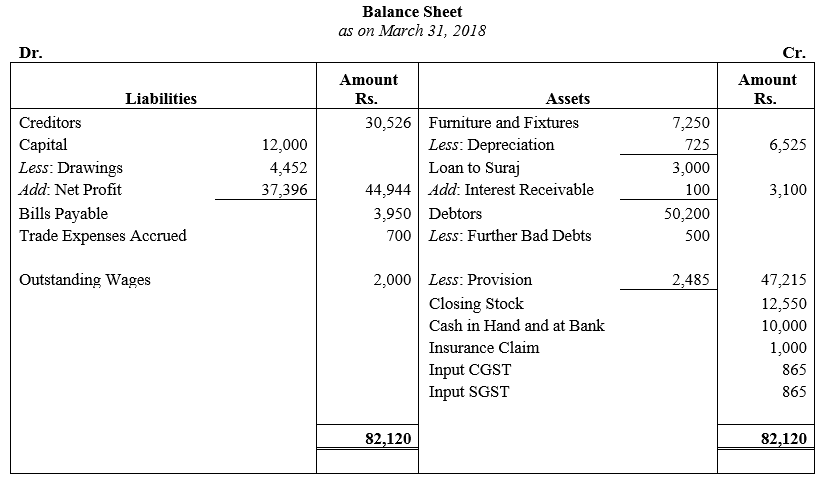
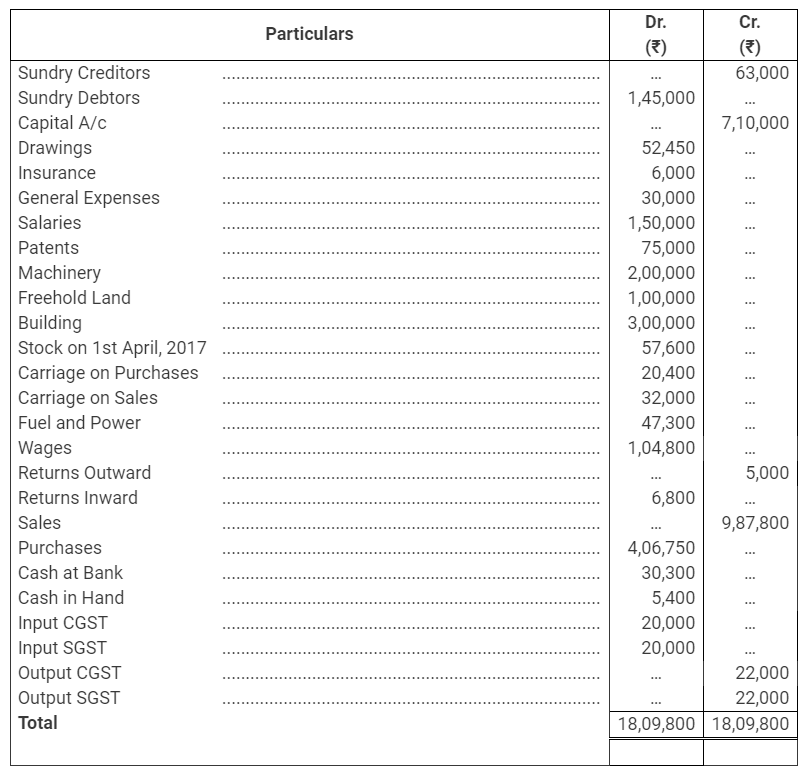
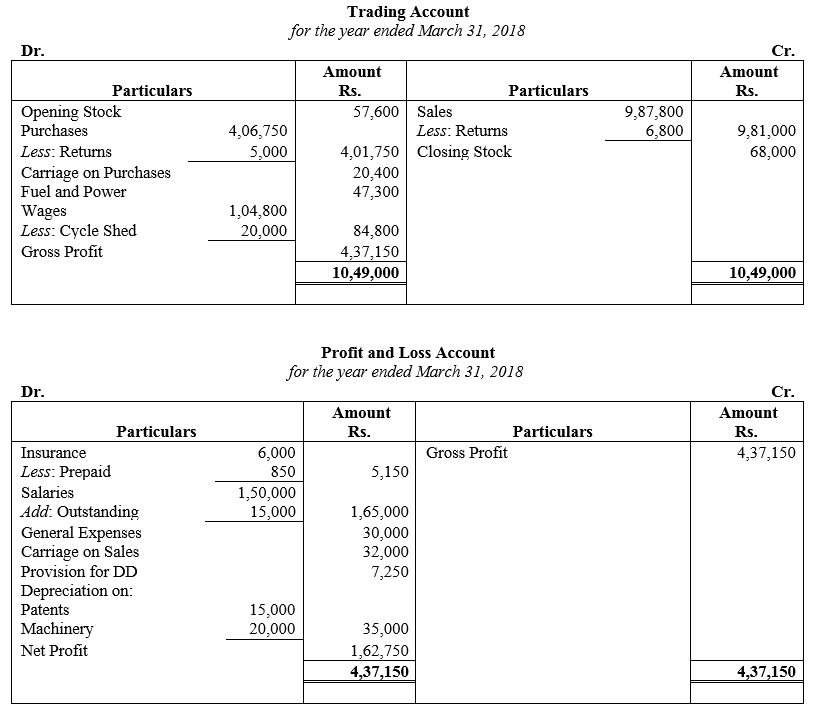
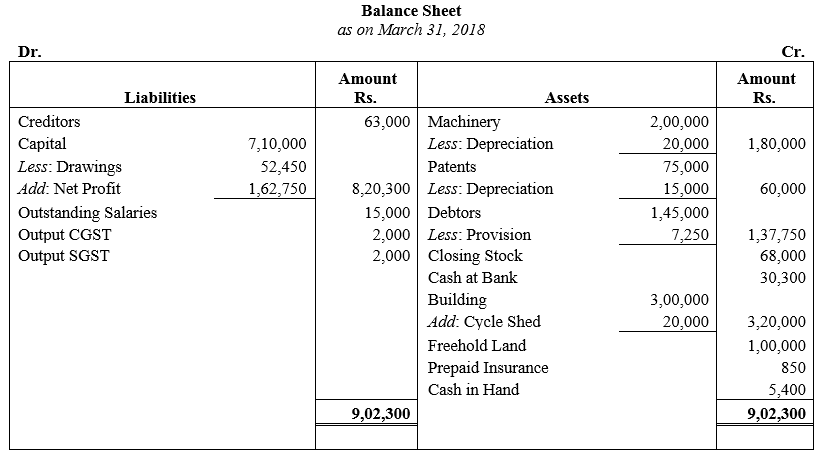
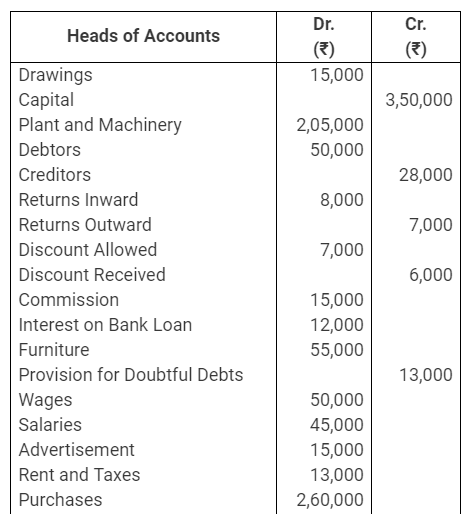
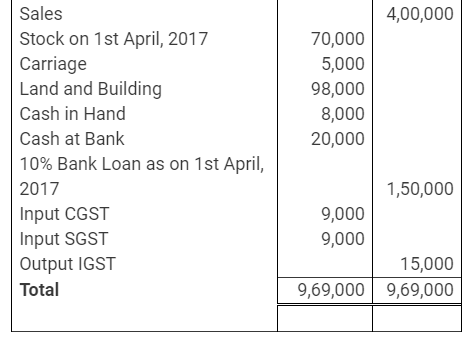
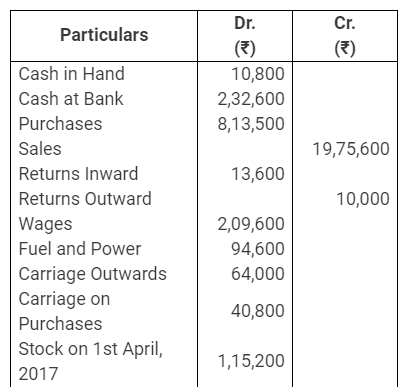
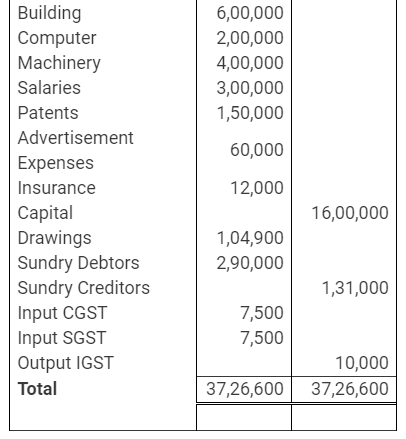
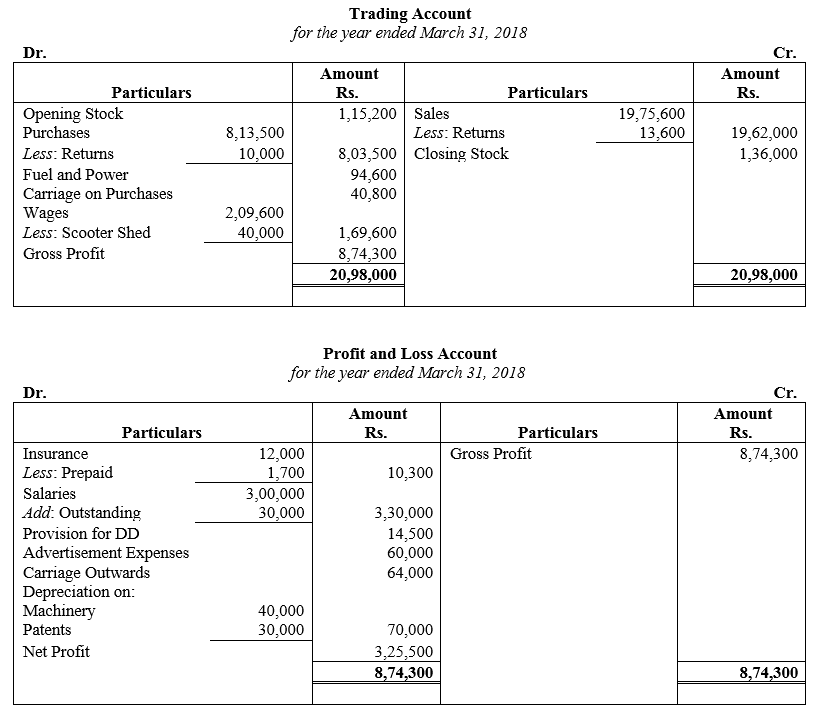
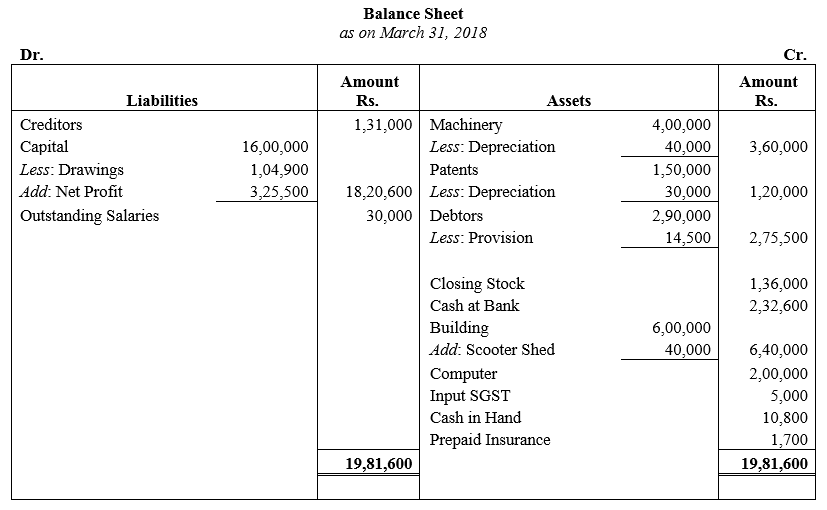
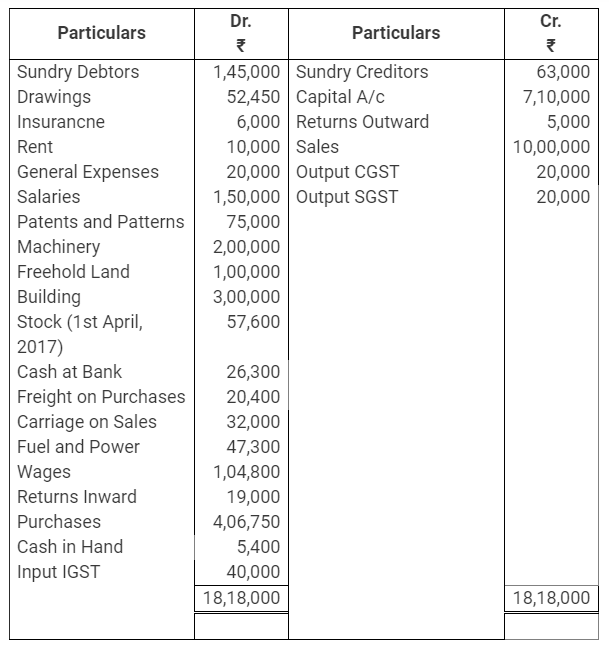
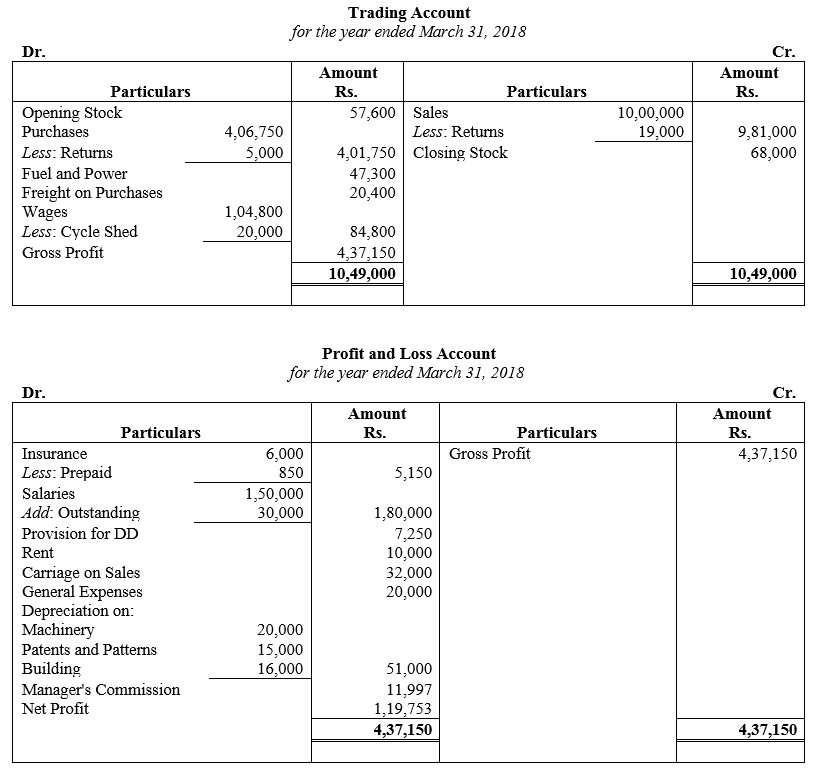
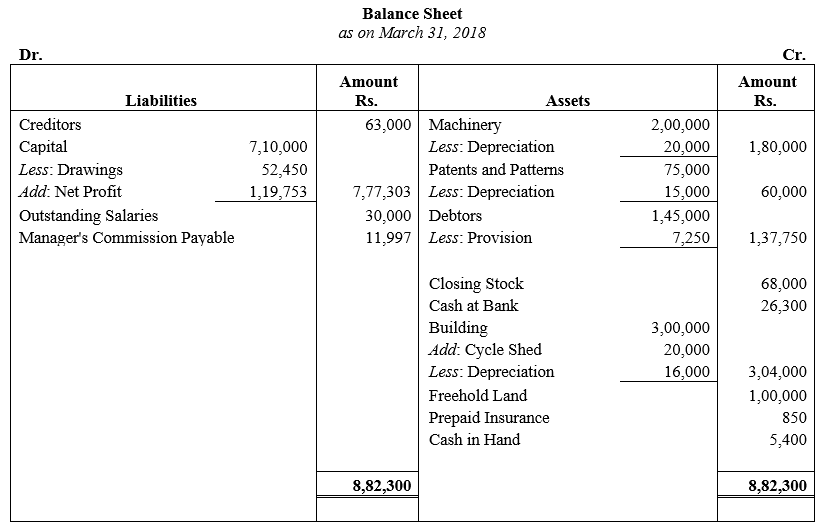
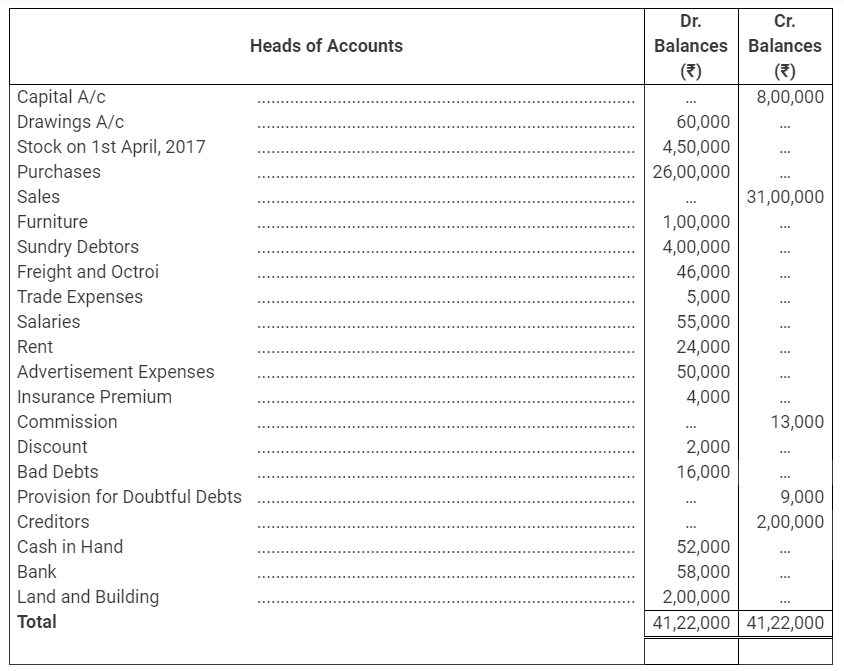
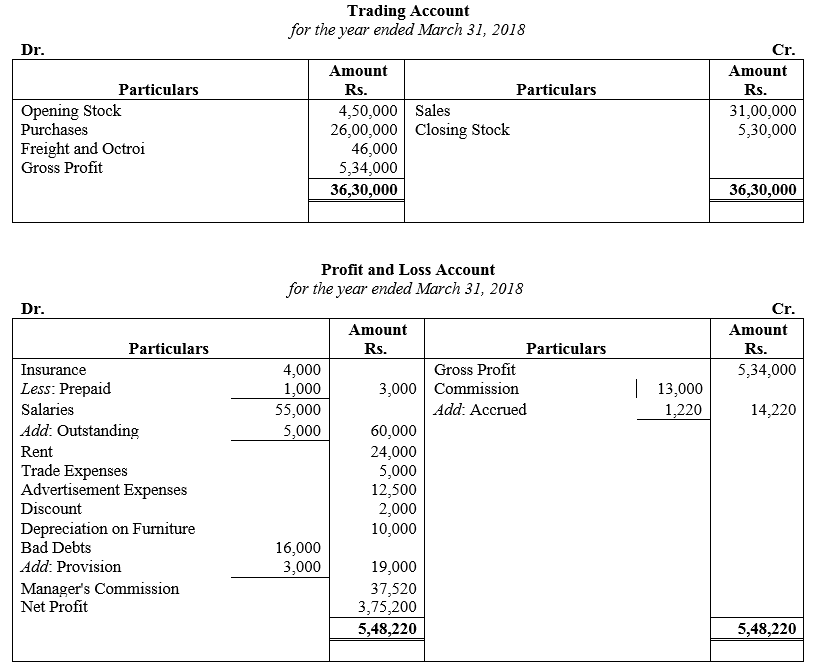
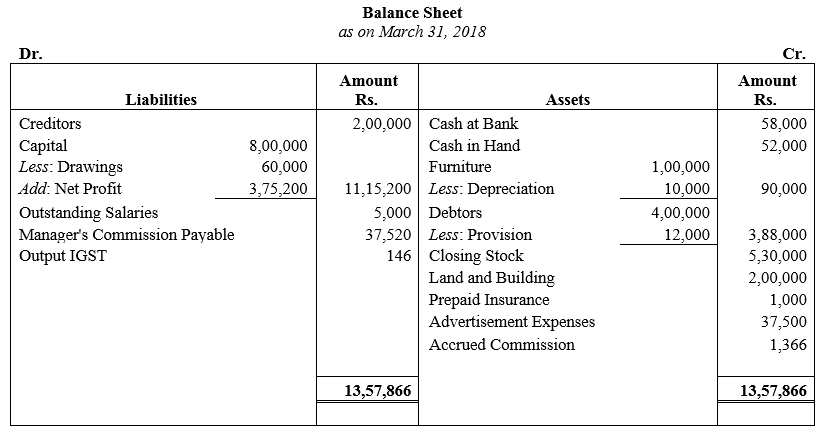
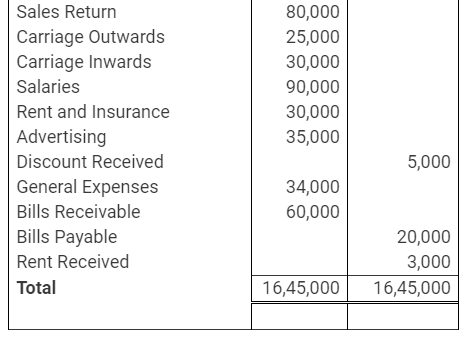
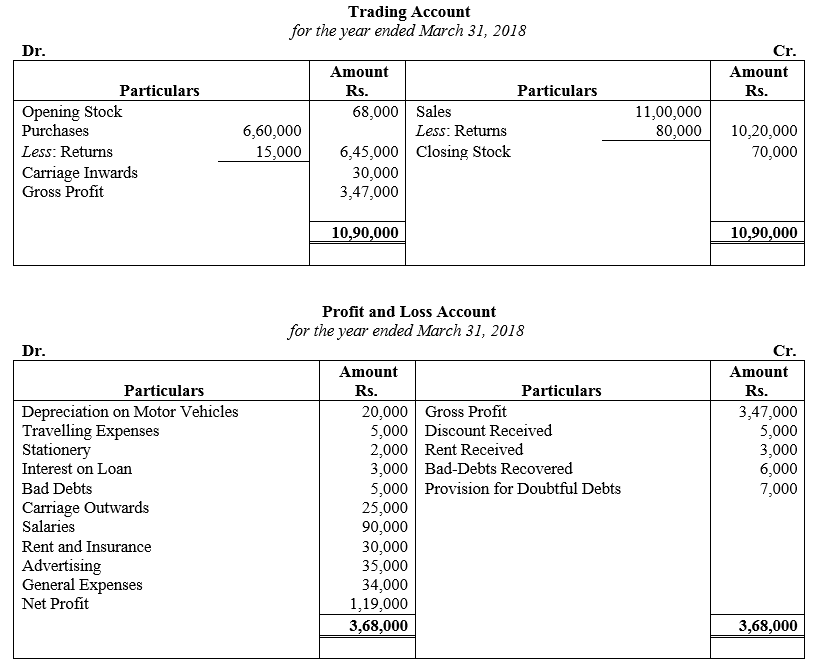
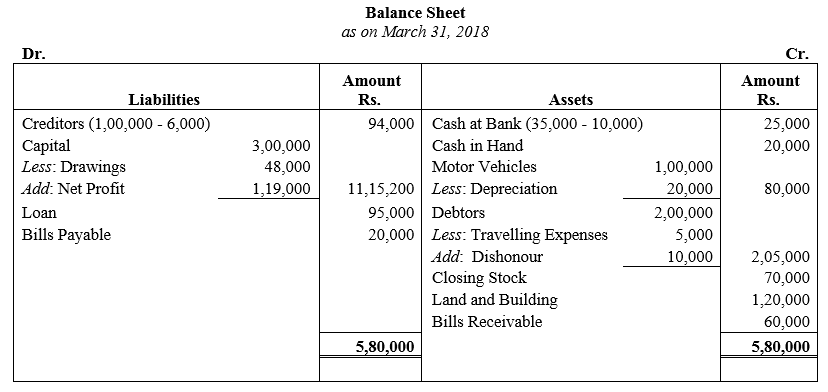
 During the year, he withdrew ₹ 2,500 per month for dometstic purposes. He also borrowed from a friend at 9% a sum of ₹ 20,000 on 1st October, 2017. He has not yet paid the interest. A provision of 5% on debotrs for doubtful debts is to be made.
During the year, he withdrew ₹ 2,500 per month for dometstic purposes. He also borrowed from a friend at 9% a sum of ₹ 20,000 on 1st October, 2017. He has not yet paid the interest. A provision of 5% on debotrs for doubtful debts is to be made.


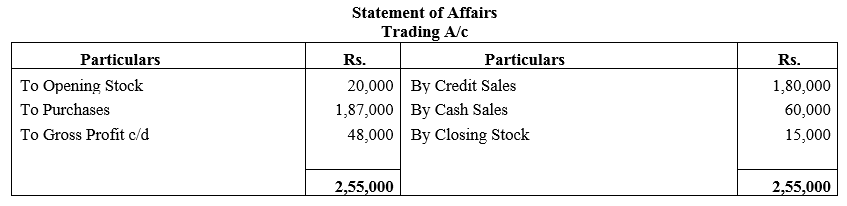
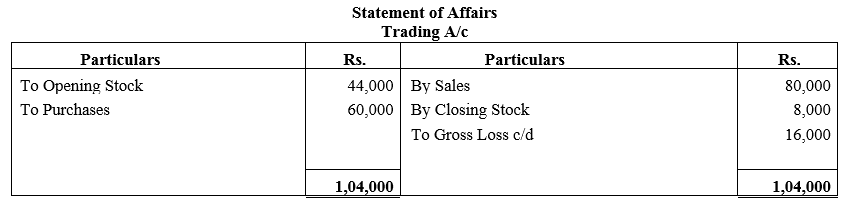
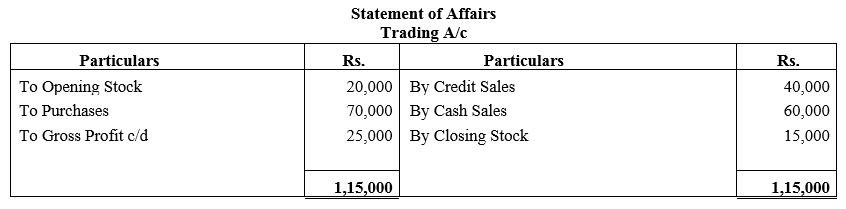
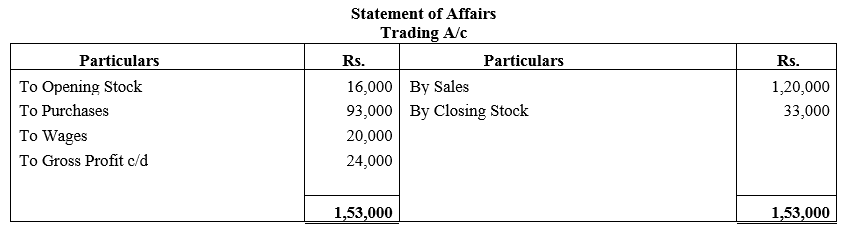

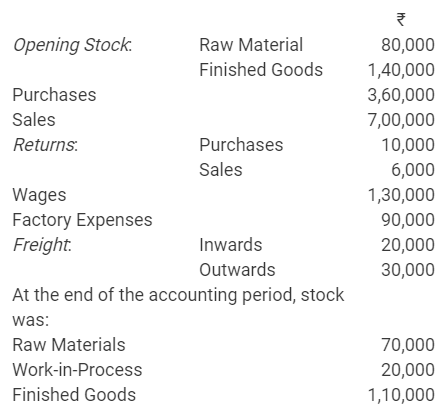
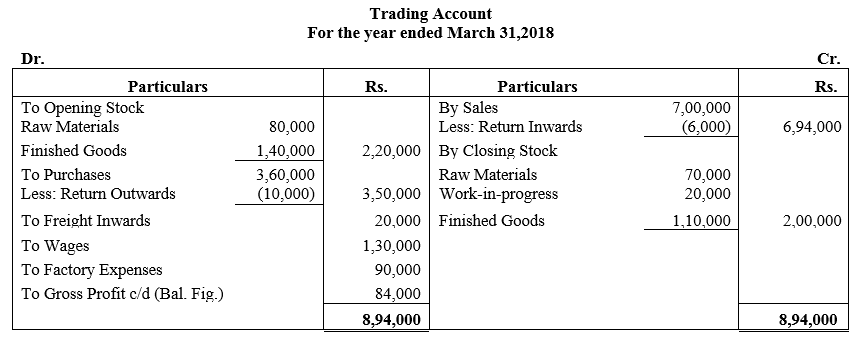
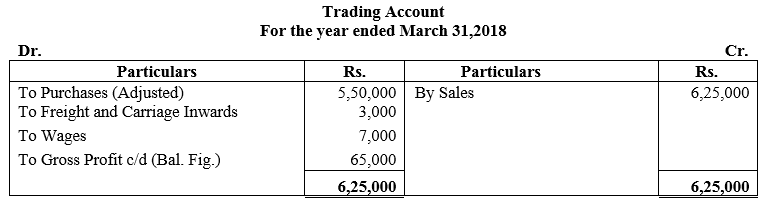
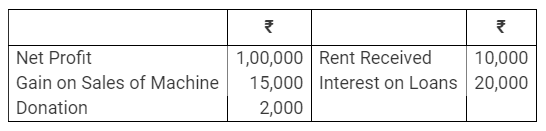
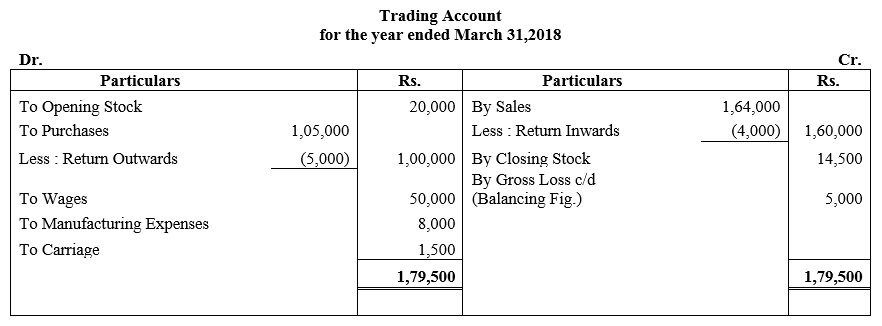
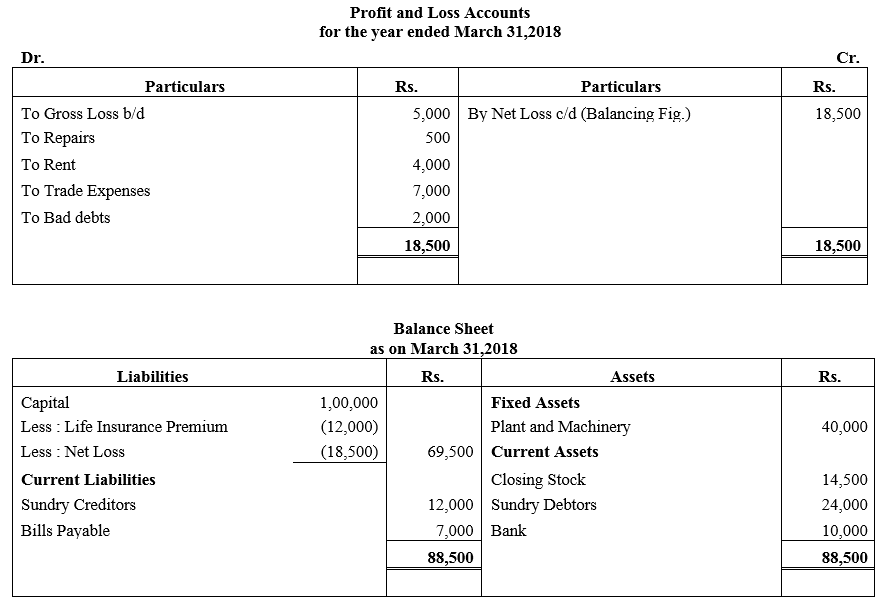
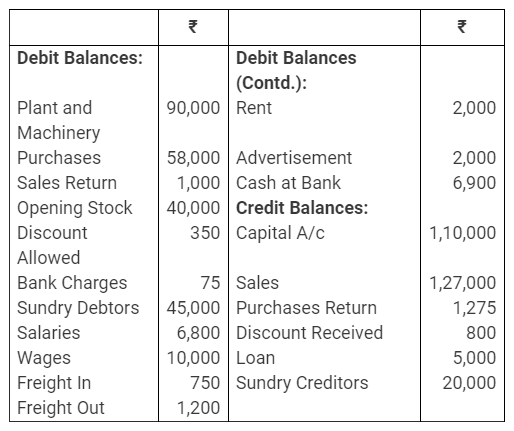
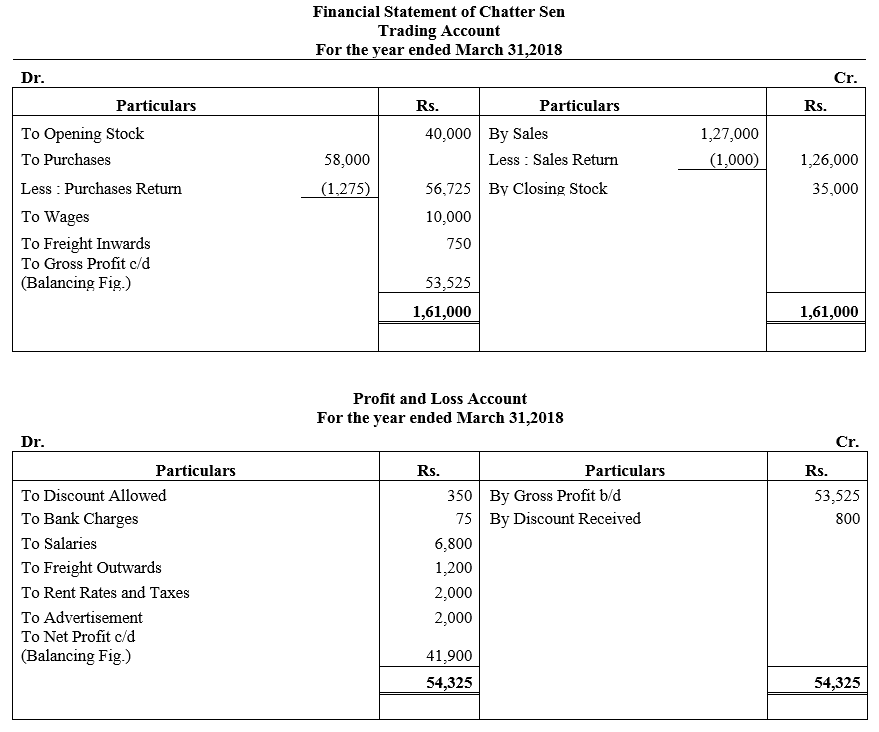
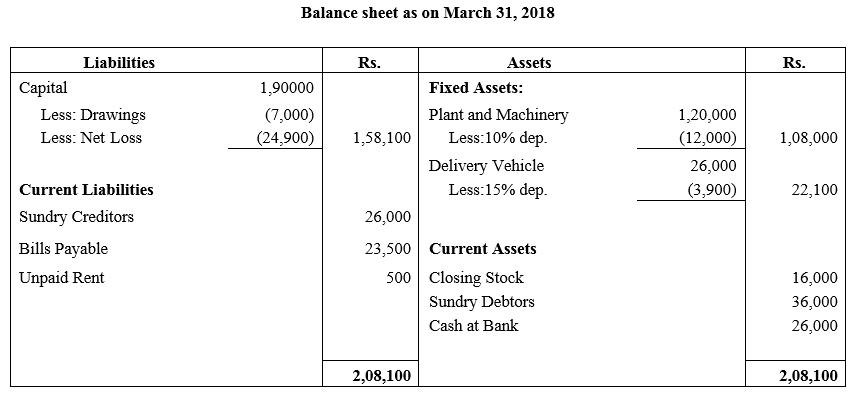
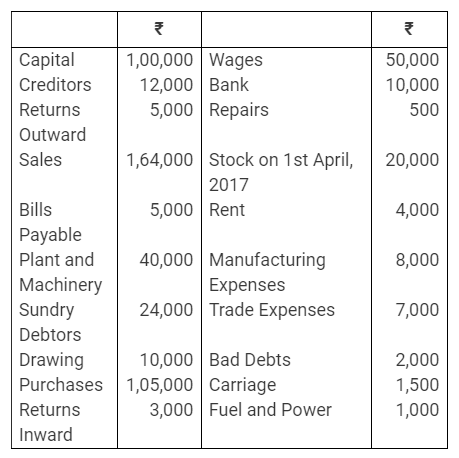
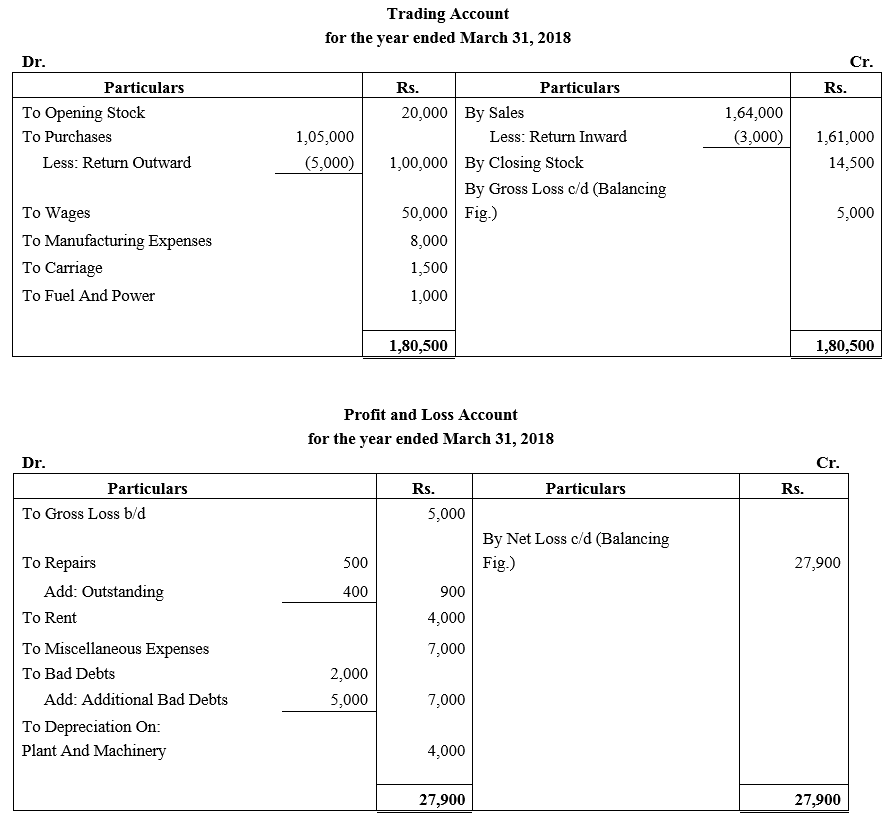
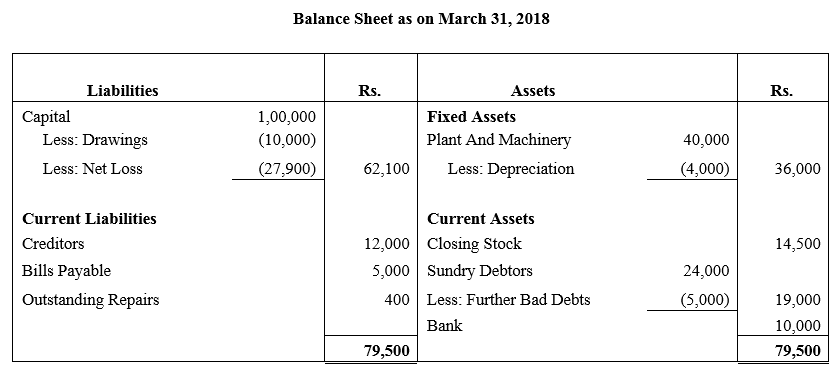




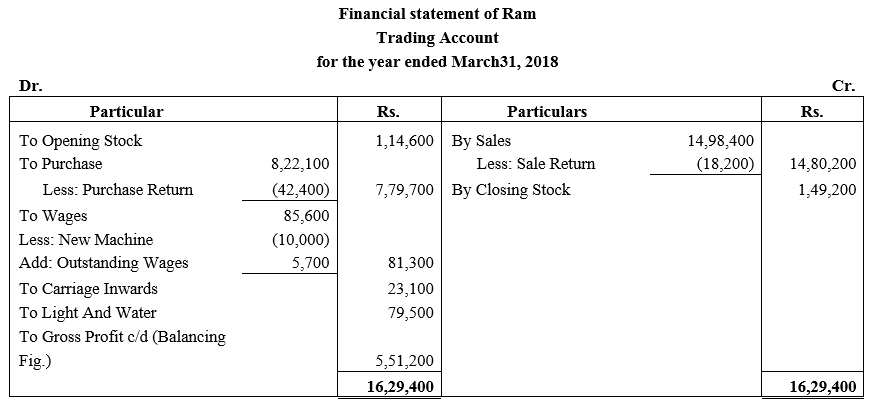
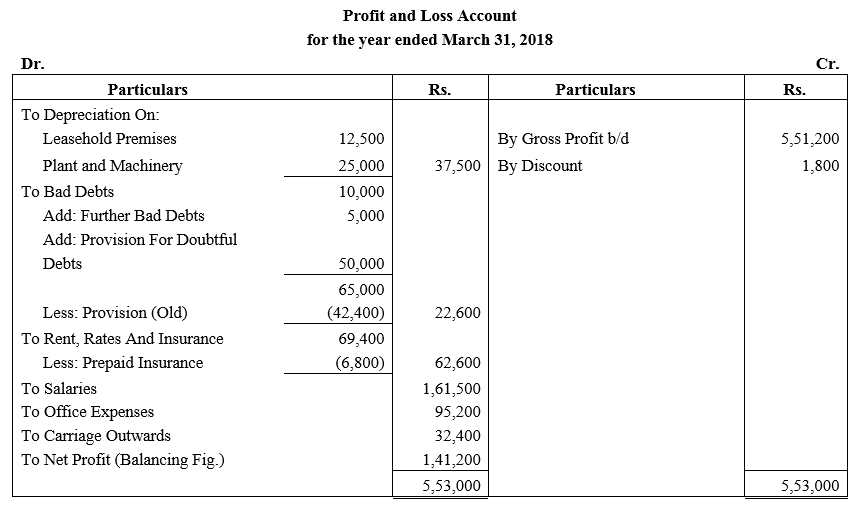
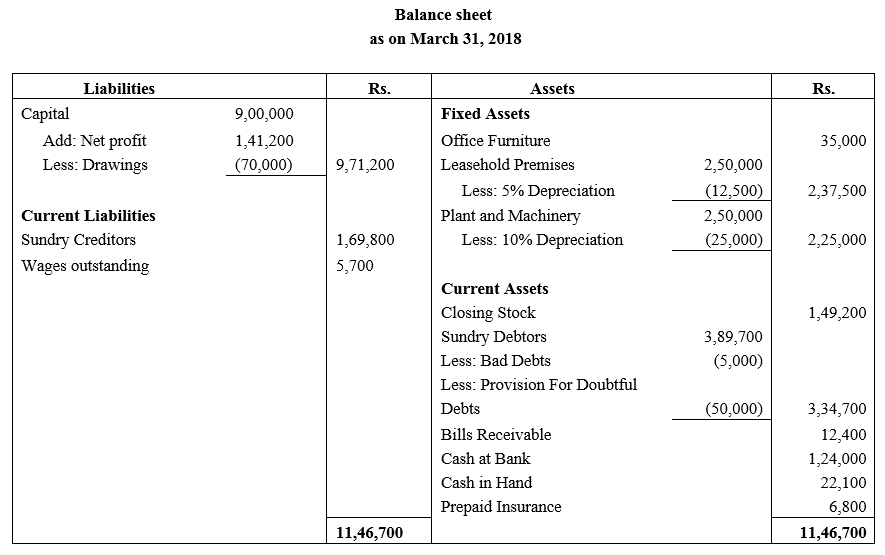
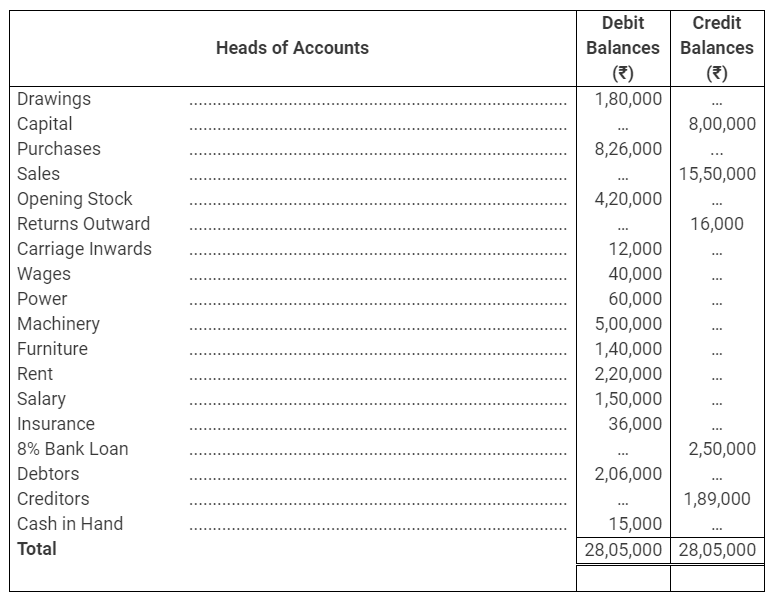
 b
b