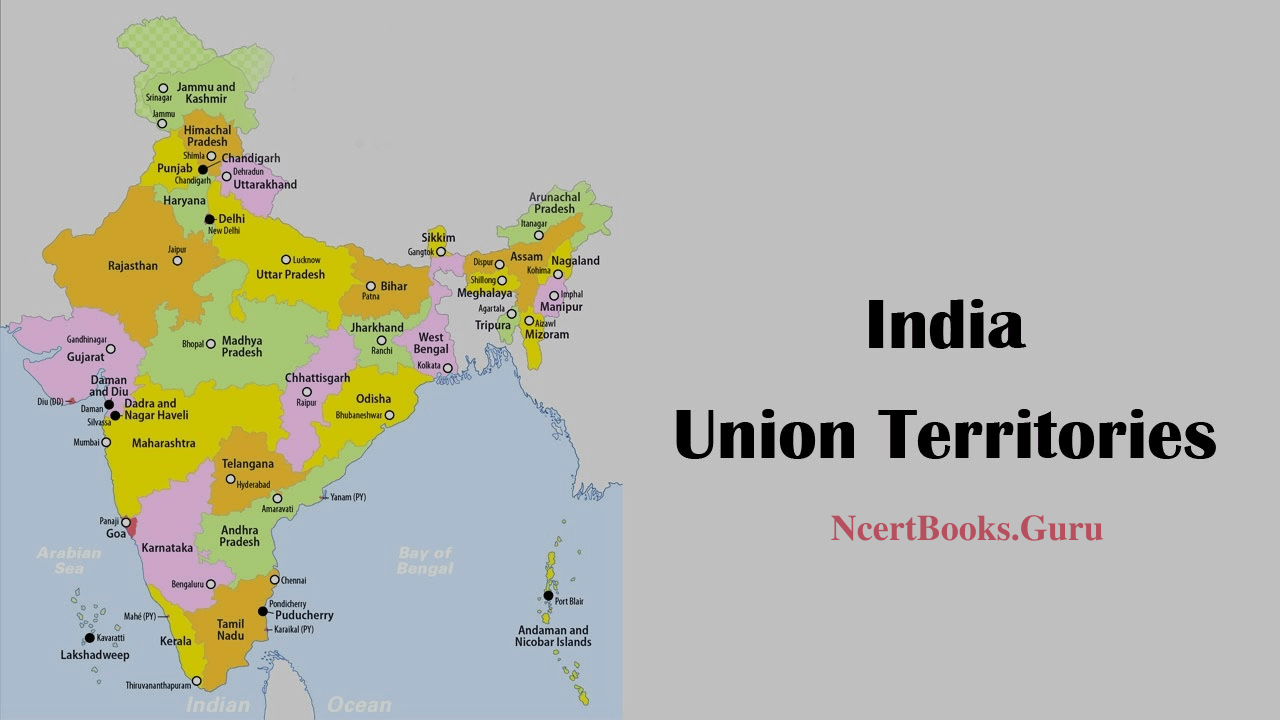
Union Territories of India: The second largest country in the world is India in terms of population. The administrative powers and responsibilities of the country are classified among central government and different units in the form of states and union territories. Today, in this article we are going to discuss the Union Territories of the country. After separating the Jammu and Kashmir, and Ladakh there is a total of 28 states and capitals along with 8 Union Territories & its capitals in India as of 2020.
Still, need some clearance about Indian UT’s then check out this ultimate guide where you will find complete details about the Union Territories of India. Here, you may found the list of UT’s of India, history, facts, differences between a state and a union territory, etc. These details are very important for all students who are preparing for various competitive exams. This topic comes under India GK and also learn more General Knowledge Topics from our site for better preparation.
More To Know:
- What are the Union Territories of India?
- How Many Union Territories in India?
- Types of UT’s in India
- List of Union Territories of India
- Union Territories and their Capitals Table
- History of Union Territories
- Important Facts on Indian UT’s
- How Delhi, Puducherry, J&K are distinct from other Union Territories?
- Difference between a State and Union Territory of India
- FAQs on Indian Union Territories
What are Union Territories?
Union Territories (UTs) are the national territories that are administered by the Union Government of India. In the Union Territories, Lieutenant Governors are elected by the President of India who works as their administrators. Union Territories have no representation in the Rajya Sabha excluding Delhi and Puducherry. Moreover, the Union territories are parted into smaller administrative blocks for adequate governance.
However, Puducherry, Jammu and Kashmir, and Delhi are the exception in this regard and have an elected legislature and government due to the status of partial statehood which was granted to them under the special Constitutional Amendment.
How Many Union Territories in India?
India, a union of states, is a Sovereign, Secular, Democratic Republic with a Political system of Government. The President is the constitutional head of the Executive of the Union. The Union territories are notionally administered by the representative of the Indian President. There are 8 Union territories in India. From first to last, each UT of India has a unique demography, history, and culture, dress, festivals, language, etc. The below modules make you understand various UTs in the Country and inspire you to explore their uniqueness.
Also Check: Largest and Smallest States of India
Types of UT’s in India
In India, there are two types of Union Territories. They are as follows:
- Union Territories with Legislature: Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, and Puducherry.
- Union Territories without Legislature: Andaman and Nicobar, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Ladakh, and Lakshadweep.
List of Union Territories of India
There are 8 Union territories in India. The list of the eight UT’s of India is given below:
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands
- Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Chandigarh
- Lakshadweep
- Puducherry
- Delhi
- Ladakh
- Jammu and Kashmir
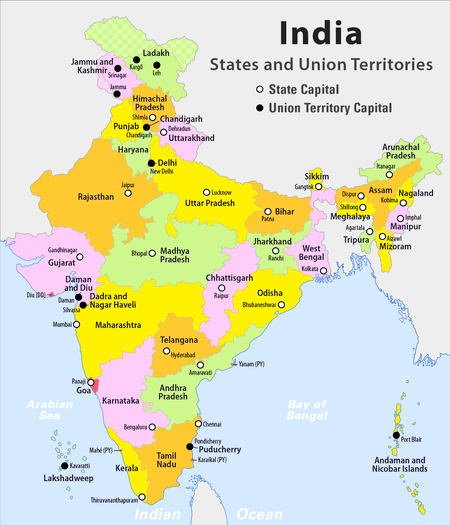
Below we have provided a piece of detailed information about each of the Indian Union Territory. Just take a look at them and gain some more knowledge regarding the UT’s of India.
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 8,249 sq. km |
| Population | 4 lakh (approx) |
| Capital | Port Blair |
| Languages | Hindi, Nicobarese, Bengali, Tamil, Malayalam, Telugu |
2. Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 491 sq km |
| Population | 4 Lakhs (Approx) |
| Capital | Silvassa |
| Languages | Gujarati, Hindi |
3. Lakshadweep
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 32 sq. km |
| Population | 64,429 ( Approx ) |
| Capital | Kavaratti |
| Principal Languages | Malayalam, Jeseri (Dweep Bhasha), and Mahal |
4. Puducherry
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 479 sq km |
| Population | 12,44,464 (Approx) |
| Capital | Puducherry |
| Principal Languages | Tamil, Telugu, Malayalam, English, and French |
5. National Capital Territory(NCT) of Delhi
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 1,483 sq. km |
| Population | 1,67,53,235 (Approx) |
| Capital | Delhi |
| Principal Languages | Hindi, Punjabi, Urdu & English |
6. Chandigarh
| Particulars | Description |
| Area | 114 sq km |
| Population | 10,54,686 (Approx) |
| Capital | Chandigarh |
| Principal Languages | Hindi, Punjabi, English |
7. Ladakh
| Leh District | Kargil District |
|
|
8. Jammu and Kashmir
| Particulars | Description |
| Capital | Jammu ( winter ), Srinagar ( summer ) |
| Area | 222,236 sq.km |
| Languages | Urdu, Dogri, Kashmiri, Pahari, Ladakhi, Balti, Gojri and Dari |
Union Territories and their Capitals Table
| Union Territory | Capital | Date of Establishment | Lt. Governor/Administrator |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | Port Blair | 1 November 1956 | Admiral D. K. Joshi (Lieutenant Governor) |
| Chandigarh | Chandigarh | 1 November 1966 | V.P. Singh Badnore (Administrator) |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu | Daman | 26 January 2020 | Praful Patel (Administrator) |
| Delhi | New Delhi | 1 November 1956 | Anil Baijal (Lieutenant Governor) |
| Jammu and Kashmir | Sri Nagar (Summer) Jammu (Winter) | 31 October 2019 | Manoj Sinha (Lieutenant Governor) |
| Ladakh | Leh (Summer) Kargil (Winter) | 31 October 2019 | Radha Krishna Mathur (Lieutenant Governor) |
| Lakshadweep | Kavaratti | 1 November 1956 | Praful Patel (Administrator) |
| Puducherry | Puducherry/Pondicherry | 16 August 1962 | Dr. Tamilisai Soundararajan (Addl. Charge) (Lieutenant Governor) |
History of Union Territories
While discussing the reorganization of states in 1956, the States Reorganisation Commission supported the creation of a separate section for these territories since they neither fit the model of a state nor do they pursue a similar pattern in terms of governance. By noting such reasons as economically unbalanced, financially weak, and administratively and politically unstable territories can’t persist as individual administrative systems without depending slowly on the Union government, the union territory was created. The first union territory of India was Andaman and Nicobar island, Chandigarh is the joint capital of Punjab and Haryana state of India.
Important Facts on Indian UT’s
- In 2020, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu were joined into a single UT and are managed by Praful Patel. The joined Union Territory is called Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.
- Some of the UT’s have Lieutenant Governors such as Andaman and Nicobar, Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, and Puducherry.
- Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Daman and Diu, and Lakshadweep have Administrators.
- The Administrator of the Union Territory of Chandigarh as well as the Governor of Punjab is V.P. Singh Badnore.
- According to Article 239, the Chief Administrator of the Union Territories is the President of India.
How Delhi, Puducherry, J&K are distinct from other Union Territories?
All Indian states and three union territories out of 8 ie., Puducherry, Delhi, and Jammu and Kashmir have an elective legislature with allowed partial statehood by an amendment to the Constitution. Also, Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, and Puducherry have their own legislative assembly and executive committee and function like states. They have a few subjects of State list with them and a few lies with the center.
Difference between a State and Union Territory of India
- The basic difference between state and union territory is that a state has a separate governing body whereas, a union territory is governed by the central government or union government excluding Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, and Puducherry.
- A state possesses a federal relationship with the Union Government and the legislative and executive powers are assigned while a Union Territory has a unitary relationship with the Union Government and all the legislative and executive powers reside with the Government of India.
- The constitutional head of the state is a Governor while the UT’s executive head is the President of India.
- The Chief Minister chosen by the people administers the State while the Union Territory is governed by an administrator or Lieutenant Governor elected by the President of India.
- In terms of Size, States are much larger compared to the Union Territories of India.
- The Indian States have self-governing powers while the Union Territories do not have self-governing powers.
FAQs on Indian Union Territories
1. How many union territories are there in India in 2020?
India has 8 union territories since 26th Jan 2020. The U.T of Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli have become a single union territory so that the count of union territories in India comes down to 8 from 9 Indian UT’s.
2. Which are the 9 union territories of India before 2020?
The 9 Union Territories of India are Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Chandigarh, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, National Capital Territory of Delhi, Jammu and Kashmir, Lakshadweep, Ladakh, and Puducherry.
3. Name the newly added Union Territories in India?
Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh have newly added to the list of Union Territories of India.
4. Which Union Territories have been united into a single Union Territory in 2020?
In 2020, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, and Daman and Diu were united into a single UT & known as Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu.