Difference Between IPV4 and IPV 6: We often come across IPV4 and IPV6, but do we know the meaning and the difference between the two terms. This article helps you comprehend the meaning and key differences between IPV4 and IVP6 terms.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the difference between IPv4 and IPv6?
IPV4 is a concept which is the fourth version of Internet Protocol (IP). This concept, IPV4, is one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods. These standards-based internetworking refer to those on the internet and other packet-switched networks.
IPV6 is a concept which is the most recent version of Internet Protocol (IP). This concept provides an identification and location system for all the computers on networks and routes across the internet.
Difference Between IPV4 and IPV 6
The key differences between IPV4 and IVP6 are as follows:
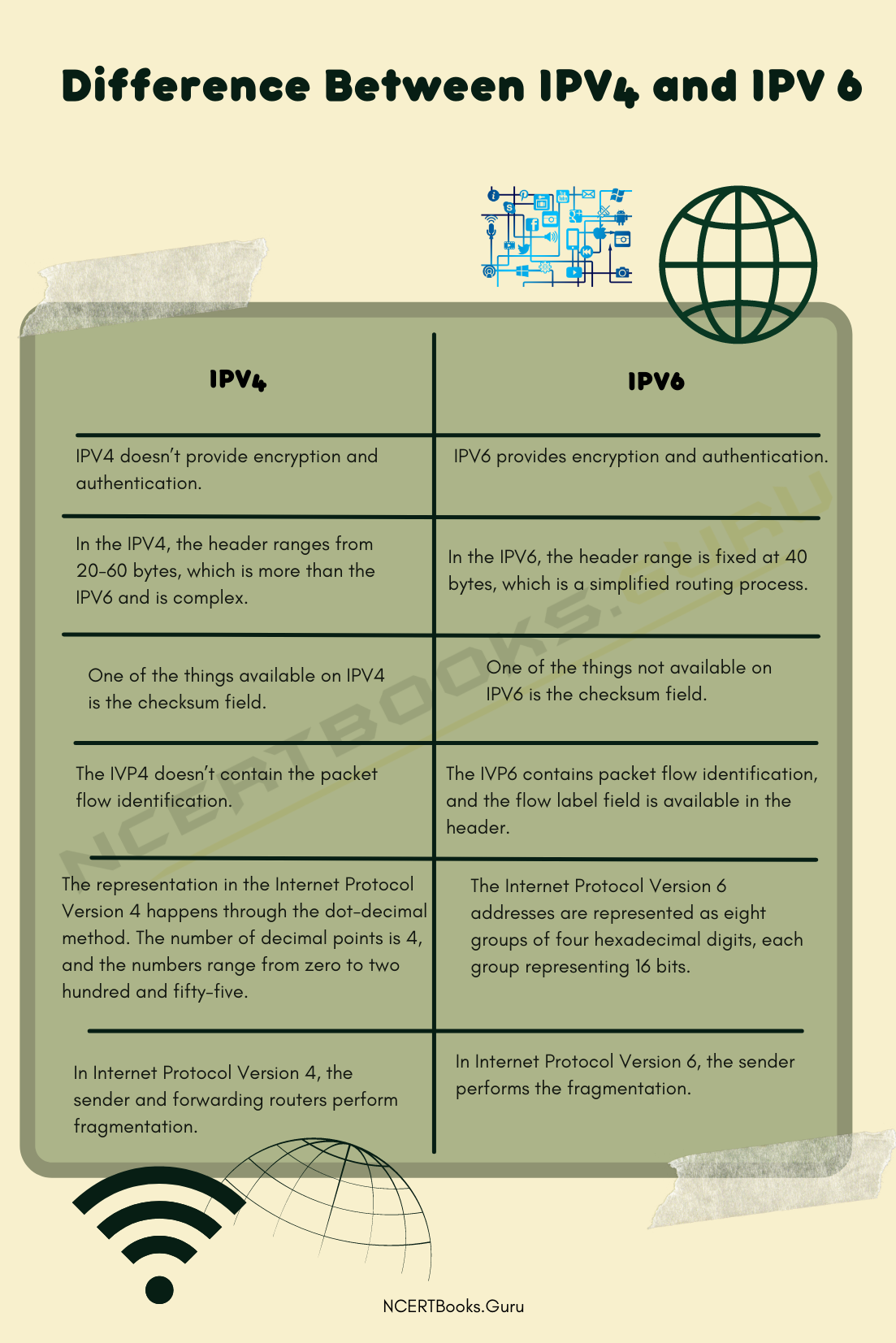
| IPV4 | IPV6 |
| IPV4 doesn’t provide encryption and authentication.
In the IPV4, the header ranges from 20-60 bytes, which is more than the IPV6 and is complex. One of the things available on IPV4 is the checksum field. The IVP4 doesn’t contain the packet flow identification. The representation in the Internet Protocol Version 4 happens through the dot-decimal method. The number of decimal points is 4, and the numbers range from zero to two hundred and fifty-five. In Internet Protocol Version 4, the sender and forwarding routers perform fragmentation. Security features in an IPV4 depend or rely on the application. In Internet Protocol Version 4, you cannot have end-to-end connection integrity. In IPV4, there is support available for DHCP and Manual address configuration. The Internet Protocol Version 4 addresses are 32-bit long. Broadcasting message transmission scheme is available on the IPV4. The quality of the service feature in an Internet Protocol Version 4 is not very efficient. The checksum error is detected and computed in the Internet Protocol Version 4. The Internet Protocol Version 4 doesn’t support any Internet Protocol host mobility function. |
IPV6 provides encryption and authentication.
In the IPV6, the header range is fixed at 40 bytes, which is a simplified routing process. One of the things not available on IPV6 is the checksum field. The IVP6 contains packet flow identification, and the flow label field is available in the header. The Internet Protocol Version 6 addresses are represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, each group representing 16 bits. In Internet Protocol Version 6, the sender performs the fragmentation. Security features in an IPV6 depend or rely on an inbuilt security feature named as IPSEC. In Internet Protocol Version 6, you can have end-to-end connection integrity. In IPV6, there is support available for renumbering and auto address configuration. The Internet Protocol Version 6 addresses are 128bits long. Multicast message transmission scheme is available in IPV6. The quality of service is high and efficient in an Internet Protocol Version 6 because it’s inbuilt. The checksum error doesn’t compute on the Internet Protocol Version 6. The Internet Protocol Version 6 host mobility feature enables the moving node to temporarily change its location in a network while maintaining the ongoing connections at the same time. |
