A constitution is a legal structure with special legal integrity that defines an institution of the government and its principal roles and sets out its standards of activity. The Constitution is framed at a point in history by a body of members properly chosen by the people. The Constitution sits above and between the two statutory and implementation mechanisms. The Constitution is a basis of authority and not a power of legislation.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference Between Constitution and Law
Law, as it encompasses the Constitution, constitutional provisions, court rulings and conventions, is a wider concept. It was established through judicial scrutiny through the reading of the Constitution. It is made up of rules and non-legal standards. Legal principles are those that can be imposed and upheld by the judiciary, while conventions, norms and traditions regulate non-legal standards.
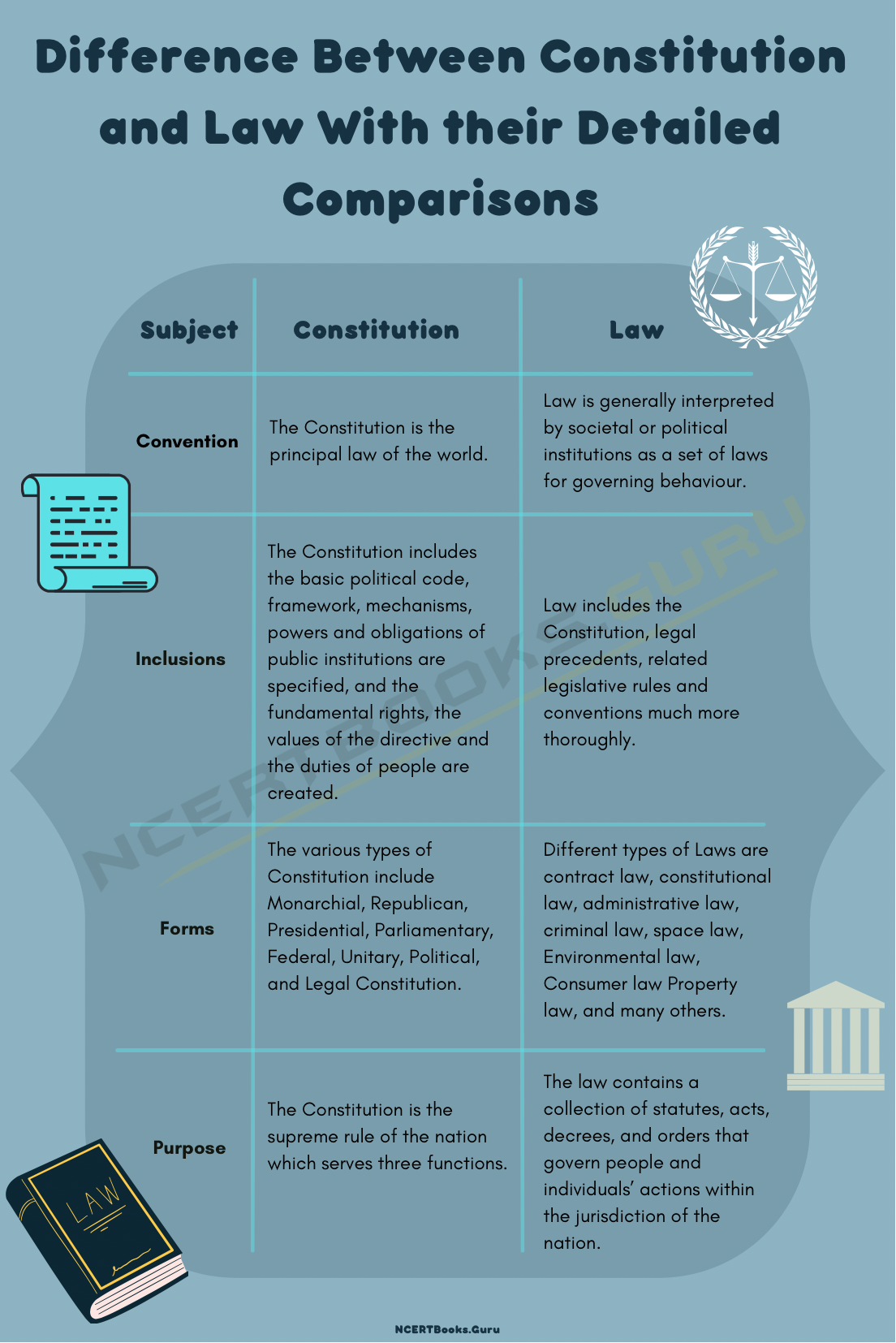
| Subject | Constitution | Law |
| Convention | The Constitution is the principal law of the world. | Law is generally interpreted by societal or political institutions as a set of laws for governing behaviour. |
| Inclusions | The Constitution includes the basic political code, framework, mechanisms, powers and obligations of public institutions are specified, and the fundamental rights, the values of the directive and the duties of people are created. | Law includes the Constitution, legal precedents, related legislative rules and conventions much more thoroughly. |
| Forms | The various types of Constitution include Monarchial, Republican, Presidential, Parliamentary, Federal, Unitary, Political, and Legal Constitution. | Different types of Laws are contract law, constitutional law, administrative law, criminal law, space law, Environmental law, Consumer law Property law, and many others. |
| Purpose | The Constitution is the supreme rule of the nation which serves three functions. | The law contains a collection of statutes, acts, decrees, and orders that govern people and individuals’ actions and activities within the jurisdiction of the nation. |
Convention
The Constitution is the principal law of the world. It is a set of basic laws which lay down how to rule a country while on the other hand Law is generally interpreted by societal or political institutions as a set of laws for governing behaviour. It is an institution that regulates political communities’ activity, with its rules, doctrines and practices.
It refers to rights defined in the constitutions of federal and state governments. This legal power is largely established in accordance with the constitutional judgments of the state and the Supreme Court. The Supreme Court interprets its constitutions in situations of disagreement between essential state duties and decides that the statute enacted by the legislature would not breach its statutory boundaries.
Inclusions
The Constitution includes the basic political code, framework, mechanisms, powers and obligations of public institutions are specified, and the fundamental rights, the values of the directive and the duties of people are created. In contrast, the Law includes the Constitution, legal precedents, related legislative rules and conventions much more thoroughly.
The Constitution legislation defines and confers upon all three individual responsibility and roles the government branches’ privileges and powers at federal, state, and local levels. It also defines the role, power, and function in the legislative, executive and judicial sphere. The Law regulates state governance and discusses a series of laws regulating ties between the governor and the governed in a State.
Forms
The various types of Constitution include Monarchial, Republican, Presidential, Parliamentary, Federal, Unitary, Political and Legal Constitution while the different types of Laws are, contract law, constitutional law, administrative law, criminal law, space law, Environmental law, Consumer law Property law, Labor law, Immigration law, Laws on human rights, company law, intellectual Property law, tax law, banking law.
Purpose
The Constitution is the supreme rule of the nation which serves three functions; Firstly, It defines a constitution, a system or a government structure; Secondly, It provides powers for the established government to help the established government to legislate, enact the laws that have been established, and address the controversy when conflict occurs when interpreting a law; Thirdly, It restricts the government’s powers.
In a democracy, three separate branches of government have three roles: in democracy as Legislative Sector; Executive Directorate and Branch of the Courts. On the other hand, the law contains a collection of statutes, acts, decrees, and orders that govern people and individuals’ actions and activities within the jurisdiction of the nation.
Generally, the Legislative Branch legislation is made by laws or acts and decrees, orders and resolution is adopted by the Executive Branch. The ConstitutionConstitution’s rules and current legislation, acts, decrees, and decrees shall not infringe on these regulations. The act is enacted by or by the Executive Branch.