Introduction
In India, monsoon comes in two specific seasons: the advanced monsoon season and the retreating monsoon season. The former comes immediately after the summer season in July, while the latter comes just before winter, September or October.
The monsoon regime in India becomes a unique phenomenon due to an interplay between these two seasons.
You can also find differences between articles on various topics that you need to know. Just tap on the quick link available and get to know the basic differences between them.
What is the Difference Between Advancing and Retreating Monsoon?
About Advancing Monsoon
The advancing monsoon season is characterised by winds blowing in a south-west direction. These winds are existent on the land surface for almost a month and are very strong. They blow at almost 30 km per hour.
During this season the Western Ghats receive very heavy rainfall. However, it is the north-eastern part of India, Mawsynram, Cherrapunji in the Khasi hills which receive the maximum rainfall. The main feature of this season is the accompanying ‘breaks’, or the wet-dry spells.
About Retreating Monsoon
When the land surface cools off by September end, the Indian ocean gets rapidly heated. Consequently, a high pressure movement takes place, and monsoon winds start blowing in a north-east direction. The south-west monsoonal winds also become quite weaker and retreat from north India.
During this season, which is also called winter monsoon, the skies remain mostly clear. The temperature shoots down rapidly. During this season it is the south-eastern coast which receives the heaviest rainfall.

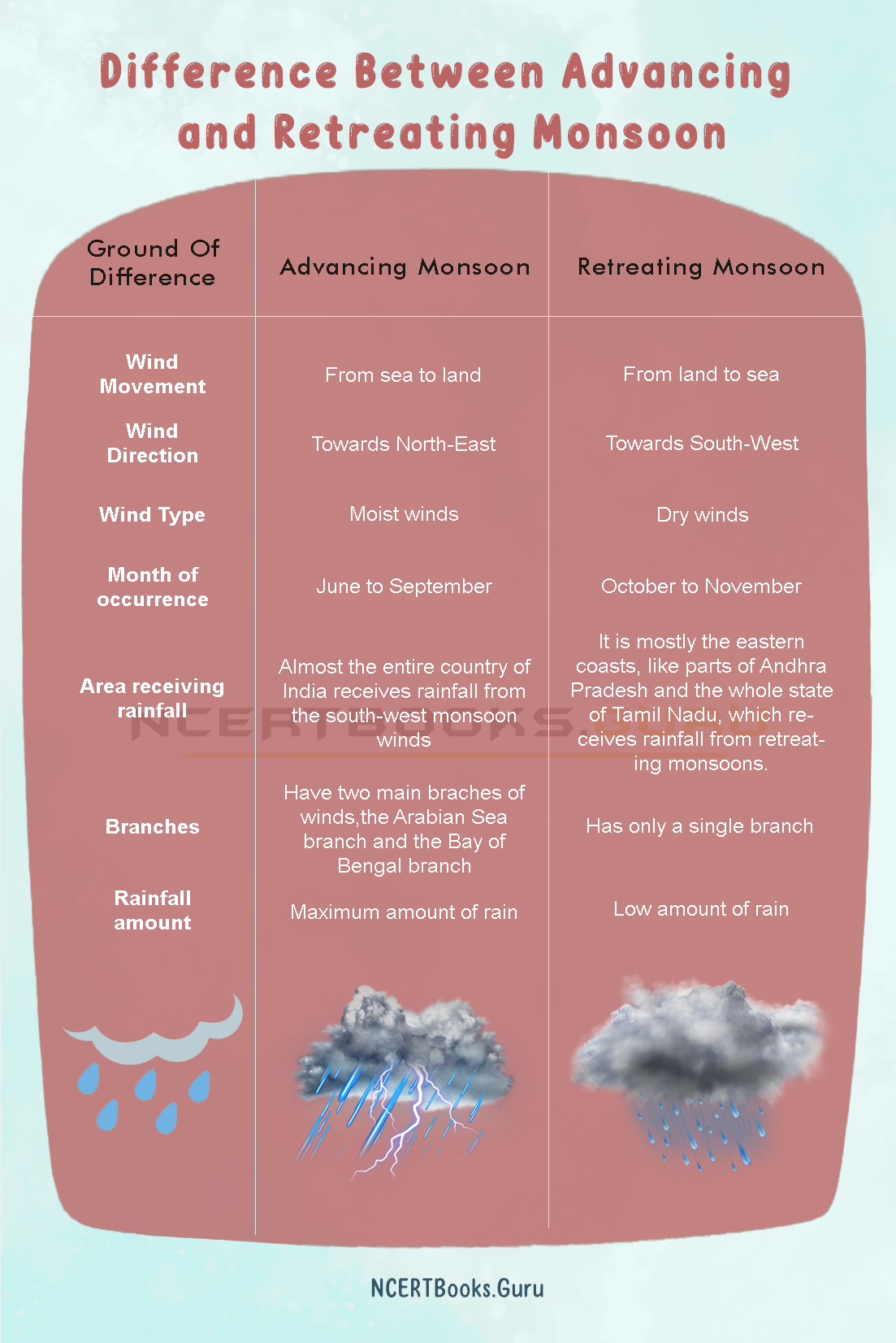
Difference Between Advancing and Retreating Monsoon
| Ground Of Difference | Advancing Monsoon | Retreating Monsoon |
| Wind Movement | From sea to land | From land to sea |
| Wind Direction | Towards North-East | Towards South-West |
| Wind Type | Moist winds | Dry winds |
| Month of occurrence | June to September | October to November |
| Area receiving rainfall | Almost the entire country of India receives rainfall from the south-west monsoon winds |
It is mostly the eastern coasts, like parts of Andhra Pradesh and the whole state of Tamil Nadu, which receives rainfall from retreating monsoons. |
| Branches | Have two main braches of winds, the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch |
Has only a single branch |
| Rainfall amount | Maximum amount of rain | Low amount of rain |
Similarities Between Advancing and Retreating Monsoon
- Both these monsoons’ development is the same; both are caused when the sea surface gets heated up rapidly, while the land surface remains comparatively cooler, thus causing air movement.
- During both these monsoon seasons, particular parts of the land area receive extremely high rainfall.
- Many times, both these monsoon regimes create widespread floods in various parts of the country.
- There are many times when both of these monsoon seasons have brought damage to life and property. They even cause damage to cattle and fodder.
- Both these monsoon seasons are uncertain and do not occur at regular intervals in the Indian subcontinent.
Frequently Asked Questions on Difference Between Advancing and Retreating Monsoon
Question
In which directions does the wind blow during advancing and retreating monsoons?
Answer:
During retreating monsoon, the wind direction is from the west towards the north-east. But in the advancing monsoons, the wind blows towards the south-west.
Question
What do you mean by the ‘break’ in monsoons?
Answer:
During the advancing monsoon session, there are short periods of reduced rainfall in various parts of the country. This is termed as the ‘break’ in monsoon. This phenomenon is caused by an occasional shift of the monsoon trough towards the Himalayan foothills.
Question
Which places receive rainfall during retreating monsoon?
Answer:
It is mostly Tamil Nadu that receives the heaviest rainfall during the retreat of monsoon.
