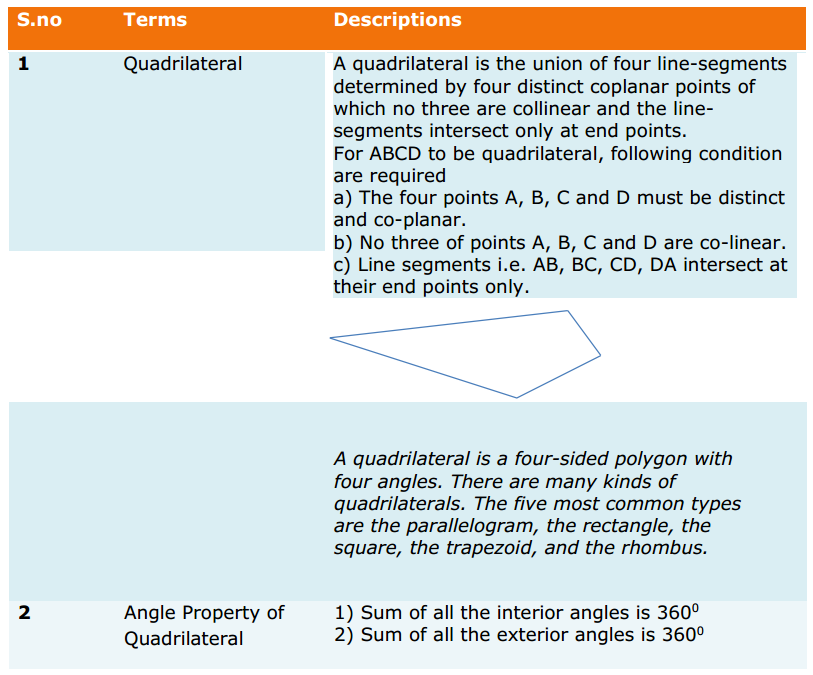
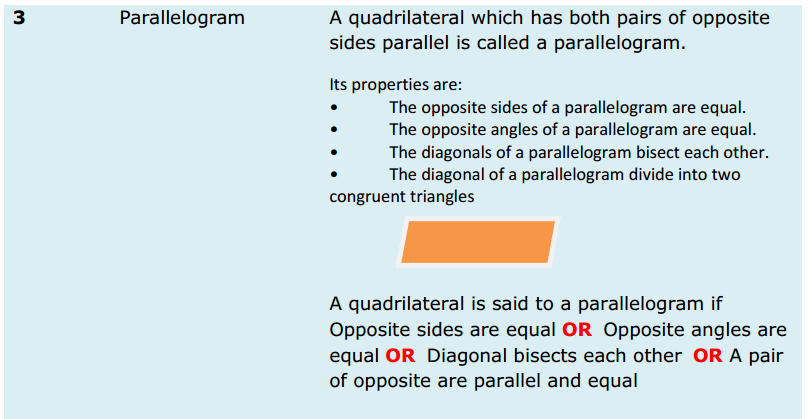
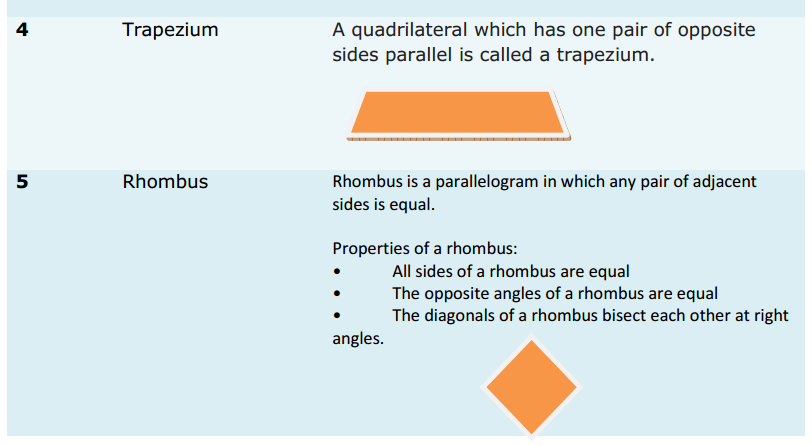
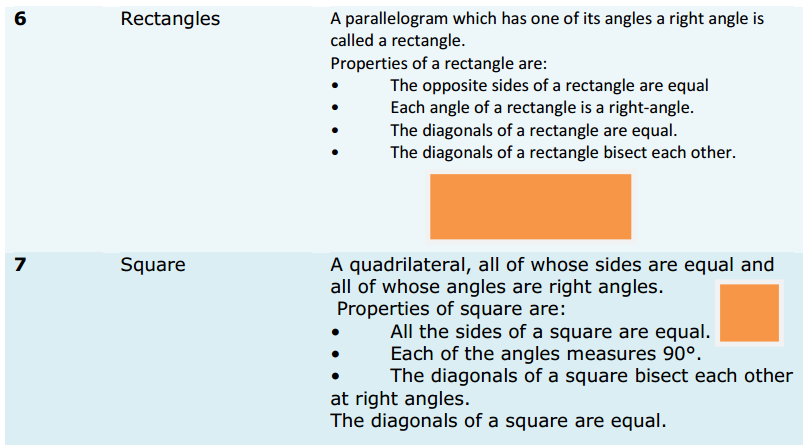
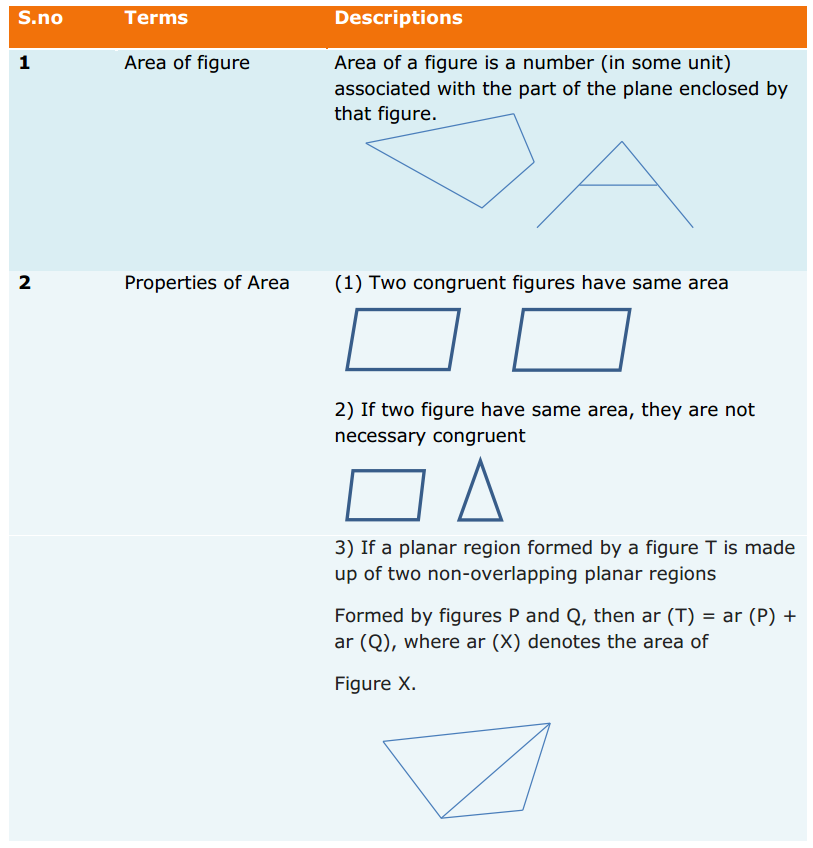
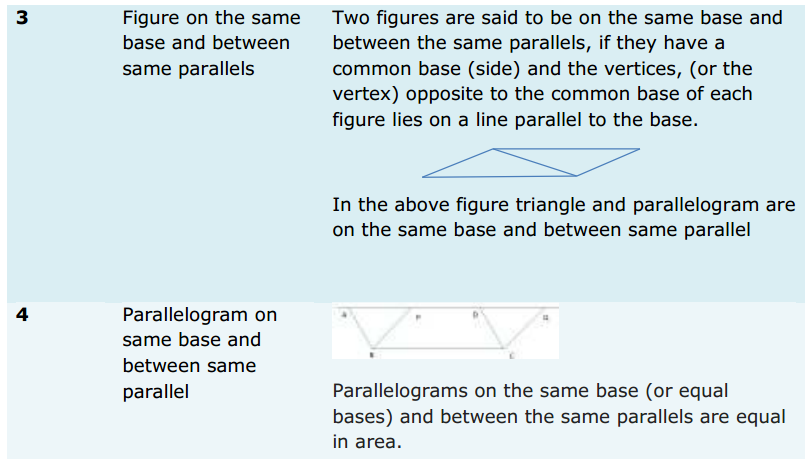
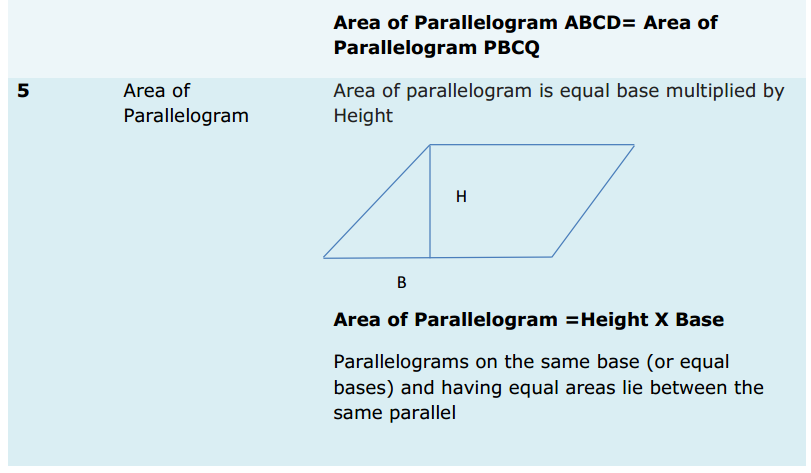
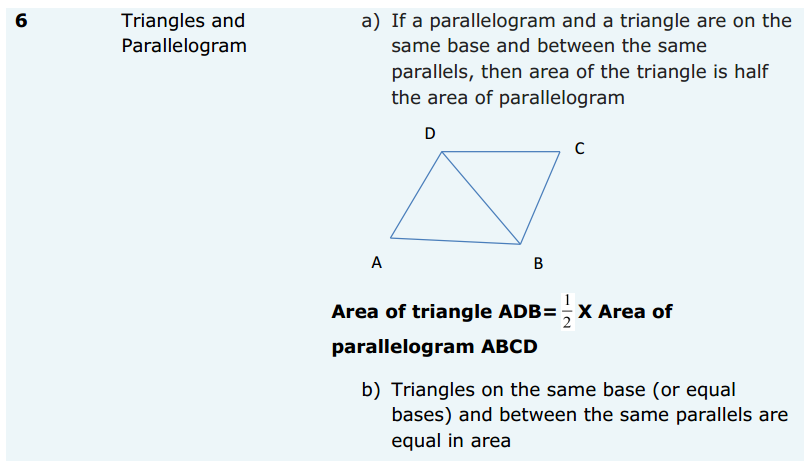
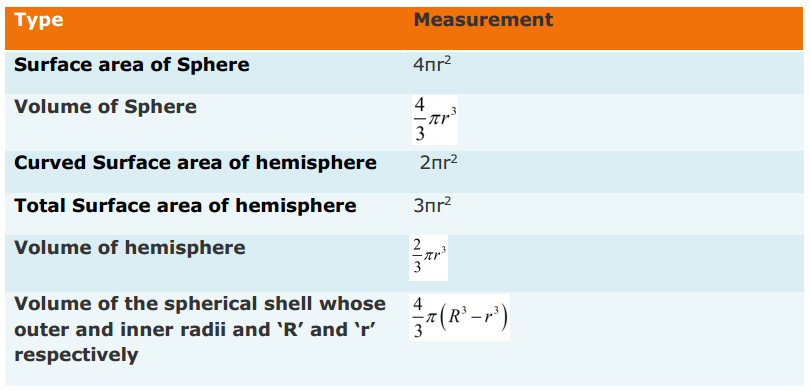
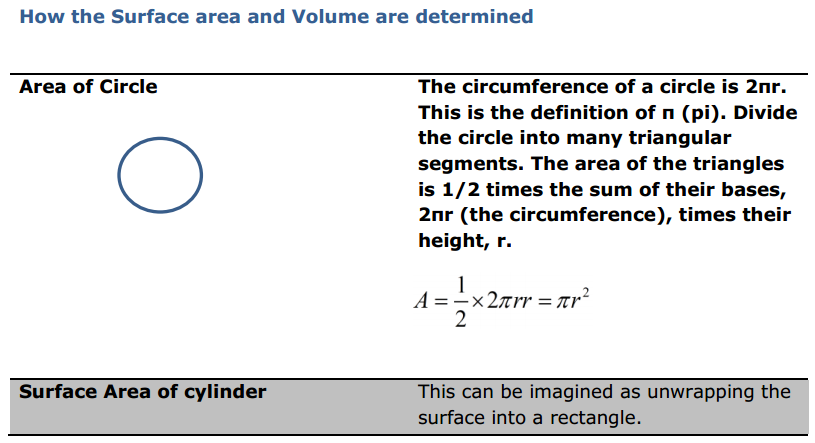
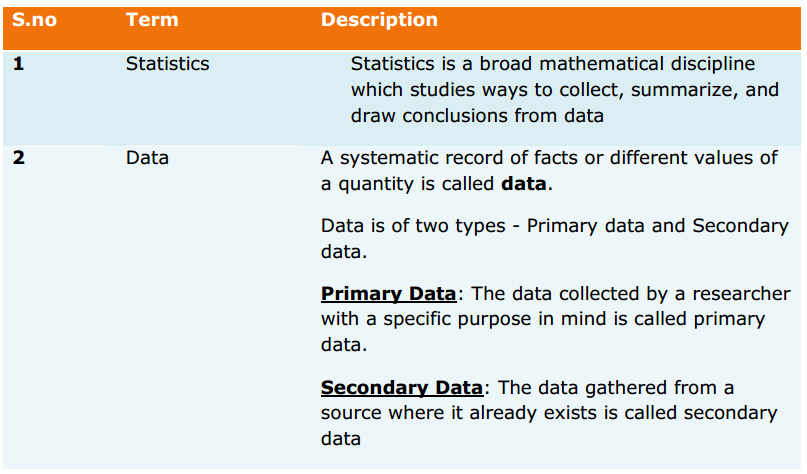
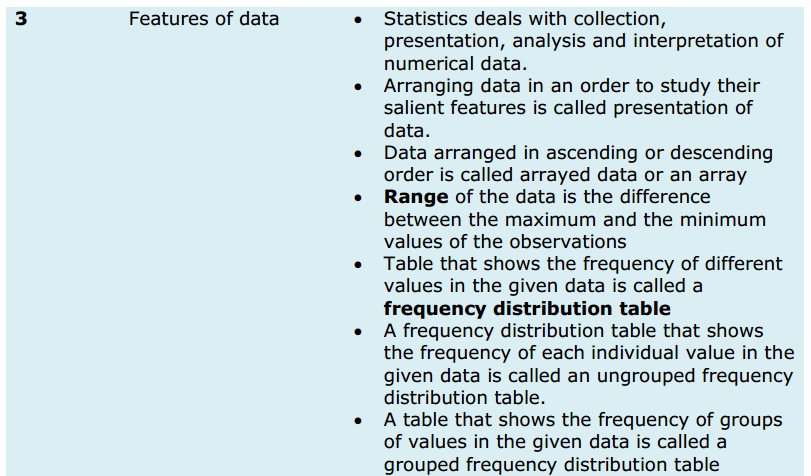
Introduction: When you think about sales, what are you thinking about?
You’re imagining some people talking.
One person is a customer speaking about buying something, and they’re probably having lots of queries.
Another man is selling that same thing, answering questions and explaining why it’s worth the value.
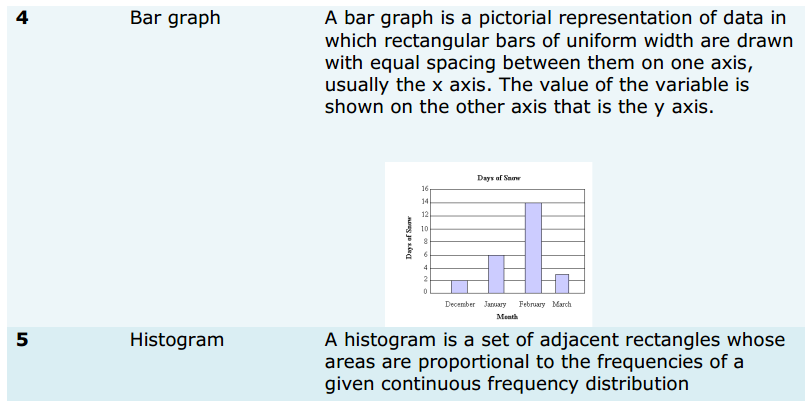
Gather Information Regarding Basic English Skills and become proficient in the language and speak fluently with confidence. Try the Tips over here and Improve your English Writing and Speaking Skills.
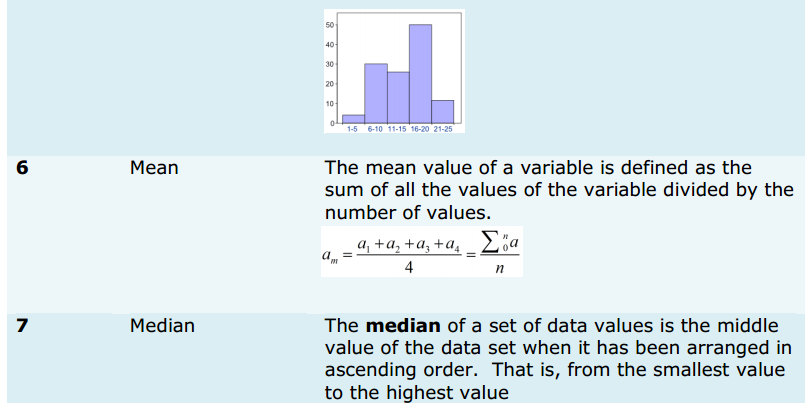
Simple Conversations Between Salesman and Customer about Shoes, Clothes, Grocery, and Vegetables
The truth is that sales are likely about interacting with people. To work in a sales job, you’ll need to get to know your customers’ needs and wants, as well as how to give them exactly what they want to pay for.
So, if you plan to shine in sales, you should start with learning how to make conversation.
Once you get that potential buyer to talk to you, the final moment when you “close the deal” (sell something) isn’t very far away.
The whole article is about the conversation between a shopkeeper/ salesman and a customer at the time buying the following three items:
- Shoes,
- Clothes,
- Grocery, and
- Vegetables and fruits (this one involves the mediation of price)
The following are the examples or sample conversations on these three items.

1. Conversation while Buying Shoes
Salesman: Mam, how may I help you?
Customer: I’m exploring your branch for a pair of sports shoes.
Salesman: May I know the foot size that you do wear usually?
Customer: Nine.
Salesman: Eight for which brand?
Customer: Does the same size mean a distinctive thing for diverse brands? It should be standard across all brands.
Salesman: For a few brands, the same size can mean slightly distinguished fitting.
Customer: Is it? I thought differently. Anyhow, I wear a size Eight of Clarks, and as I need to buy the same brand, it shouldn’t be a problem.
Salesman: Yes, it doesn’t make any change in that scenario. Take a look at this section, which has some incredible new arrivals in shoes on sale.
(The customer first glimpses through the shoes on sale.)
Customer: The variety of shoes is more limited here. Because I’m purchasing shoes for at least several years, I would like to purchase something I want. I’ll go with new arrivals.
Salesman: The majority of the shoes on sale were sold out to customers within a day of the opening of the sale. That’s why you find far less collection there.
Salesman: Why don’t you try this model of shoes?
Customer: Not these. I’m looking for a more formal look, the ones with borders and predominantly decent form.
Customer: I like to give it a try with this one.
(The customer puts on the pair of shoes and walks few yards.)
Customer: This goes perfectly. I’ll buy this one in black—size eight.
Salesman: Anything else, Mam?
Customer: No, thanks.
Salesman: Then, may I get the billing done.
Customer: Sure.
2. Conversation while Buying Grocery
Customer: I need a dozen eggs, one pouch of buttermilk, two liters of double-toned milk, a liter of soybean cooking oil, a half kg of raw grounded coconut, two kilograms of Mung dal, and three flavoured yogurts.
(Once the shop assistant collected all these items from the shelves in the store, the shopkeeper makes the bill.)
Customer: How much will all these items cost?
Shopkeeper: 10 Dollars
Customer: What’s the cost of dozen eggs?
Shopkeeper: 1 dollar a dozen.
Customer: That’s a lot more than what you sold the last time.
Shopkeeper: Rates are increased compared to the previous week.
Customer: OK. Please give me a discount as I’m purchasing quite a few items in a row.
Shopkeeper: We rarely make any margins of profit on these particular items.
Customer: I know how much you make.
Shopkeeper: OK, give me rupees 9$
Customer: Please use this Jute bag to carry the items.
3. Conversation During the Clothes Purchase
Salesman: Mam, how may I help you?
Customer: I’m looking for casual and formal T-shirts and trousers.
Salesman: You can find a T-shirt for casual wear on that side of the showroom. Yet, formal wear is on the second floor.
Customer: All right, I’ll start with formal wear.
(The customer and the salesman proceed to the formal wear section which is on the second floor.)
Salesman: What size T-shirt do you prefer mam?
Customer: I wear 32″.
Salesman: You’ll find 32″ T-shirts on this particular shelf.
Customer: Can you please take out these three T-shirts? I want T-shirts without sleeves.
Salesman: None of these is with sleeves.
(The salesman takes the chosen three shirts out and unleashes them on the waist-high table, placed in between him and the customer.)
Customer: I like the plain, light colors in white and blue.
Salesman: These are nice and comfortable T-shirts. They would go well with dark-shaded trousers, especially those in shades of grey and black. You can take a look at the trouser section as well before you try all of them together.
(They then proceed to check on trousers on the same floor.)
Customer: Can you please show me the trousers in 28″ waist size?
Salesman: These shelves are for waist size 28″.
Customer: Can you please take this and this out?
(The salesman pulls the two trousers out and lines them on the table. The customer killed a few minutes deciding between them and then, ultimately selects one.)
Customer: Where can I try them? Is there any trial room on this floor?
Salesman: Right side of the staircase.
(The customer tries the selected T-shirts and the trousers and comes back.)
Customer: I’ll buy two T-shirts and black trousers.
Salesman: OK, mam. We can now proceed to the ground floor for casual wear.
(They move down to the ground floor and proceed to the section for casual wear.)
Customer: Show me the new arrivals for the summer collection.
Salesman: You’ll really like this. You can wear these casuals for office, shopping, etc. with much comfort in the summer as the color contrast is light in shades and the pattern is simple and elegant.
Customer: I like this one. Let me try this one out.
(The customer tries the selected casual wear and comes back.)
Customer: OK. Please pack this one as well. Now, I’ve two formal T-shirts, one pair of trousers, and one casual dress.
Salesman: Would you want to see anything matching for these selected clothes mam?
Customer: Not now. Thanks.
Salesman: No problem, mam. Our tailor can measure the length of your trousers and would stitch the bottom accordingly and trim off the excess. Meanwhile, I’ll make your billing done.
Customer: When can I collect the trousers?
Salesman: In one hour.
Customer: OK, Thanks.
4. Conversation while Buying Electronics
Salesman: Hello sir, welcome to our store.
Customer: Thank you.
Salesman: How can I help you, sir.
Customer: Actually, I am planning to buy an air conditioner, so could you please help me with that.
Salesman: Sure, sir. Could you please specify me the brand so that I can be more transparent with the details?
Customer: I am using Panasonic AC these days but I am not that satisfied with its services.
Salesman: You should try the LG air conditioner. It is already in high demand.
Customer: What kind of service does it offer?
Salesman: In LG air conditioner, you will get a two-year warranty. It also has five free services. The installation is free. The maintenance is also taken care by the company.
Customer: That’s perfect.
Salesman: Sir, where do you want to install the air conditioner?
Customer: In the living hall.
Salesman: How much Tonne is required?
Customer: 1.0 Tonne would be better.
Salesman: Okay sir.
Customer: Could you please tell me the price of this air conditioner and the mode of payment?
Salesman: It will cost you around 20000/- INR including service tax. And you can pay by card, cash or cheque.
Customer: Perfect, I would like to pay by card.
Salesman: Sure, sir. Let’s complete the formalities and proceed further.
Customer: Okay!