NEET Physics is the scoring paper in the medical entrance examination. Here, you will discover the NEET Physics MCQ Questions for all Concepts as per the latest syllabus. Practice more on a regular basis with these NEET Physics objective questions on air pollution and improve your subject knowledge & problem-solving skills along with time management. NEET Physics Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation Multiple Choice Questions make you feel confident in answering the question in the exam & increases your scores to high.
MCQ on Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation
1. Light of frequency 1.9 times the threshold frequency is incident on a photosensitive material. If the frequency is halved and intensity is doubled, the photocurrent becomes
(a) doubled
(b) quadrupled
(c) halved
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (d) zero
2. For a metal having a work function W0, the threshold wavelength is λ. What is the threshold wavelength for the metal having work function 2W0?
(a) λ/4
(b) λ/2
(c) 2λ
(d) 4λ
Answer
Answer: (b) λ/2
3. Radiation of frequency ν is incident on a photosensitive metal. When the frequency of the incident radiation is doubled, what is the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons?
(a) 4E
(b) 2E
(c) E + hν
(d) E – hν
Answer
Answer: (c) E + hν
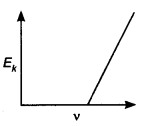
4. How does the maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron vary with the frequency (v) of the incident radiation?
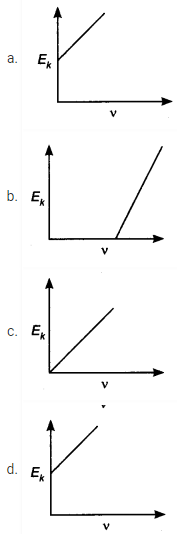
Answer
Answer: (b)
5. The stopping potential V0 for photoelectric emission from a metal surface is plotted along with the y-axis and frequency v of incident light along the x-axis. A straight line is obtained as shown. Planck’s constant is given by
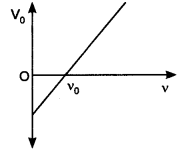
(a) product of the slope of the line and charge on the electron
(b) intercept along y-axis divided by the charge on the electron
(c) product of the intercept along x-axis and mass of the electron
(d) the slope of the line
Answer
Answer: (a) product of the slope of the line and charge on the electron
6. Calculate the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electron which has a kinetic energy of 5 eV.
(a) 5.47 Å
(b) 2.7 Å
(c) 5.9 Å
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (a) 5.47 Å
7. What is the ratio of the de Broglie wavelengths proton and an α particle if they are accelerated by the same potential difference?
(a) 2√2: 1
(b) 3:2
(c) 3√2: 1
(d) 2: 1
Answer
Answer: (a) 2√2: 1
8. Which of the following graphs represent the variation of particle momentum associated with de Broglie wavelength?
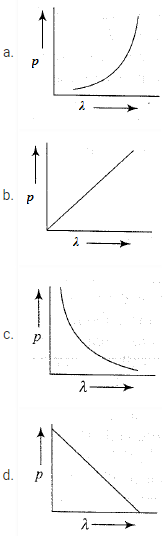
Answer
Answer: (c)
9. By what factor will the de Broglie wavelength change if the K.E if the free electron is doubled?
(a) ½
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \)
(c) 2
(d) √2
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \)
10. In photoelectric effect what determines the maximum velocity of the electron reacting with the collector?
(a) Frequency of incident radiation alone
(b) The potential difference between the emitter and the collector
(c) The work function of metal
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
11. Who among the following established that electric charge is quantised?
(a) R.A. Millikan
(b) Wilhelm Rontgen
(c) William Crookes
(d) J.J. Thomson
Answer
Answer: (a) R.A. Millikan
12. By which of the following physical processes can minimum energy required for the electron emission from the metal surface be supplied to the free electrons?
(a) Field emission
(b) Thermionic emission
(c) Photoelectric emission
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
13. Which of the following statements is true regarding the photoelectric experiment?
(a) The stopping potential increases with the increase in the intensity of incident light.
(b) The photocurrent increases with the intensity of light.
(c) The photocurrent increases with the increase in frequency
(d) All of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) The photocurrent increases with the intensity of light.