NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 People as Resource
Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
Do you notice any difference between the two friends? What are those?
Answer:
Yes there was a difference between two friends Sakai and Vilas. Sakai was an healthy boy whereas Vilas was a patient of arthritis. Sakai had done a vocational course in computers which helped him in getting a job in some private firm. Both his parents were eager to teach him. On the other hand, Vilas was illiterate. Vilas, did not have father. His mother earned a meager income of Rs. 20 to 30 a day. There was no family to support him. Therefore he could not go to school. As such he like his mother started selling fish therefore, could earn only a meager income.
Question 2.
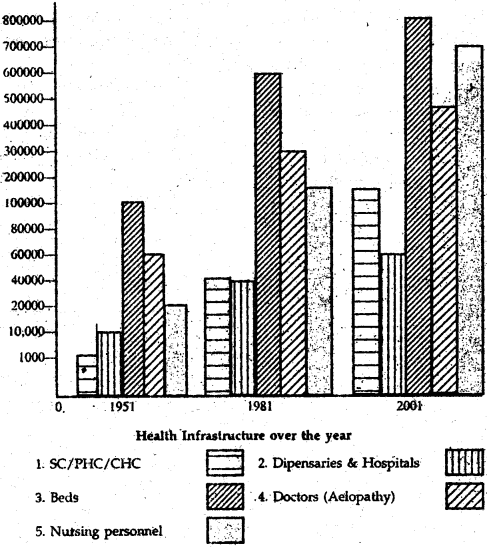
Study the graph below and answer the following questions?
1. Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951?
2. In which year India has the highest literacy rates?
3. Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
4. Why are women less educated than men?
5. How would you calculate literacy.
6. What is your projection about India’s literacy rate in 2010?
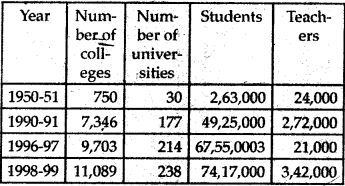
Table 2.1: Number of institutions of higher education enrolment and faculty.
Answer:
1. Literacy rates have increased from 18% in 1951 to 65% in 2001.
2. Literacy rate is highest in the year 2001.
3. Literacy rate is high among males of x India because from the very beginning girls are neglected. Equal opportunities are not given to them. In our society it is thought that boys are the bread earners, therefore, they enjoy many privileges.
4. Women are less educated because it is thought their work is to perform household chores. They are not given equal opporunities
5. Do it yourself.
6. The government of India has started many policies to increase literacy rate in India. Policies like Sarva Siksha Abhiyan, back-to-school camps, mid-day meal etc, could add to literate population of India. With such policies it seems that we will be able to achieve 100% literacy rate by 2010 at least in the age group of six to fourteen years.
Question 3.
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions.
(i) Is the increase in number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of strident.
(ii) Do you think one should have more number of universities?
(iii) What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 1998-99.
(iv) What is your idea about future college and universities?
Table 2.1: Number of institutions of higher education enrolment and faculty
Answer:
(i) Over the past fifty years, there has been a significant growth in the number of university and institutions of higher learning in specialized areas. But still as compared to the number of students the number of universities is not adequate.
(ii) Yes, we should have more number of universities.
(iii) There has been a tremendous and manifold increase in the number of teachers. In the year 1950-51, there were only 24,000 teachers. By the year 1998-99 it rose to 3,42,000.
(iv) The future college’s and universities should focus more on quality of education. They should encourage vocational courses, networking and information technology which helps in getting direct jobs They should also focus on distant education.
Question 4.
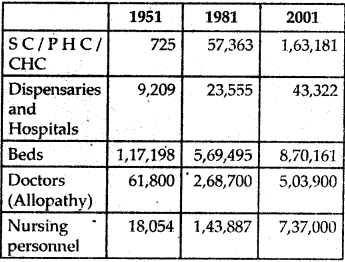
Study the table 2.2 and answer the following questions,
(i) What is the percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2001?
(ii) What is the percentage increase in doctors and nursing personnel from 1951 to 2001?
(iii) Do you think the increase in the number of doctor and nurses adequate for India ? Why?
(iv) What other facilities would you like to provide in a hospital?
(v) Discuss about the hospital you have visited?
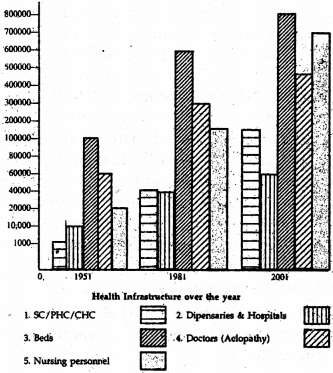
(vi) Can you draw graph using this table.
Table 2.2: Health infrastructure over the years.
Answer:
(i) The percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2001 is 370.43.
(ii) The percentage increase in doctors and nursing personnel from 1951 to 2001 is 715.37 and 3982.2.
(iii) Over the past five decades India has built up a vast health infrastructure and manpower required at primary secondary and tertiary care in government as well as private’ sector. But still as compared to our population growth the increase in number of doctprs and nurses is inadequate. For a population of above 100 crores we have only 5,03,900 doctors and 7,37,000 nurses.
(iv) Apart from routine check up and curing of illness, health centres like hospitals should provide information on nutritional values, family welfare, health awareness, etc. specially among underprivileged segment of population. Health centres should organise camps to provide information regarding hygiene, nutritious diet, viral diseases etc.
(v) Students are required to do it themselves
Question 5.
What do you understand by people as a resource?
Answer:
People as a resource is a way of referring to a country’s working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities. Like other resources population is Iso a resource. This is looking at the positive de of population. When the existing human resource is developed by providing good education and health facility it is called as human capital formation.
Question 6.
How is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Answer:
Human capital is superior to other resources like land and physical capital. It capital cannot become useful on its own. Skilled and educated population make the efficient use of other resources like land and capital.
Question 7.
What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Answer:
Education plays a vital role in human capital formation. Education opens new horizon, provides aspiration, and develop values of life. It contributes towards the growth of society. It enhances the national income, cultural richness and increase the efficiency of governance. Investment in human capital through education yields a return just like investment in physical capital. This, can be seen directly in the form of higher incomes earned because of higher productivity of the more educated or better-trained persons.
Question 8.
What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Answer:
A healthy person has higher productivity than an unhealthy person. The health of a person helps him to realise his potential and the ability to fight illness. An unhealthy person becomes the liability for an organisation which hires him. Health is an indispensable basis for realising one’s own well being. Investment in human capital via health yields greater return in future therefore, improvement in the health status of the population has been the priority of the country.
Question 9.
What part does health play in the individual’s working life.
Answer:
Health plays a vital role in an individual’s working life since no firm would be induced to employ people who might not work efficiently as healthy workers because of ill health and not only that, people who are physically or mentally ill cannot work.
Question 10.
What are the various activities undertaken in the primary sector, secondary sector, and tertiary sector?
Answer:
The various activities undertaken in different sectors are as follows—
(i) Primary sector—It includes agriculture, fishing, poultry farming, and mining.
(ii) Secondary sector— Quarrying and manufacturing is included in the secondary sector.
(iii) Tertiary sector—This sector includes trade, transport, communication, banking, education, health, tourism, services etc.
Question 11.
What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Answer:
An activity which results in generation of income is called as economic activity, for example workers working in factories, banks etc. On the other hand, an activity which does not give any income is called as non-economic activity, for example, a woman performing domestic cores. Economic activities add to national income whereas noneconomic activities do not add to it.
Question 12.
Why are women employed in low paid work?
Answer:
Education and skill are the major determinants of the earning of any individual in the market. A majority of women have meagre education and low skill formation. Therefore, women are paid low compared to men.
Question 13.
How will you explain the term unemployment?
Answer:
Unemployment is said to exist when people who are willing to work at existing wages cannot find jobs. Unemployment can be of many types. In India two types of unemployment are prominent seasonal and disguised unemployment. Unemployment leads to wastage of resources and is detrimental to the growth of an economy.
Question 14.
What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Answer:
Disguised unemployment is a situation in which number of people engaged in an activity are more than actually required for it. On the other hand, when some people get work only for me part of the year and remain unemployed for the remaining part due to seasonal nature of work, it is called as seasonal unemployment.
Question 15.
Why is educated unemployment, a peculiar problem of India.
Answer:
In India, in case of urban areas educated unemployment has become a common phenomenon. Many youth with matriculation, graduation, and post graduation degrees are not able to find job. The unemployment of graduate and post-graduate has increased faster than among matriculates. A paradoxical manpower situation is witnessed as surplus of manpower in-certain categories co-exist with shortage of manpower in others. There is unemployment among technically qualified person on one hand, while there is a dearth of technical skills required for economic growth.
Question 16.
In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity.
Answer:
India can build the maximum employment opportunity in tertiary sector. Now various new services are appearing like biotechnology information technology and so on.
Question 17.
Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Answer:
Following are some measures to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed
(i) to start vocational courses which can provide immediate job.
(ii) government can provide loan at low interest rate to help unemployed youth to start their own business.
(iii) by allowing foreign companies to set up their industries in India. This will help absorb the man-power.
(iv) by changing the education system. Instead of producing army of. unemployed graduates, universities should provide practical education which can help youth in their work fields.
Question 18.
Which capital would you consider the best—land, labour, physical capital and human capital? Why?
Answer:
Among all the factors of production viz. land, labour, physical capital and human capital, the human capital is best. It is because human capital is required to put together land, labour and physical capital to produce an output. Land and physical capital cannot become useful on its own.
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 People as Resource.