NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 Power Sharing
Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
What are the different forms of power sharing in modem democracies? Give an example of each of these.
Answer:
In modern democracies, power sharing arrangement can take any of the following terms:
1. Among different organs of government:
Power is shared among different organs of government, such as the legislative, executive and judiciary. This is known as horizontal distribution of power because it allows different organs of the government placed at the same level to exercise different powers. This arrangement ensures that none of the organs can exercise unlimited power. Example : The Mumbai Maharashtra state government to immediately take action and improve living condition for the 2,000 odd children at seven children’s homes in Mumbai.
2. Among governments at different levels :
Power can be shared among governments at different levels. For example, a general government for the entire country and governments at the provincial, sub-national or regional level. Such a general government for the entire country is usually called federal government. In those countries, where there are different levels of governments, the constitution clearly lays down the powers of different levels of governments.
Example :
The finance ministers of various states Nigeria got together and demanded that the federal government should declare its sources of income. They also wanted to know the formula by which the revenue is distributed to various state governments.
3. Among different social groups :
Power may also be shared among different social groups, such as the religious and linguistic groups. In some countries there are legal and constitutional arrangements whereby socially and economically weaker sections and women are represented in the administration and legislatures This method used to give minority communities a fair sharing power, community government in Belgium is a good ‘example of this arrangement. It is elected by people belonging to one language community Dutch, French and German speaking – no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language related issues.
Example :
The government of Ontario state in Canada has agreed to a land claim settlement with the aboriginal community The Minister responsible for Native Affairs announced that the government will work with aboriginal people in a spirit of mutual respect and co-operation.
4. Among Political Parties and Pressure Groups :
Power sharing arrangements can also be seen in the way political parties pressure groups and movements control or influence power. In such arrangements, power is shared among different political parties representing different ideologies and social groups. In a democracy we find interest groups such as those of traders, businessman, industrialists, farmers and workers. They too, will have a share in government power, either through participation in governmental committees or bringing influence on the decision making process.
Example :
Russia’s two influential political parties, the Union of Right Forces (SPS) and the liberal yabloko movement agreed to unite their organizations into strong right-wing coalition. They propose to have a common list of candidates in the next parliamentary elections.
Question 2.
State one prudential reason and one moral reason for power sharing with an example from the Indian context.
Answer:
Two different sets of reasons can be given in favour of power sharing
1. Prudential reason:
Power sharing reduces the possibility of conflict between social groups. Social conflicts often lead to violence and political instability, so power sharing ensures the stability of political order. Imposing the will of majority community over other minority groups undermines the unity of the nation. For example, India is a country of unity in diversity. People from different castes, religions and languages live in this country. So power sharing is desirable.
2. Moral reason :
Power sharing is the very spirit gf democracy. People have a right to be consulted on how they are to be govehed. For example, India is the largest democracy of the world. The government of India is a legitimate government representing the aspirations of Indian masses.
Question 3.
After reading this chapter, three students drew different conclusions. Which of these do you agree with and why? Give your reasons in about 50 words.
Thomman : Power sharing is necessary only in societies which have religious linguistic or ethnic divisions.
Mattai: Power sharing is suited only for big countries that have regional divisions.
Ousep: Every society needs some form of power sharing ,even if they are small or do not have social divisions.
Answer:
We agree with the conclusion drawn by Ousep that every society needs some form of power sharing even if they are small or do not have social divisions.
In a democracy people rule themselves through institutions of self governance. At the same time, due respect is given to the views that exist in a society and everyone’s voice is heard in shaping of public policies in a good democratic government. In a democracy political power should be distributed among as many citizens as possible.
Question 4.
The mayor of Merchtem, a town near Brussels in Belgium, has defended a ban on speaking French in the town’s schools. He said that the ban would help all non-Dutch speakers integrate in this Flemish town. Do you think that this measure is in keeping with the spirit of Belgium’s power sharing arrangements? Give your reasons in about 50 words.
Answer:
The Mayor’s view that the ban on speaking French in the town’s schools would help all non-Dutch speakers integrate in this Flemish town, is not in keeping with the s sharing arrangements because the constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government. Secondly, the community government’ is elected by people belonging to one language community – Dutch, French and German speaking no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language related issues.
Question 5.
Read the following passage and pick out any one of the of rudential reasons power sharing offered in this we need to give more power to the panchayats to realize dream of Mahatma Gandhi and the hopes our Constitution. Panchayati Raj establishes true democracy. It restores power to the makers of only place where power belongs in the hands of the people. Giving power to is also a way to reduce corruption and increase administrative efficiency. When people participate in the planning and implementation of developmental schemes, would naturally exercise greater control over these schemes. This would eliminate the corrupt middlemen. Thus Panchayati Raj will strengthen the foundations of our democracy.”
Answer:
Giving power to Panchayats is also a way to reduce corruption and increase administrative efficiency. Thus power-sharing would help to reduce the possibility of conslict between social groups.
Question 6.
Different arguments are usually put forth in favour and against power-sharing. Identify those which are in favour of power-sharing and select the answer from the codes given below? Power-sharing:
A. reduces conflict among different! communities
B. decreases the possibility of arbitrariness
C. delays decision-making process
D. accommodates diversities
E. increases instability and divisiveness.
F. promotes people’s participation in government
G. undermines the unity of a country,
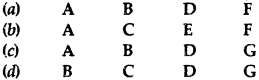
Answer:
(a) A, B, D, F
Question 7.
Consider the following statements about power sharing e arrangements in Belgium and Sri Lanka,
A. In Belgium the Dutch-speaking majority people tried to impose their domination on the minority French-speaking Community.
B. In Sri Lanka, the policies of government sought to ensure the dominance of the Sinhala- speaking majority.
C. The Tamils in Sri Lanka demanded a federal arrangement of power sharing to protect their culture, language and equality of opportunity in education and jobs.
D. The transformation of Belgium from unitary government to a federal one prevented a possible division of the country cn linguistic lines.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B, C and D.
(b) A, B and D
(c) C and D
(d) B, C and D
Answer:
(d) B, C and D
Question 8.
Match List I (forms of power sharing) with List II (forms of government) and select the correct answer using the codes given below in the lists:
| List I | List II |
| 1. Power shared among different organs of government | A. Community government |
| 2. Power shared among governments at different levels | B. Separation of powers |
| 3. Power shared by different social groups | C. Coalition government |
| 4. Power shared by two or more political parties | D. Federal government political parties |

Answer:
![]()
Question 9.
Consider the following two statements on power-sharing and select the answer using the codes given below;
(A) Power sharing is good for democracy
(B) It helps to reduce the possibility of conflict between social groups
Which of these statements are true and false?
(a) A is true but B is false
(b) Both A and B are true
(c) Both A and B are false
(d) A is false but B is true
Answer:
(b) Both A and B are true.
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Civics Chapter 1 Power Sharing.