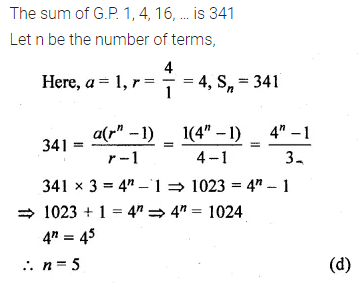ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 9 Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions MCQS
ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 9 Arithmetic and Geometric Progressions MCQS
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 33) :
Question 1.
The list of numbers – 10, – 6, – 2, 2, … is
(a) an A.P. with d = -16
(b) an A.P with d = 4
(c) an A.P with d = -4
(d) not an A.P
Solution:
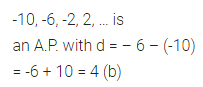
Question 2.
The 10th term of the A.P. 5, 8, 11, 14, … is
(a) 32
(b) 35
(c) 38
(d) 185
Solution:

Question 3.
The 30th term of the A.P. 10, 7, 4, … is
(a) 87
(b) 77
(c) -77
(d) -87
Solution:
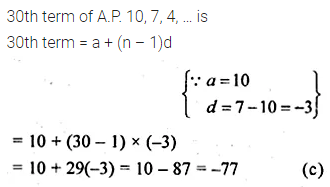
Question 4.
The 11th term of the A.P. -3, \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \), 2, … is
(a) 28
(b) 22
(c) -38
(d) -48
Solution:
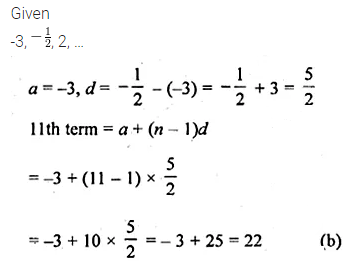
Question 5.
The 4th term from the end of the A.P. -11, -8, -5, …, 49 is
(a) 37
(b) 40
(c) 43
(d) 58
Solution:

Question 6.
The 15th term from the last of the A.P. 7, 10, 13, …,130 is
(a) 49
(b) 85
(c) 88
(d) 110
Solution:

Question 7.
If the common difference of an A.P. is 5, then a18 – a13 is
(a) 5
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 30
Solution:

Question 8.
In an A.P., if a18 – a14 = 32 then the common difference is
(a) 8
(b) -8
(c) -4
(d) 4
Solution:
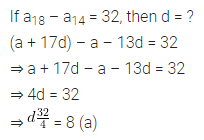
Question 9.
In an A.P., if d = -4, n = 7, an = 4, then a is
(a) 6
(d) 7
(c) 20
(d) 28
Solution:
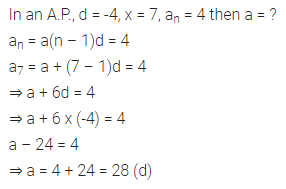
Question 10.
In an A.P., if a = 3.5, d = 0, n = 101, then an will be
(a) 0
(b) 3.5
(c) 103.5
(d) 104.5
Solution:

Question 11.
In an A.P., if a = -7.2, d = 3.6, an = 7.2, then n is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Solution:
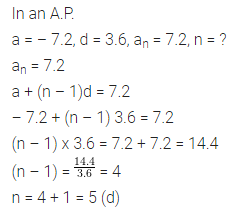
Question 12.
Which term of the A.P. 21, 42, 63, 84,… is 210?
(a) 9th
(b) 10th
(c) 11th
(d) 12th
Solution:

Question 13.
If the last term of the A.P. 5, 3, 1, -1,… is -41, then the A.P. consists of
(a) 46 terms
(b) 25 terms
(c) 24 terms
(d) 23 terms
Solution:

Question 14.
If k – 1, k + 1 and 2k + 3 are in A.P., then the value of k is
(a) – 2
(b) 0
(c) 2
(d) 4
Solution:
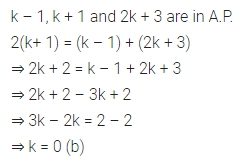
Question 15.
The 21st term of an A.P. whose first two terms are -3 and 4 is
(a) 17
(b) 137
(c) 143
(d) -143
Solution:

Question 16.
If the 2nd term of an A.P. is 13 and the 5th term is 25, then its 7th term is
(a) 30
(b) 33
(c) 37
(d) 38
Solution:

Question 17.
If the first term of an A.P. is -5 and the common difference is 2, then the sum of its first 6 terms is
(a) 0
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 15
Solution:

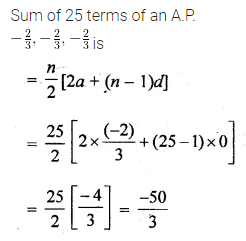
Question 18.
The sum of 25 terms of the A.P.\(-\frac { 2 }{ 3 } ,-\frac { 2 }{ 3 } ,-\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) is
(a) 0
(b) \(– \frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)
(c) \(– \frac { 50 }{ 3 } \)
(d) -50
Solution:
Question 19.
In an A.P., if a = 1, an = 20 and Sn = 399, then n is
(a) 19
(b) 21
(c) 38
(d) 42
Solution:
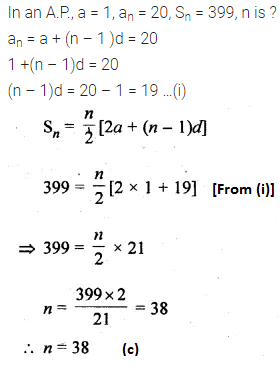
Question 20.
In an A.P., if a = -5, l = 21. and Sn = 200, then n is equal to
(a) 50
(b) 40
(c) 32
(d) 25
Solution:
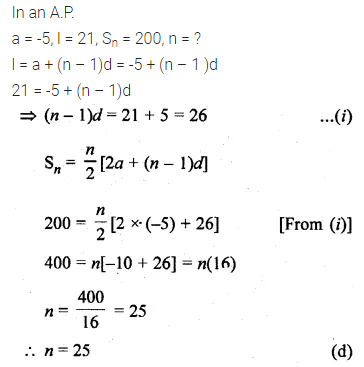
Question 21.
In an A.P., if a = 3 and S8 = 192, then d is
(a) 8
(b) 7
(c) 6
(d) 4
Solution:
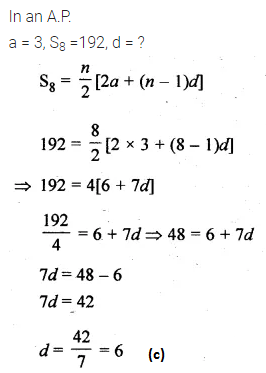
Question 22.
The sum of first five multiples of 3 is
(a) 45
(b) 55
(c) 65
(d) 75
Solution:
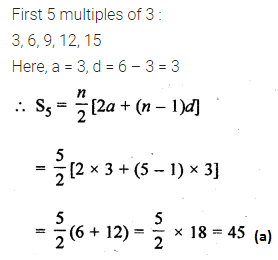
Question 23.
The number of two-digit numbers which are divisible by 3 is
(a) 33
(b) 31
(c) 30
(d) 29
Solution:

Question 24.
The number of multiples of 4 that lie between 10 and 250 is
(a) 62
(b) 60
(c) 59
(d) 55
Solution:
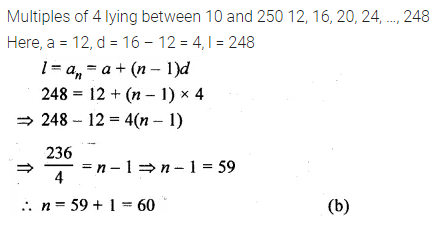
Question 25.
The sum of first 10 even whole numbers is
(a) 110
(b) 90
(c) 55
(d) 45
Solution:
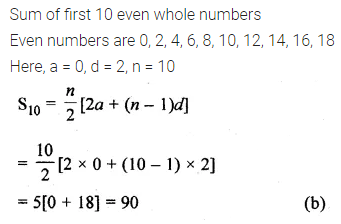
Question 26.
The list of number \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 9 } \) , \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \), 1, – 3,… is a
(a) GP. with r = – 3
(b) G.P. with r = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)
(c) GP. with r = 3
(d) not a G.P.
Solution:
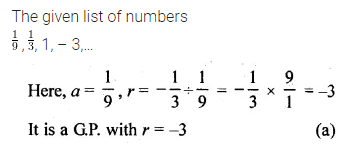
Question 27.
The 11th of the G.P. \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 8 } \) , \(– \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) , 2, – 1, … is
(a) 64
(b) -64
(c) 128
(d) -128
Solution:

Question 28.
The 5th term from the end of the G.P. 2, 6, 18, …, 13122 is
(a) 162
(b) 486
(c) 54
(d) 1458
Solution:

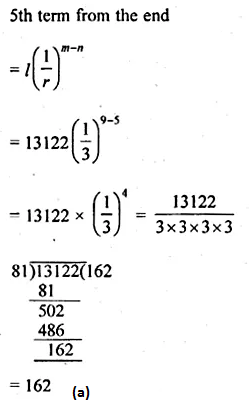
Question 29.
If k, 2(k + 1), 3(k + 1) are three consecutive terms of a G.P., then the value of k is
(a) -1
(b) -4
(c) 1
(d) 4
Solution:
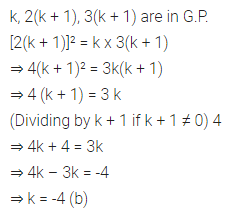
Question 30.
Which term of the G.P. 18, -12, 8, … is \(\\ \frac { 512 }{ 729 } \) ?
(a) 12th
(b) 11th
(c) 10th
(d) 9th
Solution:

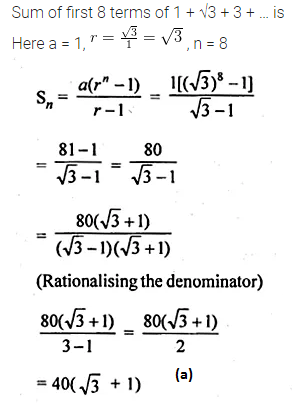
Question 31.
The sum of the first 8 terms of the series 1 + √3 + 3 + … is
Solution:
Question 32.
The sum of first 6 terms of the G.P. 1, \(– \frac { 2 }{ 3 } \) ,\(\\ \frac { 4 }{ 9 } \) ,… is
(a) \(– \frac { 133 }{ 243 } \)
(b) \(\\ \frac { 133 }{ 243 } \)
(c) \(\\ \frac { 793 }{ 1215 } \)
(d) none of these
Solution:
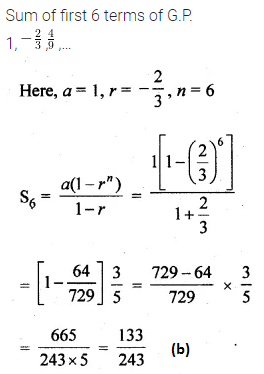
Question 33.
If the sum of the GP., 1, 4, 16, … is 341, then the number of terms in the GP. is
(a) 10
(b) 8
(c) 6
(d) 5
Solution: