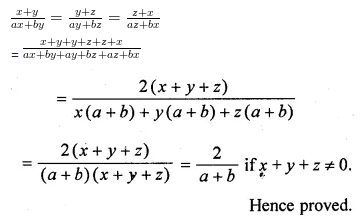ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion Ex 7.3
ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion Ex 7.3
Question 1.
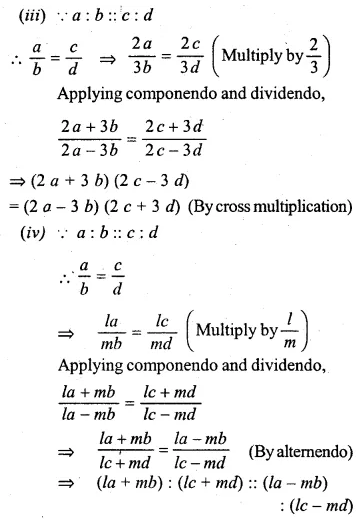
If a : b : : c : d, prove that
(i) \(\frac { 2a+5b }{ 2a-5b } =\frac { 2c+5d }{ 2c-5d } \)
(ii) \(\frac { 5a+11b }{ 5c+11d } =\frac { 5a-11b }{ 5c-11d } \)
(iii) (2a + 3b)(2c – 3d) = (2a – 3b)(2c + 3d)
(iv) (la + mb) : (lc + mb) :: (la – mb) : (lc – mb)
Solution:

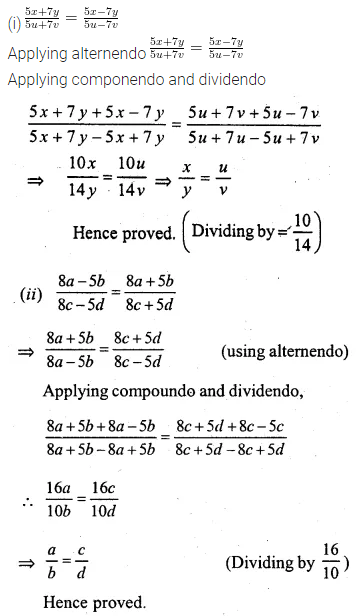
Question 2.
(i) If \(\frac { 5x+7y }{ 5u+7v } =\frac { 5x-7y }{ 5u-7v } \) , Show that \(\frac { x }{ y } =\frac { u }{ v } \)
(ii) \(\frac { 8a-5b }{ 8c-5d } =\frac { 8a+5b }{ 8c+5d } \) , prove that \(\frac { a }{ b } =\frac { c }{ d } \)
Solution:
Question 3.
If (4a + 5b) (4c – 5d) = (4a – 5d) (4c + 5d), prove that a, b, c, d are in proporton.
Solution:

Question 4.
If (pa + qb) : (pc + qd) :: (pa – qb) : (pc – qd) prove that a : b : : c : d
Solution:

Question 5.
If (ma + nb): b :: (mc + nd) : d, prove that a, b, c, d are in proportion.
Solution:
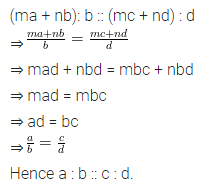
Question 6.
If (11a² + 13b²) (11c² – 13d²) = (11a² – 13b²)(11c² + 13d²), prove that a : b :: c : d.
Solution:

Question 7.
If (a + 3b + 2c + 6d) (a – 3b – 2c + 6d) = (a + 3b – 2c – 6d) (a – 3b + 2c – 6d), prove that a : b :: c : d.
Solution:

Question 8.
If \(x=\frac { 2ab }{ a+b } \) find the value of \(\frac { x+a }{ x-a } +\frac { x+b }{ x-b } \)
Solution:

Question 9.
If \(x=\frac { 8ab }{ a+b } \) find the value of \(\frac { x+4a }{ x-4a } +\frac { x+4b }{ x-4b } \)
Solution:

Question 10.
If \(x=\frac { 4\sqrt { 6 } }{ \sqrt { 2 } +\sqrt { 3 } } \) find the value of \(\frac { x+2\sqrt { 2 } }{ x-2\sqrt { 2 } } +\frac { x+2\sqrt { 3 } }{ x-2\sqrt { 3 } } \)
Solution:

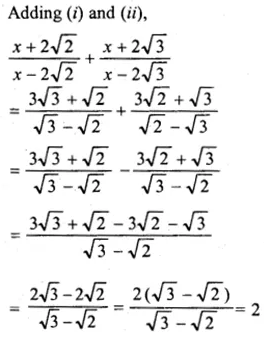
Question 11.
Solve \(x:\frac { \sqrt { 36x+1 } +6\sqrt { x } }{ \sqrt { 36x+1 } -6\sqrt { x } } =9 \)
Solution:

Question 12.
Find x from the following equations :
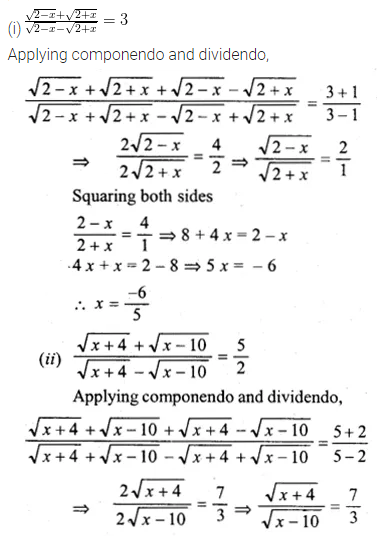
(i) \(\frac { \sqrt { 2-x } +\sqrt { 2+x } }{ \sqrt { 2-x } -\sqrt { 2+x } } =3 \)
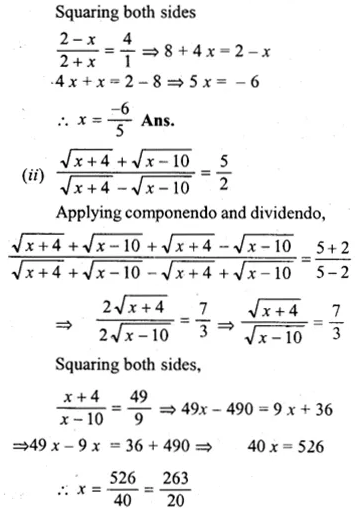
(ii) \(\frac { \sqrt { x+4 } +\sqrt { x-10 } }{ \sqrt { x+4 } -\sqrt { x-10 } } =\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)
(iii) \(\frac { \sqrt { 1+x } +\sqrt { 1-x } }{ \sqrt { 1+x } -\sqrt { 1-x } } =\frac { a }{ b } \)
(iv) \(\frac { \sqrt { 12x+1 } +\sqrt { 2x-3 } }{ \sqrt { 12x+1 } -\sqrt { 2x-3 } } =\frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
(v) \(\frac { 3x+\sqrt { { 9x }^{ 2 }-5 } }{ 3x-\sqrt { { 9x }^{ 2 }-5 } } =5 \)
(vi) \(\frac { \sqrt { a+x } +\sqrt { a-x } }{ \sqrt { a+x } -\sqrt { a-x } } =\frac { c }{ d } \)
Solution:

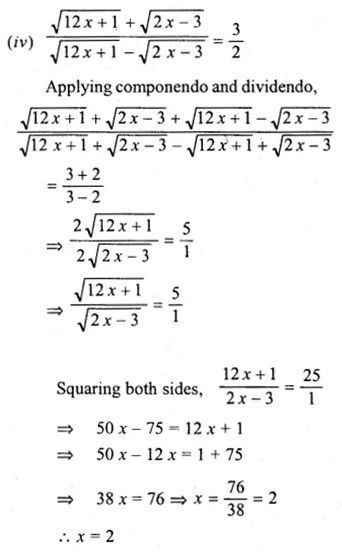
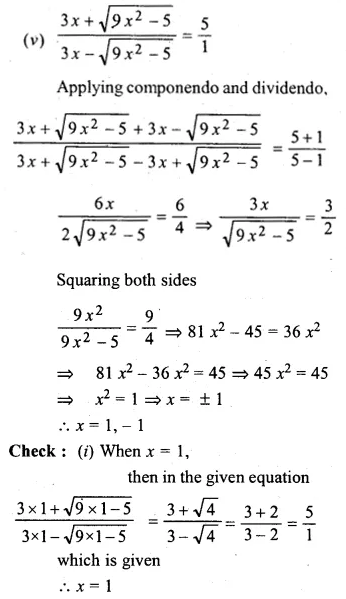
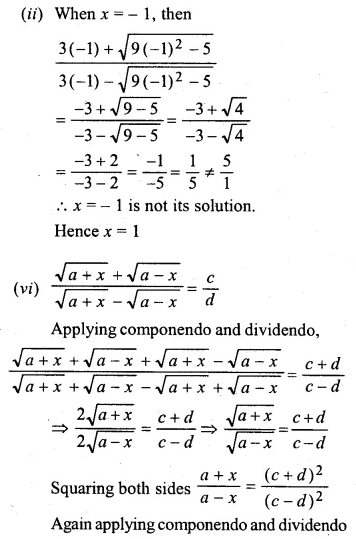
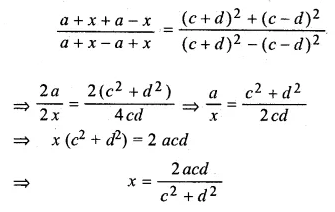
Question 13.
Solve \(\frac { 1+x+{ x }^{ 2 } }{ 1-x+{ x }^{ 2 } } =\frac { 62\left( 1+x \right) }{ 63\left( 1-x \right) } \)
Solution:

Question 14.
Solve for \(x:16{ \left( \frac { a-x }{ a+x } \right) }^{ 3 }=\frac { a+x }{ a-x } \)
Solution:

Question 15.
If \(x=\frac { \sqrt { a+x } +\sqrt { a-1 } }{ \sqrt { a+1 } -\sqrt { a-1 } } \) , using properties of proportion , show that x² – 2ax + 1 = 0
Solution:

Question 16.
Given \(x=\frac { \sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 } } +\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 } } }{ \sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }+{ b }^{ 2 } } -\sqrt { { a }^{ 2 }-{ b }^{ 2 } } } \) Use componendo and dividendo to prove that \({ b }^{ 2 }=\frac { { 2a }^{ 2 }x }{ { x }^{ 2 }+1 } \)
Solution:

Question 17.
Given that \(\frac { { a }^{ 3 }+3{ ab }^{ 2 } }{ { b }^{ 3 }+{ 3a }^{ 2 }b } =\frac { 63 }{ 62 } \). Using componendo and dividendo find a: b. (2009)
Solution:
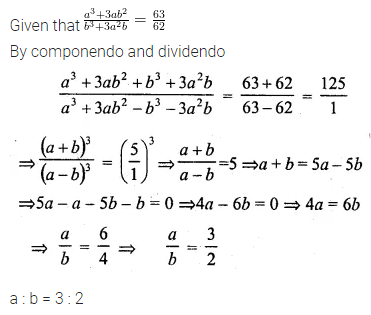
Question 18.
Give \(\frac { { x }^{ 3 }+12x }{ { 6x }^{ 2 }+8 } =\frac { { y }^{ 3 }+27y }{ { 9y }^{ 2 }+27 } \) Using componendo and dividendo find x : y.
Solution:

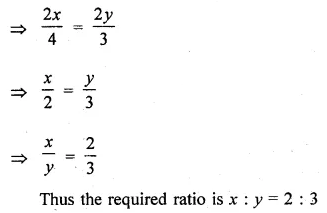
Question 19.
Using the properties of proportion, solve the following equation for x; given
\(\frac { x^{ 3 }+3x }{ { 3x }^{ 2 }+1 } =\frac { 341 }{ 91 } \)
Solution:

Question 20.
If \(\frac { x+y }{ ax+by } =\frac { y+z }{ ay+bz } =\frac { z+x }{ az+bx } \) , prove that each of these ratio is equal to \(\\ \frac { 2 }{ a+b } \) unless x + y + z = 0
Solution: