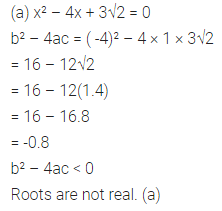ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 5 Quadratic Equations in One Variable MCQS
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (1 to 15):
Question 1.
Which of the following is not a quadratic equation ?
(a) (x + 2)2 = 2(x + 3)
(b) x2 + 3x = ( -1) (1 – 3x)
(c) (x + 2) (x – 1) = x2 – 2x – 3
(d) x3 – x2 + 2x + 1 = (x + 1)3
Solution:
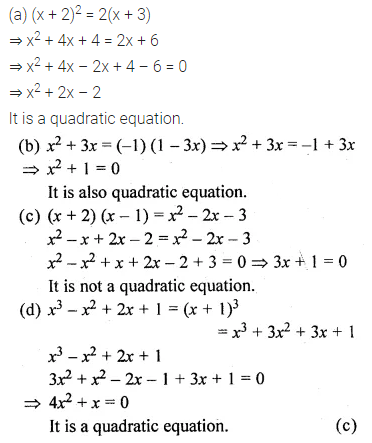
Question 2.
Which of the following is a quadratic equation ?
(a) (x – 2) (x + 1) = (x – 1) (x – 3)
(b) (x + 2)3 = 2x(x2 – 1)
(c) x2 + 3x + 1 = (x – 2)2
(d) 8(x – 2)3 = (2x – 1)3 + 3
Solution:

Question 3.
Which of the following equations has 2 as a root ?
(a) x2 – 4x + 5 = 0
(b) x2 + 3x – 12 = 0
(c) 2x2 – 7x + 6 = 0
(d) 3x2 – 6x – 2 = 0
Solution:
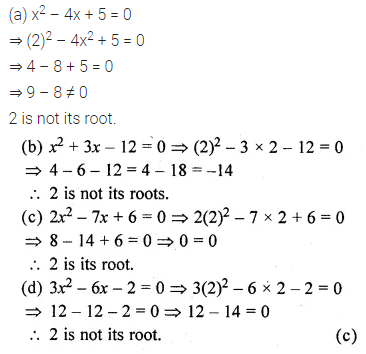
Question 4.
If \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the equation x2 + kx – \(\\ \frac { 5 }{ 4 } \) = 0, then the value of k is
(a) 2
(b) -2
(c) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)
(d) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
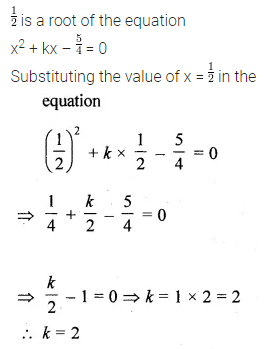
Question 5.
If \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) is a root of the quadratic equation 4x2 – 4kx + k + 5 = 0, then the value of k is
(a) -6
(b) -3
(c) 3
(d) 6
Solution:
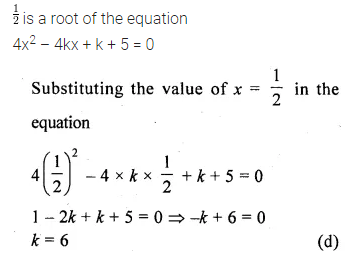
Question 6.
The roots of the equation x2 – 3x – 10 = 0 are
(a) 2, -5
(b) -2, 5
(c) 2, 5
(d) -2, – 5
Solution:
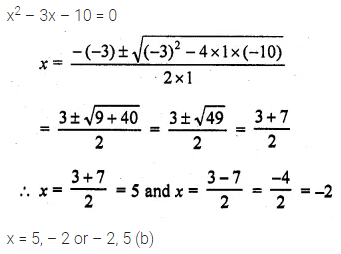
Question 7.
If one root of a quadratic equation with rational coefficients is \(\frac { 3-\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \), then the other
(a) \(\frac { -3-\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(b) \(\frac { -3+\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(c) \(\frac { 3+\sqrt { 5 } }{ 2 } \)
(d) \(\frac { \sqrt { 3 } +5 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:
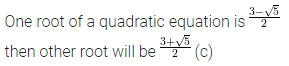
Question 8.
If the equation 2x² – 5x + (k + 3) = 0 has equal roots then the value of k is
(a) \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \)
(b) \(– \frac { 9 }{ 8 } \)
(c) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 8 } \)
(d) \(– \frac { 1 }{ 8 } \)
Solution:
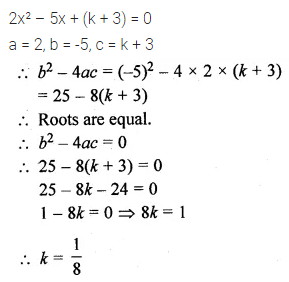
Question 9.
The value(s) of k for which the quadratic equation 2x² – kx + k = 0 has equal roots is (are)
(a) 0 only
(b) 4
(c) 8 only
(d) 0, 8
Solution:
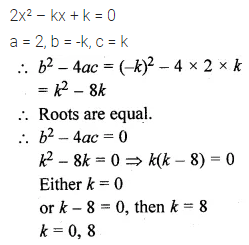
Question 10.
If the equation 3x² – kx + 2k =0 roots, then the the value(s) of k is (are)
(a) 6
(b) 0 Only
(c) 24 only
(d) 0
Solution:

Question 11.
If the equation (k + 1) x² – 2 (k – 1)x + 1 = 0 has equal roots, then the values of k are
(a) 1, 3
(b) 0, 3
(c) 0, 1
(d) 0, 1
Solution:
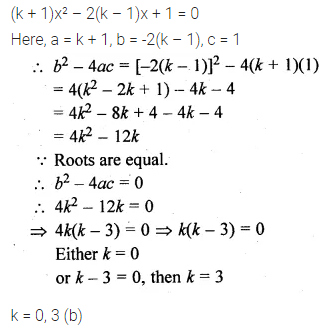
Question 12.
If the equation 2x² – 6x + p = 0 has real and different roots, then the values of p are given by
(a) p < \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(b) p ≤ \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(c) p > \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
(d) p ≥ \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 2 } \)
Solution:

Question 13.
The quadratic equation 2x² – √5x + 1 = 0 has
(a) two distinct real roots
(b) two equal real roots
(c) no real roots
(d) more than two real roots
Solution:
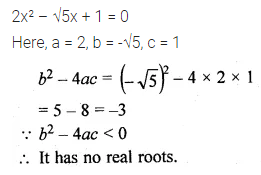
Question 14.
Which of the following equations has two distinct real roots ?
(a) 2x² – 3√2x + \(\\ \frac { 9 }{ 4 } \) = 0
(b) x² + x – 5 = 0
(c) x² + 3x + 2√2 = 0
(d) 5x² – 3x + 1 = 0
Solution:
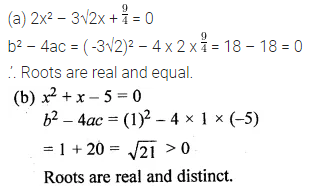
Question 15.
Which of the following equations has no real roots ?
(a) x² – 4x + 3√2 = 0
(b) x² + 4x – 3√2 = 0
(c) x² – 4x – 3√2 = 0
(d) 3x² + 4√3x + 4 = 0
Solution: