MCQ Questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 Circles with Answers
MCQs from Class 9 Maths Chapter 10 – Circles are provided here to help students prepare for their upcoming Maths exam.
MCQs from CBSE Class 9 Maths Chapter 10: Circles
1) The center of the circle lies in______ of the circle.
a. Interior
b. Exterior
c. Circumference
d. None of the above
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (a)
2) The longest chord of the circle is:
a. Radius
b. Arc
c. Diameter
d. Segment
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (c)
3) Equal _____ of the congruent circles subtend equal angles at the centers.
a. Segments
b. Radii
c. Arcs
d. Chords
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (d)
Explanation: See the figure below:
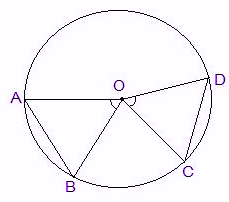
Let ΔAOB and ΔCOD are two triangles inside the circle.
OA = OC and OB = OD (radii of the circle)
AB = CD (Given)
So, ΔAOB ≅ ΔCOD (SSS congruency)
∴ By CPCT rule, ∠AOB = ∠COD.
Hence, this prove the statement.
4) If chords AB and CD of congruent circles subtend equal angles at their centres, then:
a. AB = CD
b. AB > CD
c. AB < AD
d. None of the above
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (a)
Explanation: Take the reference of the figure from above question.
In triangles AOB and COD,
∠AOB = ∠COD (given)
OA = OC and OB = OD (radii of the circle)
So, ΔAOB ≅ ΔCOD. (SAS congruency)
∴ AB = CD (By CPCT)
5) If there are two separate circles drawn apart from each other, then the maximum number of common points they have:
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (a)
6) The angle subtended by the diameter of a semi-circle is:
a. 90
b. 45
c. 180
d. 60
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (c)
Explanation: The semicircle is half of the circle, hence the diameter of the semicircle will be a straight line subtending 180 degrees.
7) If AB and CD are two chords of a circle intersecting at point E, as per the given figure. Then:
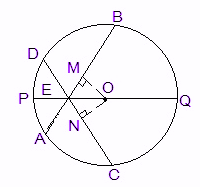
a.∠BEQ > ∠CEQ
b. ∠BEQ = ∠CEQ
c. ∠BEQ < ∠CEQ
d. None of the above
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
OM = ON (Equal chords are always equidistant from the centre)
OE = OE (Common)
∠OME = ∠ONE (perpendiculars)
So, ΔOEM ≅ ΔOEN (by RHS similarity criterion)
Hence, ∠MEO = ∠NEO (by CPCT rule)
∴ ∠BEQ = ∠CEQ
8) If a line intersects two concentric circles with centre O at A, B, C and D, then:
a. AB = CD
b. AB > CD
c. AB < CD
d. None of the above
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (a)
Explanation: See the figure below:
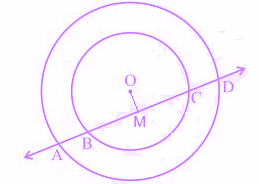
From the above fig., OM ⊥ AD.
Therefore, AM = MD — 1
Also, since OM ⊥ BC, OM bisects BC.
Therefore, BM = MC — 2
From equation 1 and equation 2.
AM – BM = MD – MC
∴ AB = CD
9) In the below figure, the value of ∠ADC is:
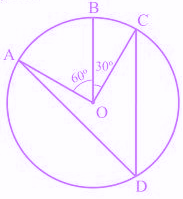
a. 60°
b. 30°
c. 45°
d. 55°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (c)
Explanation: ∠AOC = ∠AOB + ∠BOC
So, ∠AOC = 60° + 30°
∴ ∠AOC = 90°
An angle subtended by an arc at the centre of the circle is twice the angle subtended by that arc at any point on the rest part of the circle.
So,
∠ADC = 1/2∠AOC
= 1/2 × 90° = 45°
10) In the given figure, find angle OPR.
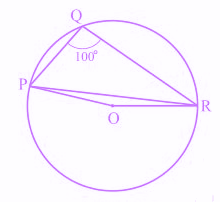
a. 20°
b. 15°
c. 12°
d. 10°
Answer/ Explanation
Answer: (d)
Explanation: The angle subtended by an arc at the centre of the circle is twice the angle subtended by that arc at any point on the circle.
So, ∠POR = 2 × ∠PQR
We know the values of angle PQR as 100°
So, ∠POR = 2 × 100° = 200°
∴ ∠POR = 360° – 200° = 160°
Now, in ΔOPR,
OP and OR are the radii of the circle
So, OP = OR
Also, ∠OPR = ∠ORP
By angle sum property of triangle, we knwo:
∠POR + ∠OPR + ∠ORP = 180°
∠OPR + ∠OPR = 180° – 160°
As, ∠OPR = ∠ORP
2∠OPR = 20°
Thus, ∠OPR = 10°
