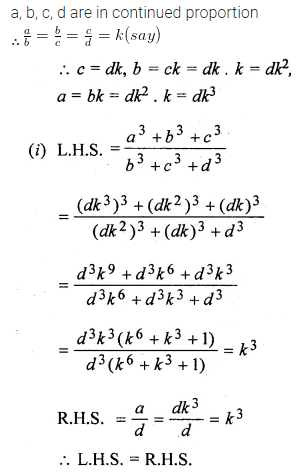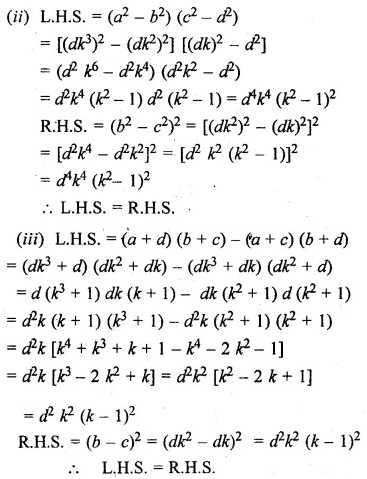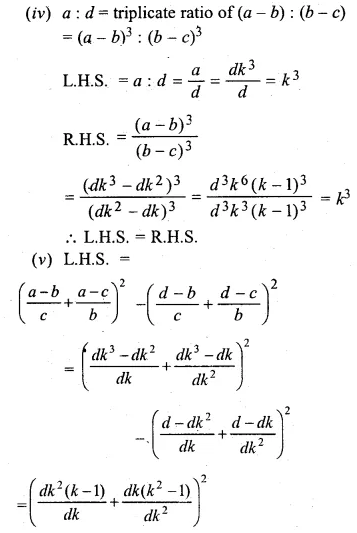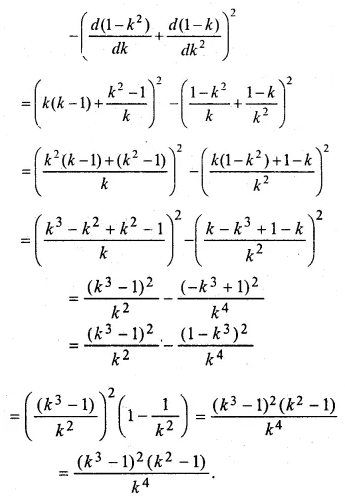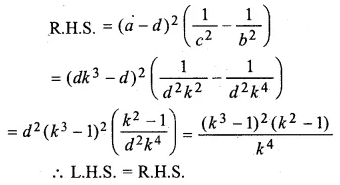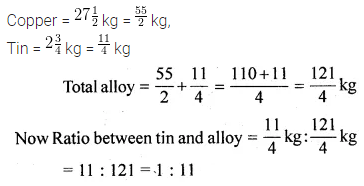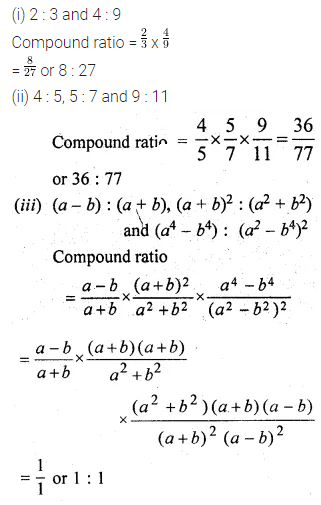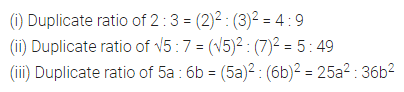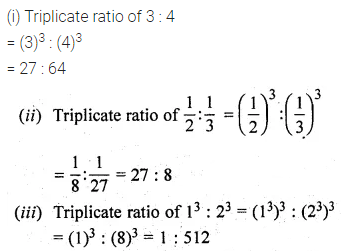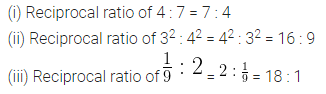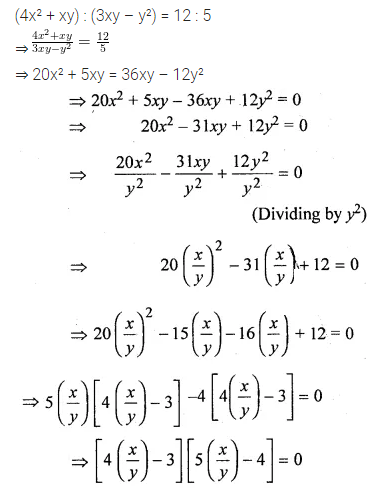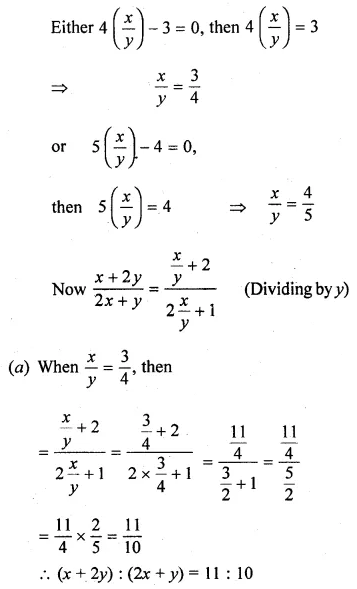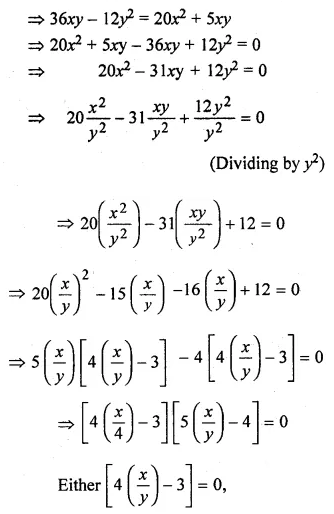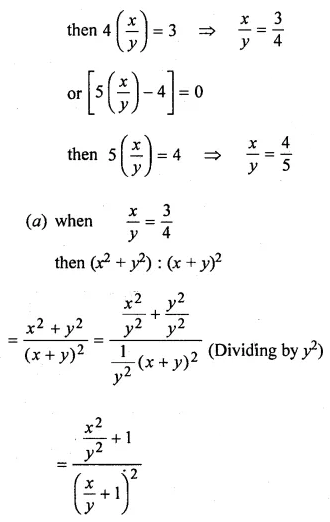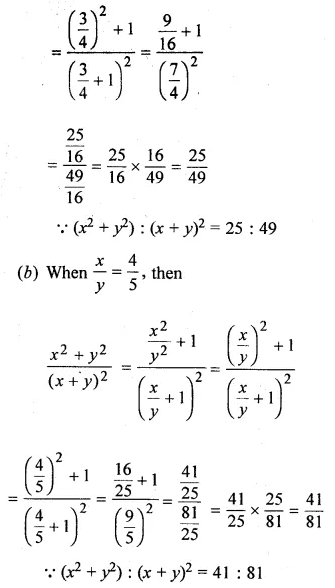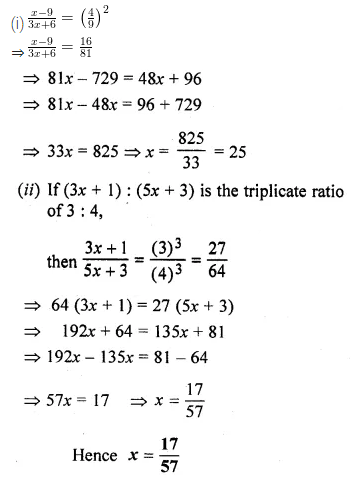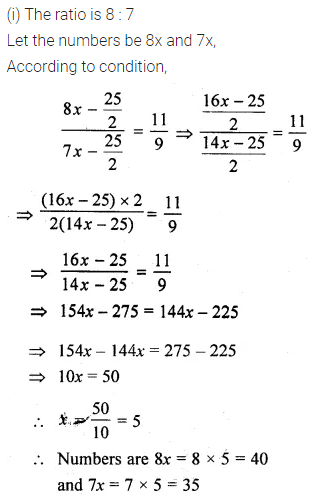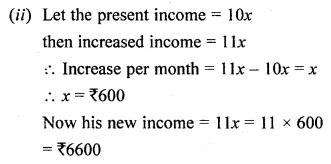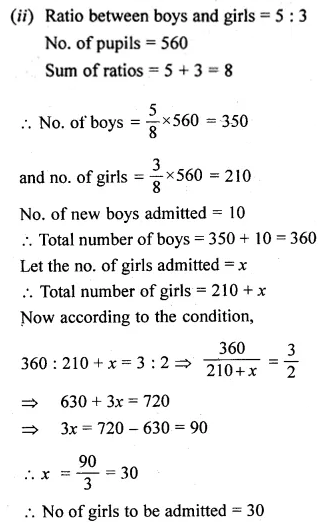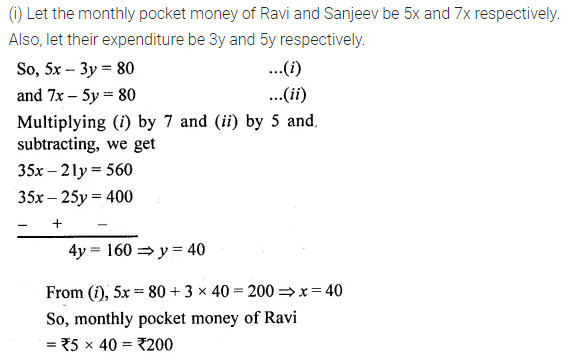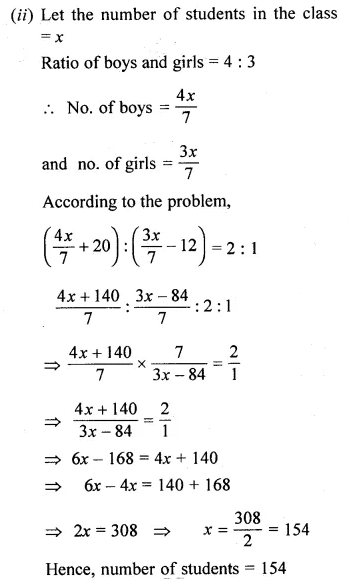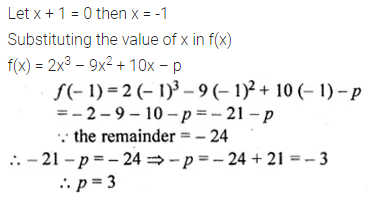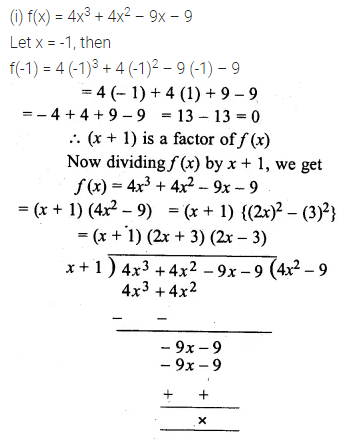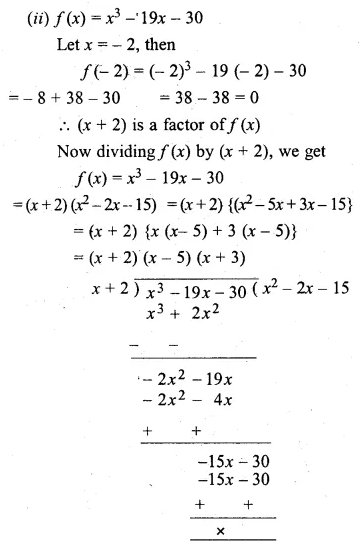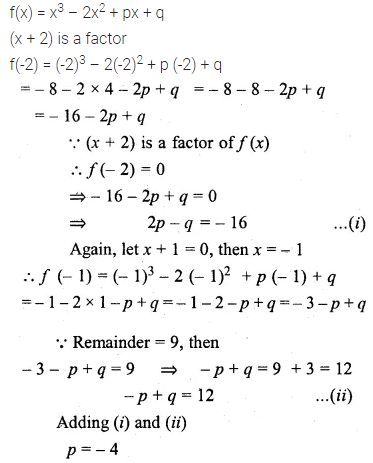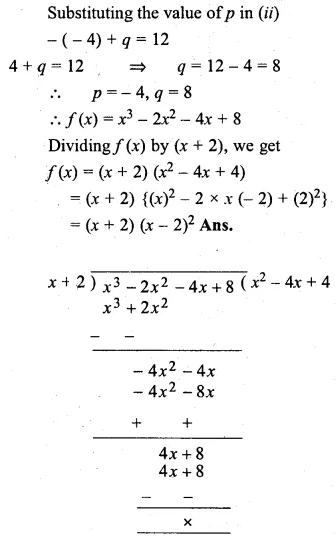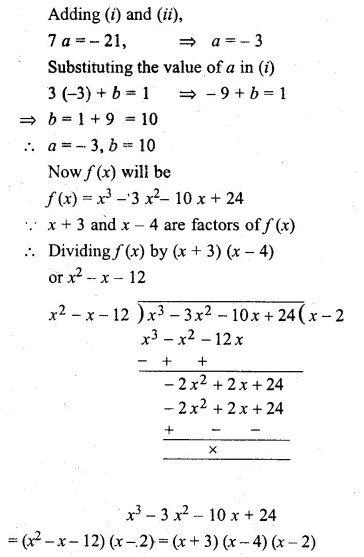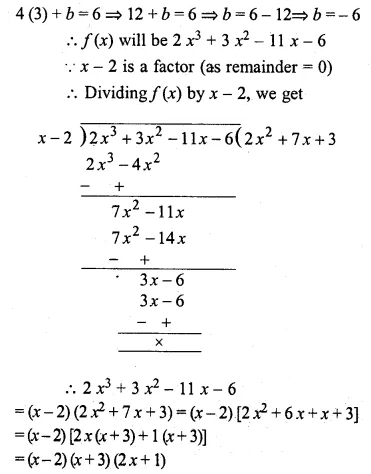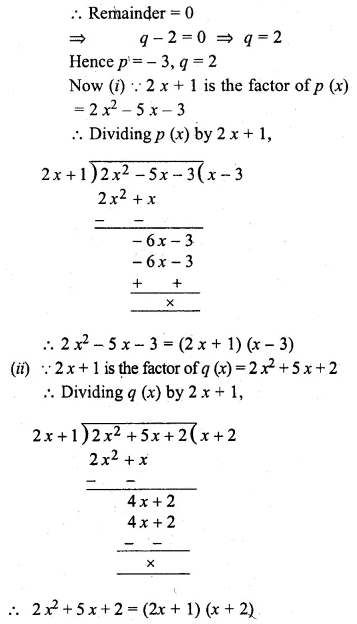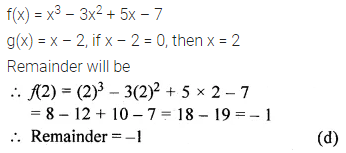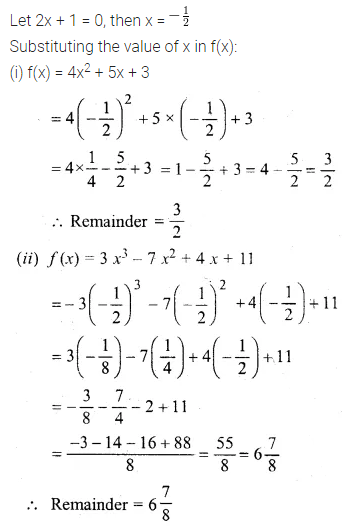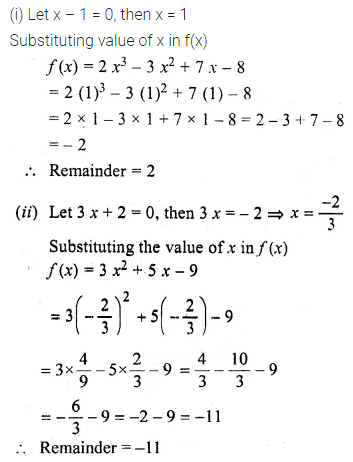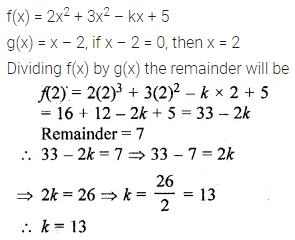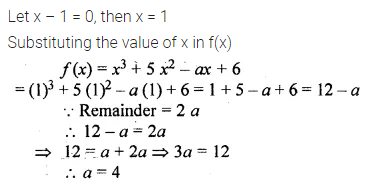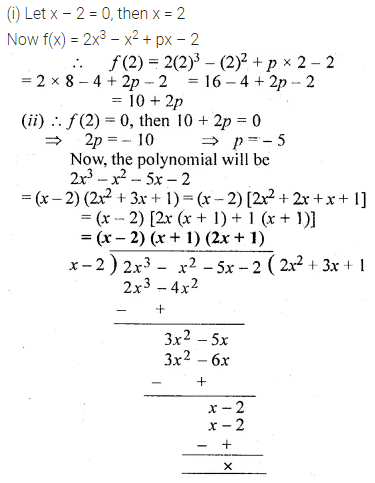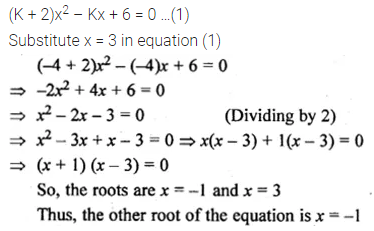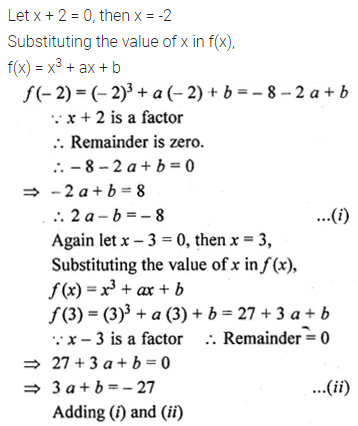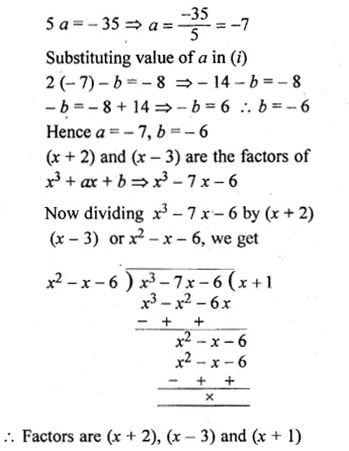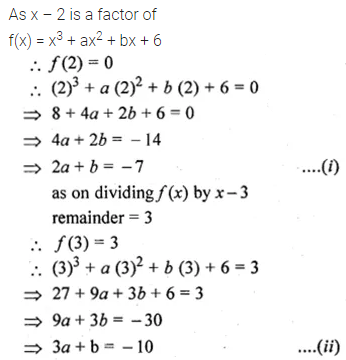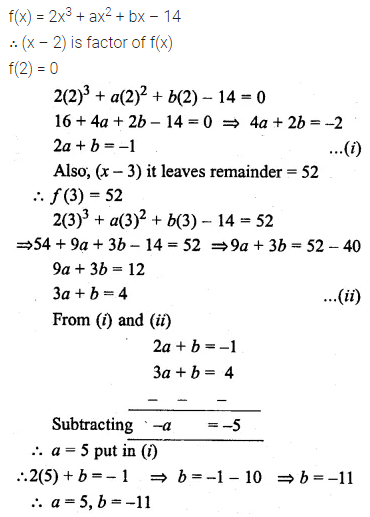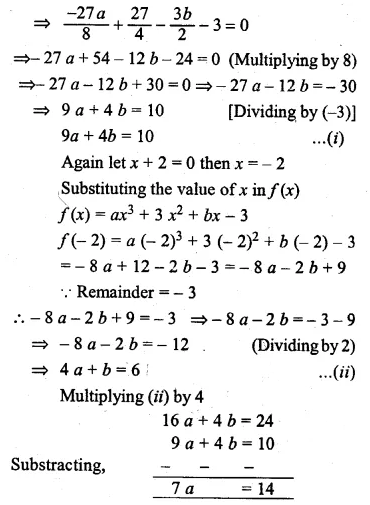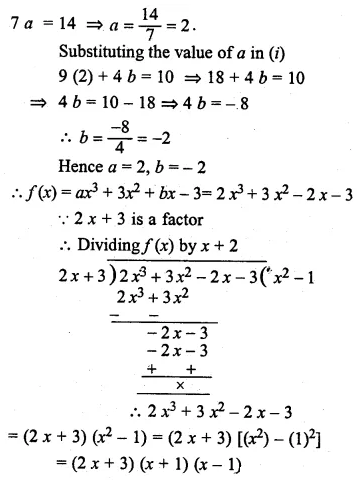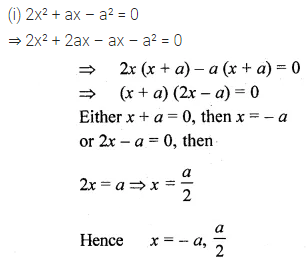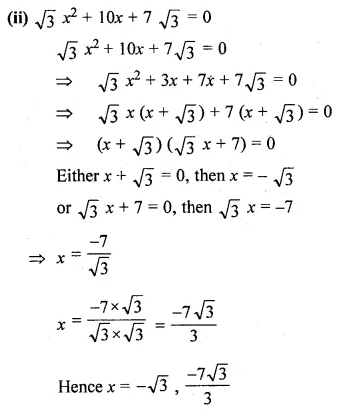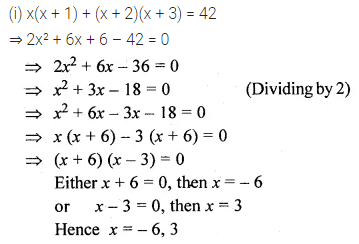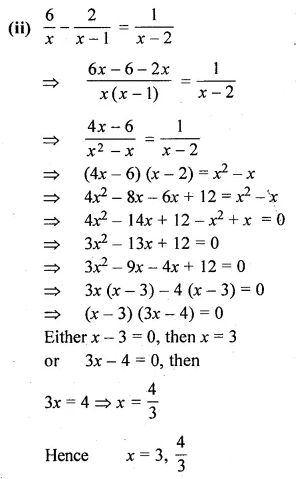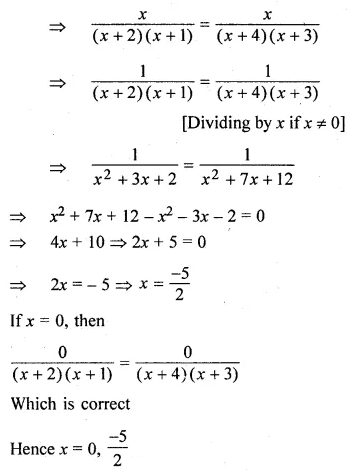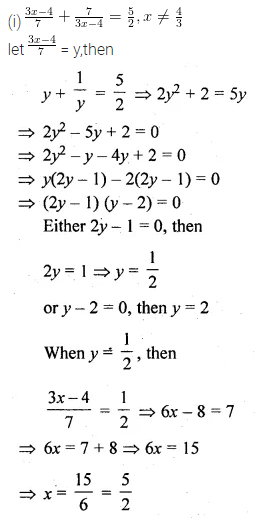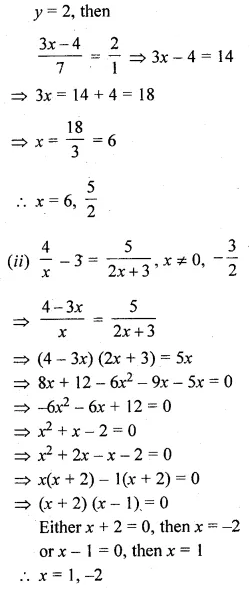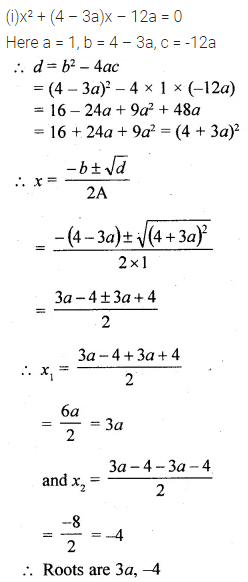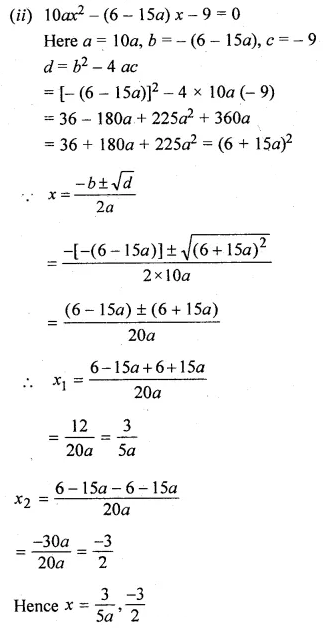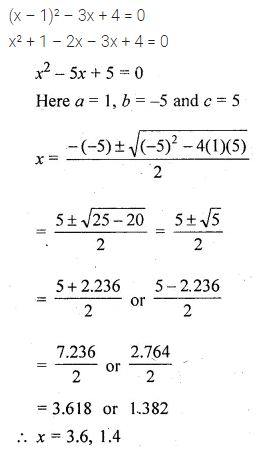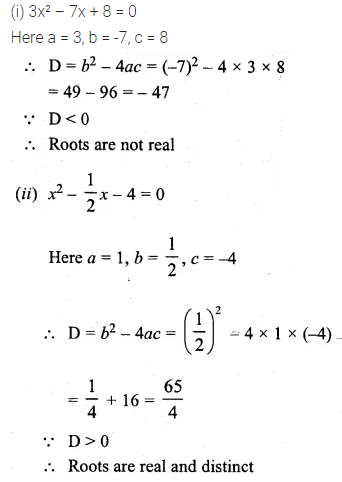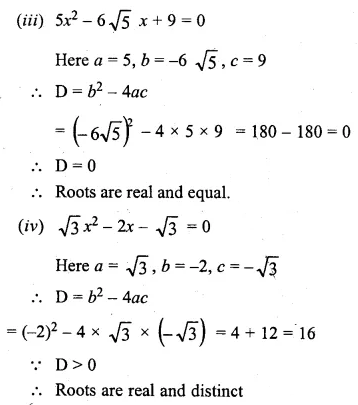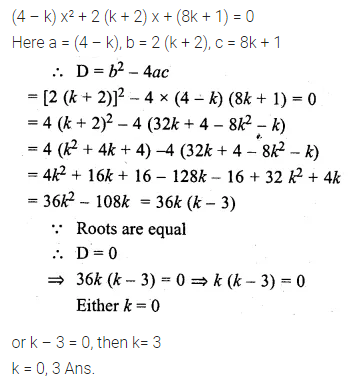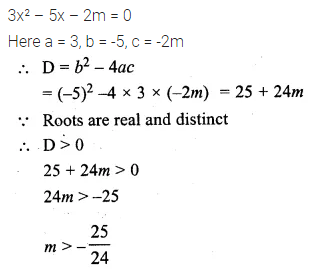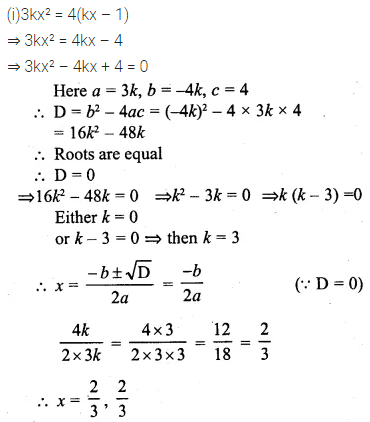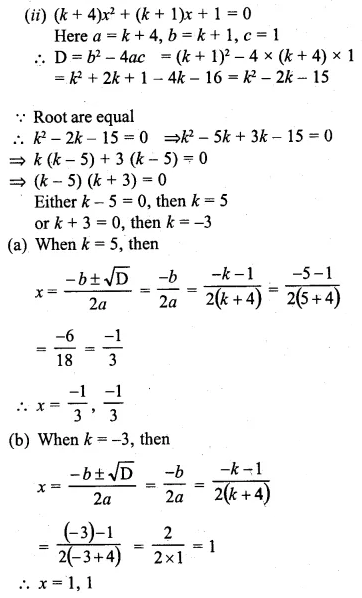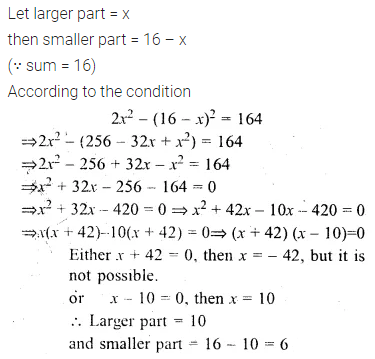ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion Ex 7.2
ML Aggarwal Class 10 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 7 Ratio and Proportion Ex 7.2
Question 1.
Find the value of x in the following proportions:
(i) 10 : 35 = x : 42
(ii) 3 : x = 24 : 2
(iii) 2.5 : 1.5 = x : 3
(iv) x : 50 :: 3 : 2
Solution:
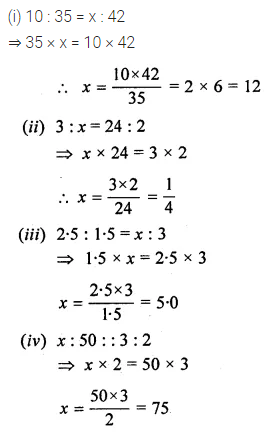
Question 2.
Find the fourth proportional to
(i) 3, 12, 15
(ii) \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } ,\frac { 1 }{ 4 } ,\frac { 1 }{ 5 } \)
(iii) 1.5, 2.5, 4.5
(iv) 9.6 kg, 7.2 kg, 28.8 kg
Solution:


Question 3.
Find the third proportional to
(i) 5, 10
(ii) 0.24, 0.6
(iii) Rs. 3, Rs. 12
(iv) \(5 \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) and 7.
Solution:


Question 4.
Find the mean proportion of:
(i) 5 and 80
(ii) \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 12 } \) and \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 75 } \)
(iii) 8.1 and 2.5
(iv) (a – b) and (a³ – a²b), a> b
Solution:

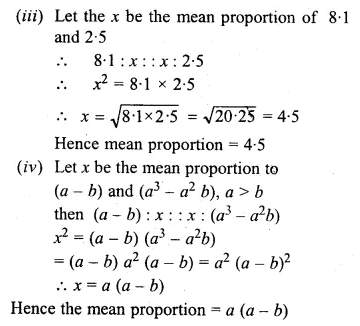
Question 5.
If a, 12, 16 and b are in continued proportion find a and b.
Solution:

Question 6.
What number must be added to each of the numbers 5, 11, 19 and 37 so that they are in proportion? (2009)
Solution:
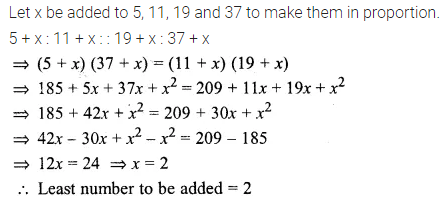
Question 7.
What number should be subtracted from each of the numbers 23, 30, 57 and 78 so that the remainders are in proportion? (2004)
Solution:

Question 8.
If 2x – 1, 5x – 6, 6x + 2 and 15x – 9 are in proportion, find the value of x.
Solution:
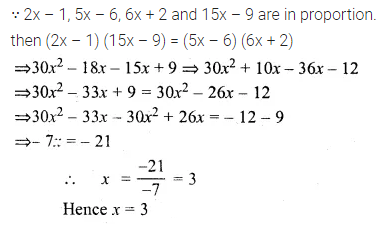
Question 9.
If x + 5 is the mean proportion between x + 2 and x + 9, find the value of x.
Solution:
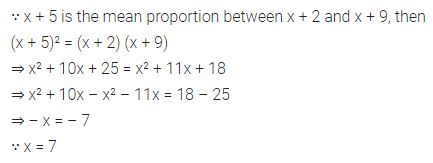
Question 10.
What number must be added to each of the numbers 16, 26 and 40 so that the resulting numbers may be in continued proportion?
Solution:

Question 11.
Find two numbers such that the mean proportional between them is 28 and the third proportional to them is 224.
Solution:

Question 12.
If b is the mean proportional between a and c, prove that a, c, a² + b², and b² + c² are proportional.
Solution:

Question 13.
If b is the mean proportional between a and c, prove that (ab + bc) is the mean proportional between (a² + b²) and (b² + c²).
Solution:

Question 14.
If y is mean proportional between x and z, prove that
xyz (x + y + z)³ = (xy + yz + zx)³.
Solution:

Question 15.
If a + c = mb and \(\frac { 1 }{ b } +\frac { 1 }{ d } =\frac { m }{ c } \), prove that a, b, c and d are in proportion.
Solution:

Question 16.
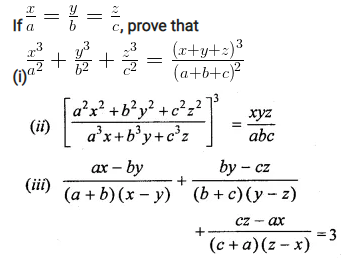
Solution:

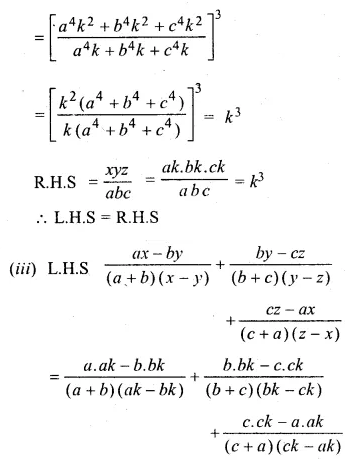
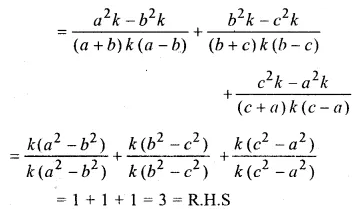
Question 17.
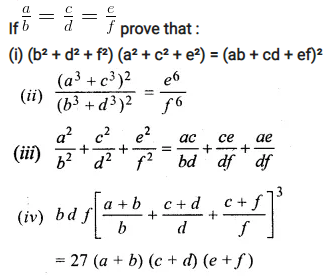
Solution:
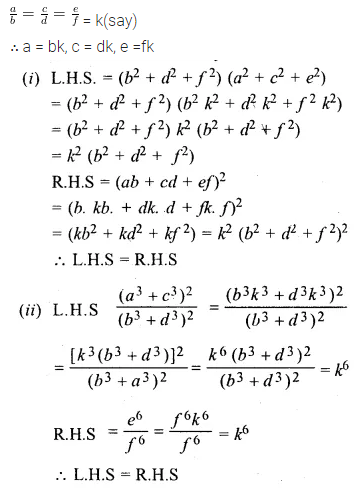
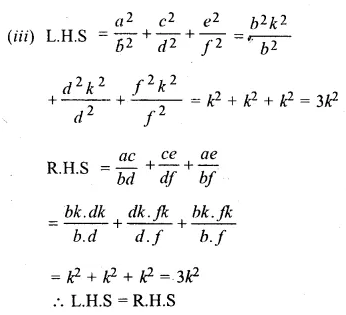
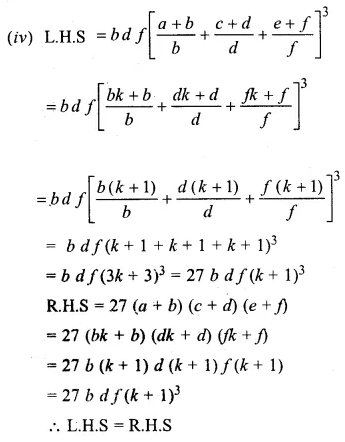
Question 18.
If ax = by = cz; prove that
\(\frac { { x }^{ 2 } }{ yz } +\frac { { y }^{ 2 } }{ zx } +\frac { { z }^{ 2 } }{ xy } \) = \(\frac { bc }{ { a }^{ 2 } } +\frac { ca }{ { b }^{ 2 } } +\frac { ab }{ { c }^{ 2 } } \)
Solution:
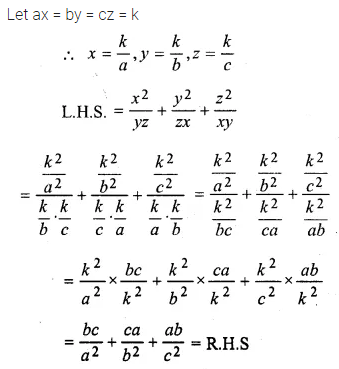
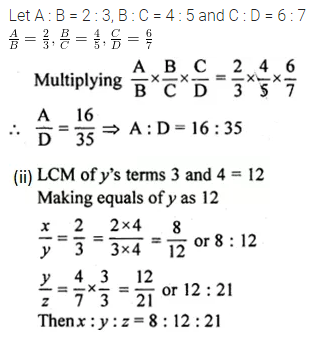
Question 19.
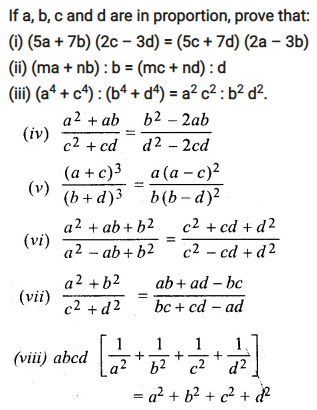
Solution:
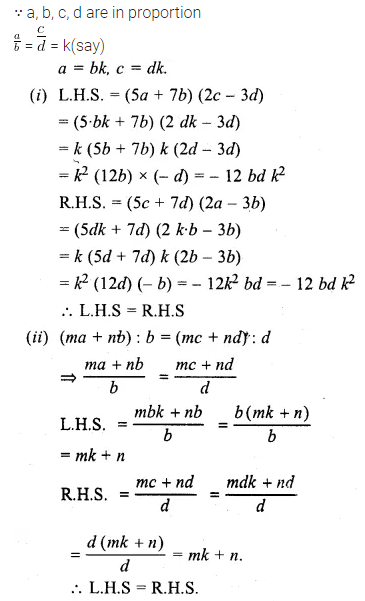
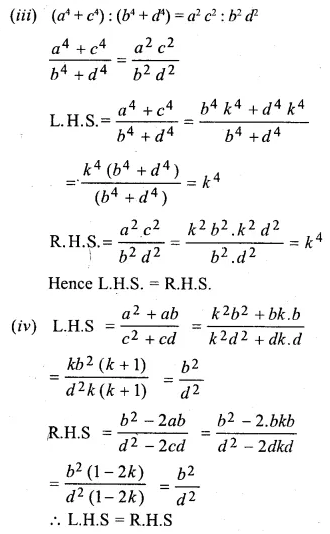
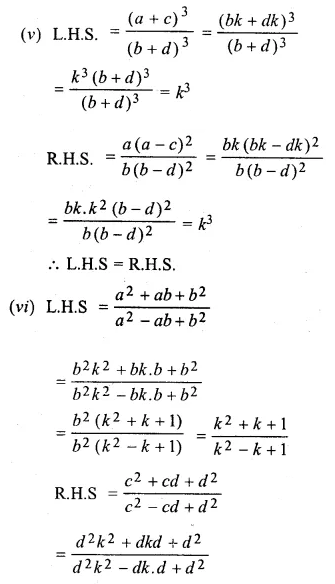
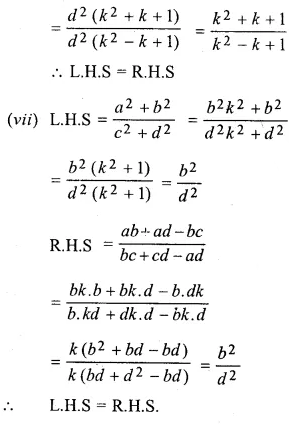
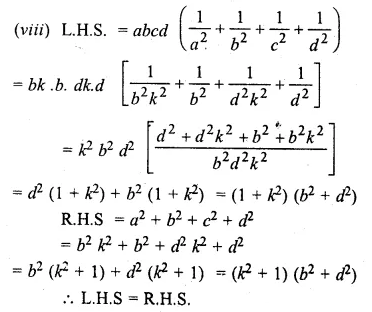
Question 20.
If x, y, z are in continued proportion, prove that:\(\frac { { \left( x+y \right) }^{ 2 } }{ { \left( y+z \right) }^{ 2 } } =\frac { x }{ z } \). (2010)
Solution:
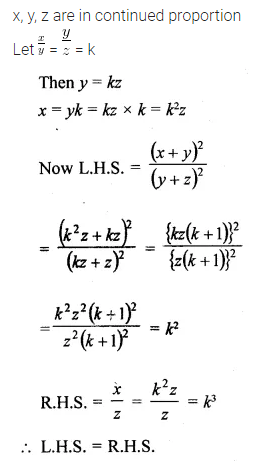
Question 21.
If a, b, c are in continued proportion, prove that:
\(\frac { { pa }^{ 2 }+qab+{ rb }^{ 2 } }{ { pb }^{ 2 }+qbc+{ rc }^{ 2 } } =\frac { a }{ c } \)
Solution:
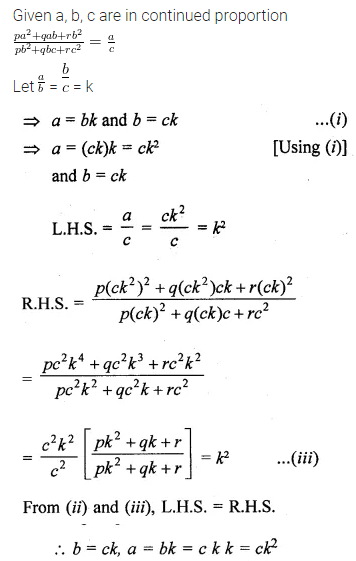
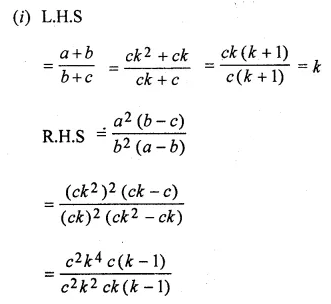
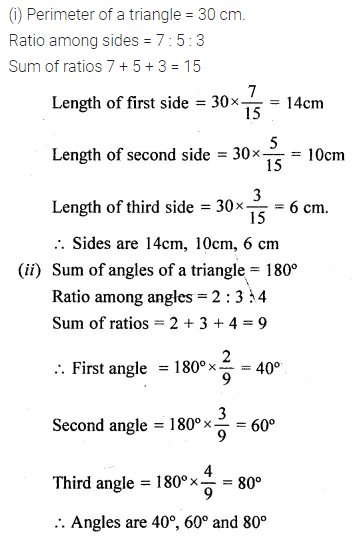
Question 22.

Solution:
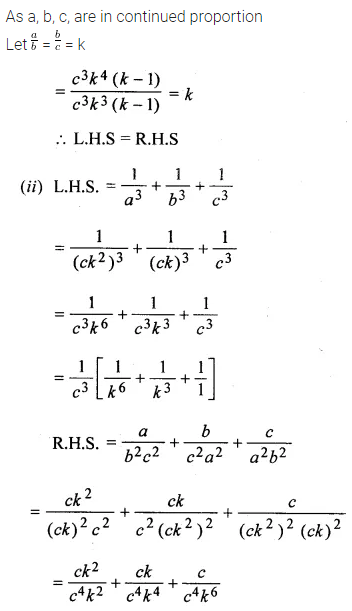
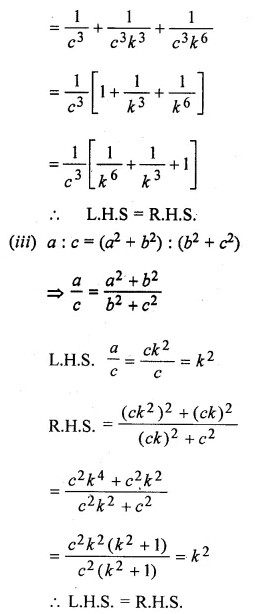
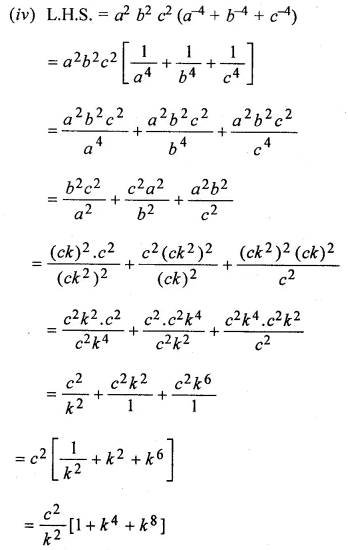
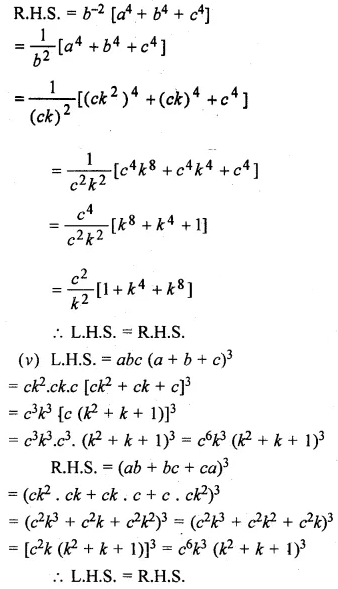
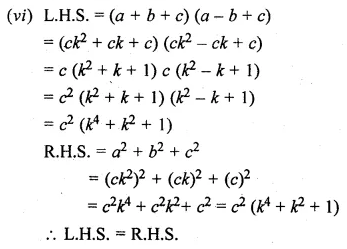
Question 23.

Solution: