MCQ Questions for Class 6 Chemistry with Answers: Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has declared a major change in the Class 6 exam pattern from 2020. Practicing & preparing each and every chapter covered in the CBSE Class 6 Science Syllabus is a necessary task to attempt the MCQs Section easily with full confidence in the board exam paper. Solving Class 6 Chemistry objective questions correctly requires a lot of critical & logical thinking. This can occur through our provided CBSE Board Class 6 Chemistry Objective Type Questions with Solutions for all chapters.
Cracking the Objective type questions needs a lot of hard work and practice. Here, we have given the quick links to avail the Chapterwise CBSE Chemistry MCQ Questions for Class 6 with Answers to ace up your preparation.
CBSE Class 6 Chemistry Objective Questions (MCQ) Chapterwise
We at NCERTBooks.guru guide students to prepare adequately for the tough Class 6 Chemistry MCQ Questions sections & let them help to score great marks in the Exams. Look at the below list of chapter wise CBSE MCQ Questions with Answers for Class 6 Chemistry & practice well.
Food: Where it Comes from? MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Idli rice
2. Kheer sugar
3. Chicken curry water
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Here, all the options are correct because idli is pre-pared by rice, for preparing kheer, sugar is needed and chicken curry cannot be prepared without water.
2. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Herbivorous eat only plants
2. Carnivores eat other animals
3. Omnivores humans
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 1 and 3
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Animals which eat only plants or plant products are called herbivores. There are some animals which eat other animals. These animals are called carnivores. Some animals which eat both plants and animals. These are called omnivores.
Components of Food MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are true for nutrients?
1. These Eire the components that are needed by our body.
2. The main carbohydrates found in our food are in the form of starch and sugars.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
The ingredients contain some components that sire needed by our body. These components are called nutrients. The major nutrients in our food are named carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. In addition, food contains dietary fibres and water which Eire Also needed by our body. The main carbohydrates found in our food are in the form of starch and sugars.
2. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Carbohydrates iodine test
2. Protein caustic soda test
3. Fats copper sulphate test
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The main carbohydrates found in our food are in the form of starch Eind sugars. Take a small quantity of a food item or a raw ingredient. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. A blue-black colour indicates that it contains starch. Add two drops of solution of copper sulphate and ten drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. A violet colour indicates presence of proteins in the food item. An oily patch on paper shows that the food item contains fat. The food items may sometimes contain a little water too.
3. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Carbohydrates provide energy to our body.
2. Proteins growth and repair of our body.
3. Vitamins mEiintain good heEdth.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Carbohydrates mainly provide energy to our body. Fats also give us energy. In fact, fats give much more energy as compared to the same amount of carbohydrates. The food containing fats and car-bohydrates are also called ‘energy-giving foods’. Proteins are needed for the growth and repair of our body. Vitamins help in protecting our body against diseases. VitEimins also help in keeping our eyes, bones, teeth and gums healthy. Minerals Eire needed by our body in small amounts. Each one is essentiEd for proper growth of our body and to maintain good health.
4. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Milk minerals
2. Carrot vitamins
3. Fish carbohydrates
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
The sources of carbohydrates are sweet potato, sugarcane, wheat, rice, bajra, melon, mango, potato, maize, meat, fish, egg, milk, ghee, etc. The sources of proteins are- gram, moong, tuar dal, beans, meat, eggs, fish, peas, soyabeans, paneer etc. The sources of vitamins are-milk, eggs, spinach, apple etc. The sources of vitamins are- papaya carrot mango, guava, lemon, amla etc.
5. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Vitamin A skin
2. Vitamin C—protect from diseases
3. Vitamin D eyes
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Vitamins help in protecting our body against dis-eases. Vitamins also help in keeping our eyes, bones, teeth and gums healthy. Vitamins are of different kinds known by different names. Some of these are Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E and K. There is also a group of vitamins called Vitamin B-complex. Our body needs all types of vitamins in small quantities. Vitamin A keeps our skin and eyes healthy. Vitamin C helps body to fight against many diseases. Vitamin D helps our body to use calcium for bones and teeth.
6. Which of the following is/are true for dietary fibres?
1. Dietary fibres are also known as roughage.
2. Roughage provides nutrient to our body.
3. Roughage is mainly provided by plant products in our foods.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Dietary fibres are also known as roughage. Roughage is mainly provided by plant products in our foods. Whole grains and pulses, potatoes, fresh fruits and vegetables are main sources of roughage. Roughage does not provide any nutrient to our body, but is an essential component of our food and adds to its bulk. This helps our body get rid of undigested food.
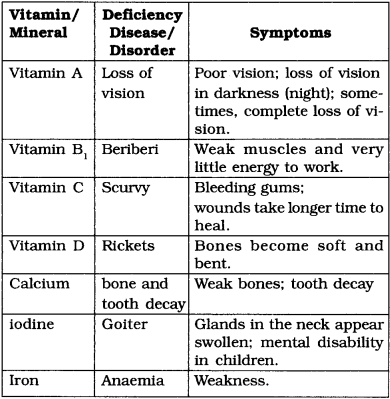
7. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Vitamin A _______ loss of vision
2. Vitamin C _______ scurvy
3. Vitamin D _______ goitre
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Fibre to Fabric MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are true for fabrics?
1. The thin strands of thread.
2. The fibres of some fabrics such as cotton, jute, silk and wool are obtained from plants.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The thin strands of thread that are made up of still thinner strands called fibres. Fabrics are made up of yams and yams are further made up of fibres. The fibres of some fabrics such as cotton, jute, silk and wool are obtained from plants and animals. These are called natural fibres.
2. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Cotton _______ plants
2. Wool _______ yak
3. Silk _______ cocoon
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
Cotton and jute are examples of fibres obtained from plants. Wool and silk fibres are obtained from animals. Wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep or goat. It is also obtained from the hair of rabbits, yak and camels. Silk fibre is drawn from the cocoon of silkworms.
3. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Ginning _______ fibres separated from seeds
2. Spinning _______ making yam from fibres
3. Weaving _______ forming fabric
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
The fruits of the cotton plant (cotton bolls) are about the size of a lemon. After maturing, the bolls burst open and the seeds covered with cotton fibres can be seen. From these bolls, cotton is usually picked by hand. Fibres are then separated from the seeds by combing. This process is called ginning of cotton. Ginning was traditionally done by hand. The process of making yam from fibres is called spinning. In this process, fibres from a mass of cotton wool are drawn out and twisted. This brings the fibres together to form a yam. The process of arranging two sets of yams together to make a fabric is called weaving.
Getting to know Plants MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are true for herbs?
1. Plants with green and tender stems.
2. They have many branches
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Plants with green and tender stems are called herbs. They are usually short and may not have many branches.
2. Which of the following is/are true for shrubs?
1. The stem is hard.
2. The stem is thick
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Some plants develop branches near the base of the stem. The stem is hard but not very thick. Such plants are called shrubs.
3. Which of the following is/are true for trees?
1. They have branches above ground.
2. They have thick stem
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Some plants are very tall and have hard and thick stem. The stems have branches in the upper part, much above the ground. Such plants are called trees.
4. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Petiole _______ part of leaf by which it is attached to the stem
2. Lamina _______ the broad, green part of the leaf
3. Midrib _______ line on leaf
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The part of leaf by which it is attached to the stem is called petiole. The broad, green part of the leaf is called lamina. The lines on the leaf are called veins. A prominent line in the middle of the leaf is called the midrib. The design made by veins in a leaf is called the leaf venation. If this design is net-like on both sides of midrib, the venation is reticulate.
5. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Tap root _______ main root
2. Pistil _______ outermost part
3. Ovules _______ small bead like structure
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
Answer: c
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
The main root is called tap root and the smellier roots are called lateral roots. Plants with roots do not have a main root. All roots seem similar and these are called fibrous roots. The innermost part of flower is called the pistil. Some small bead like structures inside the ovary are called ovules.
The Living Organism, Characteristics and Habitats MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are true for fish?
1. Fish have slippery scales on their bodies.
2. Gills present in the fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
Fish have slippery scales on their bodies. These scales protect the fish and also help in easy move-ment through water. Fish have flat fins and tails that help them to change directions and keep their body balanced in water. Gills present in the fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in water.
2. Which of the following is/are true for habitat?
1. The place where organisms live is called habitat.
2. The plants and animals that live on water are said to live in terrestrial habitats.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The place where organisms live is called habitat. Habitat means a dwelling place (a home). The habitat provides food, water, air, shelter and other needs to organisms. Several kinds of plants and animals live in the same habitat. The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats. Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions. On the other hand, the habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats. Lakes, rivers and oceans are some examples of aquatic habitats. There are large variations among terrestrial habitats like forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions located in different parts of the world.
3. Which of the following is/are true for adaptation?
1. Adaptation takes place in a short time.
2. Those organisms which cannot adapt to these changes die.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
Adaptation does not take place in a short time because the abiotic factors of a region also change very slowly. Those organisms which cannot adapt to these changes die, and only the adapted ones survive. Organisms adapt to different abiotic factors in different ways. This results in a wide variety of organisms in different habitats.
4. Which of the following is/are true for desert plant?
1. Desert plants lose very little water through transpiration
2. The leaves in desert plants are absent.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
Desert plants lose very little water through tran-spiration. The leaves in desert plants are either absent, very small, or they are in the form of spines. This helps in reducing loss of water from the leaves through transpiration. The leaf-like structure you see in a cactus is, in fact, its stem. Photosynthesis in these plants is usually carried out by the stems.
5. Which of the following is/are true for mountain plants and animals?
1. Trees are normally circular shaped and have sloping branches.
2. Yaks have long hair to keep them warm.
3. Snow leopard has thick fur on its body
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
The trees are normally cone-shaped and have sloping branches. The leaves of some of these trees are needle-like. This helps the rainwater and snow to slide off easily. There could be trees with shapes very different from these that are also present on mountains. They may have different kinds of adaptations to survive on the mountains. Animals living in the mountain regions are also adapted to the conditions there. They have thick skin or fur to protect them from cold. For example, yaks have long hair to keep them warm. The snow leopard has thick fur on its body including feet and toes. This protects its feet from the cold when it walks on the snow. The mountain goat has strong hooves for running up the rocky slopes of the mountains.
6. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Biotic _______ living components
2. Abiotic _______ non-living components
3. Predators _______ animals to eat
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The organisms, both plants and animals, living in a habitat are its biotic components. The nonliving things such as rocks, soil, air and water in the habitat constitute its abiotic components. A deer is a animal that lives in forests and grasslands. It has strong teeth for chewing hard plant stems of the forest. A deer needs to know about the presence of predators (animals like lion that make it their prey) in order to run away from them and not become their prey. Lions light brown colour helps it to hide in diy grasslands when it hunts for prey (animals to eat).
Water MCQ Questions
1. What is/are true for rainwater harvesting?
1. It is to collect rainwater and store it for later use.
2. There are two techniques for it.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
One way of increasing the availability of water is to collect rainwater and store it for later use. Collecting rainwater in this way is called rainwater harvesting. The basic idea behind rainwater harvesting is “Catch water where it falls”. Two techniques of rainwater harvesting are-
1. Rooftop rainwater harvesting: In this system, the rainwater is collected from the rooftop to a storage tank, through pipes. This water may contain soil from the roof and need filtering before it is used. Instead of collecting rainwater in the tank, the pipes can go directly into a pit in the ground. This then seeps into the soil to recharge or refill the groundwater.
2. Another option is to allow water to go into the ground directly from the roadside drains that collect rainwater.
2. Which of the following is/are true for condensation in water cycle?
1. At sufficient heights, the air becomes so cool that the water vapour present in it condenses to form tiny drops of water called droplets
2. It so happens that many droplets of water come together to form larger sized clouds
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (a)
Explanation:
The process of condensation plays an important role in bringing water back to the surface of earth. As we go higher from the surface of the earth, it gets cooler. When the air moves up, it gets cooler and cooler. At sufficient heights, the air becomes so cool that the water vapour present in it condenses to form tiny drops of water called droplets. It is these tiny droplets that remain floating in air and appear to us as clouds. It so happens that many droplets of water come together to form larger sized drops of water. Some drops of water become so heavy that they begin to fall. These falling water-drops are, what we call rain. In special conditions, it may also fall as hail or snow.
Air Around us MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Water vapour _______ important for water cycle
2. Nitrogen _______ supports burning
3. Dust _______ combination of gases
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
When air comes in contact with a cool surface, it condenses and drops of water appear on the cooled surfaces. The presence of water vapour in air is important for the water cycle in nature. The presence of some components in the air, do not support burning. The major part of air (which does not support burning candle) is nitrogen. The burning of fuel also produces smoke. Smoke contains a few gases and fine dust particles and is often harmful. That is why you see long chimneys in factories.
2. Which of the following is correct order with respect to amount present in air?
(a) Nitrogen > carbon dioxide > oxygen
(b) Nitrogen > oxygen > carbon dioxide
(c) Oxygen >nitogen > carbon dioxide
(d) Carbon dioxide > nitrogen > oxygen
Answer
Answer: (b)
Explanation:
By volume, dry air contains 78.09% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% Argon, 0.04% carbon di-oxide and small amount of other gases. Air also contains variable amount of water vapour, on av-erage around 1% at sealevel and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere.
3. Which of the following is/are true for wind mill?
1. The windmill is used to draw water from tubewells and to run flour mills.
2. Windmills are also used to generate electricity-
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
The wind makes the windmill rotate. The windmill is used to draw water from tubewells and to run flour mills. Windmills are also used to generate electricity. Air helps in the movement of sailing yachts, gliders, parachutes and aeroplanes. Birds, bats and insects can fly due to the presence of air. Air also helps in the dispersal of seeds and pollen of flowers of several plants. Air plays an important role in water cycle.
Garbage in Garbage out MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are true for red worms?
1. Preparing compost with the help of red worms is vermicomposting.
2. Redworms do not have teeth.
(a) Only 1
(b) Only 2
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
The method of preparing compost with the help of redworms is called vermi composting. Redworms do not have teeth. They have a structure called ‘gizzard’, which helps them in grinding their food. Redworms do not survive in very hot or very cold surroundings. They also need moisture around them.
Body Movements MCQ Questions
1. Which of the following is/are correctly matched?
1. Pivotal joint _______ bending head
2. Hinge joint _______ ment back and forth move-
3. Fixed joint _______ bones cannot move
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1,2 and 3
Answer
Answer: (d)
Explanation:
The joint where our neck joins the head is a pivotal joint. It allows us to bend our head forward and backwards and turn the head to our right or left. The elbow has a hinge joint that allows only a back and forth movement. The bones cannot move at these joints. Such joints are called fixed joints.

